zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Ekonom - asistent
14.3.2023 14:44 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Ekonom-asistentMany great ways EUSPA supports entrepreneurs using EU Space technologies
14.3.2023 14:30 European GNSS Agency
The link between space technology and user needs is innovation – innovation that’s happening at companies across Europe.
As the go-to-source for all things EU Space, EUSPA has played – and continues to play – a big role in supporting this innovation. “We have built a reputation for being the single point of information, expertise and market intelligence that companies of all sizes depend on when integrating European space solutions into their business solutions,” adds EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
So, how can EUSPA help turn your innovative idea into a space-based success story? Let us count the ways!
1. Funding Initiatives
As any start-up knows all-too-well, the biggest challenge to innovation is funding. Based on the conversations our Market Development team have had with entrepreneurs, there’s a clear gap in what businesses need to innovate at their full potential and the funding and support that is currently available to them. The result is that some European companies struggle to get their innovations from drawing board to prototype, let alone to market.
To help, EUSPA offers a wide-range of funding opportunities serving all entrepreneurial needs during the entire innovation cycle: from Fundamental Elements and the development of innovative chipset, antenna and receiver technologies to the very successful Horizon Calls focusing on the development of innovative space downstream applications, and finally the CASSINI activities that range from hackathons, innovation prizes and contests like the myEUspace competition that target the expansion and growth of space ventures. In addition to cash prizes, many of these initiatives come with additional perks like business support and incubation.
Likewise, Fundamental Elements is an R&D funding mechanism designed to support the development of innovative chipset, antenna and receiver technologies that industry would not yet invest in on its own initiative. In doing so, the programme helps accelerate the integration of European GNSS into market-ready devices and solutions.
To see how 38 companies have already benefited from the initiative, be sure to download our Fundamental Elements Catalogue.
Last but not least, the EUSPA Space Academy is your ticket to creating ground-breaking new apps and disruptive business solutions using the power of EU Space. The online training is open to all individuals, start-ups, entrepreneurs and SMEs who want to learn the ins and outs of building a space application business. There are numerous courses to choose from, all of which are taught by top academics, industry leaders and EUSPA experts. Oh, and did we mention that it’s 100% free?
2. Market intelligence
As an SME or start-up, you simply can’t afford to make decisions blindly. That’s why EUSPA should be your new best friend.
We are well-known across the industry as a leading source of critical market intelligence, one that is regularly relied upon by policymakers, entrepreneurs and major corporations. For example, our EO and GNSS Market Report provides in-depth analyses on the latest global trends and developments, and it does so through illustrated examples and use cases.
EUSPA’s team of market experts also carefully monitor the latest trends and developments in user technology, which we cover in our GNSS User Technology Report. Written with the advice of leading receiver and chipset manufacturers, this report serves as a valuable tool to support planning and decision-making on the development, purchasing and use of GNSS user technology.
Or maybe you want to become an active investor in the exciting field of space technology? No worries, EUSPA has you covered too. Our GNSS Investment Report, the first of its kind, quantifies the investment needs of major companies and looks at the impact the acquisition of EU companies by foreign investors has on Europe’s overall competitiveness.
With Europe’s Green Deal opening up a plethora of opportunities for innovative companies, this year EUSPA published its EU Space for Green Transformation Report. In addition to introducing the Green Deal and its implications for companies, the report also presents detailed examples of how various industries are leveraging the power of EU Space to drive their sustainability journeys.
You can download all our market intelligence publications free of charge here.
3. Innovation across all EU Space Programme components
Charged with promoting Copernicus’ services, data and market uptake, EUSPA is actively helping European companies embrace Earth Observation. For instance, we are in constant communication with European companies, advising them on how they can best leverage Copernicus data, information and services.
In addition, preparing for GOVSATCOM and IRIS2, our funding opportunities focus on various areas of satellite communications. We have launched several funding opportunities for companies, including Horizon Europe calls and CASSINI initiatives covering all space programme components.
4. Promoting the EU Space brand
In addition to supporting the development of innovative chipsets and receivers, EUSPA also works tirelessly to ensure that the world’s leading chip manufacturers include Galileo in their products. As a result of this work, over 3.9 billion Galileo-enabled smartphones have been sold worldwide – which is good news for European companies developing location-based services and applications.
5. Talent and skill development
According to European Commissioner for the Internal Market Thierry Breton, a skilled workforce is the key to sustainable growth, innovation and competitiveness. “Europe's strength resides in its talent, including engineers, researchers and entrepreneurs,” he says. “To achieve our Digital Decade and Green Deal goals, we want to support our companies, in particular SMEs, in hiring, training and keeping talent.”
Here, EUSPA offers paid traineeships where university students and graduates acquire the skills they need to enter the labour market with confidence.
An ecosystem of starts-ups and SMEs
Thanks in part to support initiatives like these, EUSPA has built a sizeable ecosystem of start-ups and SMEs, all of whom are leveraging the benefits of EU space data and services. In fact, to date, more than 1000 companies have received support from EUSPA.
Ready to add your company’s name to this list?
Then contact us today at market@euspa.europa.eu and let EUSPA be your partner in innovation!
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
rada / odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí na Ka
14.3.2023 14:03 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí na Karada / odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí na Ka
14.3.2023 14:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Liberec Katastrálního úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
rada / odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí na Ka
14.3.2023 14:03 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-vOdborný seminář: BIM pro technickou infrastrukturu
14.3.2023 13:51 czBIMBIM pro technickou infrastrukturu Informační management staveb vedle pozemního a dopravního stavitelství nachází uplatnění i v celém životním cyklu staveb a zařízení technické infrastruktury, zahrnující...
Článek Odborný seminář: BIM pro technickou infrastrukturu se nejdříve objevil na czBIM.
Odborný seminář: BIM pro technickou infrastrukturu
14.3.2023 13:51 czBIMBIM pro technickou infrastrukturu Informační management staveb vedle pozemního a dopravního stavitelství nachází uplatnění i v celém životním cyklu staveb a zařízení technické infrastruktury, zahrnující...
Článek Odborný seminář: <a href="https://www.czbim.org/events/bim-pro-technickou-infrastrukturu/">BIM pro technickou infrastrukturu</a> se nejdříve objevil na czBIM.
rada / odborný rada – metodik katastru nemovitostí v oddělení metodiky a kontroly v Kanceláři ředite
14.3.2023 12:57 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada – metodik katastru nemovitostí v oddělení metodiky a kontroly v Kanceláři řediterada / odborný rada – metodik katastru nemovitostí v oddělení metodiky a kontroly v Kanceláři ředite
14.3.2023 12:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - kancelář ředitelevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada – metodik katastru nemovitostí v oddělení metodiky a kontroly v Kanceláři ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
rada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily Ka
14.3.2023 12:47 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Semily vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily Karada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily Ka
14.3.2023 12:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Semilyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily Katastrálního úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
rada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily Ka
14.3.2023 12:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/misto-rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-katmísto rada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Sem
14.3.2023 12:47 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Semily vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti SemRada/odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily Kata
14.3.2023 12:42 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Semily vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí na Katastrálním pracovišti Semily KataCarbon dioxide monitoring mission in development
14.3.2023 11:00 ESA Observing the Earth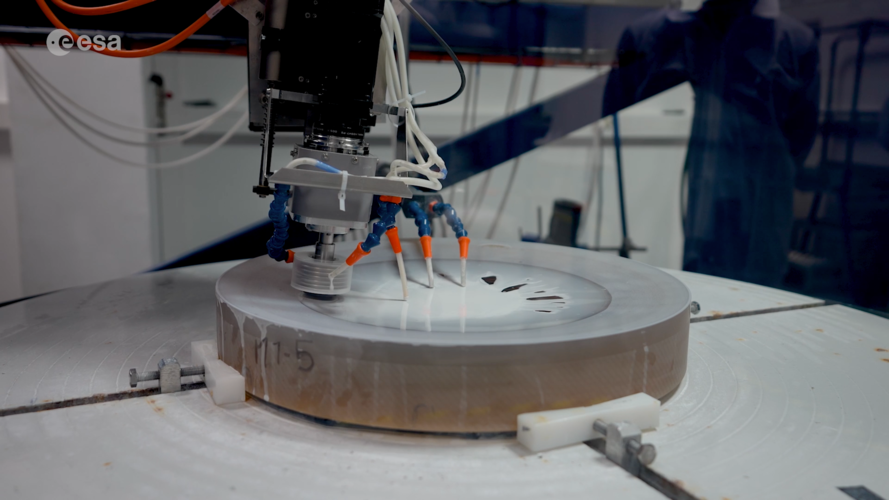 Video:
00:04:58
Video:
00:04:58
The pressure is on to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases we pump into the atmosphere – but the race is also on to support the monitoring that shows if targets are being met. Being developed by ESA on behalf of the EU, the new Copernicus Anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide Monitoring mission, or CO2M for short, is destined to be Europe’s prime mission for monitoring and tracking carbon dioxide emissions from human activity. CO2M is currently planned as a two-satellite mission, each of which will carry a near-infrared and shortwave-infrared spectrometer to measure atmospheric carbon dioxide at high spatial resolution. Engineers at Thales SESO in France explain how the development of some of the mission’s precision measuring and optical components is going.
Nová verze JVF DTM 1.4.2.2
13.3.2023 14:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do záložky JVF DTM byla přidána informace k plánované nové verzi JVF DTM 1.4.2.2. S nasazením na produkční prostředí se počítá v termínu od 1. července 2023 a její dokumentace bude vydána v termínu do 15. dubna 2023. Současně byl vystaven stručný popis změn formátu v dokumentu Plánované změny JVF DTM 1.4.2.2Omezení provozu
13.3.2023 13:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Českých Budějovicíchzveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme, že ve dnech 15. 3. 2023 a 27. 3. 2023 bude v čase od 11:00 do 15:00 v důsledku odstávky dodávky elektrické energie omezen provoz.
Omezení provozu
13.3.2023 13:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-CB/O-uradu/Aktuality/Omezeni-provozuPředběžná tržní konzultace k novému národnímu geoportálu
13.3.2023 12:53 CENIA - národní geoportál INSPIRE Česká informační agentura životního prostředí zveřejnila tržní konzultaci s cílem získat z trhu relevantní informace potřebné pro optimální a řádné nastavení zadávacích podmínek připravovaných veřejných zakázek (VZ). Pokud si myslíte, že byste jako firma mohli takový portál postavit podívejte se na další informace, které jsou uvedeny v přílohách těchto předběžných tržních konzultacích. VZ...Ukončení provozu vybraných georeportů
13.3.2023 12:39 CENIA - národní geoportál INSPIRE Vážení uživatelé Národního geoportálu INSPIRE, tímto Vám oznamujeme, že od 23. 2. 2023 byl na Národním Geoportálu INSPIRE ukončen provoz georeportů zaměřených na oblast životního prostředí. Důvodem je stáří aplikace, kterou již nebylo možné aktualizovat. Děkujeme za pochopení.Předběžná tržní informace k novému národnímu geoportálu (TZ)
13.3.2023 11:53 GISportal.cz
Česká informační agentura životního prostředí zveřejnila tržní konzultaci s cílem získat z trhu relevantní informace potřebné pro optimální a řádné nastavení zadávacích podmínek připravovaných veřejných zakázek (VZ). Pokud si myslíte, že byste jako firma mohli takový portál postavit podívejte se na další informace, které jsou uvedeny v přílohách těchto předběžných tržních konzultacích. VZ „Dodávka řešení […]
The post Předběžná tržní informace k novému národnímu geoportálu (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Předběžná tržní informace k novému národnímu geoportálu (TZ)
13.3.2023 11:53 GISportal.cz
Česká informační agentura životního prostředí zveřejnila tržní konzultaci s cílem získat z trhu relevantní informace potřebné pro optimální a řádné nastavení zadávacích podmínek připravovaných veřejných zakázek (VZ). Pokud si myslíte, že byste jako firma mohli takový portál postavit podívejte se na další informace, které jsou uvedeny v přílohách těchto předběžných tržních konzultacích. VZ „Dodávka řešení […]
The post Předběžná tržní informace k novému národnímu geoportálu (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
kontrola listin určených k záznamu
13.3.2023 11:49 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Olomouc vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo kontrola listin určených k záznamukontrola listin určených k záznamu
13.3.2023 11:49 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/kontrola-listin-urcenych-k-zaznamukontrola listin určených k záznamu
13.3.2023 11:49 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Olomoucvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
kontrola listin určených k záznamu
Předběžná tržní informace k novému národnímu geoportálu
13.3.2023 11:09 CENIA - národní geoportál INSPIRE Česká informační agentura životního prostředí zveřejnila tržní konzultaci s cílem získat z trhu relevantní informace potřebné pro optimální a řádné nastavení zadávacích podmínek připravovaných veřejných zakázek (VZ). Pokud si myslíte, že byste jako firma mohli takový portál postavit podívejte se na další informace, které jsou uvedeny v přílohách těchto předběžných tržních konzultacích. VZ...20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OPV KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OPV KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:31 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Rumburk/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230310-volne-misto-Rada-odborny-rada-v OPV-KP-Ru20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OPV KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:31 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230310-volne-misto-Rada-odborny-rada-v OPV-KP-Ru20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OPV KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OAaD KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Rumburk/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230310-volne-misto-Rada-odborny-rada-v OAaD-KP-R20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OAaD KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OAaD KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230310 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v OAaD KP Rumburk na KÚ pro Úst.kraj
13.3.2023 7:27 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230310-volne-misto-Rada-odborny-rada-v OAaD-KP-R20230313-nové info ke zkouškám ÚOZI
13.3.2023 6:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nové informace ke zkouškám ÚOZI a vzniku České komory zeměměřičů naleznete zde.20230313-nové info ke zkouškám ÚOZI
13.3.2023 6:30 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Nové informace ke zkouškám ÚOZI a vzniku České komory zeměměřičů naleznete zde.The Information Delivery Specification (IDS) Candidate Standard is now out for review by the Standards Committee.
10.3.2023 20:00 buildingSMART.orgThe Information Delivery Specification (IDS) Candidate Standard has been issued to the Standards Committee for their review and feedback. The vote closes Friday 2nd June 2023. The IDS is a…
The post The Information Delivery Specification (IDS) Candidate Standard is now out for review by the Standards Committee. appeared first on buildingSMART International.
Galileo: no way without time
10.3.2023 14:55 ESA Navigation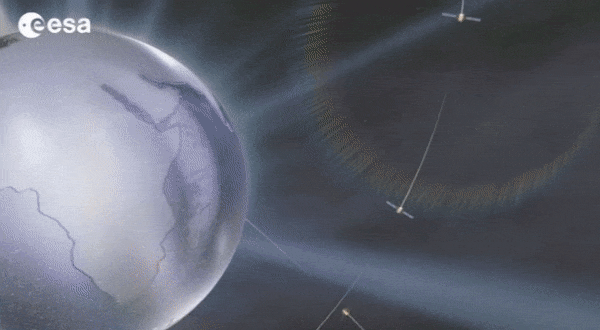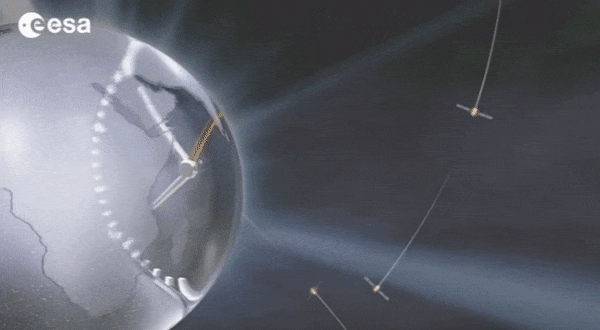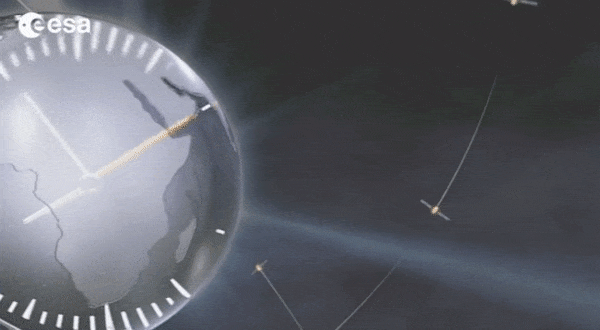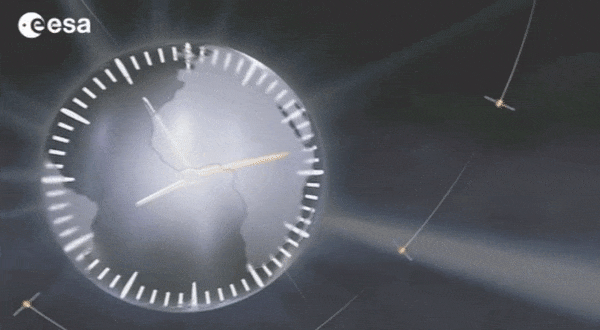
Europe’s Galileo is the world’s most precise satellite navigation system, providing metre-level accuracy and very precise timing to its four billion users. An essential ingredient to ensure this stays the case are the atomic clocks aboard each satellite, delivering pinpoint timekeeping that is maintained to a few billionths of a second. These clocks are called atomic because their ‘ticks’ come from ultra-rapid, ultra-stable oscillation of atoms between different energy states. Sustaining this performance demands, in turn, even more accurate clocks down on the ground to keep the satellites synchronised and ensure stability of time and positioning for users.
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – oddělení aktualizace KN
10.3.2023 14:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Varyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – oddělení aktualizace KN
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – oddělení aktualizace KN
10.3.2023 14:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-oddeleni-aktualOdborný referent/vrchní referent – oddělení aktualizace KN
10.3.2023 14:38 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent – oddělení aktualizace KNGalileo on the ground – infographic
10.3.2023 13:56 ESA Navigation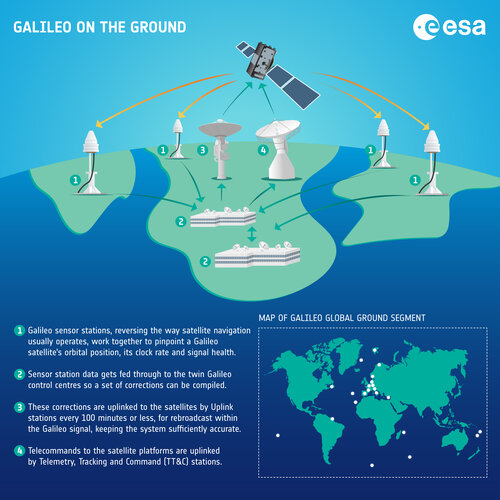 Image:
Galileo on the ground – infographic
Image:
Galileo on the ground – infographic
Galileo on the ground – infographic
10.3.2023 13:56 ESA Navigation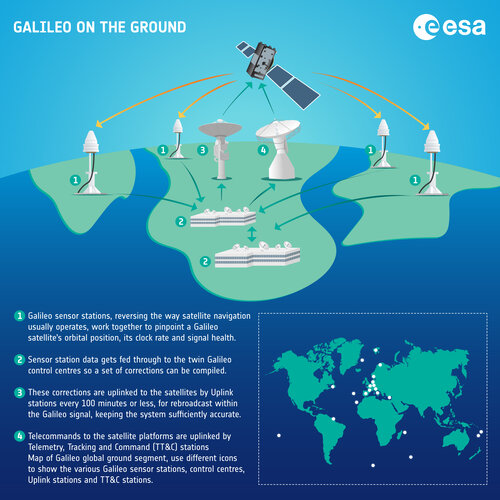 Image:
Galileo on the ground – infographic
Image:
Galileo on the ground – infographic
Galileo on the ground – infographic
10.3.2023 13:56 ESA Navigation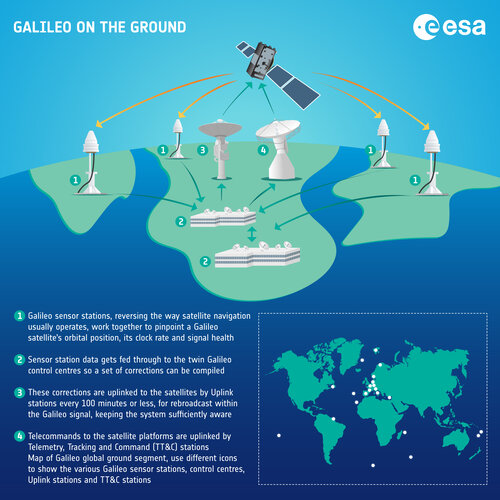 Image:
Galileo on the ground – infographic
Image:
Galileo on the ground – infographic
Nedostupné produkční ISÚI
10.3.2023 13:35 ČÚZK /ruian/Editacni-agendovy-system-ISUI/Provozni-informace-a-odstavky/Archiv-PROD/Nedostupne-produkcni-ISUI-(4)rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
10.3.2023 13:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Šumperkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
10.3.2023 13:31 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Šumperk vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladuEarth from Space: Graham Coast, Antarctica
10.3.2023 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth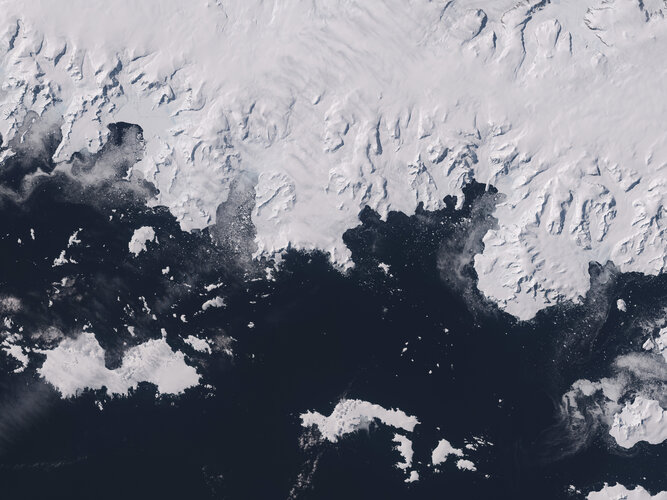 Image:
The icy landscape of Graham Coast, which lies on the west side of the Antarctic Peninsula, is featured in this Copernicus Sentinel-2 image.
Image:
The icy landscape of Graham Coast, which lies on the west side of the Antarctic Peninsula, is featured in this Copernicus Sentinel-2 image.
Unikátní podzemní vodojem v Brně – Žlutý kopec
10.3.2023 9:12 Hrdlička Zaměření hlavního vstupu a únikových schodišť k VDJ na Žlutém kopci.TurboCAD Designer 28 CZ – pro kreslení přesných projektů ve 2D
10.3.2023 9:00 ŠPINAR - software TurboCAD Designer 28 CZ v akční ceně do 19. 3. 2023,Rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
10.3.2023 8:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
10.3.2023 8:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-a-dokumenRada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
10.3.2023 8:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-a-dokumenrada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
10.3.2023 8:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rumburkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
10.3.2023 8:30 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviRada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
10.3.2023 8:30 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi20230310_Odborný/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního
10.3.2023 8:19 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230310_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obnovy-k20230310_Odborný/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního
10.3.2023 8:19 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu"20230310_Odborný/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního
10.3.2023 8:19 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230310_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obno-(1)20230310_Odborný/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního
10.3.2023 8:19 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu"Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu
10.3.2023 8:14 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj technická sekce vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátuOdborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu
10.3.2023 8:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralnOdborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu
10.3.2023 8:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj technická sekcevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
10.3.2023 7:57 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště RumburkRada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
10.3.2023 7:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
10.3.2023 7:57 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemRada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
10.3.2023 7:57 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemrada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
10.3.2023 7:57 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburkrada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
10.3.2023 7:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rumburkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk
Nová funkčnost Ověřit v registrech
10.3.2023 7:02 ČÚZK /ruian/Novinky-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-RUIAN/2023/Nova-funkcnost-Overit-v-registrechDigitalizace, vizualizace a dostupnost virtuální sbírky glóbů: případová studie glóbu Josefa Jüttnera [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
10.3.2023 0:00 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK V časopise ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information v rámci speciálního čísla věnovanému kartografii a geomédiím právě vyšel článek o digitalizaci glóbů z pera pracovníků z Mapové sbírky a Katedry aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie.Konec životního cyklu BIM 360 Team produktů: Co to znamená pro uživatele?
9.3.2023 15:56 Adeon
Společnost Autodesk oznámila již loni proces ukončení životního cyklu produktů BIM 360 Team. Rádi by jsme v tomto článku shrnuli […]
The post Konec životního cyklu BIM 360 Team produktů: Co to znamená pro uživatele? appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Galileo saving lives – infographic
9.3.2023 15:43 ESA Navigation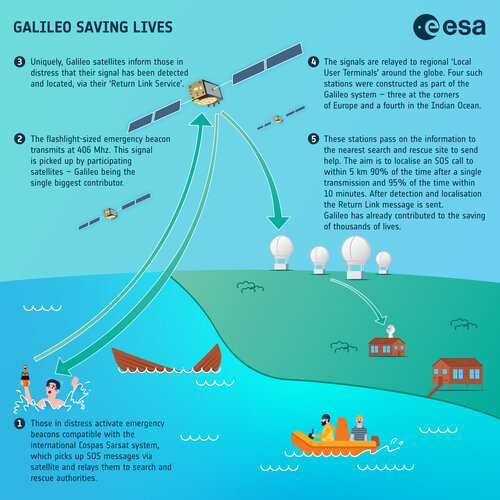 Image:
Galileo saving lives – infographic
Image:
Galileo saving lives – infographic
20230309 - VŘ Administrace UNIX
9.3.2023 14:45 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa rada/odborný rada - Administrace UNIX.20230309 - VŘ Administrace UNIX
9.3.2023 14:45 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2023/20230309-VR-Administrace-UNIX20230309 - VŘ Administrace UNIX
9.3.2023 14:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa rada/odborný rada - Administrace UNIX.How does Galileo help other space missions?
9.3.2023 12:30 ESA Navigation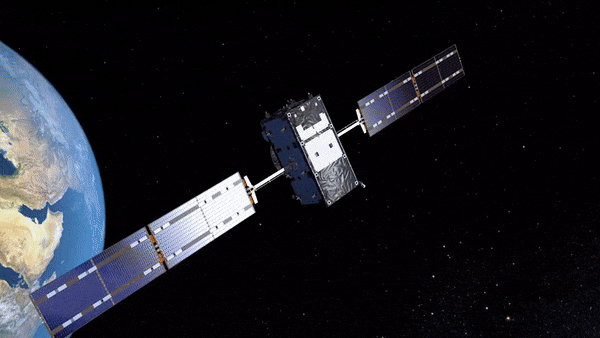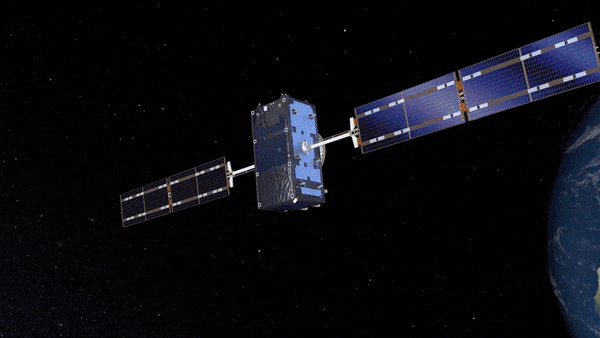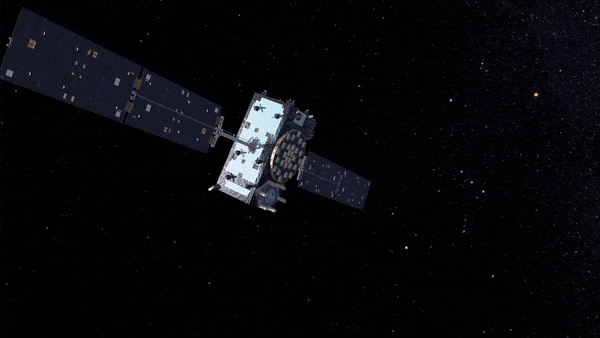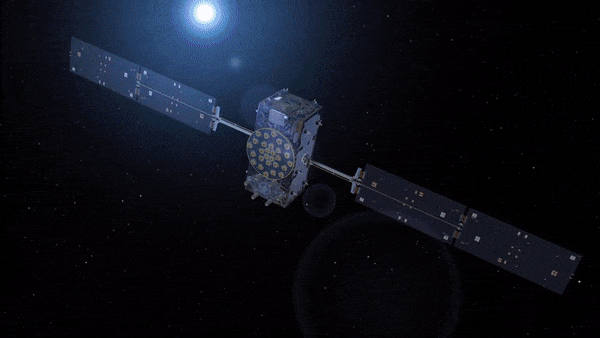
In 2023 satnav receivers are everywhere: in our phones, our cars, and drones, in fixed infrastructure, aboard boats, trains and aircraft. They are also in space: more than 95% of all the satellites in low-Earth orbit carry satnav receivers to calculate their position. The additional signals from Europe’s Galileo satellites are providing a big boost to the coverage, availability, redundancy, and accuracy of spaceborne receivers, in turn enlarging the possible scope of future missions, and extending the useful range of satnav much further out into space – to the Moon and beyond.
Možnost se zúčastnit letní školy "Geomatics and Aeronautical Engineering Summer Schools" v Polsku
9.3.2023 10:53 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČUPodrobné informace naleznete na následujícím odkaze: https://summerschools.spinaker.edition1.pw.edu.pl/Geomatics-and-Aeronautical-Engineering-Summer-Schools
From First Fix to High Accuracy Service, Galileo scores high
9.3.2023 10:36 European GNSS Agency
"From a historical perspective this was one the greatest achievements of the EU," says EUSPA Executive director Rodrigo da Costa. "Determining a position on the ground using only Galileo was essentially the first step towards shielding our autonomy and sovereignty in space." he highlights.
This first position fix of longitude, latitude and altitude using the Galileo constellation took place at the Navigation Laboratory at ESA’s technical heart ESTEC, in Noordwijk, Netherlands on the morning of 12 March, with a level of accuracy between 10 and 15 metres.
Since then, Galileo has been growing, exceeding performance expectations, and enabling a multitude of applications thanks to the broad range of services it offers.
A significant milestone was marked in 2016 with the declaration of Galileo Initial Services to become available at the end of that year providing guaranteed services to users. As of today, the EU’s positioning system offers a set of services to end users with more currently under development.
With 28 satellites currently in orbit the system offers:
Open Service (OS): Open Service (OS) enables free-of-charge, global ranging, positioning and timing, using the Galileo OS Signal-In-Space (SIS).
Search and Rescue Service (SAR): The Galileo Search and Rescue service allows for the location of people in distress within 10 minutes and a radius below 5km. All you need is a Galileo-enabled Personal Location Beacon (PLB).
High Accuracy Service (HAS): On the basis of this brand new service, declared operational on the 24/01/2023, Galileo becomes the first GNSS system providing, globally and free of charge, corrections to the Galileo and GPS signals to enable a positioning accuracy down to decimetre level (when processed by a Precise Point Positioning (PPP) algorithm by the user).
"The main power of Galileo is felt in the downstream sector, especially if we think that over 4 billion Galileo-enabled smartphones have been sold and that millions of users in many sectors rely on it.” concludes EUSPA Executive Director, Rodrigo da Costa.
Read this: Another step for EU’s positioning system: Nikolina joins the Galileo family!
What’s next?
The Galileo is being continuously improved to ensure seamless, safe and secured service delivery 24/7 to users worldwide. EUSPA is currently working on delivering next-generation services based on Galileo’s precise signals, timing capabilities and robust performance.
Likewise, upon a successful public observation phase ongoing since November 2021, the Galileo OSNMA is expected to become operational within the coming year. The OSNMA is a new, breakthrough feature of Europe’s positioning system that meets a clear user need: improve the trustworthiness of GNSS signals. This service provides an authentication mechanism to allow Open Service users to verify that the navigation data they have received comes directly from Galileo and has not been modified.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
From First Fix to High Accuracy Service, Galileo scores high
9.3.2023 10:36 European GNSS Agency
"From a historical perspective this was one the greatest achievements of the EU," says EUSPA Executive director Rodrigo da Costa. "Determining a position on the ground using only Galileo was essentially the first step towards shielding our autonomy and sovereignty in space." he highlights.
This first position fix of longitude, latitude and altitude using the Galileo constellation took place at the Navigation Laboratory at ESA’s technical heart ESTEC, in Noordwijk, Netherlands on the morning of 12 March, with a level of accuracy between 10 and 15 metres.
Since then, Galileo has been growing, exceeding performance expectations, and enabling a multitude of applications thanks to the broad range of services it offers.
A significant milestone was marked in 2016 with the declaration of Galileo Initial Services to become available at the end of that year providing guaranteed services to users. As of today, the EU’s positioning system offers a set of services to end users with more currently under development.
With 28 satellites currently in orbit the system offers:
Open Service (OS): Open Service (OS) enables free-of-charge, global ranging, positioning and timing, using the Galileo OS Signal-In-Space (SIS).
Search and Rescue Service (SAR): The Galileo Search and Rescue service allows for the location of people in distress within 10 minutes and a radius below 5km. All you need is a Galileo-enabled Personal Location Beacon (PLB).
High Accuracy Service (HAS): On the basis of this brand new service, declared operational on the 24/01/2024, Galileo becomes the first GNSS system providing, globally and free of charge, corrections to the Galileo and GPS signals to enable a positioning accuracy down to decimetre level (when processed by a Precise Point Positioning (PPP) algorithm by the user).
"The main power of Galileo is felt in the downstream sector, especially if we think that over 4 billion Galileo-enabled smartphones have been sold and that millions of users in many sectors rely on it.” concludes EUSPA Executive Director, Rodrigo da Costa.
Read this: Another step for EU’s positioning system: Nikolina joins the Galileo family!
What’s next?
The Galileo is being continuously improved to ensure seamless, safe and secured service delivery 24/7 to users worldwide. EUSPA is currently working on delivering next-generation services based on Galileo’s precise signals, timing capabilities and robust performance.
Likewise, upon a successful public observation phase ongoing since November 2021, the Galileo OSNMA is expected to become operational within the coming year. The OSNMA is a new, breakthrough feature of Europe’s positioning system that meets a clear user need: improve the trustworthiness of GNSS signals. This service provides an authentication mechanism to allow Open Service users to verify that the navigation data they have received comes directly from Galileo and has not been modified.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
From First Fix to High Accuracy Service, Galileo scores high
9.3.2023 10:36 European GNSS Agency
"From a historical perspective this was one the greatest achievements of the EU," says EUSPA Executive director Rodrigo da Costa. "Determining a position on the ground using only Galileo was essentially the first step towards shielding our autonomy and sovereignty in space." he highlights.
This first position fix of longitude, latitude and altitude using the Galileo constellation took place at the Navigation Laboratory at ESA’s technical heart ESTEC, in Noordwijk, Netherlands on the morning of 12 March 2013, with a level of accuracy between 10 and 15 metres.
Since then, Galileo has been growing, exceeding performance expectations, and enabling a multitude of applications thanks to the broad range of services it offers.
A significant milestone was marked in 2016 with the declaration of Galileo Initial Services to become available at the end of that year providing guaranteed services to users. As of today, the EU’s positioning system offers a set of services to end users with more currently under development.
With 28 satellites currently in orbit the system offers:
Open Service (OS): Open Service (OS) enables free-of-charge, global ranging, positioning and timing, using the Galileo OS Signal-In-Space (SIS).
Search and Rescue Service (SAR): The Galileo Search and Rescue service allows for the location of people in distress within 10 minutes and a radius below 5km. All you need is a Galileo-enabled Personal Location Beacon (PLB).
High Accuracy Service (HAS): On the basis of this brand new service, declared operational on the 24/01/2023, Galileo becomes the first GNSS system providing, globally and free of charge, corrections to the Galileo and GPS signals to enable a positioning accuracy down to decimetre level (when processed by a Precise Point Positioning (PPP) algorithm by the user).
"The main power of Galileo is felt in the downstream sector, especially if we think that over 4 billion Galileo-enabled smartphones have been sold and that millions of users in many sectors rely on it.” concludes EUSPA Executive Director, Rodrigo da Costa.
Read this: Another step for EU’s positioning system: Nikolina joins the Galileo family!
What’s next?
The Galileo is being continuously improved to ensure seamless, safe and secured service delivery 24/7 to users worldwide. EUSPA is currently working on delivering next-generation services based on Galileo’s precise signals, timing capabilities and robust performance.
Likewise, upon a successful public observation phase ongoing since November 2021, the Galileo OSNMA is expected to become operational within the coming year. The OSNMA is a new, breakthrough feature of Europe’s positioning system that meets a clear user need: improve the trustworthiness of GNSS signals. This service provides an authentication mechanism to allow Open Service users to verify that the navigation data they have received comes directly from Galileo and has not been modified.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
9.3.2023 7:12 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KNposkytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
9.3.2023 7:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Šumperkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
9.3.2023 7:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Volna-mista/DMS/poskytovani-informaci-KN-a-PK,-poskytovani-podkladposkytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
9.3.2023 7:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
9.3.2023 7:12 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Šumperk vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo poskytování informací KN a PK, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KNRailway Room Charter
8.3.2023 20:00 buildingSMART.orgPlease follow the link to view the document. Go to document
The post Railway Room Charter appeared first on buildingSMART International.
Nová série rovinných laserů CL1
8.3.2023 13:55 3gon S hrdostí oznamujeme, že se nabídka měřicích přístrojů společnosti Nivel System rozšířila o novou řadu rovinných laserů s horizontálním paprskemValné zhromaždenie
8.3.2023 13:43 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Valné zhromaždenie appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Valné zhromaždenie
8.3.2023 13:43 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Valné zhromaždenie appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Navigation Lab exploring Galileo’s future – and beyond
8.3.2023 13:00 ESA Navigation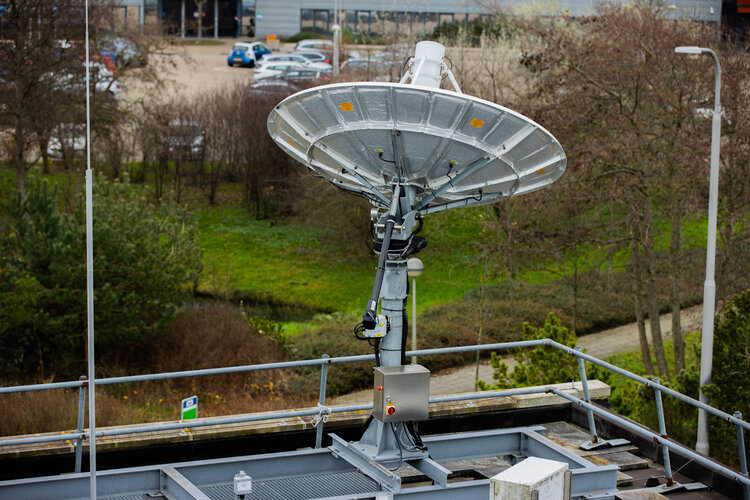
Would you like to know the future of satellite navigation? Try ESA’s Navigation Laboratory. This is a site where navigation engineers test prototypes of tomorrow's user receivers, using simulated versions of the navigation signals planned for the coming decade, such as set to be transmitted from Galileo’s Second Generation satellites.
Valné zhromaždenie KGK 2023
8.3.2023 12:45 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Valné zhromaždenie KGK 2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Fotogrametrické skenovanie v geodézii
8.3.2023 12:26 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Fotogrametrické skenovanie v geodézii appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Fotogrametrické skenovanie v geodézii
8.3.2023 12:26 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Fotogrametrické skenovanie v geodézii appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 14/2023
8.3.2023 12:03 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 14/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 13/2023
8.3.2023 11:47 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 13/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Aktualizace harmonogramu IS DMVS
8.3.2023 9:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V záložce Předpokládané termíny realizace byly aktualizovány milníky projektu DMVS a navázaných DTM krajů a dokument Rámcový harmonogram klíčových kroků při budování IS DMVSPorucha na telefonní ústředně
8.3.2023 9:11 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Semily/O-uradu/Aktuality/Porucha-na-telefonni-ustrednePorucha na telefonní ústředně
8.3.2023 9:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Máme poruchu na telefonní ústředně a nelze se na naše pracoviště dovolat. Za vzniklé problémy seomlouváme.
8.3. 2023
ředitel KP Semily
Ing. Jiří Bekr
Odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
8.3.2023 8:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hodonínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
Odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
8.3.2023 8:52 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hodonín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti HodonínOdborný referent v oddělení aktualizace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
8.3.2023 8:52 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-KN-na-Kata20230308_Rada / odborný rada – interní auditor
8.3.2023 8:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Rada / odborný rada – interní auditor V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada / odborný rada – interní auditor"20230308_Rada / odborný rada – interní auditor
8.3.2023 8:37 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(12)Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2022 je již na YouTube
8.3.2023 8:18 GISportal.cz
Pokud jste nestihli osobně letošní Konferenci GIS Esri v ČR, tak na YouTube kanále ARCDATA PRAHA naleznete nových 36 videí z této akce.
The post Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2022 je již na YouTube appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2022 je již na YouTube
8.3.2023 8:18 GISportal.cz
Pokud jste nestihli osobně letošní Konferenci GIS Esri v ČR, tak na YouTube kanále ARCDATA PRAHA naleznete nových 36 videí z této akce.
The post Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2022 je již na YouTube appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
8.3.2023 8:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2023Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
8.3.2023 8:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
2023
20230308_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
8.3.2023 8:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I. V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I."20230308_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
8.3.2023 8:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-vychod/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(5)Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
8.3.2023 8:06 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-PI-KNOdborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
8.3.2023 8:06 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východ vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
8.3.2023 8:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.

















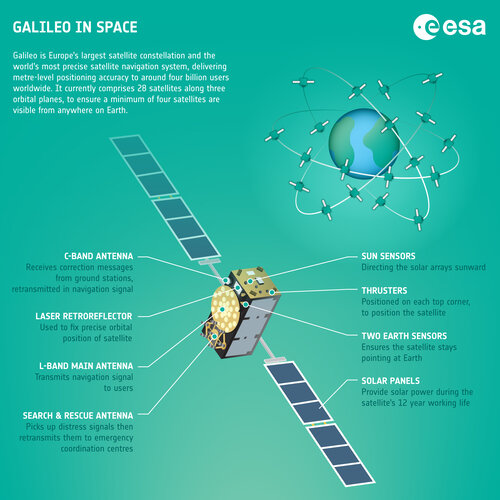 Image:
Galileo in space – infographic
Image:
Galileo in space – infographic