ESA Observing the Earth 
zdroje zpráv:
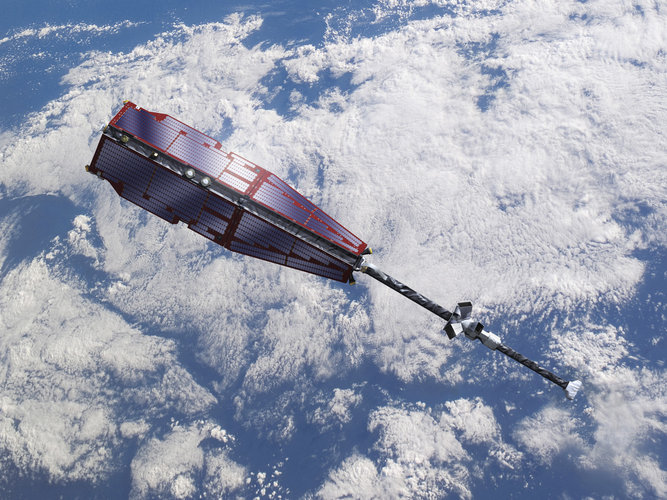
Call for Media: launch of the first Meteosat Third Generation satellite MTG-I1
8.11.2022 9:37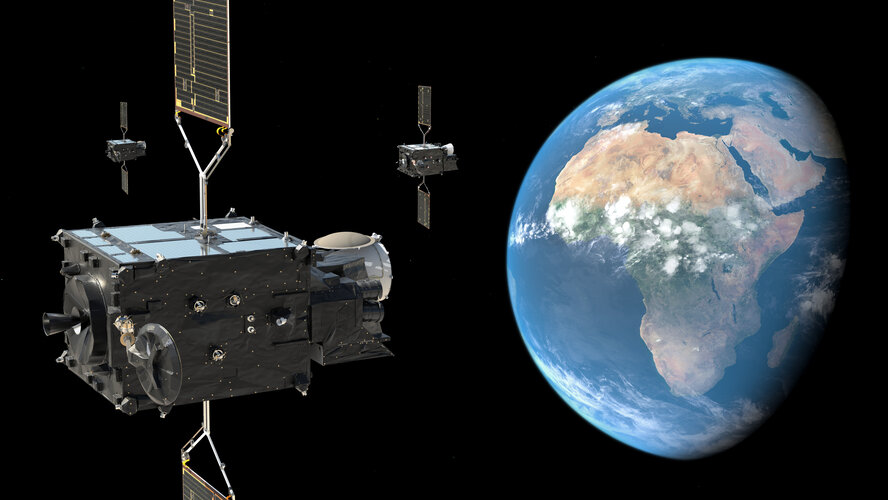
Call for Media: launch of the first MTG satellite MTG-I1
Earth from Space: Nushagak Bay, Alaska
4.11.2022 10:00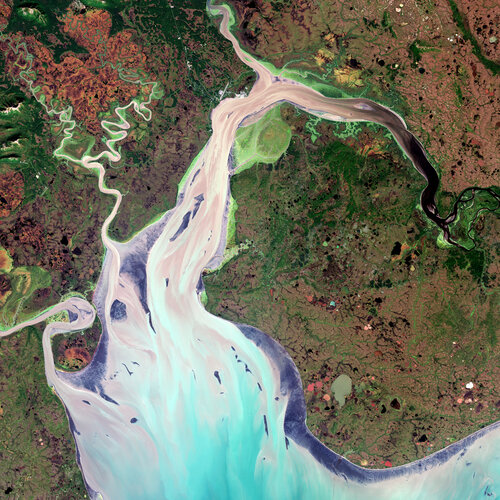
The complex and diverse landscape that surrounds Nushagak Bay in Alaska is featured in this true-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Earth Observation Excellence Award deadline approaching
3.11.2022 10:45
In a little over a month, the window of opportunity for nominating deserving scientists for the prestigious ESA-EGU Earth Observation Excellence Award will close. With the period for lodging nominations closing on 7 December, past nominators and winners reflect on how this award has increased the visibility of their scientific research and opened new avenues to working partnerships.
Give climate some MAGIC
31.10.2022 15:44
There are times when we could all do with a bit of magic in our lives. And, with the Global Climate Observing System announcement of ‘terrestrial water storage’ as a completely new Essential Climate Variable, the world of climate research and climate crisis response would certainly benefit from a satellite mission called MAGIC.
Earth from Space: Svalbard
28.10.2022 10:00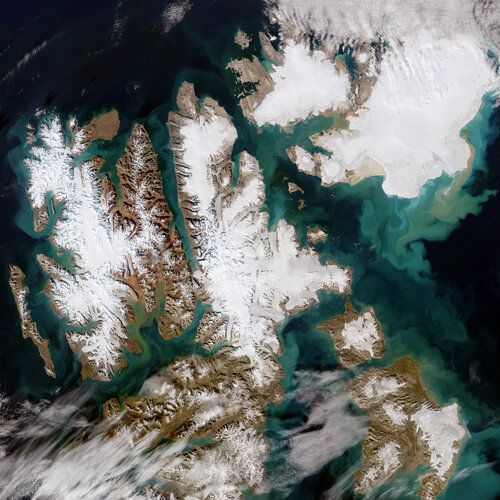
Extremely high temperatures recorded this summer caused record melting across Svalbard – one of the fastest warming places on the planet. The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission captured this rare, cloud-free acquisition of the Norwegian archipelago in August 2022.
Earth from Space: Svalbard
28.10.2022 10:00
Extremely high temperatures recorded this summer caused record melting across Svalbard – one of the fastest warming places on the planet. The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission captured this rare, cloud-free acquisition of the Norwegian archipelago in August 2022.
From Rome to Cannes
25.10.2022 8:45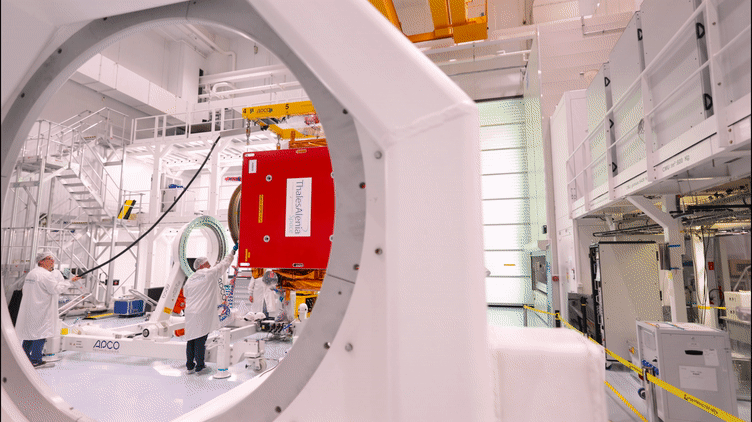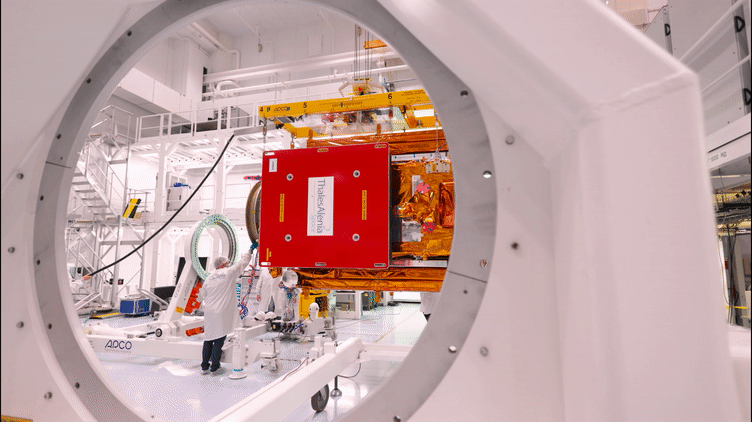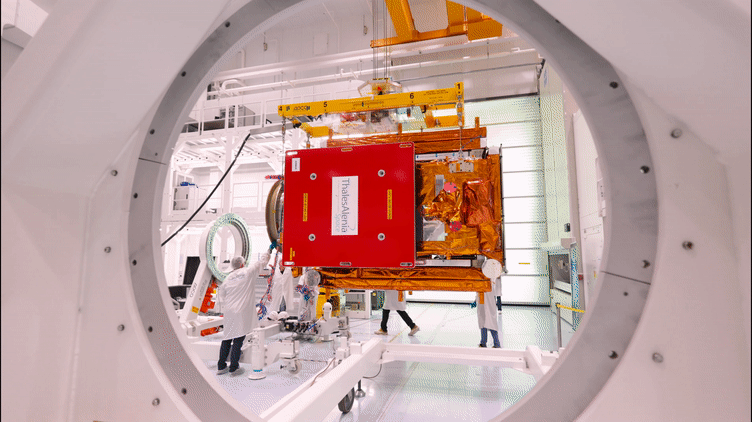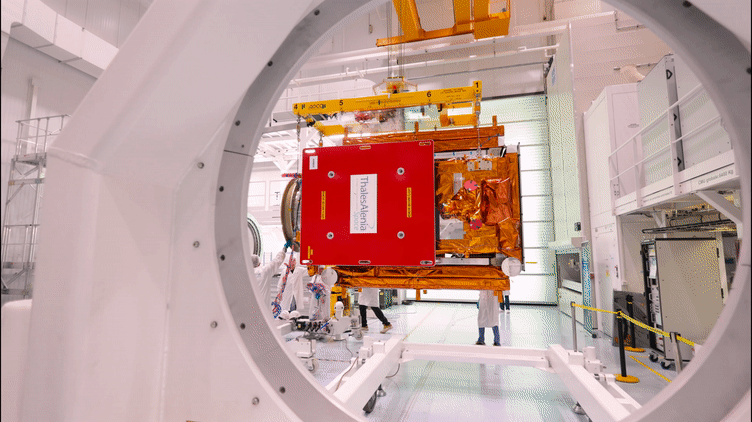
The Copernicus Sentinel-1C satellite is currently in Cannes undergoing a series of demanding tests in preparation for launch in 2023. The third member of the Sentinel-1 radar family, part of Europe’s Copernicus programme, will continue the critical task of delivering key radar imagery of Earth’s surface for a wide range of services and scientific applications.
Boosting Earth science
24.10.2022 13:47
With science at the core of the Earth Observation FutureEO programme, ESA has opened a new scientific facility, the Science Hub, which offers new opportunities for collaborative research to further boost the Agency’s and its Member States scientific output.
The scary sound of Earth’s magnetic field
24.10.2022 8:00
Despite being essential to life on Earth, the magnetic field isn’t something we can actually see in itself, or ever hear. But, remarkably, scientists at the Technical University of Denmark have taken magnetic signals measured by ESA’s Swarm satellite mission and converted them into sound – and for something that protects us, the result is pretty scary.
Earth from Space: Inhambane Bay, Mozambique
21.10.2022 10:00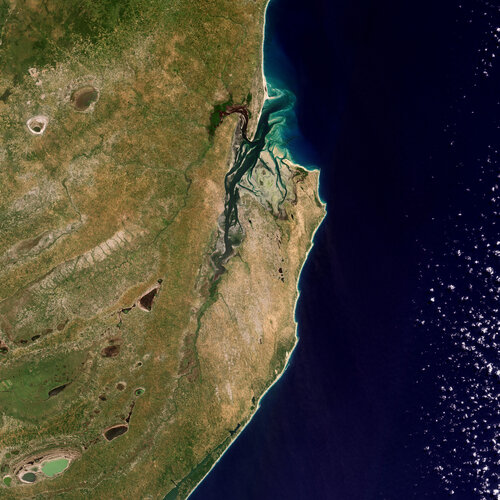
Inhambane Bay, in southeast Mozambique, is featured in this true-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Europe’s all-new weather satellite arrives at launch site
18.10.2022 10:30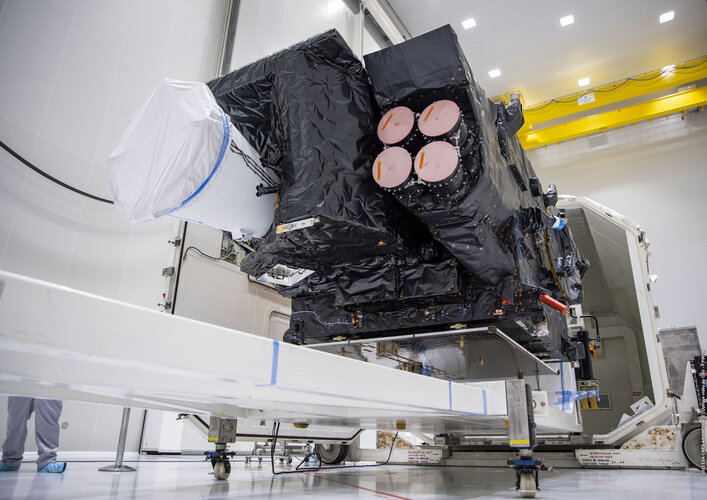
After a two-week voyage across the Atlantic Ocean, the ship transporting the first Meteosat Third Generation satellite docked at Pariacabo in French Guiana and the precious cargo unloaded. Now safe and sound in one of the spaceport’s cleanrooms, satellite engineers will ready it for liftoff on an Ariane 5 rocket in December. Once in geostationary orbit, this new satellite, which carries two new extremely sensitive instruments, promises to further bolster Europe's leadership in weather forecasting.
Earth from Space: Mississippi River
14.10.2022 10:00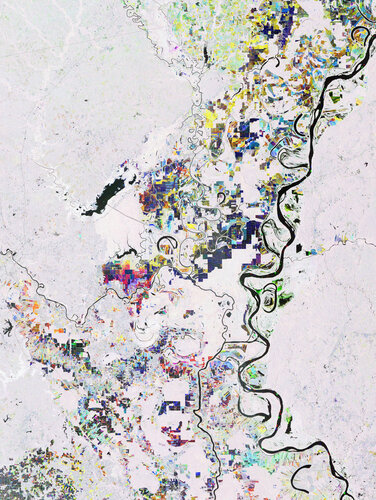
Mississippi River, one of the longest rivers in North America, is featured in this multi-temporal radar image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission.
Earth from Space: Mississippi River
14.10.2022 10:00
Mississippi River, one of the longest rivers in North America, is featured in this multi-temporal radar image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission.
Seasonal changes in Antarctic ice sheet flow dynamics detected for the first time
12.10.2022 11:00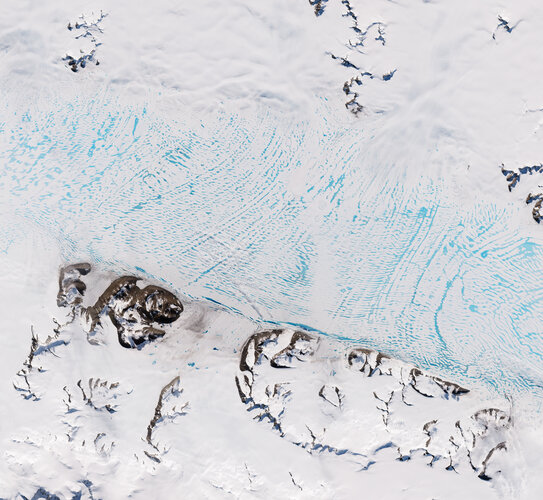
Certain estimates of Antarctica’s total contribution to sea-level rise may be over, or even underestimated, after researchers detected a previously unknown source of ice loss variability. In a new paper published in The Cryosphere, researchers using Copernicus Sentinel-1 data, found that glaciers feeding the George VI Ice Shelf speed up by approximately 15% during the Antarctic summer. This is the first time that such seasonal cycles have been detected on land ice flowing into ice shelves in Antarctica.
Italy’s Stromboli erupts
10.10.2022 16:00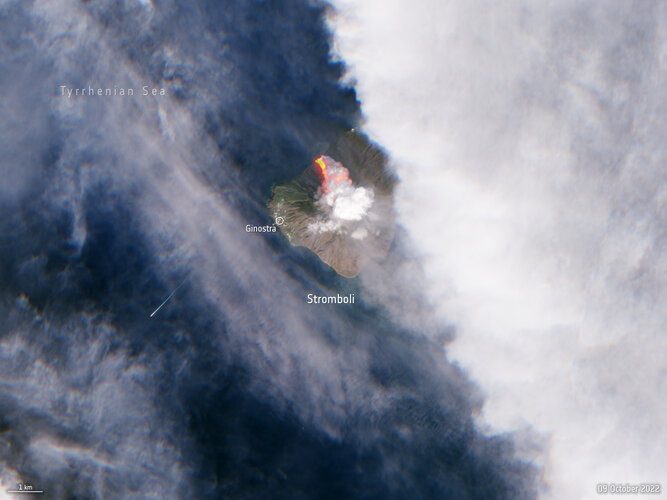 Image:
A volcano on the Italian island of Stromboli erupted early on Sunday morning, releasing huge plumes of smoke and a lava flow pouring into the sea. The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission captured this image of the aftermath less than five hours after the eruption.
Image:
A volcano on the Italian island of Stromboli erupted early on Sunday morning, releasing huge plumes of smoke and a lava flow pouring into the sea. The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission captured this image of the aftermath less than five hours after the eruption.
TRUTHS on the table at ESA’s Ministerial Council
10.10.2022 14:45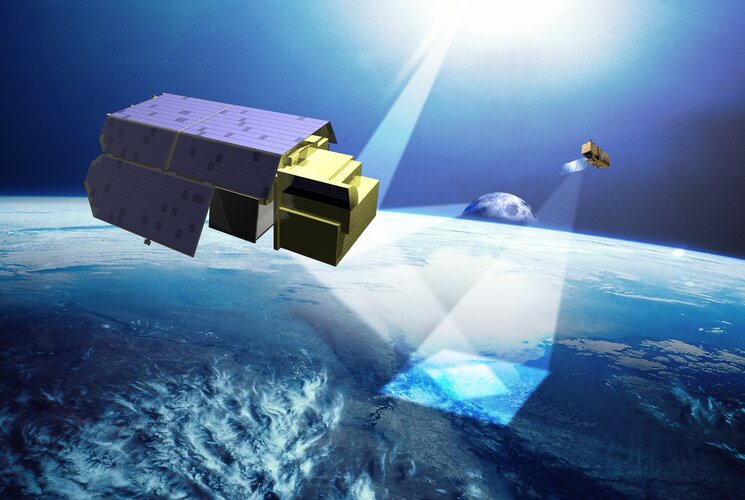
With the satellite and instrument design consolidated and the scientific community assured it will deliver the data they need, TRUTHS has been approved as part of Earth Observation Programme proposal for the upcoming ESA Council Meeting at Ministerial Level. Carrying a primary International System of Units reference system, TRUTHS promises to set the gold standard for climate measurements.
Earth observation inspires global inventiveness
10.10.2022 11:35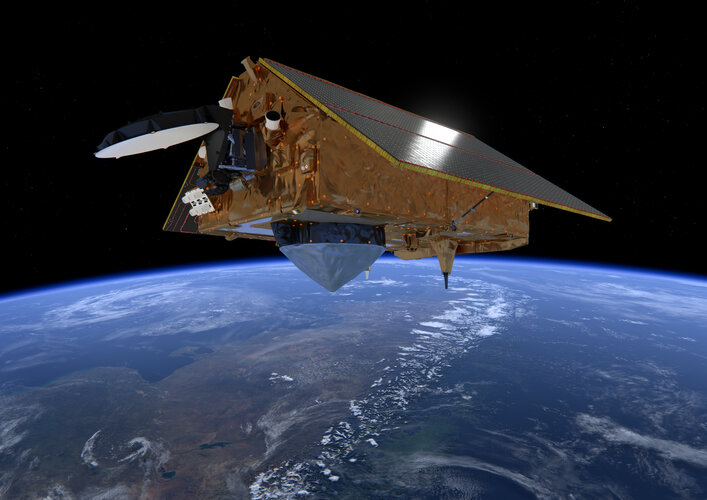
Today our home planet Earth is being more closely monitored than at any time in its history. Some 1 460 Earth-observing satellites have been launched during the last two decades, with Europe’s Copernicus Sentinel fleet in the forefront of environmental data gathering. A new report led by the European Patent Office examining associated patent filings reveals a 1 800% increase in the same period – with European activity comparatively stagnant compared to international competitors.
Earth from Space: Bouches-du-Rhône
7.10.2022 10:00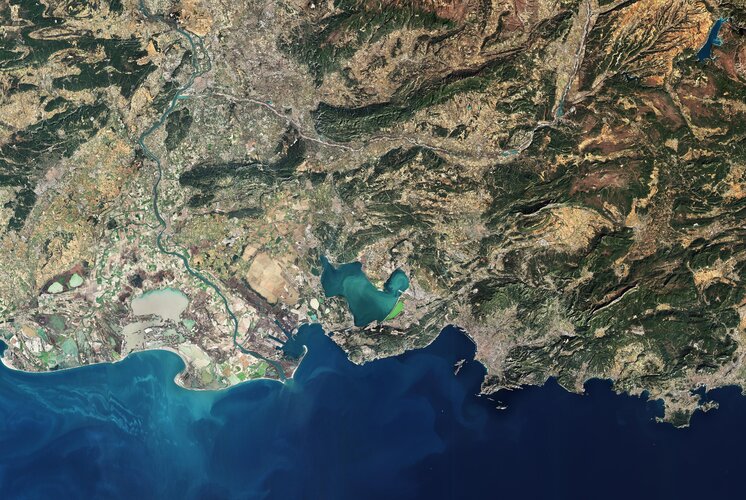
The port town of Fos-Sur-Mer, in the southern part of Bouches-du-Rhône, France, is featured in this image captured by Copernicus Sentinel-2. It is from here where the first Meteosat Third Generation Imager satellite set sail last week on its journey to Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
Earth from Space: Bouches-du-Rhône
7.10.2022 10:00
The port town of Fos-Sur-Mer, in the southern part of Bouches-du-Rhône, France, is featured in this image captured by Copernicus Sentinel-2. It is from here where the first Meteosat Third Generation Imager satellite set sail last week on its journey to Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana.
Satellites detect methane plume in Nord Stream leak
6.10.2022 10:02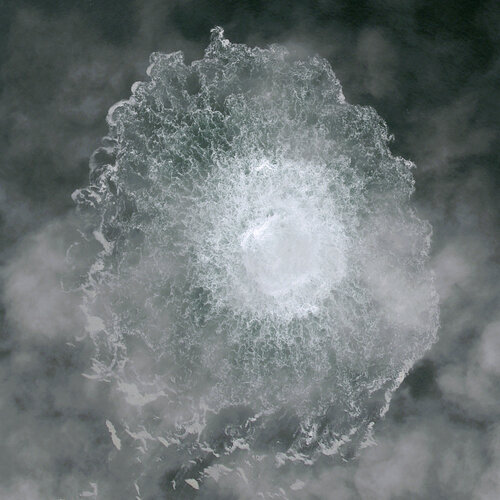
Following unusual seismic disturbances in the Baltic Sea, several leaks were discovered last week in the underwater Nord Stream 1 and 2 gas pipelines, near Denmark and Sweden. Neither pipeline was transporting gas at the time of the blasts, but they still contained pressurised methane – the main component of natural gas – which spewed out producing a wide stream of bubbles on the sea surface.
With the unexplained gas release posing a serious question about the incident’s environmental impact, a suite of complementary Earth observation satellites carrying optical and radar imaging instruments were called upon to characterise the gas leak bubbling in the Baltic.
Europe’s new weather satellite sets sail
30.9.2022 10:45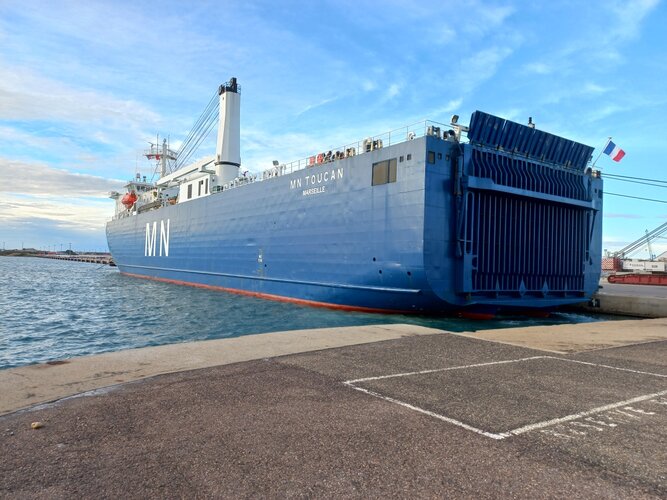
The first of Europe’s Meteosat Third Generation satellites is now safely aboard a ship and making its way across the Atlantic to French Guiana where it will be readied for liftoff in December. Once launched into geostationary orbit, 36 000 km above Earth, this new satellite, which carries two new extremely sensitive instruments, will take weather forecasting to the next level.
Europe’s new weather satellite sets sail
30.9.2022 10:45
The first of Europe’s Meteosat Third Generation satellites is now safely aboard a ship and making its way across the Atlantic to French Guiana where it will be readied for liftoff in December. Once launched into geostationary orbit, 36 000 km above Earth, this new satellite, which carries two new extremely sensitive instruments, will take Europe's leadership in weather forecasting to the next level.
Earth from Space: Melt ponds in West Greenland
30.9.2022 10:00
During spring and summer, as the air warms up and the sun beats down on the Greenland Ice Sheet, melt ponds pop up. Melt ponds are vast pools of open water that form on both sea ice and ice sheets and are visible as turquoise-blue pools of water in this Copernicus Sentinel-2 image.
Earth from Space: Melt ponds in West Greenland
30.9.2022 10:00
During spring and summer, as the air warms up and the sun beats down on the Greenland Ice Sheet, melt ponds pop up. Melt ponds are vast pools of open water that form on both sea ice and ice sheets and are visible as turquoise-blue pools of water in this Copernicus Sentinel-2 image.
New weather satellite on its way to launch
30.9.2022 9:00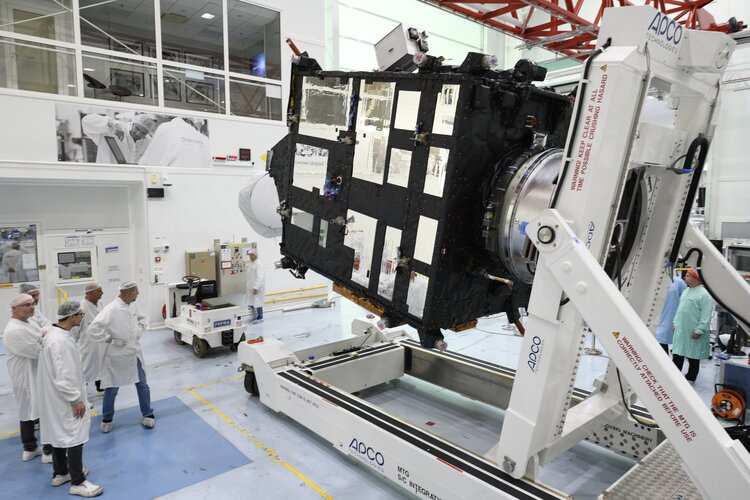 Video:
00:04:04
Video:
00:04:04
The final pre-launch preparations for the first Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) satellite are underway. The first satellite, called MTG-I1, built by a European industrial consortium led by Thales Alenia Space carries two imagers: an advanced Flexible Combined Imager and, in a first for Europe, a Lightning Imager that will allow the earlier detection of storms and extreme weather events, as well as improve aviation safety.
Building on the long-standing partnership between ESA and Eumetsat, the MTG-I1 will be one of six satellites operating in a fleet, of three at a time, to ensure the continuity of data from the previous Meteosat satellites over the next 20 years. The first Meteosat was launched in 1977 and this third generation of spacecraft will be the most advanced yet, with improved image resolution and providing close to real time data for users, or ‘nowcasting’ of fast-developing, high-impact weather.
The launch is currently scheduled for the end of 2022.
The film includes soundbites from ESA Director of Earth Observation Programmes: Simonetta Cheli, ESA Meteosat Programme Manager: Paul Blythe, ESA Meteosat Third Generation Payload Manager: Donny Aminou and EUMETSAT, Meteosat Third Generation Programme Manager: Alexander Schmid.
New weather satellite on its way to launch
30.9.2022 9:00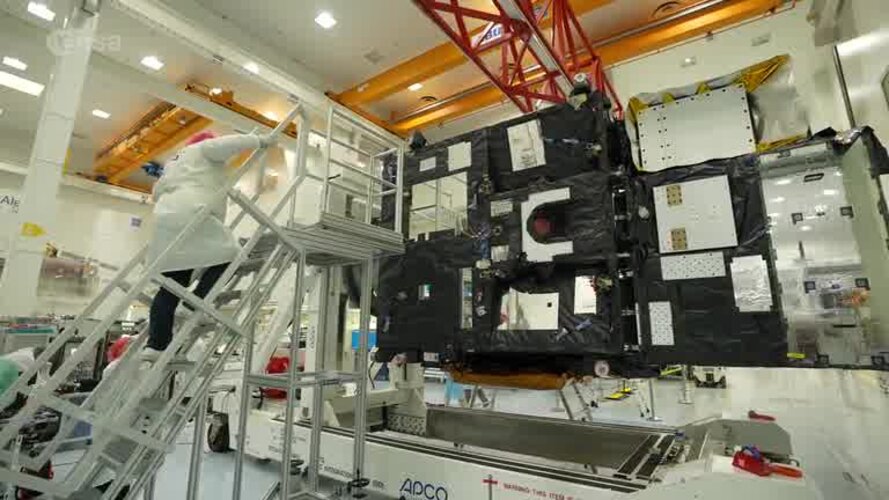 Video:
00:04:04
Video:
00:04:04
The final pre-launch preparations for the first Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) satellite are underway. The first satellite, called MTG-I1, built by a European industrial consortium led by Thales Alenia Space carries two imagers: an advanced Flexible Combined Imager and, in a first for Europe, a Lightning Imager that will allow the earlier detection of storms and extreme weather events, as well as improve aviation safety.
Building on the long-standing partnership between ESA and Eumetsat, the MTG-I1 will be one of six satellites operating in a fleet, of three at a time, to ensure the continuity of data from the previous Meteosat satellites over the next 20 years. The first Meteosat was launched in 1977 and this third generation of spacecraft will be the most advanced yet, with improved image resolution and providing close to real time data for users, or ‘nowcasting’ of fast-developing, high-impact weather.
The launch is currently scheduled for the end of 2022.
The film includes soundbites from ESA Director of Earth Observation Programmes: Simonetta Cheli, ESA Meteosat Programme Manager: Paul Blythe, ESA Meteosat Third Generation Payload Manager: Donny Aminou and EUMETSAT, Meteosat Third Generation Programme Manager: Alexander Schmid,
Please find more information at: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Meteorological_missions/meteosat_third_generation
New weather satellite on its way to launch
30.9.2022 9:00 Video:
00:04:04
Video:
00:04:04
The final pre-launch preparations for the first Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) satellite are underway. The first satellite, called MTG-I1, built by a European industrial consortium led by Thales Alenia Space carries two imagers: an advanced Flexible Combined Imager and, in a first for Europe, a Lightning Imager that will allow the earlier detection of storms and extreme weather events, as well as improve aviation safety.
Building on the long-standing partnership between ESA and Eumetsat, the MTG-I1 will be one of six satellites operating in a fleet, of three at a time, to ensure the continuity of data from the previous Meteosat satellites over the next 20 years. The first Meteosat was launched in 1977 and this third generation of spacecraft will be the most advanced yet, with improved image resolution and providing close to real time data for users, or ‘nowcasting’ of fast-developing, high-impact weather.
The launch is currently scheduled for the end of 2022.
The film includes soundbites from ESA Director of Earth Observation Programmes: Simonetta Cheli, ESA Meteosat Programme Manager: Paul Blythe, ESA Meteosat Third Generation Payload Manager: Donny Aminou and EUMETSAT, Meteosat Third Generation Programme Manager: Alexander Schmid.
Earth from Space: Lake Trasimeno
23.9.2022 10:00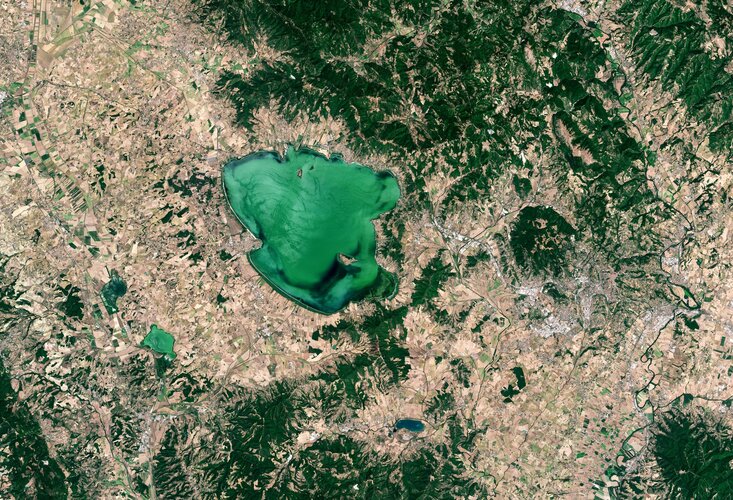
Lake Trasimeno, the fourth largest lake in Italy, is featured in this week’s Earth from Space image.
ESA selects Harmony as tenth Earth Explorer mission
22.9.2022 16:20
Following preparatory activities and a stringent process ESA Member States today formally selected Harmony for implementation as the tenth Earth Explorer mission within the FutureEO programme . This unique satellite mission concept is, therefore, now set to become a reality to provide a wealth of new information about our oceans, ice, earthquakes and volcanoes – which will make significant contributions to climate research and risk monitoring.
ESA selects Harmony as tenth Earth Explorer mission
22.9.2022 16:20
Following preparatory activities and a stringent process ESA Member States today formally selected Harmony for implementation as the tenth Earth Explorer mission within the FutureEO programme. This unique satellite mission concept is, therefore, now set to become a reality to provide a wealth of new information about our oceans, ice, earthquakes and volcanoes – which will make significant contributions to climate research and risk monitoring.
Mediterranean Sea hit by marine heatwave
22.9.2022 13:20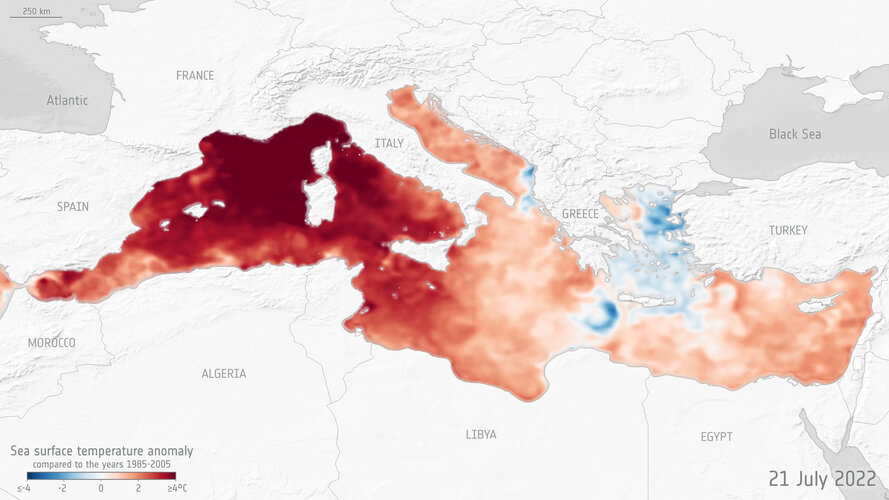
Many parts of Europe saw record-breaking temperatures over the summer, but it wasn’t just the continental mainland that was affected: the Mediterranean Sea also suffered a major marine heatwave. An ESA-funded project, CAREHeat, detected one of the most intense Mediterranean marine heatwaves observed during the satellite era – with sea surface temperatures reaching 5°C higher than average.
Zooming in on drought from space
21.9.2022 10:20
We are all aware that the summer of 2022 has been one of the hottest on record, causing drought and raging wildfires in many parts of Europe. Satellite data have been used to report the baking temperatures of the land surface and map fires, but the Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar mission has also been used to zoom in and provide very high-resolution measurements of the actual moisture content of the surface soils. Maps of northern Italy, for example, show how dry this summer has been compared to two years ago.
How do satellites monitor the ozone layer?
16.9.2022 14:25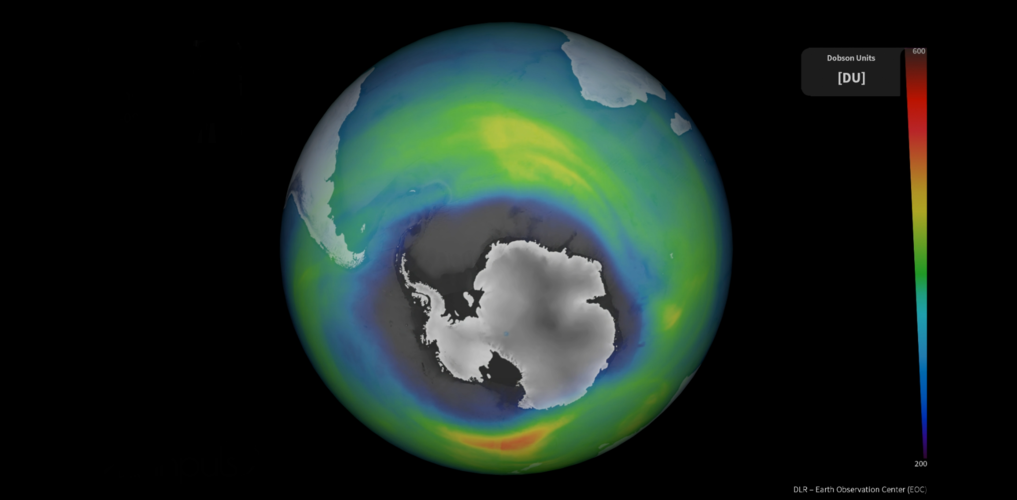
The ozone layer in our upper atmosphere protects Earth from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation. The use of human-produced chemicals in our atmosphere used for many years depleted Earth’s ozone layer. However, the reduction in the consumption of ozone-depleting substances driven by the Montreal Protocol – an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer – has allowed for the ozone hole to slowly recover. This global agreement demonstrates the power of international commitment and immediate global action in protecting our environment.
ESA has been involved in monitoring the ozone for over two decades. Today, 16 September, marks the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer and we take a closer look at how satellite instruments carefully monitor the ozone layer over the South Pole.
Earth from Space: UK heatwave
16.9.2022 10:00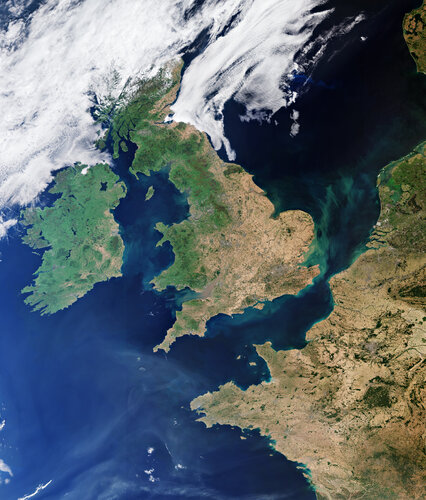
This summer, heatwaves struck Europe, North Africa, the US and Asia with temperatures reaching over 40°C in places – breaking many long-standing records. Images from the Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission show the scale of Britain’s heatwave as it baked in extreme temperatures in August.
Taking the dazzle out of CryoSat yields a first
14.9.2022 17:00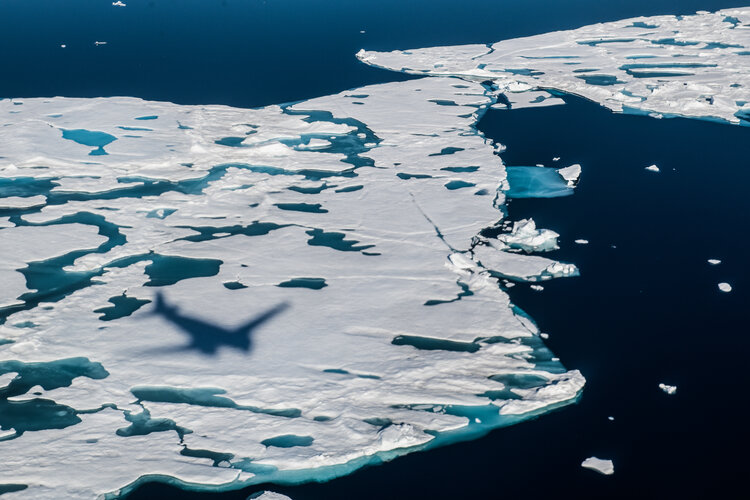
Since it was launched more than 12 years ago, ESA’s CryoSat ice mission has dazzled by way of its sheer technological and scientific excellence. This superb Earth Explorer satellite has returned a wealth of information that has transformed our understanding of Earth’s ice and how it is responding to climate change. In some circumstances, however, being dazzled isn’t a good thing, particularly when it comes to measuring the height of sea ice from space during the summer.
A paper published in Nature describes how scientists have now found an ingenious way of removing the pesky problem of dazzle from surface meltwater to yield the first ever continuous, year-round, altimetry measurements of sea-ice thickness in the Arctic Ocean.
Media invitation: International Astronautical Congress 2022 in Paris
13.9.2022 9:33Press Release N° 46–2022
The International Astronautical Congress 2022 (IAC) will be hosted in Paris, France, from Sunday to Thursday, 18-22 September 2022, at the Paris Convention Centre (1 place de la Porte de Versailles, 75015 Paris).
MTG-I1 weather satellite shows off
9.9.2022 9:33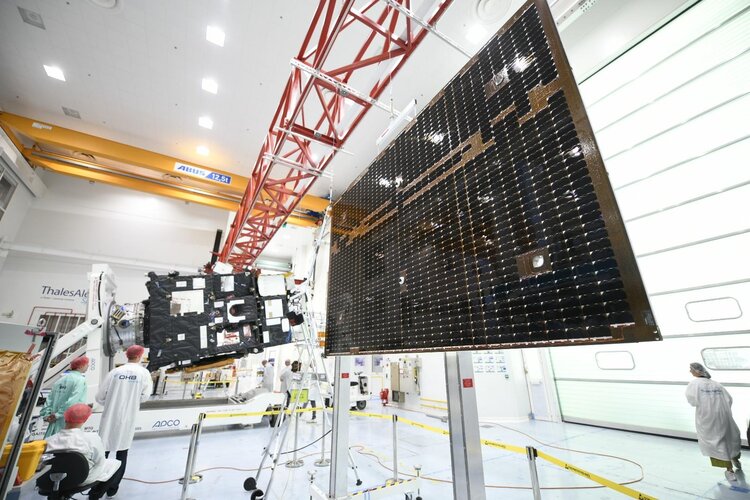
Before Europe’s first Meteosat Third Generation Imager leaves the south of France at the end of the month aboard a ship bound for French Guiana, this remarkable new weather satellite has been taking centre stage at Thales Alenia Space’s facilities in Cannes.
ESA–EGU Excellence Award 2023 open for nominations
7.9.2022 14:00
Following the success of the inaugural ESA–EGU Earth Observation Excellence Award in 2021, it’s now time to lodge your nomination for someone or for a team that deserves recognition for their innovative use of Earth observation. The call for nomination opens today and will close on 7 December.
The award winners will be announced and presented at the European Geosciences Union (EGU) General Assembly, which takes place on 23–28 April 2023.
Pakistan inundated
1.9.2022 12:02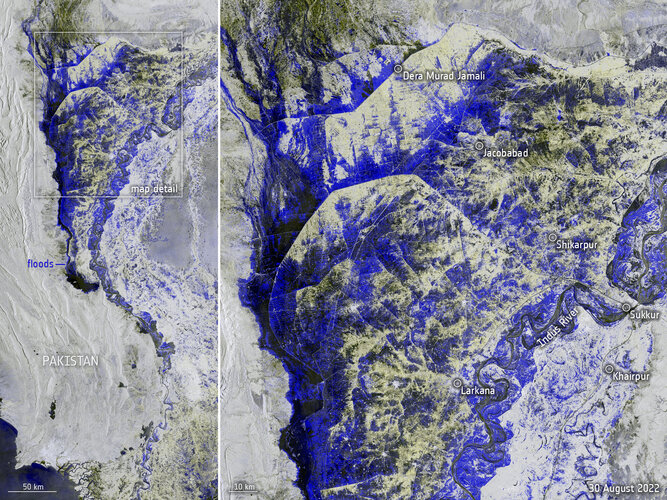 Image:
Data captured from space by Copernicus Sentinel-1 on 30 August was used to map the extent of flooding that is currently devastating Pakistan.
Image:
Data captured from space by Copernicus Sentinel-1 on 30 August was used to map the extent of flooding that is currently devastating Pakistan.
Pakistan inundated
1.9.2022 9:02 Image:
Captured from space by Copernicus Sentinel-1 on 30 August 2022, this image shows the extent of flooding that is currently devastating Pakistan. Heavy monsoon rainfall has led to more than a third of the country now being underwater.
Image:
Captured from space by Copernicus Sentinel-1 on 30 August 2022, this image shows the extent of flooding that is currently devastating Pakistan. Heavy monsoon rainfall has led to more than a third of the country now being underwater.
Pakistan inundated
1.9.2022 9:02 Image:
Data captured from space by Copernicus Sentinel-1 on 30 August was used to map the extent of flooding that is currently devastating Pakistan .Heavy monsoon rainfall has led to more than a third of the country now being underwater.
Image:
Data captured from space by Copernicus Sentinel-1 on 30 August was used to map the extent of flooding that is currently devastating Pakistan .Heavy monsoon rainfall has led to more than a third of the country now being underwater.
Drought causes Yangtze to shrink
24.8.2022 10:25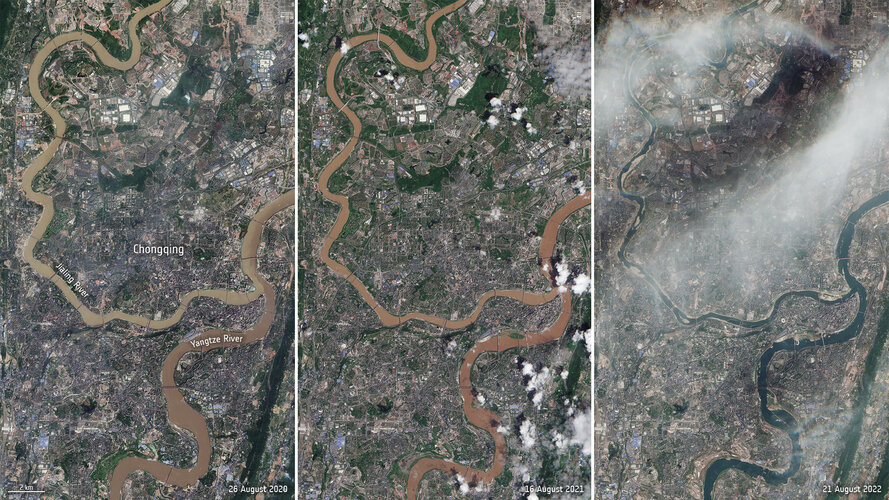 Image:
A record-breaking drought has caused parts of the Yangtze River to dry up – affecting hydropower, shipping routes and limiting drinking water supplies. Images captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission show a comparison of the Yangtze and Jialing rivers, near Chongqing, over the last three years.
Image:
A record-breaking drought has caused parts of the Yangtze River to dry up – affecting hydropower, shipping routes and limiting drinking water supplies. Images captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission show a comparison of the Yangtze and Jialing rivers, near Chongqing, over the last three years.
Heatwaves and climate change
18.8.2022 11:00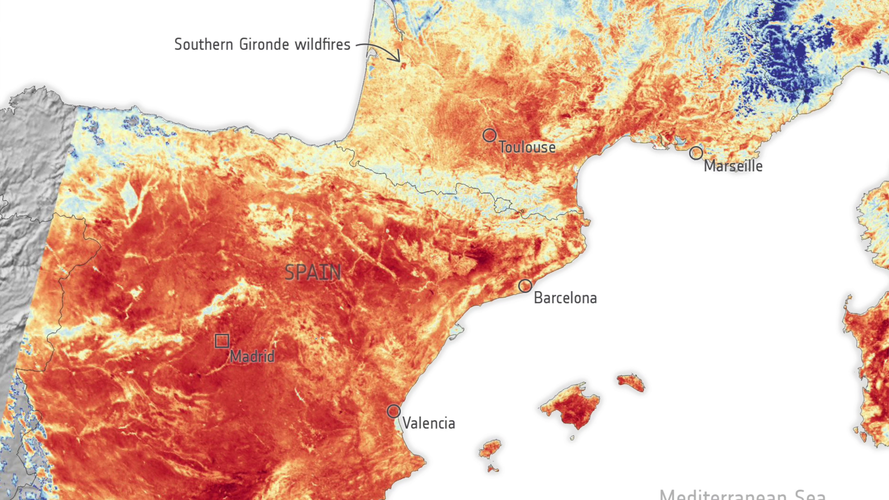 Video:
00:02:50
Video:
00:02:50
The series of heatwaves we are currently experiencing in western Europe is a clear sign of human-induced global warming. ESA’s Clement Albergel explains how we monitor these events using satellites such as the Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission and puts them in the context of the long-term climate data record generated via ESA’s Climate Change Initiative.
Rhine river runs dry
17.8.2022 12:20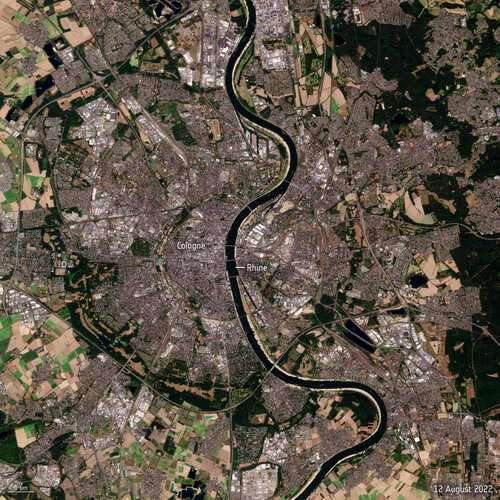 Image:
Water levels on the Rhine River have continued to drop owing to soaring temperatures and lack of rainfall - preventing many vessels from navigating through the river's waters at full capacity. These Copernicus Sentinel-2 images show the stark difference between August 2021 and August 2022.
Image:
Water levels on the Rhine River have continued to drop owing to soaring temperatures and lack of rainfall - preventing many vessels from navigating through the river's waters at full capacity. These Copernicus Sentinel-2 images show the stark difference between August 2021 and August 2022.
Invitation to media – Viewing Europe’s MTG-I weather satellite before launch in Cannes
9.8.2022 16:03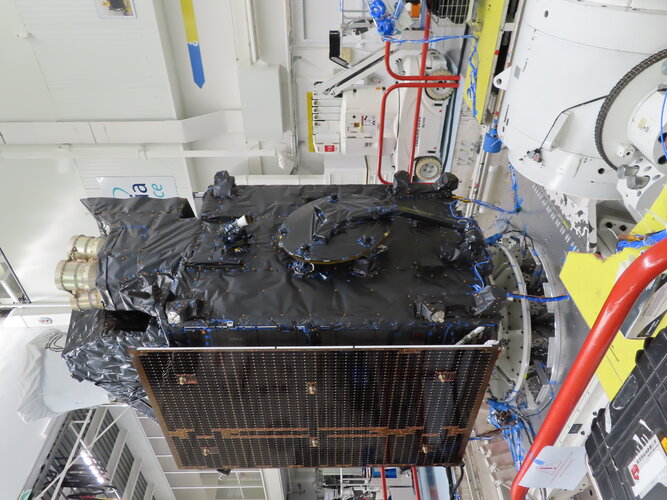
Call for Media: view MTG-I weather satellite before launch
Mission ends for Copernicus Sentinel-1B satellite
3.8.2022 11:00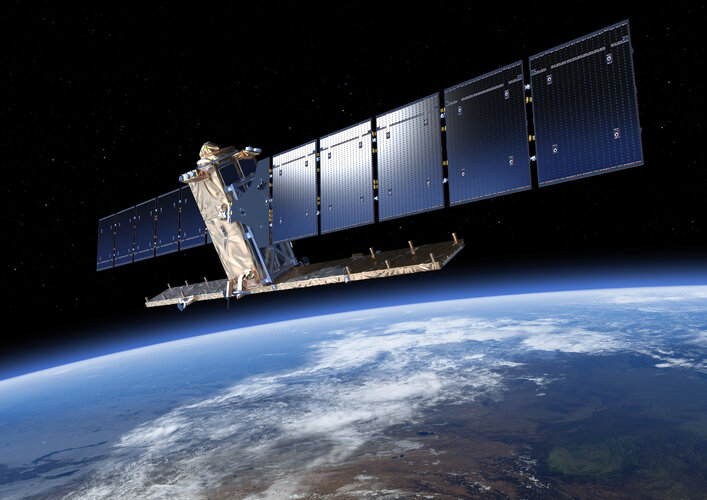
On 23 December 2021, Copernicus Sentinel-1B experienced an anomaly related to the instrument electronics power supply provided by the satellite platform, leaving it unable to deliver radar data. Since then spacecraft operators and engineers have been working tirelessly to rectify the issue. Unfortunately, despite all concerted efforts, ESA and the European Commission announce that it is the end of the mission for Sentinel-1B. Copernicus Sentinel-1A remains fully operational and plans are in force to launch Sentinel-1C as soon as possible.
Utah’s Great Salt Lake is disappearing
1.8.2022 17:20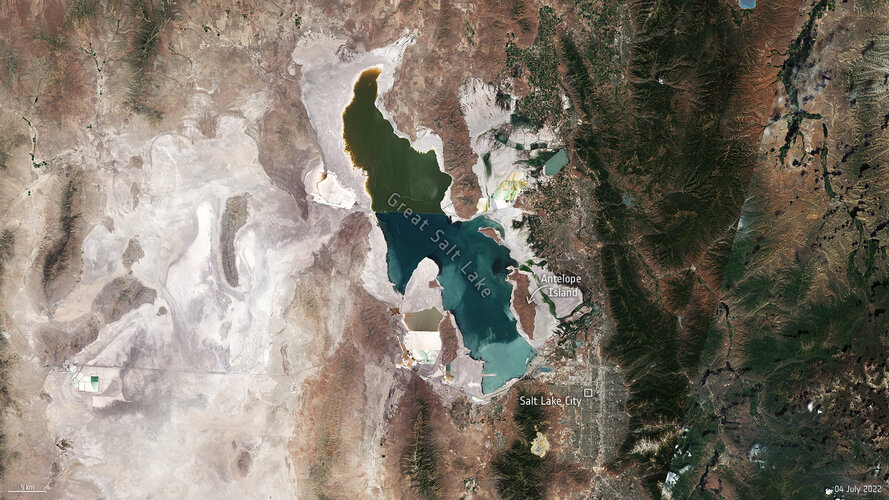
Utah’s Great Salt Lake dropped to its lowest recorded water level last month as a megadrought persists across the US southwest, forcing the fast-growing city to curb its water use. From space, satellite images show how water levels have fallen from 1985 to 2022 – exposing large expanses of lakebed.
Operation centres in tune for upcoming weather satellite
28.7.2022 15:40
In just a few months’ time Europe’s first Meteosat Third Generation satellite will soar into the skies on an Ariane 5 rocket from French Guiana. From geostationary orbit, this new satellite, carrying two new highly sensitive instruments, will take weather forecasting to the next level. Taking a significant step towards launch, the satellite operations teams at two different centres have completed an all-important suite of tests ensuring that their procedures are fully compatible with the satellite.
Tap into Europe in motion
26.7.2022 14:48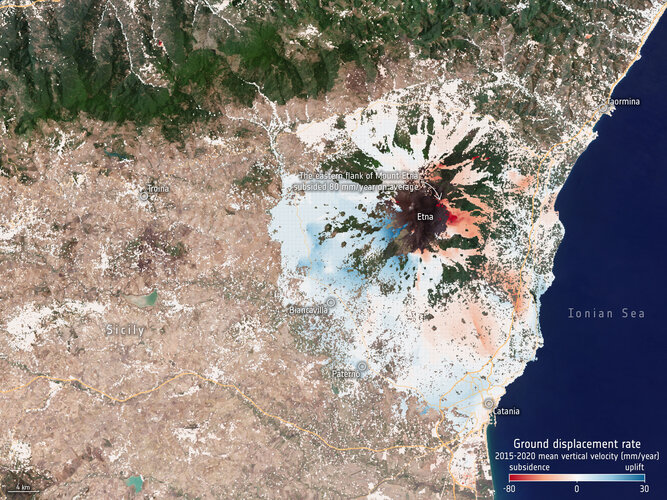
Any movement beneath our feet – from barely perceptible subsidence to the sudden appearance of a sinkhole or a crashing landslide – spells big trouble. Even relatively modest subsidence can weaken buildings and infrastructure and lead to issues such as flooding, and at worst the abrupt disappearance of sections of land brings immediate threat to life. Monitoring and predicting our shifting land is clearly essential for adopting mitigating strategies.
And now, thanks to Europe’s environmental Copernicus programme and the Sentinel-1 radar satellite mission, the first Europe-wide subsidence and soil movement analysis service is available to the public.
Greece battles wildfires on Lesbos island
25.7.2022 16:36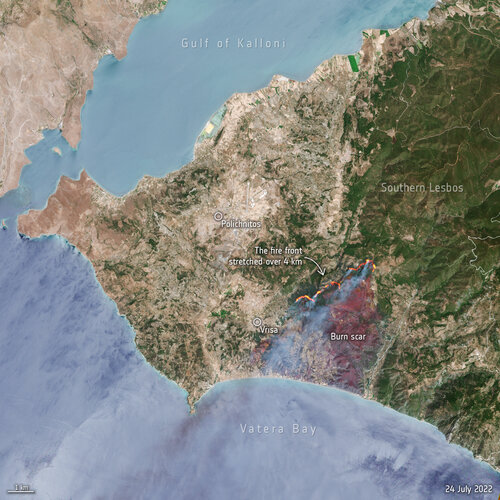 Image:
Hundreds of residents and tourists have been evacuated from the Greek island of Lesbos after a wildfire broke out on the morning of 23 July. This image, captured by Sentinel-2, shows the active fire front which stretches for more than four km.
Image:
Hundreds of residents and tourists have been evacuated from the Greek island of Lesbos after a wildfire broke out on the morning of 23 July. This image, captured by Sentinel-2, shows the active fire front which stretches for more than four km.
EarthCARE takes a big stretch
21.7.2022 13:04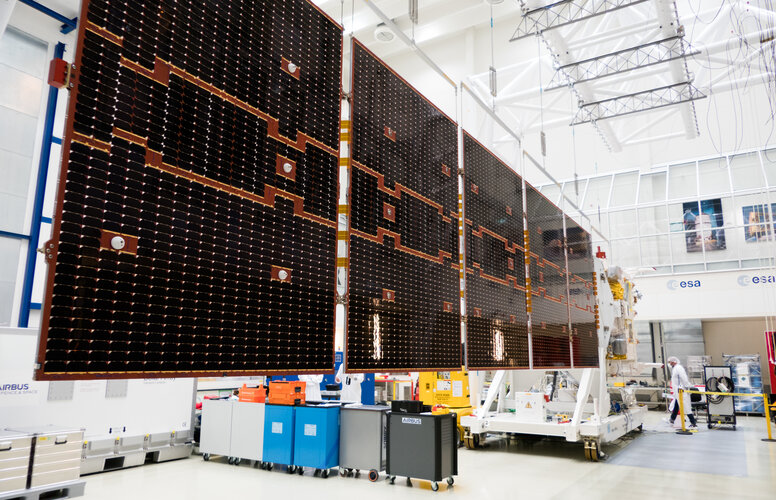
ESA’s upcoming EarthCARE satellite mission has just taken a big stretch. Engineers have gently unfolded this new satellite’s huge five-panel solar wing to test that it will deploy correctly once it is in space. The solar wing is a critical part of the satellite, providing the energy for EarthCARE to do its job: to quantify the role that clouds and aerosols play in heating and cooling Earth’s atmosphere.
TRUTHS shines
20.7.2022 14:00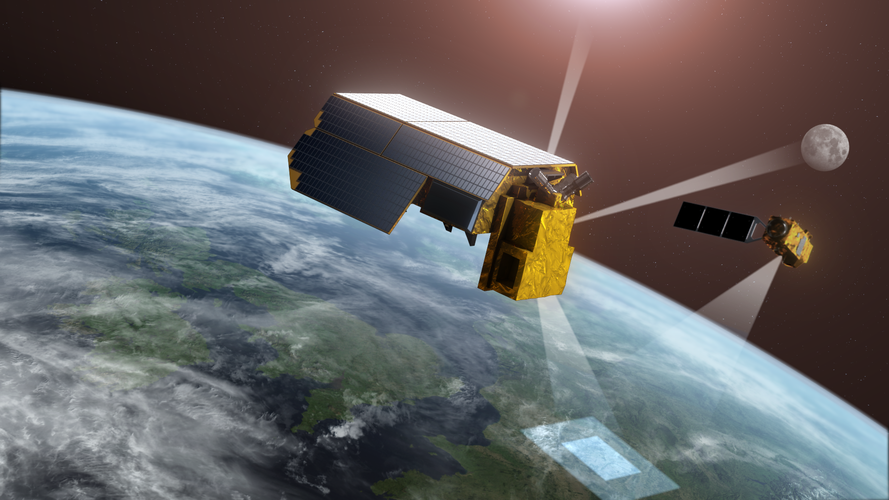
Satellites are essential for delivering key data to understand and monitor how the climate crisis is impacting our world, but, in turn, decision-makers need to be confident in the data they use for mitigation strategies and policymaking. TRUTHS, a new ESA mission, will do just this – and, now having passed an important milestone, it is one step closer to becoming a reality.
Feeling the heat from space
20.7.2022 9:49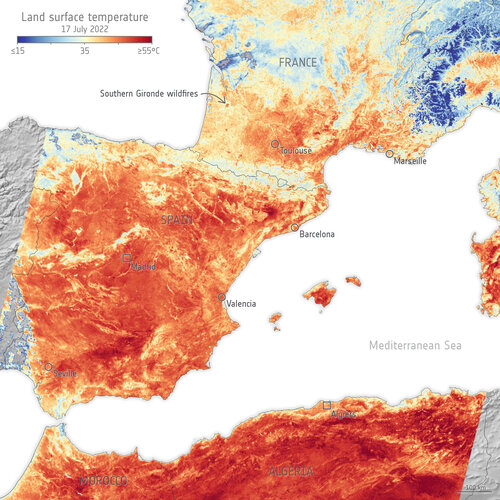
With searing temperatures and a string of record highs being smashed across western Europe, the current heatwave is all too apparent. Extreme heat warnings have been issued in several countries including France, Spain and Portugal, and deadly wildfires have forced thousands to flee their homes. The satellite images here are an example of how the crisis is being viewed by satellites orbiting Earth.
Wildfire near Salamanca: before-and-after
15.7.2022 15:00 Image:
These Copernicus Sentinel-2 images, one year apart, show the area affected by wildfire around Las Batuecas - Sierra de Francia Nature Reserve near Salamanca in western Spain.
Image:
These Copernicus Sentinel-2 images, one year apart, show the area affected by wildfire around Las Batuecas - Sierra de Francia Nature Reserve near Salamanca in western Spain.
Earth from Space: Fuerteventura and Lanzarote
8.7.2022 10:00
Fuerteventura and Lanzarote, part of the Canary Islands lying in the North Atlantic Ocean, are featured in this false-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
User Consultation Meeting on Harmony: watch the replay
6.7.2022 15:00
User Consultation Meeting on Harmony: watch the replay
Follow the discussions on Harmony – the candidate mission for ESA’s tenth Earth Explorer
City heat extremes
6.7.2022 13:30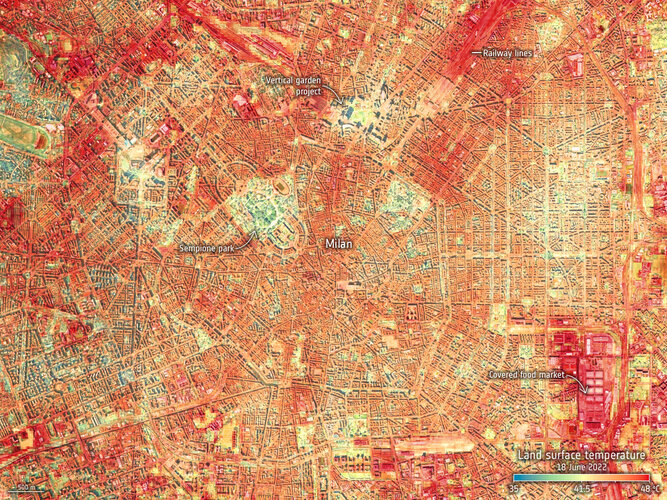
With air temperatures in excess of 10°C above the average for the time of year in parts of Europe, the United States and Asia, June 2022 has gone down as a record breaker. The fear is that these extreme early-season heatwaves are a taste of what could soon be the norm as climate change continues to take hold. For those in cities, the heat dissipates slower creating ‘urban heat islands’, which make everyday life even more of a struggle.
An instrument, carried on the International Space Station, has captured the recent land-surface temperature extremes for some European cities, including Milan, Paris and Prague.
Watch: Earth Explorer 10 Consultation
4.7.2022 12:30
Watch: Earth Explorer 10 Consultation
On 5 July, follow the discussion on Harmony at the User Consultation Meeting for ESA's tenth Earth Explorer
Earth from Space: Patagonia
1.7.2022 10:00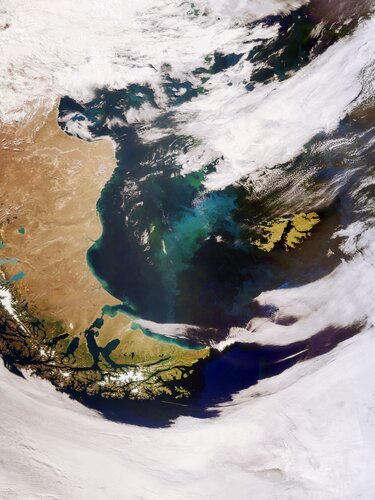
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission captured this impressive, wide-angled view of Patagonia at the southern end of South America, as well as the Falkland Islands.
Earth from Space: Patagonia
1.7.2022 10:00
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission captured this impressive, wide-angled view of Patagonia at the southern end of South America, as well as the Falkland Islands (Malvinas).
Copernicus Sentinel-1 maps Bangladesh flood
30.6.2022 17:00 Image:
Copernicus Sentinel-1 maps Bangladesh flood
Image:
Copernicus Sentinel-1 maps Bangladesh flood
Tenoumer Crater, Mauritania
30.6.2022 10:00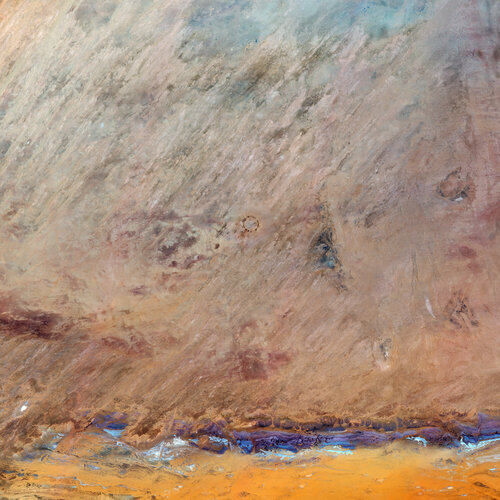 Image:
Deep within the Sahara Desert lies one of the best-preserved craters on Earth. On Asteroid Day, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over the almost-perfectly circular Tenoumer Crater in Mauritania.
Image:
Deep within the Sahara Desert lies one of the best-preserved craters on Earth. On Asteroid Day, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over the almost-perfectly circular Tenoumer Crater in Mauritania.
Contract secures design for ESA’s FORUM satellite
28.6.2022 9:00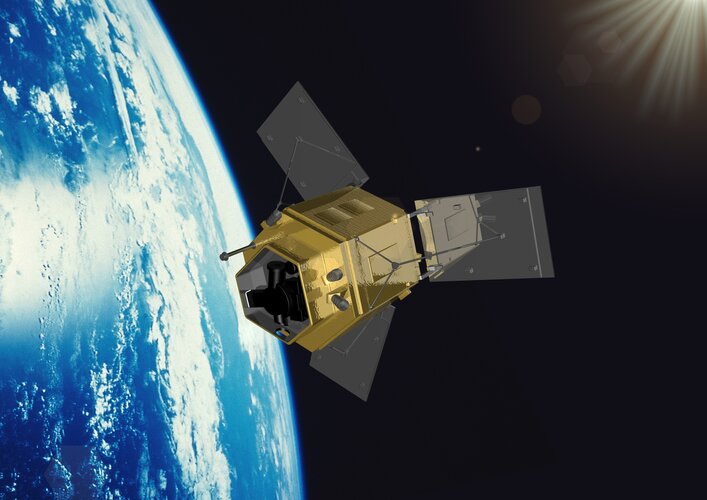
ESA has awarded a contract worth €160 million to Airbus in the UK to build the Earth Explorer FORUM satellite. This exciting new mission will yield unique insight into the planet’s radiation budget and how it is controlled – thereby filling in a critical missing piece of the climate jigsaw.
Short for Far-infrared Outgoing Radiation Understanding and Monitoring, FORUM is ESA’s ninth Earth Explorer mission.
Po River dries up
27.6.2022 9:30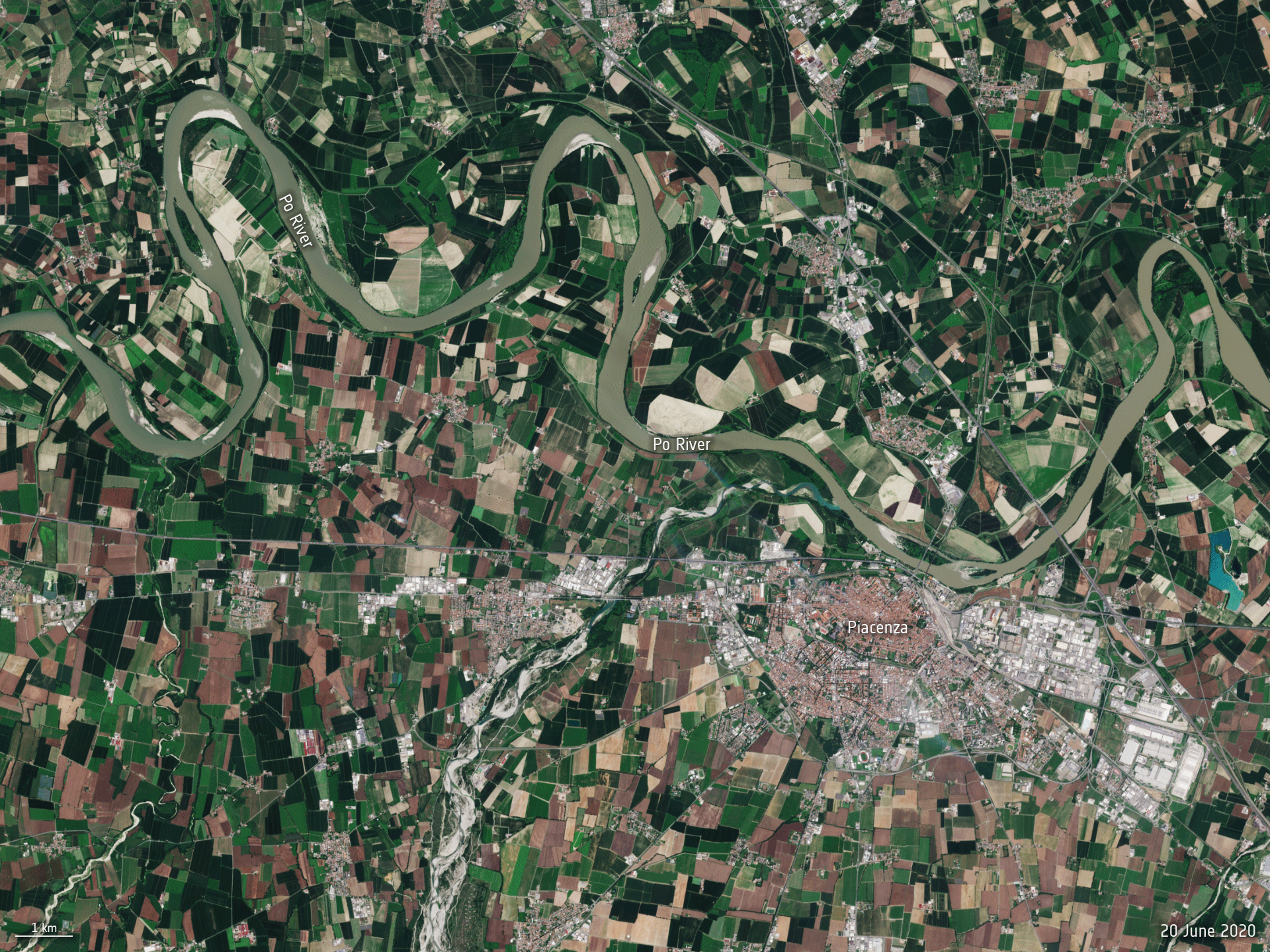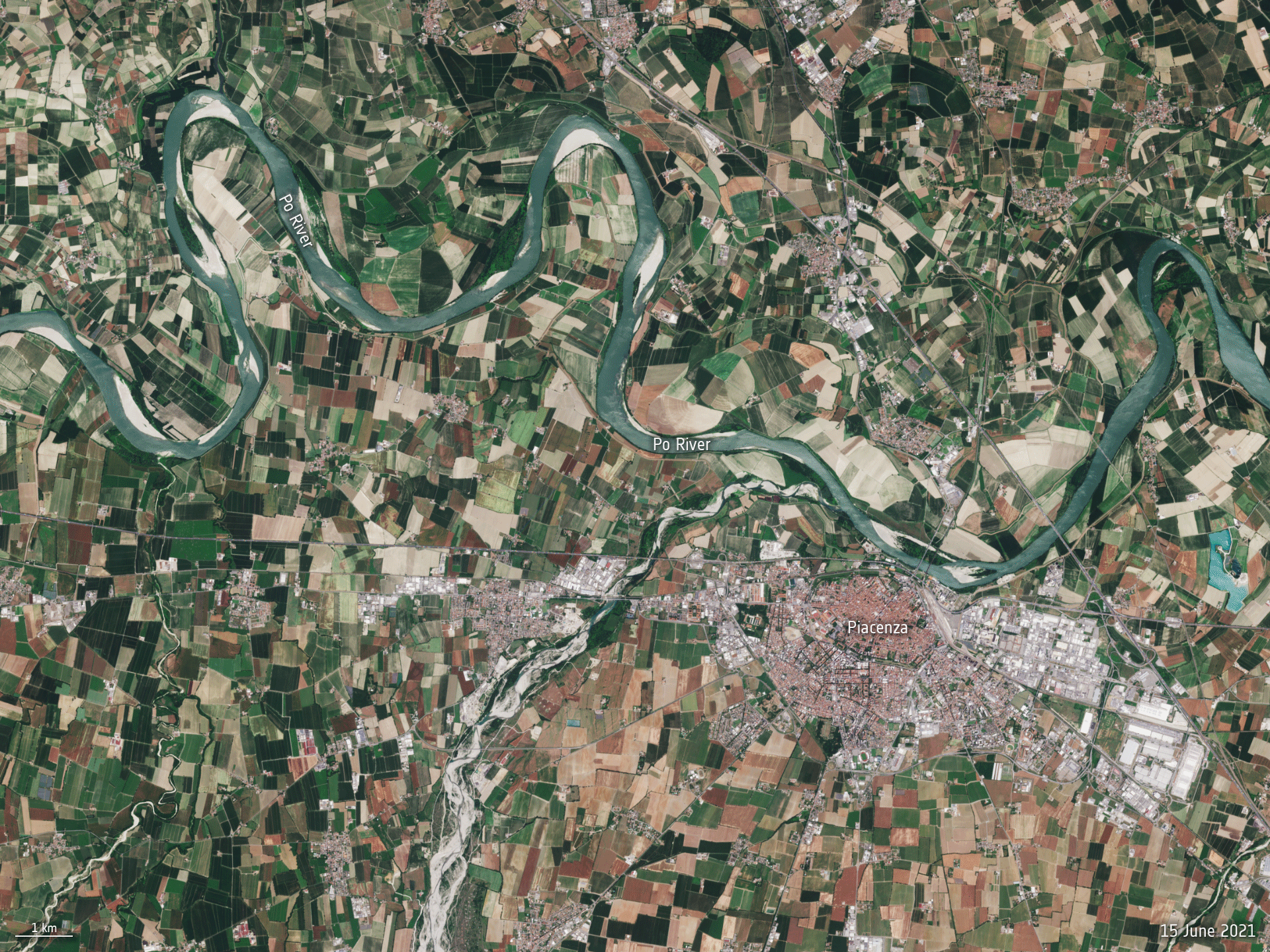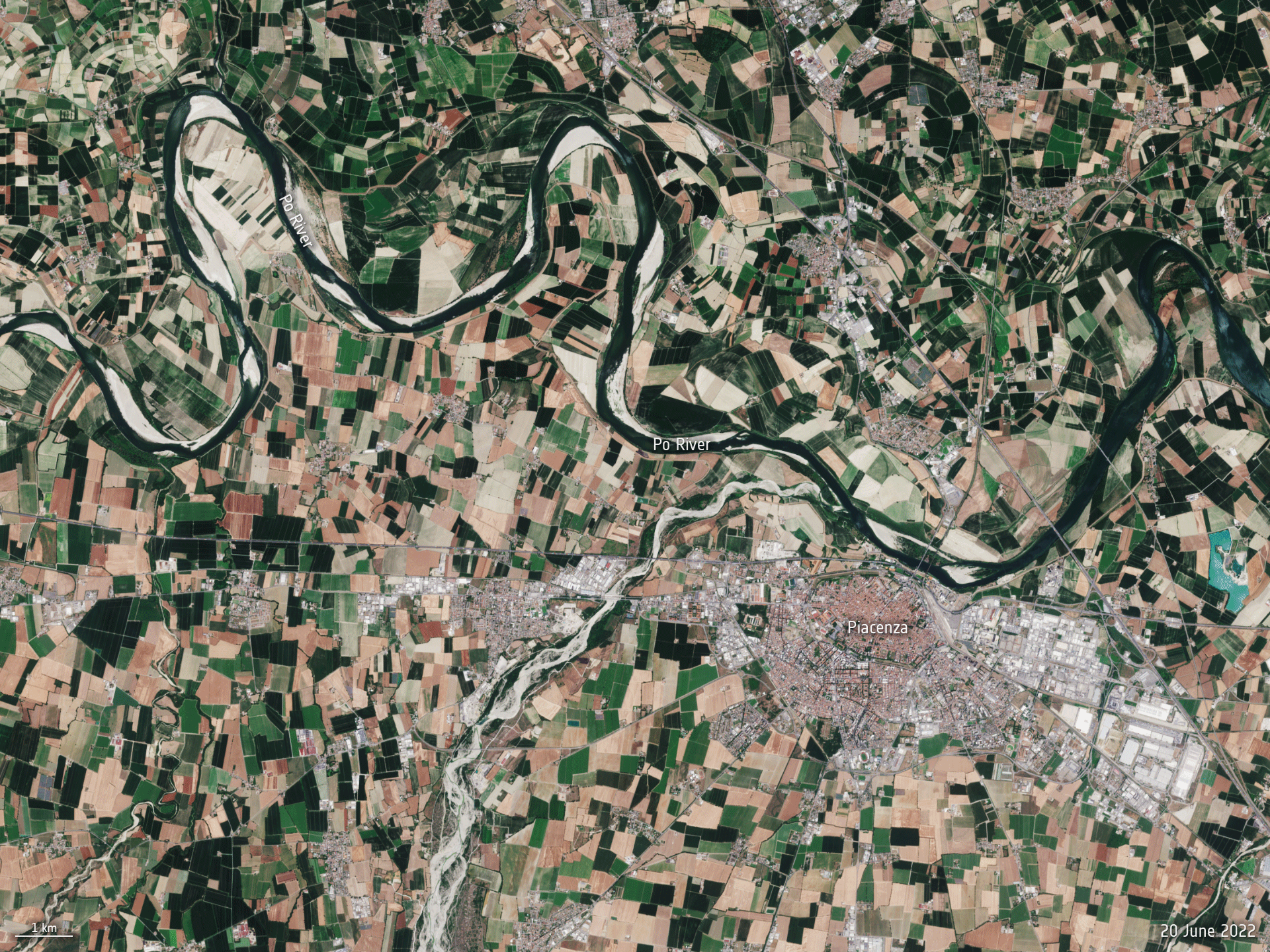 Image:
The Po River, the longest river in Italy, is hitting record low water levels after months without heavy rainfall. This Copernicus Sentinel-2 animation reveals how the river has significantly shrunk between June 2020 and June 2022.
Image:
The Po River, the longest river in Italy, is hitting record low water levels after months without heavy rainfall. This Copernicus Sentinel-2 animation reveals how the river has significantly shrunk between June 2020 and June 2022.
Earth from Space: Lake Balkhash
24.6.2022 10:00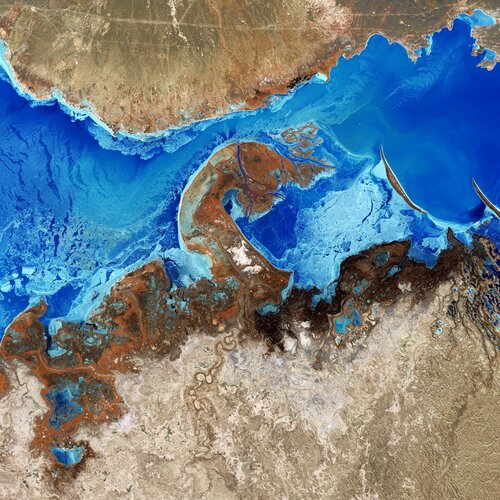
Lake Balkhash, the largest lake in Central Asia, is featured in this false-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Earth from Space: Lake Balkhash
24.6.2022 10:00
Lake Balkhash, the largest lake in Central Asia, is featured in this false-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Methane levels surged in 2020 despite lockdowns
23.6.2022 14:45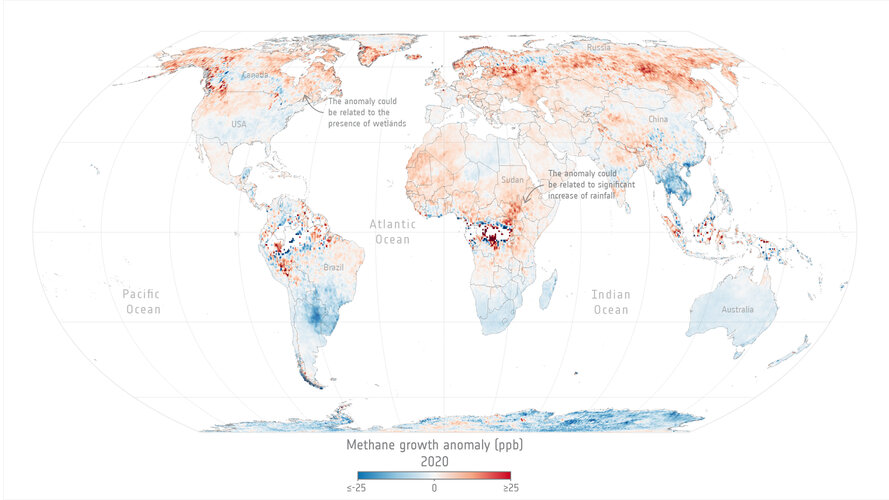
Levels of methane, the second most important greenhouse gas in our atmosphere, continued their unrelenting rise in 2020 despite the economic slowdown caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
A team of scientists, from the University of Leeds, have used data from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite to pinpoint locations with large surges of methane emissions. These findings were presented during ESA’s Living Planet Symposium which took place last month in Bonn, Germany.
Earth from Space: Glacier Bay, Alaska
17.6.2022 10:00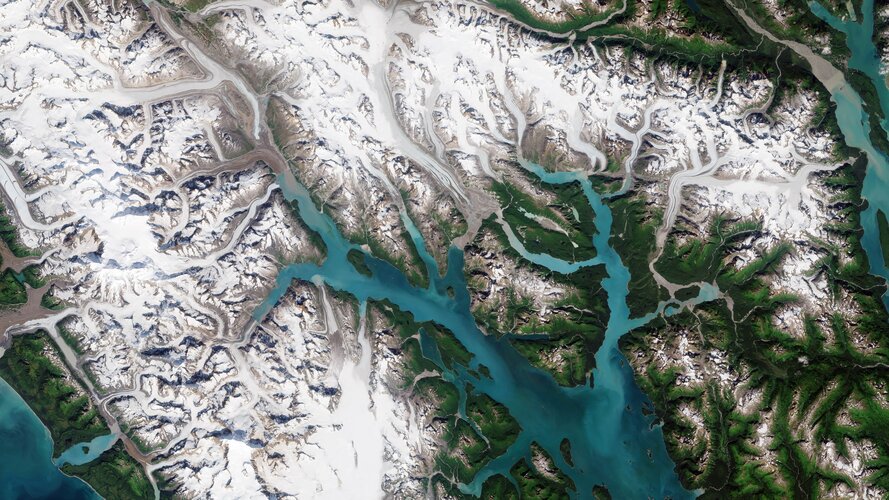
Part of the Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve, which lies along the coast of southeast Alaska, is featured in this image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Earth from Space: Singapore
10.6.2022 10:00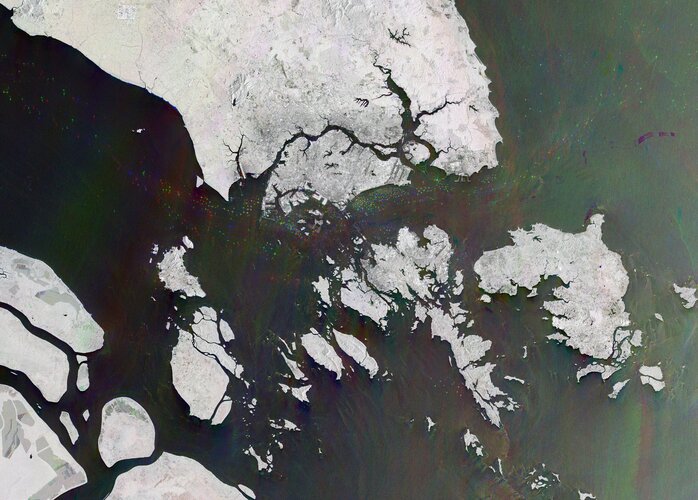
This radar image, captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission, shows us the only city-island-nation – Singapore – and one of the busiest ports in the world.
Earth from Space: Singapore
10.6.2022 10:00
This radar image, captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission, shows us the only city-island-nation – Singapore – and one of the busiest ports in the world.
Methane emissions detected over offshore platform in the Gulf of Mexico
9.6.2022 16:30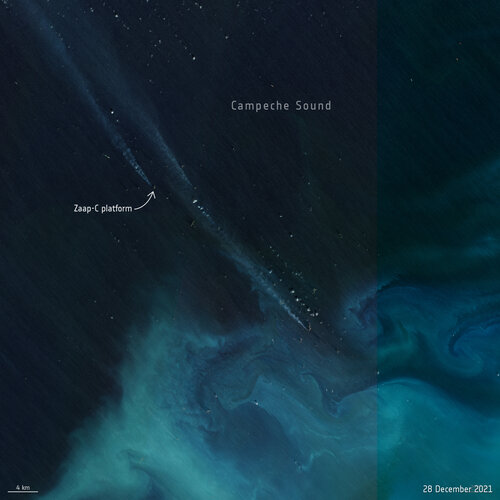
A team of scientists have used satellite data to detect methane plumes from an offshore platform in the Gulf of Mexico. This is the first time that individual methane plumes from offshore platforms are mapped from space.
Charting sea level from space
8.6.2022 16:00 Video:
00:12:21
Video:
00:12:21
Satellite images of our planet have become essential to our survival, offering a new outlook of our world. With rising seas being one of the biggest threats to society, satellite altimeter missions such as Copernicus Sentinel-6 are essential in monitoring global and regional changes in sea level.
Unbeknown to many, the island of Crete, Greece, plays an important role in the Copernicus satellite altimetry constellation and on an international stage. Satellite altimetry data have to be continuously monitored at the ESA’s Permanent Facility for Altimetry Calibration where different techniques have pioneered the use of transponders to provide the best measurements to validate satellite altimeters in space soon after launch.
This documentary explains how measurements are taken from the top of the White Mountains to make sure users get the best data on sea height from satellite altimetry.
It features interviews with Craig Donlon, Head of ESA’s Earth Surfaces and Interior Earth and Mission Science Division and Stelios Mertikas, Director of Laboratory of Geodesy & Geomatics Engineering at the Technical University of Crete.
Earth from Space: Puglia, Italy
3.6.2022 10:00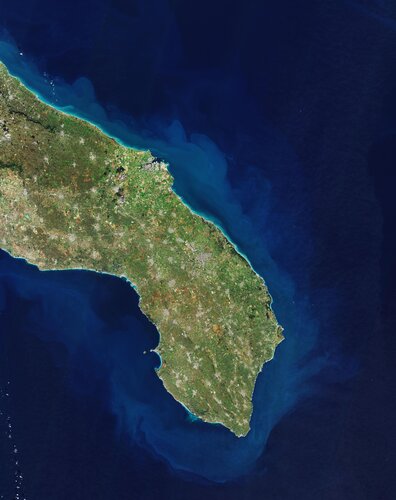
Part of Puglia, or Apulia, a region in southern Italy, is featured in this image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Revisit Living Planet Symposium: watch session replays
30.5.2022 11:00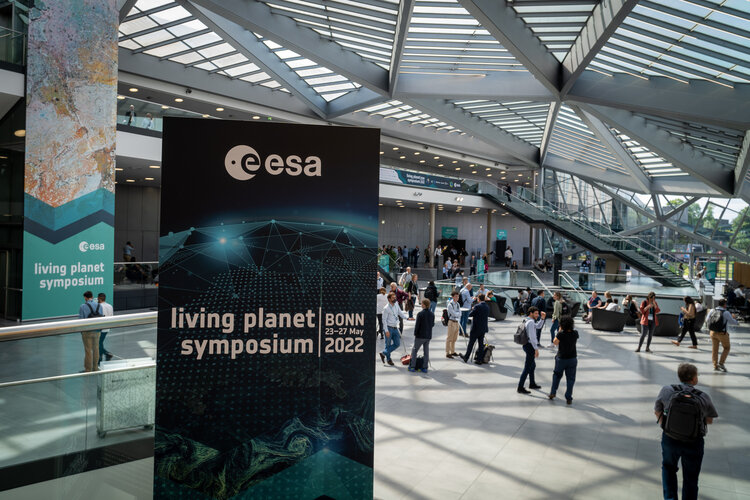
Revisit Living Planet Symposium: watch session replays
Living Planet concludes with record numbers
27.5.2022 13:42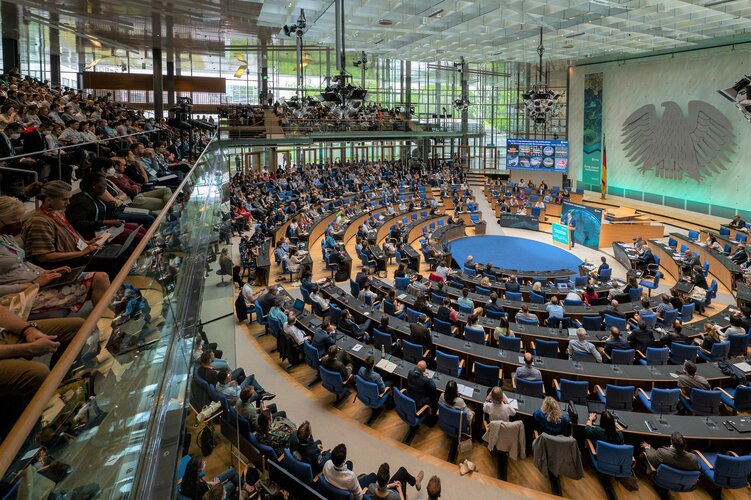
With more than 5000 participants, 240 science sessions and over 1300 oral presentations, ESA’s Living Planet Symposium comes to a close with record-breaking numbers. Held on 23-27 May at the World Conference Center in the German city of Bonn, the symposium brought together world-class scientists, business leaders, representatives from space agencies and international organisations and industry from around the world. Throughout the week, they showcased the latest advances in Earth observation and highlighted the essential role of Earth observation for decision making regarding the ongoing climate crisis. As the week draws to a close, we look back at some of the highlights of the week.
Boosting commercial Earth observation
27.5.2022 11:45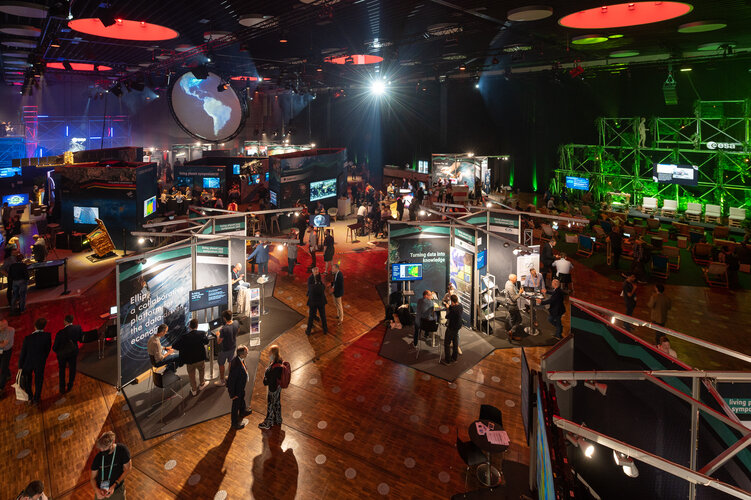
One of the objectives of the Living Planet Symposium, taking place this week in Bonn, is to foster interaction between the institutional and commercial sectors to boost the Earth observation space economy. This is being achieved by highlighting existing partnerships, expanding the number of data users and facilitating access to private funds for companies.
Oceans and Climate
26.5.2022 17:15 Video:
00:03:33
Video:
00:03:33
Earth’s oceans are huge heat stores, soaking up 93% of the excess heat from human activity over the past 70 years. Ocean currents redistribute heat around the planet, from the Equator to the poles. Where this ocean heat goes influences weather patterns and regional climate. As well as absorbing heat, oceans are a natural carbon sink, absorbing a quarter of carbon dioxide emissions from human activity. This has led to the acidification of ocean water, threating marine life.
The amount of heat and carbon dioxide absorbed depends on a number of ocean variables, all of which can be measured from space.
Taking climate monitoring into the future with quantum
26.5.2022 17:00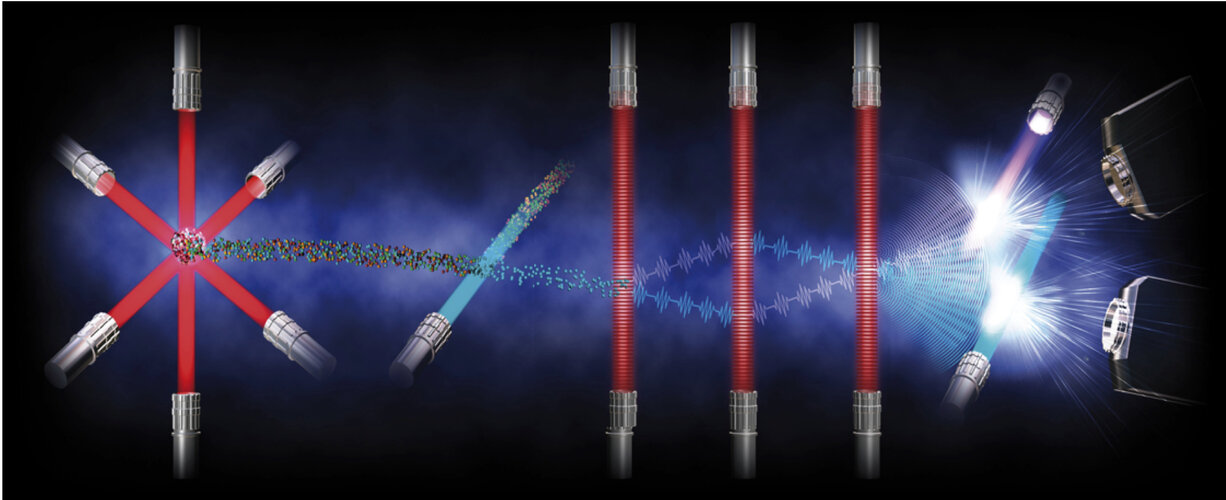
Over the last decades, satellites measuring the many aspects of Earth have certainly demonstrated their worth with the information they yield to understand and monitor our environment and, importantly, to provide undeniable evidence of climate change for policymaking. While Europe is currently firmly placed as a world leader in Earth observation, it’s critical to stay ahead of the game by examining how even more sophisticated space technologies can be developed to return even more precise information in the future.
Today, at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, being held in Bonn, scientists dug deep into the potential of spaceborne quantum gravity sensors to do just this.
Taking climate monitoring into the future with quantum
26.5.2022 17:00
Over the last decades, satellites measuring the many aspects of Earth have certainly demonstrated their worth with the information they yield to understand and monitor our environment and, importantly, to provide undeniable evidence of climate change for policymaking. While Europe is currently firmly placed as a world leader in Earth observation, it’s critical to stay ahead of the game by examining how even more sophisticated space technologies can be developed to return even more precise information in the future. Today, at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, being held in Bonn, scientists dug deep into the potential of spaceborne quantum gravity sensors to do just this.
Water cycle
26.5.2022 12:47 Video:
00:03:23
Video:
00:03:23
Imagine the world without water: as cold and lifeless as the planet Mars. Earth is unique in our solar system in being able to sustain liquid water on its surface. Water is essential for life and for Earth’s climate, helping transport heat around the planet, but it is difficult to track through the whole water cycle. The global view offered by satellites helps. ESA’s Climate Change Initiative is looking at a range of climate variables linked to the water cycle.
Putting the future in FutureEO
26.5.2022 12:45
With scientific excellence at the very heart of ESA’s FutureEO programme, participants at this week’s Living Planet Symposium have been making it clear that new research missions to advance Earth science must continue to be realised in the future.
What can satellites reveal about climate tipping points?
26.5.2022 9:01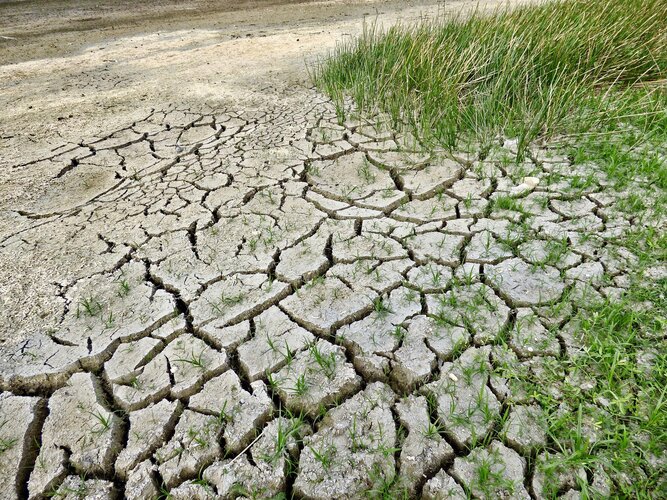
The effects of our warming climate are seen across a multitude of measures, usually as incremental changes: more frequent extreme weather, heatwaves, droughts and wildfires. The cumulative impact of these changes, however, can cause fundamental parts of the Earth system to change more quickly and drastically. These ‘tipping points’ are thresholds where a tiny change pushes the system into an entirely new state.
This week, at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, scientists came together to discuss the latest research evidence for climate tipping points and identify the opportunities and challenges of using remote sensing data to understand them.
Historic Greenland ice sheet rainfall unravelled
25.5.2022 15:30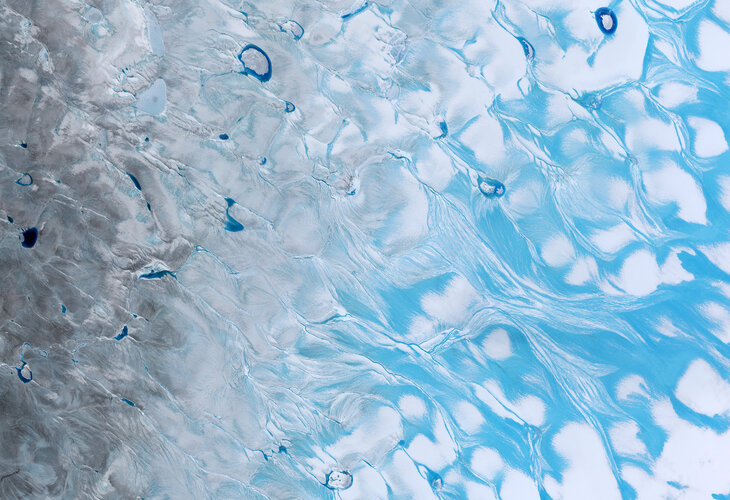
For the first time ever recorded, in the late summer of 2021, rain fell on the high central region of the Greenland ice sheet. This extraordinary event was followed by the surface snow and ice melting rapidly. Researchers now understand exactly what went on in those fateful summer days and what we can learn from it.
From Rome to Bonn by bike
25.5.2022 13:55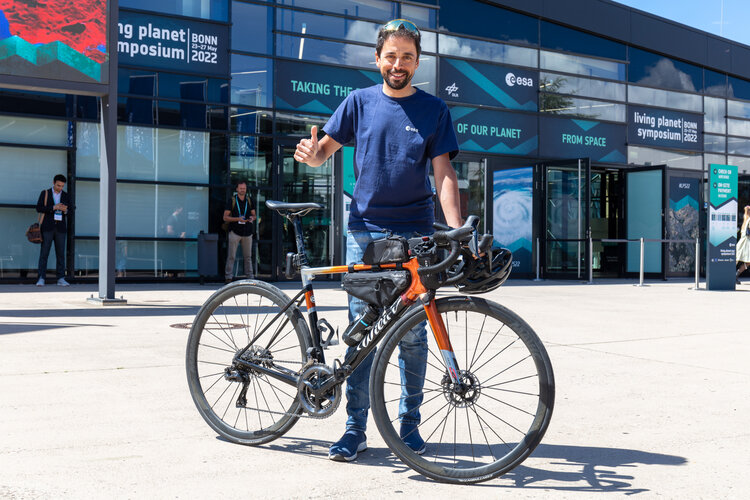 Image:
Omar di Felice, an extreme cyclist, has biked from Rome to Bonn to take part at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium. Tune in today at 15:30 live from Bonn on ESA Earth Observation Instagram as he’s joined by ESA Astronaut Luca Parmitano and ESA CryoSat Mission Geophysicist Alessandro di Bella.
Image:
Omar di Felice, an extreme cyclist, has biked from Rome to Bonn to take part at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium. Tune in today at 15:30 live from Bonn on ESA Earth Observation Instagram as he’s joined by ESA Astronaut Luca Parmitano and ESA CryoSat Mission Geophysicist Alessandro di Bella.
From Rome to Bonn by bike
25.5.2022 13:55 Image:
Omar Di Felice, an extreme cyclist, has biked from Rome to Bonn to take part at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium. Tune in today at 15:30 live from Bonn on ESA Earth Observation Instagram as he’s joined by ESA Astronaut Luca Parmitano and ESA CryoSat Mission Geophysicist Alessandro di Bella.
Image:
Omar Di Felice, an extreme cyclist, has biked from Rome to Bonn to take part at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium. Tune in today at 15:30 live from Bonn on ESA Earth Observation Instagram as he’s joined by ESA Astronaut Luca Parmitano and ESA CryoSat Mission Geophysicist Alessandro di Bella.
Supporting the Paris Agreement from space
25.5.2022 12:15
Earth observation is already capable of supporting national climate action, but there are many more opportunities on the horizon, according to discussions today among leading scientists and policymakers at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium being held in Bonn, Germany.
GHGSat joins ESA’s Third Party Mission Programme
24.5.2022 18:15
GHGSat, a leader in high-resolution greenhouse gas monitoring from space, has officially joined ESA’s prestigious Third Party Mission Programme. Announced today at the Living Planet Symposium currently taking place in Bonn, data from the company’s fleet of commercial satellites will be provided, free of charge, to researchers working in the fields of Earth science and climate change. Users will be able to access greenhouse gas measurements from sites all around the world.
Revealing coastline dynamics of the Danube Delta
24.5.2022 16:45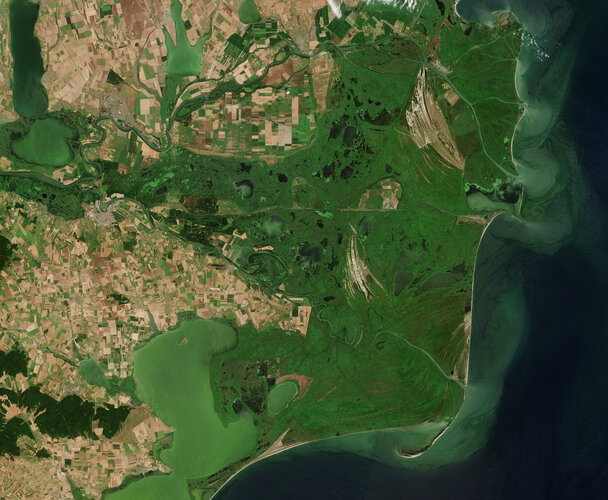
Hundreds of satellite images spanning 30 years have been compiled to show the evolution of the Danube Delta – the second largest river delta in Europe. These findings were presented today at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium taking place this week in Bonn, Germany.
Africa in the spotlight at Living Planet Symposium
24.5.2022 15:11
We live in uncertain times. The detrimental impacts of climate change are being felt around the world and threatening our future, we are emerging from the global COVID pandemic that halted life as we know it for more than two years, and now the Ukraine crisis is not only a tragedy for those directly affected but its rippling effects are jeopardising energy and food security far and wide. Some nations are able to weather these storms better than others, but a number of countries in Africa, for example, are already on the back foot, particularly when it comes to food security. Today, at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, much of the focus was on furthering the uptake of Earth observation and advancing the digital transformation in Africa to address societal challenges.
Africa in the spotlight at Living Planet Symposium
24.5.2022 15:11
We live in uncertain times. The detrimental impacts of climate change are being felt around the world and threatening our future, we are emerging from the global COVID pandemic that halted life as we know it for more than two years, and now the Ukraine crisis is not only a tragedy for those directly affected but its rippling effects are jeopardising energy and food security far and wide. Some nations are able to weather these storms better than others, but a number of countries in Africa, for example, are already on the back foot, particularly when it comes to food security.
Today, at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, much of the focus was on furthering the uptake of Earth observation and advancing the digital transformation in Africa to address societal challenges.
It’s a kind of MAGIC
24.5.2022 15:00
With well over 4000 scientists, academics, space industry personnel, institutional stakeholders, data users, students and citizens all gathered at the Living Planet Symposium, this world-renowned Earth observation event is already proving to be a bit like magic, especially after the gruelling two-year COVID pandemic. However, there’s also another kind of magic in the air creating a buzz – no, not the band Queen singing their hit single, but a potential new satellite mission called MAGIC that would shed new light on where Earth’s water is stored and how it moves from place to place.
SNAP spurs Earth observation innovation with one million downloads
24.5.2022 12:00
An open-access Earth observation analysis tool that has continued to grow in popularity in the seven years since its launch has now been projected to reach one million downloads, ESA announced today at the Living Planet Symposium.
Accelerators gear up at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium
24.5.2022 8:58
Global climate change is the single most challenging issue faced by humanity – affecting every region, continent and ocean on Earth. It fuels a range of other top-level challenges such as food security, migration, biodiversity loss, risks to human health and economic losses.
This week, at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium taking place in Bonn, high-level ESA representatives, along with a mix of academia and policy experts, came together to discuss ESA’s ‘Space for a Green Future Accelerator’ – a major ESA initiative aiming to accelerate the use of space in Europe.
Full steam ahead for carbon dioxide monitoring mission
23.5.2022 18:00
The Copernicus Anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide Monitoring mission has taken another step forward as ESA authorises the mission’s prime contractor, OHB, to continue the development of the first satellite that will take it to being launch-ready and, in parallel, start production on the mission’s second satellite. Celebrated at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium in Bonn, this contract rider follows an initial contract that was signed in 2020.
Swarm unveils magnetic waves deep down
23.5.2022 15:00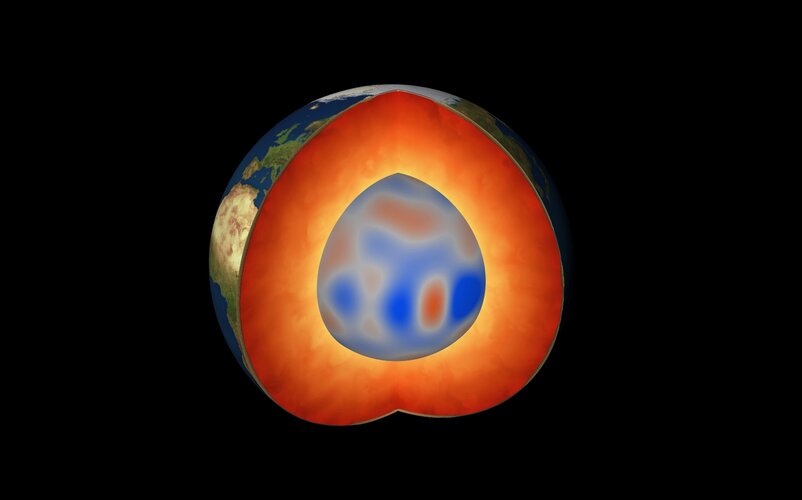
While volcanic eruptions and earthquakes serve as immediate reminders that Earth’s insides are anything but tranquil, there are also other, more elusive, dynamic processes happening deep down below our feet. Using information from ESA’s Swarm satellite mission, scientists have discovered a completely new type of magnetic wave that sweeps across the outermost part of Earth’s outer core every seven years. This fascinating finding, presented today at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, opens a new window into a world we can never see.
Living Planet Symposium kicks off
23.5.2022 13:00
ESA’s Living Planet Symposium has opened with a flourish with over 4000 participants including scientists, academics, space industry representatives, institutional stakeholders, data users, students and citizens gathered to discuss the latest findings on our changing planet, as well as advances in satellite technologies, new opportunities in the commercial world, and ESA’s plans for the future.
Live now: Living Planet Symposium
23.5.2022 8:20
Live now: Living Planet Symposium
Watch the Opening Session live from Bonn
Watch live: Living Planet Symposium 2022
20.5.2022 14:55
The time has finally come for ESA’s Living Planet Symposium – one of the largest Earth observation conferences in the world. Follow our live streaming all week on ESA Web TV, starting with the Opening Ceremony on Monday 23 May at 09:00 (CEST).
Watch live: Living Planet Symposium 2022
20.5.2022 14:55
The time has finally come for ESA’s Living Planet Symposium – one of the largest Earth observation conferences in the world. Follow our live streaming all week on ESA Web TV.
Earth from Space: Bonn, Germany
20.5.2022 10:00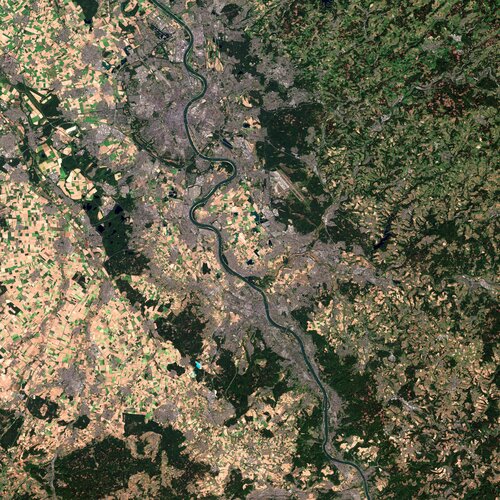
ESA’s Living Planet Symposium – one of the largest Earth observation conferences in the world – is being held on 23–27 May in Bonn, Germany. Held every three years, the symposium brings together scientists and researchers, as well as industry and users of Earth observation data, from all over the world to present and discuss the latest findings on Earth science.
Space agencies provide global view of our changing environment
19.5.2022 14:59
International collaboration among space agencies is central to the success of satellite Earth observation and data analysis. ESA, NASA and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) have continued their joined effort to develop a storytelling dashboard that combines their resources and expertise to strengthen our global understanding of the changing environment and its economic effects.
Earth from Space: Arc de Triomphe
13.5.2022 10:00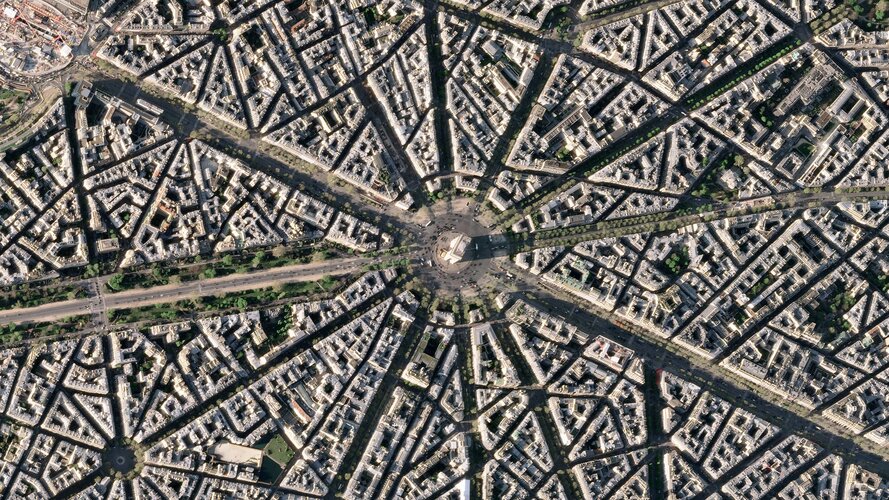
This striking, high-resolution image of the Arc de Triomphe, in Paris, was captured by Planet SkySat – a fleet of satellites that have just joined ESA’s Third Party Mission Programme in April 2022.
Last chance to register for ESA’s Living Planet Symposium
9.5.2022 14:54
ESA’s Living Planet Symposium is fast approaching. Taking place on 23–27 May in Bonn, Germany, the symposium gives you the opportunity to network with the most eminent scientists in the field of Earth science, learn more about Earth science and innovative concepts such as New Space and, if you’re lucky, rub elbows with a few ESA astronauts.
This is your last chance to register to one of the largest Earth observation conferences in the world!
Last chance for register to ESA’s Living Planet Symposium
9.5.2022 14:54
ESA’s Living Planet Symposium is fast approaching. Taking place on 23–27 May in Bonn, Germany, the symposium gives you the opportunity to network with the most eminent scientists in the field of Earth science, learn more about Earth science and innovative concepts such as New Space and, if you’re lucky, rub elbows with a few ESA astronauts.
This is your last chance to register to one of the largest Earth observation conferences in the world!
Earth from Space: Rhine River, Germany
6.5.2022 10:00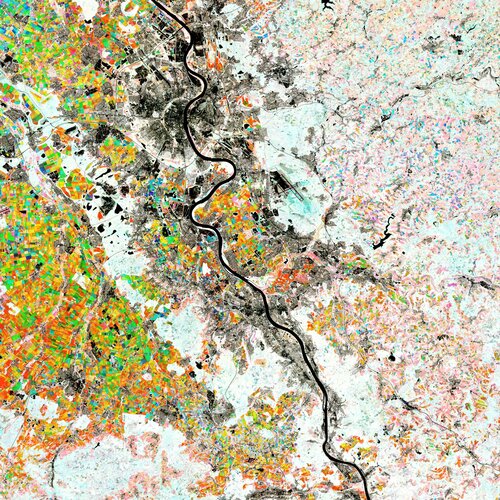
The Rhine River, the longest river in Germany, is featured in this colourful image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission. Along this river lies the city of Bonn: the host of this year’s Living Planet Symposium – one of the largest Earth observation conferences in the world – taking place on 23–27 May 2022.
Tracking agricultural-related deforestation
5.5.2022 11:27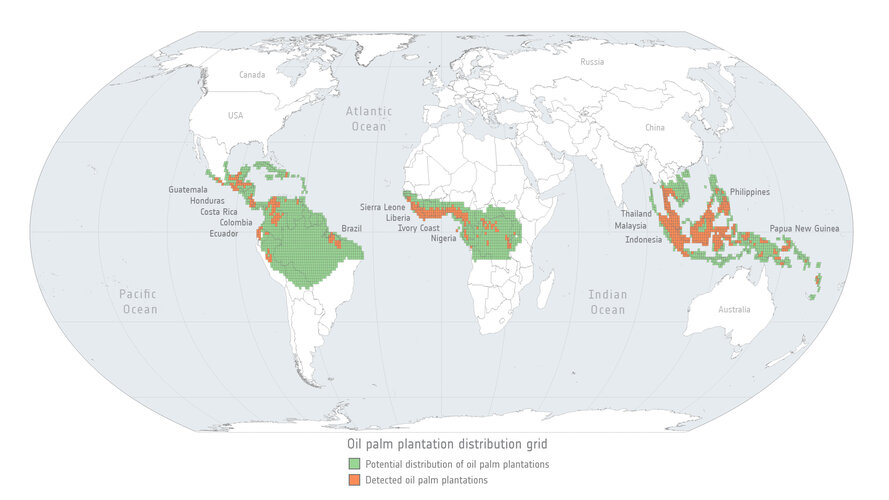
The global trade in agricultural commodities provides food, fuel and fibre to consumers around the world. Commodity production, however, is also linked with negative environmental impacts, including the loss and degradation of forested land.
Approximately 90% of global deforestation is driven by agricultural expansion – a phenomenon which has roots in the global demand for products such as palm oil, soy and beef. New research reveals how satellites can be used to map and monitor forest-cover changes and help implement effective zero deforestation commitments.
Tracking agricultural-related deforestation
5.5.2022 11:27
The global trade in agricultural commodities provides food, fuel and fibre to consumers around the world. Commodity production, however, is also linked with negative environmental impacts, including the loss and degradation of forested land.
Approximately 90% of global deforestation is driven by agricultural expansion – a phenomenon which has roots in the global demand for products such as palm oil, soy and beef. New research reveals how satellites can be used to map and monitor forest-cover changes and help implement effective zero deforestation commitments.
Call for Media: Join ESA’s Living Planet Symposium in Bonn
3.5.2022 11:30
Call for Media: Join ESA’s Living Planet Symposium in Bonn
Heatwave across India
29.4.2022 15:15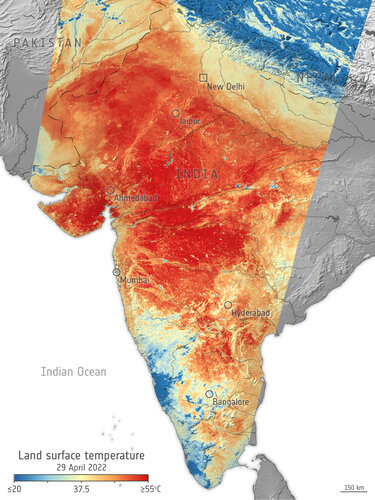 Image:
India is currently facing a prolonged heatwave, with temperatures exceeding 42°C in numerous cities across the country. This map, generated using data from Copernicus Sentinel-3, shows the land surface temperature on 29 April.
Image:
India is currently facing a prolonged heatwave, with temperatures exceeding 42°C in numerous cities across the country. This map, generated using data from Copernicus Sentinel-3, shows the land surface temperature on 29 April.
Earth from Space: Mount Aso, Japan
29.4.2022 10:00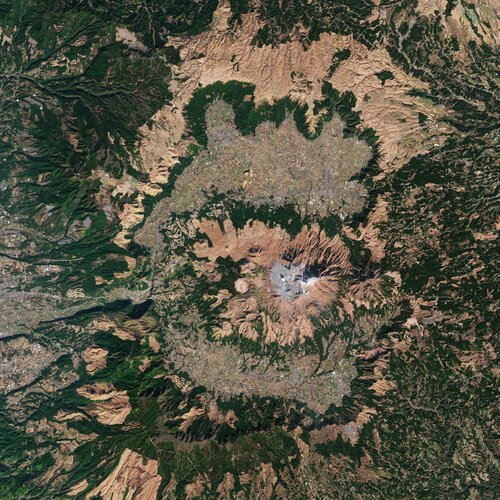
Mount Aso, the largest active volcano in Japan, is featured in this image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Earth from Space: Mount Aso, Japan
29.4.2022 10:00
Mount Aso, the largest active volcano in Japan, is featured in this image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Living Planet Symposium: apply for student grants
26.4.2022 15:20Living Planet Symposium: apply for student grants
Keeper of the winds shines on
26.4.2022 10:00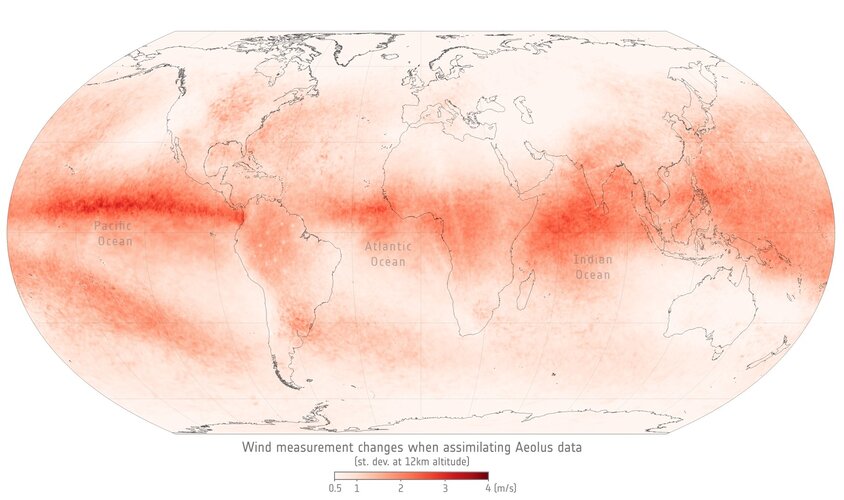
Launched back in 2018, Aeolus has outlived its 36-month in-orbit design life – but going above and beyond, it continues to deliver excellent data. This shows that there’s life yet in the satellite, meaning ESA’s wind mission is now expected to continue shining a light on the wind for another year.
Key findings from the European State of the Climate Report
22.4.2022 12:45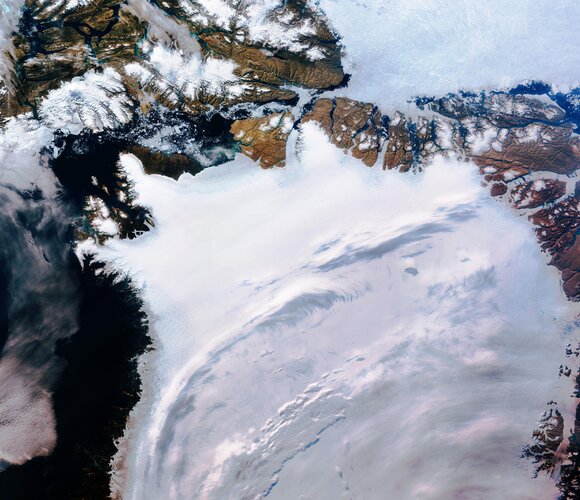
Europe experienced its warmest summer on record in 2021, accompanied by severe floods in western Europe and dry conditions in the Mediterranean. These are just some of the key findings from the Copernicus Climate Change Service’s European State of the Climate report released today. The in-depth report provides key insights and a comprehensive analysis of climate conditions in 2021, with a special focus on Europe and the Arctic.
Key findings from the European State of the Climate Report
22.4.2022 12:45
Europe experienced its warmest summer on record in 2021, accompanied by severe floods in western Europe and dry conditions in the Mediterranean. These are just some of the key findings from the Copernicus Climate Change Service’s European State of the Climate report released today. The in-depth report provides key insights and a comprehensive analysis of climate conditions in 2021, with a special focus on Europe and the Arctic.
















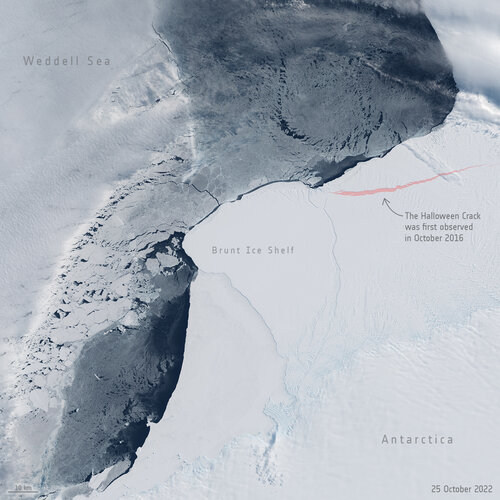 Image:
Halloween Crack for Halloween
Image:
Halloween Crack for Halloween
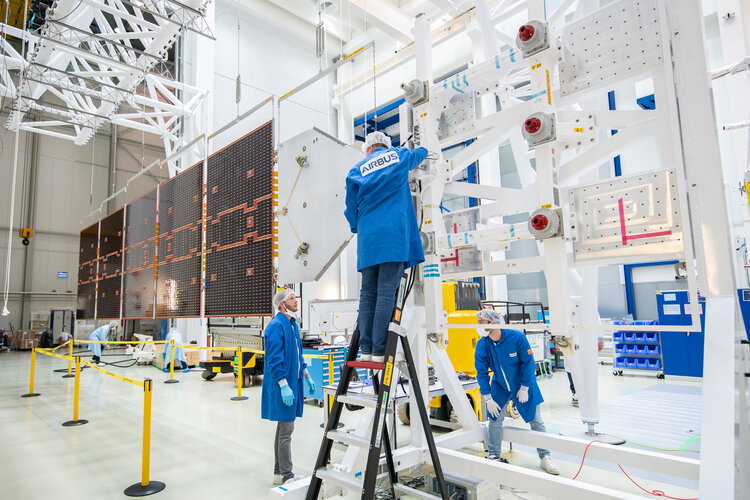 Image:
EarthCARE taking wing
Image:
EarthCARE taking wing

