zprávy
zdroje zpráv:OGC zve k připomínkám třetí verze konceptuálního modelu CityGML, používaného pro 3D modely
14.12.2020 23:23 GeoBusinessSdružení Open Geospatial vyzvalo k veřejným připomínkám třetí verze konceptuálního modelu CityGML. Tento jazyk se používá pro tvorbu 3D modelů měst. Rozvoj jazyka CityGML je důležitý zejména kvůli trendu s 3D modelováním pro BIM a tzv. digitální dvojčata, možnostmi budoucích 3D vizualizací v rozšířené realitě či vizualizacemi technické infrastruktury například pro Digitální technickou mapu ČR. […]
The post OGC zve k připomínkám třetí verze konceptuálního modelu CityGML, používaného pro 3D modely appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Public comment sought on CityGML 3.0 Conceptual Model for storage and exchange of 3D city models
14.12.2020 22:25 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars CityGML 3.0 defines a common information model for the representation of 3D urban objects that can be shared over different applications, improving …Robotic Skies Raises New Investment to Grow Drone Support Services
14.12.2020 20:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Robotic Skies, Inc, the first and only global maintenance marketplace for commercial Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), announced today a new round of …odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Nác
14.12.2020 16:31 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Náchod vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Nácodborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Nác
14.12.2020 16:31 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-ak-(1)odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Nác
14.12.2020 16:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Náchodvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Náchod
Kleos Space Opens U.S. Engineering Office in Denver Colorado
14.12.2020 16:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars December 14, 2020 -- Luxembourg/ Denver (U.S.) - Kleos Space S.A. (ASX: KSS, Frankfurt: KS1,) a space-powered Radio Frequency Reconnaissance …NV5 Awarded $13 Million in North Carolina Department of Transportation Contracts
14.12.2020 16:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HOLLYWOOD, Fla., Dec. 14, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- NV5 Global, Inc. (the “Company” or “NV5”) (Nasdaq: NVEE), a provider of compliance, …Quantum Acquires Square Box Systems Ltd, Maker of CatDV, to Help Businesses Get More Value from Unstructured Data
14.12.2020 16:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Acquisition Adds Data Cataloging, AI Analytics and Automation Software for Data Enrichment and OrchestrationSAN JOSE, Calif., Dec. 14, 2020 — …
Obmedzenia pri poskytovaní služieb na OÚ Rožňava a Komárno
14.12.2020 16:25
ÚGKK SR
Obmedzenia pri poskytovaní služieb na OÚ Rožňava a Komárno spôsobené personálnym výpadkom niektorých zamestnancov v súvislosti s ochorením na Covid-19.
OÚ Rožňava – agenda katastra
Bude fungovať len podateľňa, a to v obmedzenom režime.
OÚ Komárno – agenda katastra
Bude fungovať len podateľňa, a to v obmedzenom režime.
rada/odborný rada – inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Pardubicích
14.12.2020 15:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Pardubicíchvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Pardubicích
rada/odborný rada – inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Pardubicích
14.12.2020 15:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Pardubicic/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-–-inspektor-Zememerickeho-a-katarada/odborný rada – inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Pardubicích
14.12.2020 15:59 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Pardubicích vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v PardubicíchArcGIS Experience Builder
14.12.2020 14:24 blog ARCDATA Novým moderním nástrojem pro budování webových aplikací je na platformě Esri ArcGIS Experience Builder. Proč tu máme další „builder“? Jaké jsou jeho přednosti? Bude starý známý Web AppBuilder nahrazen? Odpovědi na tyto i další otázky naleznete v tomto článku.ISSS 2020 – Digitalizace stavebního řízení a územního plánování
14.12.2020 13:58 ZeměměřičLetoční ročník konference ISSS, která se v předchozích letech vždy konala v dubnu v Hradci Králové, letos organizátoři museli přesunout do online podoby. Jedna z diskuzních debat je věnována digitalizaci stavebního řízení a územního plánování. V moderované diskuzi, která se týká připravovaného Portálu stavebníka, jednotlivých datových úložišť, nového geoportálu, vystupují Martin Kupka (místopředseda Výboru pro veřejnou správu a místní rozvoj, Poslanecká […]
The post ISSS 2020 – Digitalizace stavebního řízení a územního plánování appeared first on Zeměměřič.
ISSS 2020 – Digitalizace stavebního řízení a územního plánování
14.12.2020 13:58 ZeměměřičLetoční ročník konference ISSS, která se v předchozích letech vždy konala v dubnu v Hradci Králové, letos organizátoři museli přesunout do online podoby. Jedna z diskuzních debat je věnována digitalizaci stavebního řízení a územního plánování. V moderované diskuzi vystupují Martin Kupka (místopředseda Výboru pro veřejnou správu a místní rozvoj, Poslanecká sněmovna Parlamentu ČR), Stanislav Bogdanov (ředitel odboru národních a EU informačních systémů, […]
The post ISSS 2020 – Digitalizace stavebního řízení a územního plánování appeared first on Zeměměřič.
ISSS 2020 – Digitalizace stavebního řízení a územního plánování
14.12.2020 13:58 ZeměměřičLetoční ročník konference ISSS, která se v předchozích letech vždy konala v dubnu v Hradci Králové, letos organizátoři museli přesunout do online podoby. Jedna z diskuzních debat je věnována digitalizaci stavebního řízení a územního plánování. V moderované diskuzi, která se týká připravovaného Portálu stavebníka, jednotlivých datových úložišť, nového geoportálu, vystupují Martin Kupka (místopředseda Výboru pro veřejnou správu a místní rozvoj, Poslanecká […]
The post ISSS 2020 – Digitalizace stavebního řízení a územního plánování appeared first on Zeměměřič.
CryoSat reveals surprising ebb and flow of subglacial lakes
14.12.2020 13:50 ESA Observing the Earth
Hidden from view by ice kilometres thick, there is a vast network of lakes and streams at the base of the Antarctic ice sheet. This subsurface meltwater affects the speed with which the ice sheet flows towards the ocean. Using a decade of altimetry data from ESA’s CryoSat satellite, scientists have made an unexpected discovery about how lakes beneath Thwaites glacier have drained and recharged in quick succession.
CryoSat reveals surprising ebb and flow of subglacial lakes
14.12.2020 13:50 ESA Observing the Earth
Hidden from view by ice kilometres thick, there is a vast network of lakes and streams at the base of the Antarctic ice sheet. This subsurface meltwater affects the speed with which the ice sheet flows towards the ocean. Using a decade of altimetry data from ESA’s CryoSat satellite, scientists have made an unexpected discovery about how lakes beneath Thwaites glacier have drained and recharged in quick succession. Hidden from view by ice kilometres thick, there is a vast network of lakes and streams at the base of the Antarctic ice sheet.
Doktorské řízení - Olga Halásová
14.12.2020 11:30 Geografický ústav MUDne 14. 12. se na Geografickém ústavu koná státní doktorská zkouška a obhajoba disertační práce
Mgr. Olgy Halásové vypracované na téma "Přívalové povodně na Moravě a ve Slezsku v 19. a 20. století".
Jednání proběhne on-line a z veřejné části obhajoby bude pořízen záznam.
Let us have your feedback on Galileo/EGNOS – User satisfaction survey launched
14.12.2020 11:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) is launching the 2020 editions of its Galileo User Satisfaction Survey and EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey. These surveys play an important role in the evolution of the EGNSS programmes by feeding users’ needs and requirements into programme development.
Our motto at the GSA is ‘linking space to user needs’ and these are not empty words – users have always been at the heart of Galileo and EGNOS service provision, and feedback from users on their experience of the programmes is invaluable in shaping our services, making sure that they develop in line with market needs and continue to meet user requirements in the best way possible.
A targeted approach
The Galileo and EGNOS User Satisfaction Surveys are addressing all users and market segments including.: Aviation, Maritime, Rail, Road, Location Based Services, Agriculture, Surveying and Mapping and LBS. When responding to the survey, select the market segment in which you operate; the market segment that corresponds to your main area of activity; or the market segment that is the most important for your company or organisation, if you are active in multiple market segments. The Galileo User Satisfaction survey is also looking for user feedback on the support provided to the users via the Galileo Service Center. You can access the Galileo survey here.
Take part to the Galileo survey here.
In addition to the various market segments, the EGNOS survey also covers all the EGNOS services, including the Open Service, the Safety of Life Service and the EGNOS Data Access Service (EDAS). It also assesses the EGNOS service provider’s management of EGNOS User Support Services. For the EGNOS survey, click here.
Take part to the EGNOS survey here.
The feedback was positive in the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey, with a global user satisfaction score of 8.6 out of 10, up from 8.3 in the previous year. User satisfaction with EGNOS support was up across all the support services – the website, documentation and the helpdesk.
Based on the feedback, recommendations were drawn up for improvements across all the EGNOS services and support to users. For an overview of the results of the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey and the recommendations it generated, click here. We strongly encourage Galileo or EGNOS users to take part in the survey and help us fine-tune our service provision. The more users respond, from all market segments, the better the GSA and the Galileo and EGNOS systems will be able to go on meeting the requirements of the entire user community. The surveys only takes a few minutes to complete and your feedback will make a real difference.
In the 2019 Galileo User Satisfaction Survey, we were pleased to see that overall satisfaction with the service was up from the previous year, with 94% of users satisfied with the service and 97% of users happy to recommend the service to others. Based on user feedback, a number of recommendations were drawn up to strengthen the GNSS Service Centre (GSC).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Let us have your feedback on Galileo/EGNOS – User satisfaction survey launched
14.12.2020 11:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) is launching the 2020 editions of its Galileo User Satisfaction Survey and EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey. These surveys play an important role in the evolution of the EGNSS programmes by feeding users’ needs and requirements into programme development.
Our motto at the GSA is ‘linking space to user needs’ and these are not empty words – users have always been at the heart of Galileo and EGNOS service provision, and feedback from users on their experience of the programmes is invaluable in shaping our services, making sure that they develop in line with market needs and continue to meet user requirements in the best way possible.
A targeted approach
The Galileo and EGNOS User Satisfaction Surveys are addressing all users and market segments including.: Aviation, Maritime, Rail, Road, Location Based Services, Agriculture and Surveying and Mapping. When responding to the survey, select the market segment in which you operate; the market segment that corresponds to your main area of activity; or the market segment that is the most important for your company or organisation, if you are active in multiple market segments. The Galileo User Satisfaction survey is also looking for user feedback on the support provided to the users via the Galileo Service Center. You can access the Galileo survey here.
Take part to the Galileo survey here.
In addition to the various market segments, the EGNOS survey also covers all the EGNOS services, including the Open Service, the Safety of Life Service and the EGNOS Data Access Service (EDAS). It also assesses the EGNOS service provider’s management of EGNOS User Support Services. For the EGNOS survey, click here.
Take part to the EGNOS survey here.
The feedback was positive in the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey, with a global user satisfaction score of 8.6 out of 10, up from 8.3 in the previous year. User satisfaction with EGNOS support was up across all the support services – the website, documentation and the helpdesk.
Based on the feedback, recommendations were drawn up for improvements across all the EGNOS services and support to users. For an overview of the results of the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey and the recommendations it generated, click here. We strongly encourage Galileo or EGNOS users to take part in the survey and help us fine-tune our service provision. The more users respond, from all market segments, the better the GSA and the Galileo and EGNOS systems will be able to go on meeting the requirements of the entire user community. The surveys only takes a few minutes to complete and your feedback will make a real difference.
In the 2019 Galileo User Satisfaction Survey, we were pleased to see that overall satisfaction with the service was up from the previous year, with 94% of users satisfied with the service and 97% of users happy to recommend the service to others. Based on user feedback, a number of recommendations were drawn up to strengthen the GNSS Service Centre (GSC).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Let us have your feedback on Galileo/EGNOS – User satisfaction survey launched
14.12.2020 11:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) is launching the 2020 editions of its Galileo User Satisfaction Survey and EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey. These surveys play an important role in the evolution of the EGNSS programmes by feeding users’ needs and requirements into programme development.
Our motto at the GSA is ‘linking space to user needs’ and these are not empty words – users have always been at the heart of Galileo and EGNOS service provision, and feedback from users on their experience of the programmes is invaluable in shaping our services, making sure that they develop in line with market needs and continue to meet user requirements in the best way possible.
A targeted approach
The Galileo and EGNOS User Satisfaction Surveys are addressing all users and market segments including.: Aviation, Maritime, Rail, Road, Location Based Services, Agriculture and Surveying and Mapping. When responding to the survey, select the market segment in which you operate; the market segment that corresponds to your main area of activity; or the market segment that is the most important for your company or organisation, if you are active in multiple market segments. The Galileo User Satisfaction survey is also looking for user feedback on the support provided to the users via the Galileo Service Center. You can access the Galileo survey here.
Take part in the Galileo survey here.
In addition to the various market segments, the EGNOS survey also covers all the EGNOS services, including the Open Service, the Safety of Life Service and the EGNOS Data Access Service (EDAS). It also assesses the EGNOS service provider’s management of EGNOS User Support Services. For the EGNOS survey, click here.
Take part in the EGNOS survey here.
The feedback was positive in the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey, with a global user satisfaction score of 8.6 out of 10, up from 8.3 in the previous year. User satisfaction with EGNOS support was up across all the support services – the website, documentation and the helpdesk.
Based on the feedback, recommendations were drawn up for improvements across all the EGNOS services and support to users. For an overview of the results of the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey and the recommendations it generated, click here. We strongly encourage Galileo or EGNOS users to take part in the survey and help us fine-tune our service provision. The more users respond, from all market segments, the better the GSA and the Galileo and EGNOS systems will be able to go on meeting the requirements of the entire user community. The surveys only takes a few minutes to complete and your feedback will make a real difference.
In the 2019 Galileo User Satisfaction Survey, we were pleased to see that overall satisfaction with the service was up from the previous year, with 94% of users satisfied with the service and 97% of users happy to recommend the service to others. Based on user feedback, a number of recommendations were drawn up to strengthen the GNSS Service Centre (GSC).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Let us have your feedback on Galileo/EGNOS – User satisfaction survey launched
14.12.2020 11:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) is launching the 2020 editions of its Galileo User Satisfaction Survey and EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey. These surveys play an important role in the evolution of the EGNSS programmes by feeding users’ needs and requirements into programme development.
Our motto at the GSA is ‘linking space to user needs’ and these are not empty words – users have always been at the heart of Galileo and EGNOS service provision, and feedback from users on their experience of the programmes is invaluable in shaping our services, making sure that they develop in line with market needs and continue to meet user requirements in the best way possible.
A targeted approach
The Galileo and EGNOS User Satisfaction Surveys are addressing all users and market segments including.: Aviation, Maritime, Rail, Road, Location Based Services, Agriculture, Surveying and Mapping and LBS. When responding to the survey, select the market segment in which you operate; the market segment that corresponds to your main area of activity; or the market segment that is the most important for your company or organisation, if you are active in multiple market segments. The Galileo User Satisfaction survey is also looking for user feedback on the support provided to the users via the Galileo Service Center. You can access the Galileo survey here.
Take part to the Galileo survey here.
In addition to the various market segments, the EGNOS survey also covers all the EGNOS services, including the Open Service, the Safety of Life Service and the EGNOS Data Access Service (EDAS). It also assesses the EGNOS service provider’s management of EGNOS User Support Services. For the EGNOS survey, click here.
Take part to the EGNOS survey here.
The feedback was positive in the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey, with a global user satisfaction score of 8.6 out of 10, up from 8.3 in the previous year. User satisfaction with EGNOS support was up across all the support services – the website, documentation and the helpdesk.
Based on the feedback, recommendations were drawn up for improvements across all the EGNOS services and support to users. For an overview of the results of the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey and the recommendations it generated, click here. We strongly encourage Galileo or EGNOS users to take part in the survey and help us fine-tune our service provision. The more users respond, from all market segments, the better the GSA and the Galileo and EGNOS systems will be able to go on meeting the requirements of the entire user community. The surveys only takes a few minutes to complete and your feedback will make a real difference.
In the 2019 Galileo User Satisfaction Survey, we were pleased to see that overall satisfaction with the service was up from the previous year, with 94% of users satisfied with the service and 97% of users happy to recommend the service to others. Based on user feedback, a number of recommendations were drawn up to strengthen the GNSS Service Centre (GSC).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Let us have your feedback on Galileo/EGNOS – User satisfaction survey launched
14.12.2020 11:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) is launching the 2020 editions of its Galileo User Satisfaction Survey and EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey. These surveys play an important role in the evolution of the EGNSS programmes by feeding users’ needs and requirements into programme development.
Our motto at the GSA is ‘linking space to user needs’ and these are not empty words – users have always been at the heart of Galileo and EGNOS service provision, and feedback from users on their experience of the programmes is invaluable in shaping our services, making sure that they develop in line with market needs and continue to meet user requirements in the best way possible.
A targeted approach
The Galileo and EGNOS User Satisfaction Surveys are addressing all users and market segments including.: Aviation, Maritime, Rail, Road, Location Based Services, Agriculture, Surveying and Mapping and LBS. When responding to the survey, select the market segment in which you operate; the market segment that corresponds to your main area of activity; or the market segment that is the most important for your company or organisation, if you are active in multiple market segments. The Galileo User Satisfaction survey is also looking for user feedback on the support provided to the users via the Galileo Service Center. You can access the Galileo survey here.
Take part to the Galileo survey here.
In addition to the various market segments, the EGNOS survey also covers all the EGNOS services, including the Open Service, the Safety of Life Service and the EGNOS Data Access Service (EDAS). It also assesses the EGNOS service provider’s management of EGNOS User Support Services. For the EGNOS survey, click here.
Take part to the EGNOS survey here.
The feedback was positive in the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey, with a global user satisfaction score of 8.6 out of 10, up from 8.3 in the previous year. User satisfaction with EGNOS support was up across all the support services – the website, documentation and the helpdesk.
Based on the feedback, recommendations were drawn up for improvements across all the EGNOS services and support to users. For an overview of the results of the 2019 EGNOS User Satisfaction Survey and the recommendations it generated, click here. We strongly encourage Galileo or EGNOS users to take part in the survey and help us fine-tune our service provision. The more users respond, from all market segments, the better the GSA and the Galileo and EGNOS systems will be able to go on meeting the requirements of the entire user community. The surveys only takes a few minutes to complete and your feedback will make a real difference.
In the 2019 Galileo User Satisfaction Survey, we were pleased to see that overall satisfaction with the service was up from the previous year, with 94% of users satisfied with the service and 97% of users happy to recommend the service to others. Based on user feedback, a number of recommendations were drawn up to strengthen the GNSS Service Centre (GSC).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Aktualizace ISKN na verzi 5.5
14.12.2020 10:43 ARCDATAV souvislosti s dopadem Zákona č. 51/2020 Sb. o územně správním členění státu došlo v rámci instalace nové verze ISKN 9.1 ke změně ve struktuře výměnného formátu ISKN.
Nová verze nese označení VF ISKN 5.5 a od 7. 11. 2020 jsou všechny exporty vydávány právě v této v verzi. Tato změna byla promítnuta i do ISKN Studia tak, že byly vytvořeny nové šablony verze 5.5.
Taktéž je k dispozici i nová verze aplikace ISKN Studio 10.x.4, která podporuje aktuální, i starší verze systému ArcGIS. Více informací o funkcích a vlastnostech softwaru ISKN Studio naleznete na samostatné stránce.
Aktualizace IKSN na verzi 5.5
14.12.2020 10:43 ARCDATAV souvislosti s dopadem Zákona č. 51/2020 Sb. o územně správním členění státu dojde v rámci instalace nové verze ISKN 9.1 k příslušné změně ve struktuře výměnného formátu ISKN.
Nová verze nese označení VF ISKN 5.5 a od 7. 11. 2020 jsou všechny exporty vydávány právě v této v verzi.
Mapping high-resolution methane emissions from space
14.12.2020 9:51 ESA Observing the Earth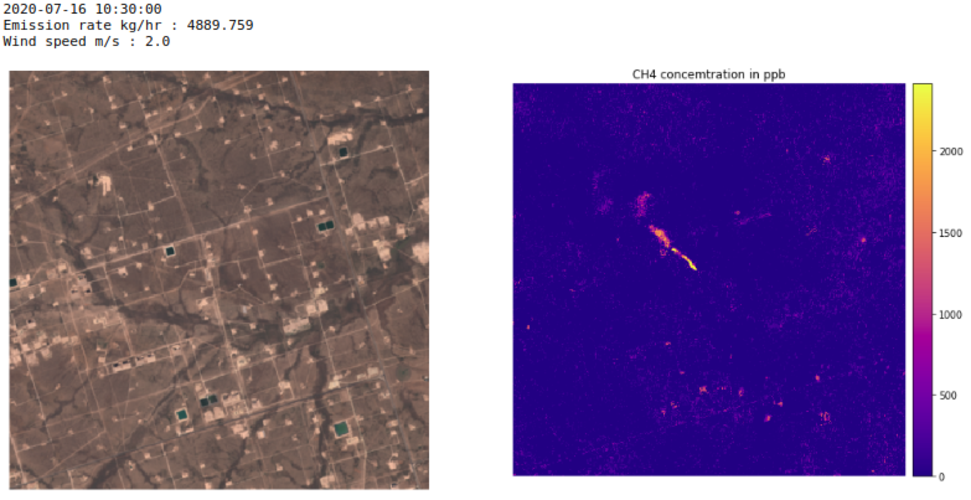
Scientists have used satellite data from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission, combined with the Sentinel-5P satellite, to detect individual methane emissions from space.
Upozornění
13.12.2020 11:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Plzni zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Plzni oznamuje, že s ohledem na opatření přijatá usnesením vlády ČR č. 1202 ze dne 20. listopadu 2020 má až do odvolání omezený provoz pro veřejnost.Upozornění
13.12.2020 11:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Plzni/O-uradu/Aktuality/Upozorneni-(5)Innoviz Technologies, a Global Leader in LiDAR Sensors and Perception Software for Autonomous Driving, to be Listed on Nasdaq Through Business Combination with Collective Growth Corporation
11.12.2020 17:03 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars - Innoviz Technologies Ltd. ("Innoviz") to become publicly listed through business combination with Collective Growth Corporation (NASDAQ: CGRO) …Kongsberg Geospatial Announces New Tactical UAS Sensor Data Management Solution
11.12.2020 17:03 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Kongsberg Geospatial MIDAS is a Processing, Exploitation and Dissemination (PED) Solution for rapid intelligence analysis of data from Tactical …Iceberg on collision course with South Georgia
11.12.2020 12:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:02:06
Video:
00:02:06
The giant A-68A iceberg could strike land this month – wreaking havoc near the waters of the South Georgia Island.
Since its ‘birth’ in 2017, the iceberg has travelled thousands of kilometres from the Larsen C ice shelf, in Antarctica, and now lies around 120 km from South Georgia. If it remains on its current path, the iceberg could ground in the shallow waters offshore – threatening wildlife, including penguins and seals.
Satellite missions are being used to track the berg on its journey over the past three years. The Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar mission, with its ability to see through clouds and the dark, has been instrumental in mapping the polar regions in winter.
Video credits:
Animation: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2017-18), processed by Swansea University-A. Luckman
Radar images: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
A-68A map: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA; Antarctic Iceberg Tracking Database
Sentinel-1 animations: ESA/ATG Medialab
Penguins footage: Getty
Iceberg on collision course with South Georgia
11.12.2020 12:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:02:06
Video:
00:02:06
The giant A-68A iceberg could strike land this month – wreaking havoc near the waters of the South Georgia Island.
Since its ‘birth’ in 2017, the iceberg has travelled thousands of kilometres from the Larsen C ice shelf, in Antarctica, and now lies around 120 km from South Georgia. If it remains on its current path, the iceberg could ground in the shallow waters offshore – threatening wildlife, including penguins and seals.
Satellite missions are being used to track the berg on its journey over the past three years. The Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar mission, with its ability to see through clouds and the dark, has been instrumental in mapping the polar regions in winter.
Iceberg on collision course with South Georgia
11.12.2020 12:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:02:06
Video:
00:02:06
The giant A-68A iceberg could strike land this month – wreaking havoc near the waters of the South Georgia Island.
Since its ‘birth’ in 2017, the iceberg has travelled thousands of kilometres from the Larsen C ice shelf, in Antarctica, and now lies around 120 km from South Georgia. If it remains on its current path, the iceberg could ground in the shallow waters offshore – threatening wildlife, including penguins and seals.
Satellite missions are being used to track the berg on its journey over the past three years. The Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar mission, with its ability to see through clouds and the dark, has been instrumental in mapping the polar regions in winter.
Video credits:
Animation: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2017-18), processed by Swansea University-A. Luckman
Radar images: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
A-68A map: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA; Antarctic Iceberg Tracking Database
Sentinel-1 animations: ESA/ATG Medialab
Penguins footage: Getty
Iceberg on collision course with South Georgia
11.12.2020 12:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:02:06
Video:
00:02:06
The giant A-68A iceberg could strike land this month – wreaking havoc near the waters of the South Georgia Island.
Since its ‘birth’ in 2017, the iceberg has travelled thousands of kilometres from the Larsen C ice shelf, in Antarctica, and now lies around 120 km from South Georgia. If it remains on its current path, the iceberg could ground in the shallow waters offshore – threatening wildlife, including penguins and seals.
Satellite missions are being used to track the berg on its journey over the past three years. The Copernicus Sentinel-1 radar mission, with its ability to see through clouds and the dark, has been instrumental in mapping the polar regions in winter.
Video credits:
Animation: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2017-18), processed by Swansea University-A. Luckman
Radar images: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
A-68A map: contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2020), processed by ESA; Antarctic Iceberg Tracking Database
Sentinel-1 animations: ESA/ATG Medialab
Penguin footage: Getty Images
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžn
11.12.2020 10:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnouvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžn
11.12.2020 10:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-do-(1)Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžn
11.12.2020 10:59 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace Katastrálního pracoviště Rychnov nad KněžnBIM3D - moderní geodetické technologie a služby
11.12.2020 10:44 Hrdlička Profesionální pořizování 3D dat se zpracováním BIM modelů a zajištění leteckých snímků.MawisPhoto – dokumentujte stavby
11.12.2020 10:31 Hrdlička MawisPhoto je aplikací, která nově rozšiřuje Mawis – portál profesionálního stavebníka.Kyiv, Ukraine
11.12.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kyiv – the capital and most populous city of Ukraine.
Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kyiv – the capital and most populous city of Ukraine.
Earth from Space: Kyiv
11.12.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:03:17
Video:
00:03:17
In this week's edition of the Earth from Space programme, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kyiv – the capital and most populous city of Ukraine.
See also Kyiv, Ukraine to download the image.
Seequent introduces next-generation digital twin technologies for infrastructure and environmental projects
11.12.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Seequent builds stronger digital twin solutions to deliver a faster, clearer picture for civil infrastructure and environmental …Geospatial Analytics® Democratizes Analytics for Front Line Workers Transforming the Real Estate Services Industry
11.12.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars PHOENIX, Dec. 7, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — Geospatial Analytics®, a real estate software development company, announced …xyzt.ai Announces the Closing of its First Round of Funding with Business Angels.
11.12.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars We are thrilled to announce that xyzt.ai has closed its first external funding round, with Heidi Rakels and Eric Lafortune becoming …GPI Geospatial relocates flight acquisition and operations teams to Sheltair's new FBO facility at Orlando Executive airport
11.12.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars ORLANDO, Fla., Dec. 10, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — GPI Geospatial Inc. (GPI), an established geospatial and survey solutions provider, has …Vrchní referent / rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií v oddělení podpory ICT tec
11.12.2020 8:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnívypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií v oddělení podpory ICT technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
Vrchní referent / rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií v oddělení podpory ICT tec
11.12.2020 8:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - technický útvarvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií v oddělení podpory ICT technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
Vrchní referent / rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií v oddělení podpory ICT tec
11.12.2020 8:07 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - technický útvar vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií v oddělení podpory ICT tec20201211 - omezení chodu úřadu
11.12.2020 7:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozornění Katastrálního pracoviště!Do 23.12.2020 dochází na Katastrálním pracovišti Cheb k omezení služeb pro veřejnost.
Více informací: Získat podrobnější informace k omezení služeb pro veřejnost (soubor ve formátu PDF)
20201211 - omezení chodu úřadu
11.12.2020 7:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozornění Katastrálního pracoviště!Do 23.12.2020 dochází na Katastrálním pracovišti Cheb k omezení služeb pro veřejnost.
Více informací: Získat podrobnější informace k omezení služeb pro veřejnost (soubor ve formátu PDF)
20201211 - omezení chodu úřadu
11.12.2020 7:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Cheb/O-uradu/Aktuality/20201211-omezeni-chodu-uradu20201210 - omezení chodu úřadu
11.12.2020 7:34 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20201210-omezeni-chodu-uradu20201210 - omezení chodu úřadu
11.12.2020 7:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozornění Katastrálního úřadu!Do 23.12.2020 dochází na Katastrálním úřadu pro Karlovarský kraj k omezení služeb pro veřejnost.
Více informací: Získat podrobnější informace k omezení služeb pro veřejnost (soubor ve formátu PDF)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
ArcGIS Experience Builder
11.12.2020 7:06 GeoBusinessJan Šarata z firmy Arcdata Praha ve svém článku na firemním blogu vysvětluje nový webový ArcGIS Experience Builder, který doplňující stávající Web AppBuilder, sloužící pro tvorbu webových aplikací na platformě Esri ArcGIS. Experience Builder je součástí ArcGIS Online, ArcGIS Enterprise a pro vývoj svých vlastních aplikací si můžete stáhnout také vývojářskou verzi (Developer Edition). Základní […]
The post ArcGIS Experience Builder appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Charles Heazel receives OGC’s 2020 Gardels Award
10.12.2020 22:04 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Congratulations to Charles “Chuck” Heazel awarded the 2020 Gardels Award for their continued contributions to the creation and …CoreLogic’s Property Data Now Available on Amazon Web Services Data Exchange
10.12.2020 18:56 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars AWS customers can now simply and quickly access CoreLogic’s property dataIRVINE, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — December 10, 2020 …
Measure Ensures FAA Compliance for CoStar Group's Industry-Leading Drone Program
10.12.2020 18:56 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WASHINGTON and AUSTIN, Texas, Dec. 10, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — Measure, a leading aerial intelligence company, has enabled CoStar Group, …Bentley’s Year in Infrastructure dives deep into digital twins
10.12.2020 17:54 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Schnitger Corp, US
Read the articleBentley Systems and Microsoft to digitise urban planning
10.12.2020 17:50 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
The Record, UK
Read the articleHighways England project planning provides a springboard for latest Bentley launch
10.12.2020 17:48 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
New Civil Engineer, UK
Read the articleMark Bew's consultancy PCSG bought by Bentley
10.12.2020 17:45 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
BIM+, UK
Read the articleVelodyne Lidar Introduces Solid State Sensor for Autonomous Mobile Robotics and Last-Mile Delivery
10.12.2020 16:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Velarray M1600 Provides Advanced Perception for Rapidly Growing Autonomous Robot MarketSAN JOSE, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — December 10, …
Quantum Spatial, North America's Largest Provider of Geospatial Data Services and Solutions, Rebrands as NV5 Geospatial
10.12.2020 16:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Innovative Remote Sensing, Acquisition and Analytics Solutions are Key Capabilities in NV5 Global's Comprehensive Engineering PortfolioHOLLYWOOD, …
Built Environment Consultancy Acquired
10.12.2020 16:27 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Insider Media Limited, UK
Read the articleSiemens and Bentley help manage performance of oil & gas assets
10.12.2020 16:18 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Gas to Power Journal, UK
Read the articleShell Deepwater Selects Bentley’s iTwin Platform for Project Delivery
10.12.2020 15:57 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
GeoConnexion, UK
Read the articleReef Support wins Copernicus Masters top prize
10.12.2020 15:25 ESA Observing the Earth
Reef Support won this year’s Copernicus Masters competition, and were honoured during the online Space Awards on 8 December as part of the European Space Week 2020. The innovative idea uses Copernicus Sentinel data and artificial intelligence to detect coral bleaching, algal blooms, sediment plumes and human debris.
Návod: Jak vytvořit 3D pohled na terén s pomocí Google Maps a modelovacího softwaru Blender
10.12.2020 15:03 GeoBusinessV YouTube kanálu CG Geek je většina videí věnována 3D modelování a animování pro filmy. Pro ukázky v následujícím videu CG Geek použil open source 3D modelovací software Blender a družicové snímky z Google Maps. Výsledkem je 3D model terénu.
The post Návod: Jak vytvořit 3D pohled na terén s pomocí Google Maps a modelovacího softwaru Blender appeared first on GeoBusiness.
HOTOVOSTNÍ PLATBY V ZÁVĚRU ROKU 2020
10.12.2020 14:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/HOTOVOSTNI-PLATBY-V-ZAVERU-ROKU-2020HOTOVOSTNÍ PLATBY V ZÁVĚRU ROKU 2020
10.12.2020 14:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:HOTOVOSTNÍ PLATBY V ZÁVĚRU ROKU 2020
Upozorňujeme, že v posledním týdnu roku, tj. dne 28. a 30. 12. 2020 nebude možná úhrada správních poplatků v hotovosti.
Správní poplatek bude možné uhradit platební kartou nebo bezhotovostním převodem, příp. kolkovou známkou zakoupenou u prodejců cenin.
Děkujeme za pochopení a přejeme klientům příjemné prožití vánočních svátků.
Ing. Daniel Janošík, ředitel úřadu
Geomatics on the Move: the results are in
10.12.2020 14:15 European GNSS Agency
Alphamonitoring System, from the joint Italian-French team Alphageomega, has taken the Traditional Geomatics prize in this year’s Geomatics on the Move Competition, while the Integrated Geomatics Prize went to the Greek team 3 Deep Vision for their project Bathymetry from UAV Imagery and Machine Learning. The winners shared in the overall prize of EUR 30,000, with a total of 8 prizes offered in the two categories.
The Traditional Geomatics category looked for solutions in which the main innovation was based on the use of EGNSS, employing traditional equipment such as surveying or GIS grade GNSS receivers. In this category, Alphageomega designed and built an all-in-one system that helps to improve remote real-time knowledge of displacements at sensitive critical infrastructures and the surrounding environment.
Meanwhile, the Integrated Geomatics category targeted integrated surveying solutions that use Galileo or EGNOS along with tools and technologies such as drones, mobile mapping, laser scanners or Augmented/Mixed Reality, both within geomatics applications or beyond.
The winner in this category - Bathymetry from UAV Imagery and Machine Learning - aims to implement a scalable and transferable web service for mapping shallow waters. This web service will facilitate the detailed and accurate monitoring and mapping of sensitive coastal areas, especially in times of climate crisis, taking as input georeferenced UAV images or 3D point clouds.
Targeted solutions
“With the Geomatics on the Move Prize, born from our collaboration with the CLGE and the CLGE Young Surveyors’ Prize, we are encouraging innovators to leverage space technology and target real needs in the mapping and surveying community. Despite being the first edition in this new format, I was very impressed with the quality of the entries and congratulate the worthy winners,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani.
Read this: Want to know more about EGNSS for geomatics?
This year’s Geomatics on the Move competition marks the ninth year of partnership between the Council of European Geodetic Surveyors and the GSA. Through this initiative, the GSA aims to further increase the use of Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus in the field of geomatics and to increase awareness of the benefits these EU Space Programmes provide toward fostering innovative geomatics applications.
Geomatics on the Move is an ideas competition. The contenders had to present their solutions and demonstrate them through a written submission in the form of a poster and a live pitch at the finals. The prizes were awarded at an online ceremony on December 9, held as part of European Space Week.
Alphamonitoring system wins Geomatics on the Move traditional prize
10.12.2020 14:15 European GNSS Agency
Alphamonitoring System, from the joint Italian-French team Alphageomega, has taken the Traditional Geomatics prize in this year’s Geomatics on the Move Competition, while the Integrated Geomatics Prize went to the Greek team 3 Deep Vision for their project Bathymetry from UAV Imagery and Machine Learning. The winners shared in the overall prize of EUR 30,000, with a total of 10 prizes offered in the two categories.
The Traditional Geomatics category looked for solutions in which the main innovation was based on the use of EGNSS, employing traditional equipment such as surveying or GIS grade GNSS receivers. In this category, Alphageomega designed and built an all-in-one system that helps to improve remote real-time knowledge of displacements at sensitive critical infrastructures and the surrounding environment.
Meanwhile, the Integrated Geomatics category targeted integrated surveying solutions that use Galileo or EGNOS along with tools and technologies such as drones, mobile mapping, laser scanners or Augmented/Mixed Reality, both within geomatics applications or beyond.
The winner in this category - Bathymetry from UAV Imagery and Machine Learning - aims to implement a scalable and transferable web service for mapping shallow waters. This web service will facilitate the detailed and accurate monitoring and mapping of sensitive coastal areas, especially in times of climate crisis, taking as input georeferenced UAV images or 3D point clouds.
Targeted solutions
“With the Geomatics on the Move Prize, born from our collaboration with the CLGE and the CLGE Young Surveyors’ Prize, we are encouraging innovators to leverage space technology and target real needs in the mapping and surveying community. Despite being the first edition in this new format, I was very impressed with the quality of the entries and congratulate the worthy winners,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani.
Read this: Want to know more about EGNSS for geomatics?
This year’s Geomatics on the Move competition marks the ninth year of partnership between the Council of European Geodetic Surveyors and the GSA. Through this initiative, the GSA aims to further increase the use of Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus in the field of geomatics and to increase awareness of the benefits these EU Space Programmes provide toward fostering innovative geomatics applications.
Geomatics on the Move is an ideas competition. The contenders had to present their solutions and demonstrate them through a written submission in the form of a poster and a live pitch at the finals. The prizes were awarded at an online ceremony on December 9, held as part of European Space Week.
Geomatics on the Move: the results are in
10.12.2020 14:15 European GNSS Agency
Alphamonitoring System, from the joint Italian-French team Alphageomega, has taken the Traditional Geomatics prize in this year’s Geomatics on the Move Competition, while the Integrated Geomatics Prize went to the Greek team 3 Deep Vision for their project Bathymetry from UAV Imagery and Machine Learning. The winners shared in the overall prize of EUR 30,000, with a total of 10 prizes offered in the two categories.
The Traditional Geomatics category looked for solutions in which the main innovation was based on the use of EGNSS, employing traditional equipment such as surveying or GIS grade GNSS receivers. In this category, Alphageomega designed and built an all-in-one system that helps to improve remote real-time knowledge of displacements at sensitive critical infrastructures and the surrounding environment.
Meanwhile, the Integrated Geomatics category targeted integrated surveying solutions that use Galileo or EGNOS along with tools and technologies such as drones, mobile mapping, laser scanners or Augmented/Mixed Reality, both within geomatics applications or beyond.
The winner in this category - Bathymetry from UAV Imagery and Machine Learning - aims to implement a scalable and transferable web service for mapping shallow waters. This web service will facilitate the detailed and accurate monitoring and mapping of sensitive coastal areas, especially in times of climate crisis, taking as input georeferenced UAV images or 3D point clouds.
Targeted solutions
“With the Geomatics on the Move Prize, born from our collaboration with the CLGE and the CLGE Young Surveyors’ Prize, we are encouraging innovators to leverage space technology and target real needs in the mapping and surveying community. Despite being the first edition in this new format, I was very impressed with the quality of the entries and congratulate the worthy winners,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani.
Read this: Want to know more about EGNSS for geomatics?
This year’s Geomatics on the Move competition marks the ninth year of partnership between the Council of European Geodetic Surveyors and the GSA. Through this initiative, the GSA aims to further increase the use of Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus in the field of geomatics and to increase awareness of the benefits these EU Space Programmes provide toward fostering innovative geomatics applications.
Geomatics on the Move is an ideas competition. The contenders had to present their solutions and demonstrate them through a written submission in the form of a poster and a live pitch at the finals. The prizes were awarded at an online ceremony on December 9, held as part of European Space Week.
20201210 - omezení chodu úřadu
10.12.2020 13:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Karlovy-Vary/O-uradu/Aktuality/20201210-omezeni-chodu-uradu20201210 - omezení chodu úřadu
10.12.2020 13:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozornění Katastrálního pracoviště!Do 23.12.2020 dochází na Katastrálním pracovišti Karlovy Vary k omezení služeb pro veřejnost.
Více informací: Získat podrobnější informace k omezení služeb pro veřejnost (soubor ve formátu PDF)
Odborný referent/vrchní referent personálního oddělení v kanceláři ředitele katastrálního úřadu na K
10.12.2020 10:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-personalniho-oddeOdborný referent/vrchní referent personálního oddělení v kanceláři ředitele katastrálního úřadu na K
10.12.2020 10:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj kancelář úřaduvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent personálního oddělení v kanceláři ředitele katastrálního úřadu na Katastrálním pracovišti pro Jihomoravský kraj
Odborný referent/vrchní referent personálního oddělení v kanceláři ředitele katastrálního úřadu na K
10.12.2020 10:26 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj kancelář úřadu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent personálního oddělení v kanceláři ředitele katastrálního úřadu na KNová verze TurboCAD 27 CZ pro rok 2020/2021 již v prodeji!
10.12.2020 10:21 ŠPINAR - software Vážení zákazníci, dovolujeme si Vám nabídnout nové verze programů TurboCAD 27 CZ (2020/2021) pro kreslení ve 2D / 3D včetně vizualizací. Trvalá licence v českém nebo anglickém jazyce. Skvělý poměr silného výkonu / ceny! Vyberte si verzi TurboCADu, která Vám nejvíce bude vyhovovat. Novinky programu TurboCAD Platinum naleznete zde Demoverzi programu TuboCAD Platinum stáhnete zde. Novinky programu TurboCAD Professional naleznete zde Demoverzi programu TuboCAD Professional stáhnete zde. Novinky programu TurboCAD Deluxe naleznete zde ...Read moreNová verze TurboCAD 27 CZ pro rok 2020/2021 již v prodeji!
10.12.2020 10:21 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci, dovolujeme si Vám nabídnout nové verze programů TurboCAD 27 CZ (2020/2021) pro kreslení ve 2D / 3D včetně vizualizací. Trvalá licence v českém nebo anglickém jazyce. Skvělý poměr silného výkonu / ceny! Vyberte si verzi TurboCADu, která Vám nejvíce bude vyhovovat. Novinky programu TurboCAD Platinum naleznete zde Demoverzi programu TuboCAD Platinum stáhnete zde. Novinky programu TurboCAD Professional naleznete zde Demoverzi programu TuboCAD Professional stáhnete zde. Novinky programu TurboCAD Deluxe naleznete zde ...Read more
The post Nová verze TurboCAD 27 CZ pro rok 2020/2021 již v prodeji! appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Sea-level monitoring satellite first results surpass expectations
10.12.2020 10:08 ESA Observing the Earth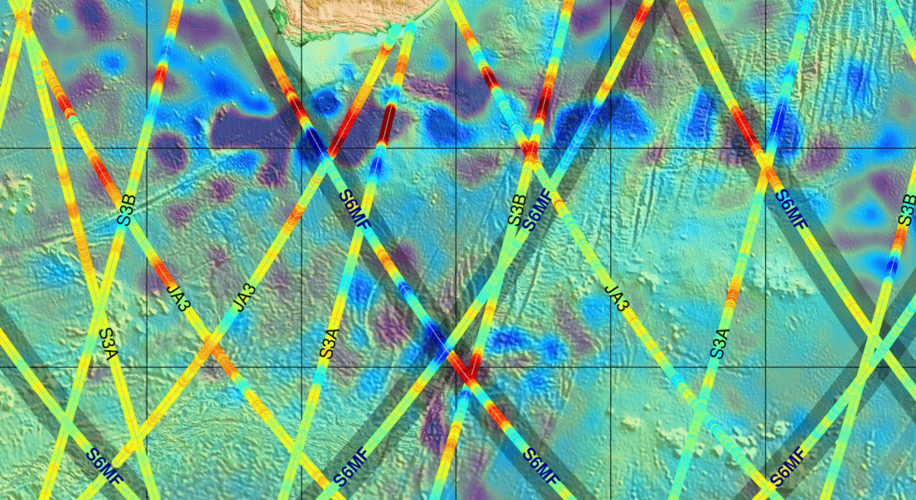
Launched less than three weeks ago, the Copernicus Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite has not only returned its first data, but results also show that it is functioning far better than expected. Thanks to its new, sophisticated, altimetry technology, Sentinel-6 is poised to deliver exceptionally precise data on sea-level height to monitor the worrying trend of sea-level rise.
Ředitel/ka Ekonomického odboru
10.12.2020 8:35 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Ředitel/ka Ekonomického odboru
Ředitel/ka Ekonomického odboru
10.12.2020 8:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Reditel-ka-Ekonomickeho-odboruŘeditel/ka Ekonomického odboru
10.12.2020 8:35 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Ředitel/ka Ekonomického odboruŘeditel/ka Ekonomického odboru
10.12.2020 8:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Ředitel/ka Ekonomického odboru
Brněnský GNSS seminář 2021 přesunut na příští rok 2022
10.12.2020 7:18 ZeměměřičV lednu se již od roku 2015 v Brně scházejí zájemci o využívání družicových metod v geodézii a katastru. Organizátoři letos rozhodli, že se seminář za stávající situace v lednu 2021 neuskuteční. Josef Weigel z pořádajícího Ústavu geodézie na Stavební fakultě VUT v Brně zaslal účastníkům loňského ročníku zprávu, ve které sděluje přesunutí semináře na začátek roku 2022. —————————————————————————————- Vážené kolegyně a kolegové […]
The post Brněnský GNSS seminář 2021 přesunut na příští rok 2022 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Brněnský GNSS seminář 2021 přesunut na příští rok 2022
10.12.2020 7:18 ZeměměřičV lednu se již od roku 2015 v Brně scházejí zájemci o využívání družicových metod v geodézii a katastru. Organizátoři letos rozhodli, že se seminář za stávající situace v lednu 2021 neuskuteční. Josef Weigel z pořádajícího Ústavu geodézie na Stavební fakultě VUT v Brně zaslal účastníkům loňského ročníku zprávu, ve které sděluje přesunutí semináře na začátek roku 2022. —————————————————————————————- Vážené kolegyně a kolegové […]
The post Brněnský GNSS seminář 2021 přesunut na příští rok 2022 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Obec Markvartice letos převzala poslední z prioritních společných zařízení pozemkových úprav
10.12.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Od zahájení pozemkových úprav v katastrálním území Markvartice uplynulo 10 let a do obce Markvartice přibylo několik povedených zrealizovaných opatření.Obec Markvartice leží v Ústeckém kraji, v okrese Děčín a rozkládá se v Českém středohoří v údolí říčky Bystrá. Od Děčína je vzdálena 11 km a má 681 obyvatel. Spolupráce s Pobočkou Děčín (dřívějším pozemkovým úřadem) odstartovala v roce 2010. V té době na Děčínsku nebyl pojem pozemkové úpravy příliš rozšířen. Pro ukázky zrealizovaných opatření musel tehdejší pozemkový úřad sahat převážně do jiných okresů. Přesto vlastníci zemědělské půdy v této krajině projevili zájem o pozemkové úpravy v jejich území a dnes jsou právě tato opatření prezentována dalším obcím, které začínají na pozemkovém úřadu tvořit frontu coby žadatelé pozemkových úprav.
Worldwide Server Market Revenue Grew 2.2% Year Over Year in the Third Quarter of 2020, According to IDC
9.12.2020 23:05 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars FRAMINGHAM, Mass. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — December 9, 2020 —According to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Quarterly …
Hexagon | NovAtel introduces new marine-certified GNSS receiver for nearshore applications
9.12.2020 20:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The multi-constellation MarinePak7 GNSS receiver supports Oceanix Correction Service and SPAN GNSS+INS technology for an assured 3D positioning …dSPACE and LeddarTech Join Forces to Drive Development of Lidar Innovations for Self-Driving Cars
9.12.2020 20:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars PADERBORN, Germany, and QUEBEC CITY, Canada, Dec. 09, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- dSPACE and LeddarTech®, a leader in level 1-5 ADAS and AD sensing …Esri's Web-Based Redistricting Solution to Be Used by Colorado
9.12.2020 20:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Esri Redistricting Brings Data and Transparency to Governments and Residents Redrawing District BoundariesREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) …
Financování pozemkových úprav z rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství v roce 2021
9.12.2020 17:00 ZeměměřičPřed pár dny vláda odsouhlasila navýšení rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství. Redakce Zeměměřiče se na ministerstvu zeptala, jak to s finančními prostředky bude. Z tiskového oddělení MZe nám přišla odpověď, že “finanční prostředky, o kterých se v tiskové zprávě hovoří, jsou rozpočtem na pozemkové úpravy pro rok 2021. Na pozemkové úpravy je tak připraven rozpočet ve výši 2 mld. Kč […]
The post Financování pozemkových úprav z rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství v roce 2021 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Financování pozemkových úprav z rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství v roce 2021
9.12.2020 17:00 ZeměměřičPřed pár dny vláda odsouhlasila navýšení rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství. Redakce Zeměměřiče se na ministerstvu zeptala, jak to s finančními prostředky bude. Z tiskového oddělení MZe nám přišla odpověď, že „finanční prostředky, o kterých se v tiskové zprávě hovoří, jsou rozpočtem na pozemkové úpravy pro rok 2021. Na pozemkové úpravy je tak připraven rozpočet ve výši 2 mld. Kč […]
The post Financování pozemkových úprav z rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství v roce 2021 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Financování pozemkových úprav z rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství v roce 2021
9.12.2020 17:00 ZeměměřičPřed pár dny vláda odsouhlasila navýšení rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství. Redakce Zeměměřiče se na ministerstvu zeptala, jak to s finančními prostředky bude. Z tiskového oddělení MZe nám přišla odpověď, že „finanční prostředky, o kterých se v tiskové zprávě hovoří, jsou rozpočtem na pozemkové úpravy pro rok 2021. Na pozemkové úpravy je tak připraven rozpočet ve výši 2 mld. Kč […]
The post Financování pozemkových úprav z rozpočtu ministerstva zemědělství v roce 2021 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
vrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrá
9.12.2020 15:28 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Český Krumlov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo vrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrávrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrá
9.12.2020 15:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Český Krumlovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
vrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Český Krumlov (ID SM 30000154/30003778)
ČÚZK ve čtvrtek 10.12.2020 od
9.12.2020 15:27 GEUSware ČÚZK ve čtvrtek 10.12.2020 od 16:30 do cca 18:00 zcela přeruší provoz Dálkového přístupu (DP) i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu (WSDP). Z tohoto důvodu budou v GEUSu nefunkční Podklady měření a Odesílání GP.Spanish team wins Farming by Satellite Prize 2020
9.12.2020 14:58 European GNSS Agency
Graniot, a team from Spain, has won this year’s 1st Farming by Satellite Prize. The winning team developed a web application that uses European satellite technologies to help agronomists and farmers monitor crops, reduce water waste and avoid poor fertilisation practices. The Farming by Satellite Prize promotes the use of GNSS and Earth observation in Europe and includes a special Africa Prize.
The Italian team Genuine received second prize in the competition for a web-based solution that identifies crop stress the optimal tractor path for irrigation and fertilisation using Copernicus, EGNOS and Galileo. The third prize went to AI4OceanFarming, also from Spain, for a solution that uses satellite data to identify ocean farming threats such as harmful algal blooms (HABs), ocean acidification (OA), and invasive species. Finally, the Special Africa Prize went to the Kenyan-Italian team GeoM&E for a solution that uses European satellite technology to monitor coffee diseases.
The winners beat stiff competition from 40 other young teams with innovative ideas. The judges selected first a short list of the best teams to then take their ideas forward to a ‘Deep Dive’ phase. The selected eight grand finalists had the opportunity to pitch their solutions during a final ‘live’ judging round.
An inspiring experience
“We’re honoured to be chosen as winners of the Farming by Satellite Prize 2020. We will put the EUR 5,000 cash prize to good use developing our satellite crop monitoring web application further. The whole journey has been a great experience that would not have be possible without the support of UGREmprendedora and the Andalucia Agrotech Digital Innovation Hub,” said Pablo Romero Díaz and Manuel Castro Ruiz from Graniot. “We’ve learnt so much. We have been inspired by the feedback from the judges and have enjoyed seeing the entries from all the grand finalists during the awards ceremony.”
Read this: A “Cerealist’s Diary”, the testimony of a wheat farmer
“The innovation and wide variety of agriculture applications submitted by young innovators this year has been wonderful to see. It confirms the value of encouraging the next generation of farmers to explore the use of satellite technologies in agriculture to enable sustainable farming practices,” said Joaquín Reyes González, who judged the competition on behalf of the European GNSS Agency (GSA).
Hans Dufourmont, a judge for the European Environment Agency (EEA), highlighted the environmental credentials of the entries: “The agricultural sector needs to continue developing sustainable food production practices and improve their impact on the environment and climate. It’s great to see Galileo and Copernicus convincing young farmers to become tech savvy entrepreneurs and develop competitive yet sustainable agriculture.”
Increased use of EGNSS and Copernicus in agriculture
The Farming by Satellite Prize is an initiative of the GSA and the EEA, supported by agricultural engineering equipment manufacturer CLAAS. The competition aims to increase the use of Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus in European agriculture. The Prize also intends to raise awareness on the benefits the EU Space Programme provides toward fostering innovative and sustainable farming solutions. The objective of the Special Africa Prize is to encourage young Africans to develop satellite-based solutions that cater to the specific needs and resources of communities and lands in Africa.
Watch this: European Satellites for Agriculture
Commenting on the winning idea, Marcel Fölsch from CLAAS said: “The Graniot team has consistently presented a high-quality solution throughout all stages of this year’s competition. It is great to see their focus on olive farming in southern Europe, allowing them to narrow in on specific customer needs and present a compelling remote sensing solution to their users. We’re pleased to award the top prize to a team clearly driving the adoption of sustainable agriculture practises in Europe.”
Contestants were tasked with creating a new sustainable and environmentally friendly agriculture solution using Galileo, EGNOS and/or Copernicus. Solutions had to demonstrate a novel approach to the use of satellite services for farming, while ensuring accurate technical feasibility and a maximum impact on the farming industry.
Participation was open to young farmers, academics, and professionals between the ages of 18 and 32. They could take part as individuals or as a team of up to four. For the Special Africa Prize, at least one applicant was required to be a citizen of or resident in an African country.
For more information, click here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
9.12.2020 14:21 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu Katastrální pracoviště Praha vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knihrada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
9.12.2020 14:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Prahavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
9.12.2020 14:21 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-–-vedouci-oddeleni-informaci-z-Krada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
9.12.2020 14:21 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Praha vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knihrada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
9.12.2020 14:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu Katastrální pracoviště Prahavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení informací z KN a veřejných knih
ArcRevue 2/2020 v digitální podobě
9.12.2020 13:20 ARCDATANejnovější číslo časopisu ArcRevue si již můžete přečíst ve formátu PDF. Naleznete v něm články o nových aplikacích Zeměměřického úřadu, o tom, jak GIS pomáhaly Armádě ČR v krizovém štábu COVID-19, o Základní topografické mapě 1 : 5000, o projektu Digitální technická mapa ČR a o mnoha dalších tématech.
Novinkou je i rozdělení časopisu v našem archivu po jednotlivých článcích, takže je můžete pohodlněji stahovat a sdílet.
MawisPhoto – dokumentujte stavby
9.12.2020 12:40 Hrdlička MawisPhoto je aplikací, která nově rozšiřuje Mawis – portál profesionálního stavebníka.MawisPhoto – dokumentujte stavby za pomoci mobilního telefonu skrze 3D modely
9.12.2020 12:38 Hrdlička MawisPhoto je aplikací, která nově rozšiřuje Mawis – portál profesionálního stavebníkaPlaces in Antarctica named in honour of ice scientists
9.12.2020 12:04 ESA Observing the Earth
Celebrating 200 years since the discovery of the Antarctic continent, the UK Committee for Antarctic Place-Names has named 28 mountains, glaciers and bays after modern-day scientists who have advanced our understanding of this remote continent. Four of the names on the list have strong links to ESA, having either worked on the development of polar-orbiting altimetry missions such as ERS-1, ERS-2, Envisat and CryoSat, or subsequently by using their data together with other satellite missions for key polar research projects.
Omezení provozu kontaktního místa v Bystřici nad Pernštejnem
9.12.2020 10:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu, Katastrální pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou oznamuje, že dne 28. 12. 2020 bude Kontaktní místo Bystřice nad Pernštejnem z provozních důvodů uzavřeno. V případě potřeby se obracejte na podatelnu Katastrálního pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou, se sídlem Strojírenská 8, 591 27 Žďár nad Sázavou.Angsa Robotics wins overall prize in Galileo Masters 2020
9.12.2020 10:14 European GNSS Agency
Angsa Robotics has won the overall prize in the Galileo Masters 2020 with “Clive,” Germany’s first autonomous trash collection robot, which collects small pieces of rubbish left on grass or gravel that would otherwise cause ecological and economic problems.
Thanks to its unique artificial neural network architecture, “Clive” can move independently while detecting and localising individual objects, which enables it to clean grass and gravel areas. Individual objects such as bottle caps or cigarette butts are targeted for collection but insects are spared, in a win-win solution for the environment. Since conventional sweeping machines are designed for flat asphalt surfaces, they are unsuitable for these types of surfaces, so these surfaces have typically had to be cleaned manually.
“Clive” also creates an economic benefit for its customers. Its target use cases include the cleaning of festival venues after events and the daily cleaning of parks and other green spaces. Precise localisation via GNSS is essential to its operation: With better localisation, the robot can plan a more efficient path and clean a given area faster.
Forward-thinking applications
“Angsa Robotics is combining precise GNSS localisation with further state-of-the art techniques such as artificial intelligence and robotics. Its innovative solution is an impressive reflection of what the Agency was looking for with its three challenges in this year’s edition of Galileo Masters: forward-thinking applications of space for future generations,” European GNSS Agency (GSA) Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa said at the digital Space Awards.
After winning both the GSA Space for Our Planet Challenge and the Galileo Prize Bavaria, Angsa Robotics was presented with a EUR 10,000 cash prize as the Overall Winner of Galileo Masters 2020, having beat out 23 other challenge and prize winners. In addition, the pioneering start-up was selected as one of the winners of the Galileo Incubation Programme, which includes an incubation and acceleration prize package worth up to EUR 62,000.
The winners of the Galileo Masters 2020 international innovation competition were announced during the online Space Awards on 8 December as part of European Space Week 2020. Seventeen winners selected by the Galileo Prize Partners had the chance to present their ideas to an international audience at a Space Pitches session at EUSW on 7 December.
EGNSS driving innovation
European GNSS and the accurate, highly reliable positioning data it delivers is an essential element in the uptake of autonomous vehicles such as cars, drones, or robots. Autonomous vehicles are already a growing segment in the transport and automotive sector, in urban air mobility, and in the drone market.
By combining GNSS with on-board sensors and systems such as cameras, radar, or inertial sensors, robotic applications are also being developed for the construction, manufacturing, maintenance, monitoring, and the healthcare and household sectors. Satellite navigation data provides the accuracy, integrity, reliability, and availability required to operate autonomous vehicles.
Global innovation network for Galileo
Galileo Masters’ network of 101 partners from 18 countries focuses on the regional implementation of the competition to ensure a high level of diversity while enhancing both job growth potential and regional development opportunities. The competition’s backbone consists of 17 Prize Partners that are involved in specific areas at the local level, providing participants with valuable support in launching their businesses across Europe.
“Galileo Masters has given a significant boost to the rise of the GNSS industry in Europe,” said AZO CEO Thorsten Rudolph. “The top 100 companies that have grown out of the innovative ideas of more than 13,000 Galileo Masters participants since 2004 have created more than 3,300 jobs and generated EUR 178 million in total turnover in 2019. In recent years, these companies have also raised around EUR 524 million in venture capital.”
By fostering entrepreneurs and start-ups, Galileo Masters’ long-term objective is to strengthen Europe’s competitiveness with high-tech space solutions on a global scale. This was why the European Commission established Europe’s unique Galileo Incubation programme for the top six winners of Galileo Masters. For the fourth time, this programme will offer the year’s winners access to dedicated incubation services (worth up to EUR 372,000 in total) at their preferred incubation centre in the Europe-wide Galileo Masters network.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Rada/odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
9.12.2020 10:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemRada/odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
9.12.2020 10:02 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hodonín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti HodonínRada/odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
9.12.2020 10:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hodonínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín















