zprávy
zdroje zpráv:New Chair of knowledge exchange expert group aims to INSPIRE development of European Spatial Data Infrastructure
2.4.2021 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars March 29, 2021 -- Marcin Grudzień from the Head Office of Geodesy and Cartography (GUGIK) in Poland has been named the new Chair of a European …Cesium Releases Free 'Cesium for Unreal' for All Creators
2.4.2021 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Open source plugin unlocks global 3D data and geospatial technology for Unreal Engine and is now available for free on Epic Games' Unreal Engine …Drony (dotazník)
2.4.2021 8:34 GISportal.cz
Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl (UAVA) prosí o vyplnění krátkého anonymního dotazníku pro průzkum k tématu dronů. Dotazník zabere maximálně 3 minuty času, prosíme o vyplnění do 12. 4. 2021, kdy bude průzkum uzavřen.
The post Drony (dotazník) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Teledyne Clears Canada and Germany Antitrust Reviews for the FLIR Acquisition
2.4.2021 1:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars THOUSAND OAKS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 1, 2021 —Teledyne Technologies Incorporated (NYSE:TDY) announced today that it …
NGA Accelerator Announces Startups for Inaugural Cohort
1.4.2021 20:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The NGA Accelerator Powered by Capital Innovators recently selected eight companies to participate in the launch of the inaugural cohort of its …ÚCL zveřejnilo postupy a dokumenty k oprávnění provozu ve Specifické kategorii
1.4.2021 19:39 UAVAÚřad pro civilní letectví zveřejnil postupy včetně dokumentů potřebných k vydání Oprávnění k provozu ve Specifické kategorii, jehož platnost bude dvouletá. ÚCL doporučuje využít nyní provozovatelům s prodlouženou platností Leteckých prací (do konce roku 2021) plynulý přechod do Specifické kategorie a současně úpravu schválené provozní příručky do šablony dokumentu ConOps . Více zde: https://www.caa.cz/provoz/bezpilotni-letadla/specificka-kategorie-specific/postupy-a-formulare-dokumentu-k-agende-opravneni-k-provozu/
The post ÚCL zveřejnilo postupy a dokumenty k oprávnění provozu ve Specifické kategorii appeared first on UAV Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl.
Applications of Location-Based & Geospatial Intelligence Data
1.4.2021 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, April 1, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Enterprises, government agencies, and law enforcement use Cobwebs Technologies' …Hexagon publishes the Annual Report and Sustainability Report 2020
1.4.2021 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars STOCKHOLM, April 1, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Hexagon's Annual Report 2020 and separate Sustainability Report is now available at Hexagon's …Velodyne Lidar Announces Multi-Year Agreement With AGM Systems LLC
1.4.2021 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars AGM Systems Launches New Velodyne Lidar-Based UAV Mapping Solution for Leading Energy Companies WorldwideSAN JOSE, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) …
Trimble Releases 2020 Sustainability Report
1.4.2021 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SUNNYVALE, Calif., April 1, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Trimble (NASDAQ: TRMB) announced today the release of its 2020 Sustainability Report. …Trimble and Florida International University Establish Trimble Technology Lab at the Moss School of Construction, Infrastructure and Sustainability
1.4.2021 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SUNNYVALE, Calif. and MIAMI, April 1, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Building on a commitment to cultivate a highly-trained workforce that …Dynamic Infrastructure to Reveal Major Technological Breakthrough of Drone (UAS) Photos Analysis Captured While Inspecting Bridges
1.4.2021 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK and BERLIN, April 1, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Automatic processing of drone photos according to AASHTO standards while …Úřední hodiny od 12.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Třinec zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 12. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Třinec provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Sběrný box na budově úřadu bude zavedením rozšířených úředních hodin zrušen.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 12.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:48 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Ostrava/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uredni-hodiny-od-12-4-2021Úřední hodiny od 12.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:48 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ostrava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 12. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Ostrava provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Sběrný box na vstupních dveřích úřadu bude zavedením rozšířených úředních hodin zrušen.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 12.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místek zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 12. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Sběrný box na budově úřadu bude zavedením rozšířených úředních hodin zrušen.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:31 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Opava/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uredni-hodiny-od-8-4-2021Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Opava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 8. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Sběrný box na budově úřadu bude zavedením rozšířených úředních hodin zrušen.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Novy-Jicin/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uredni-hodiny-od-8-4-2021Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Nový Jičín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 8. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Nový Jičín provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Krnov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 8. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Krnov provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:23 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Krnov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uredni-hodiny-od-8-4-2021Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:19 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Karvina/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uredni-hodiny-od-8-4-2021Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:19 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karviná zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 8. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Karviná provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Bruntál zveřejnil novou aktualitu: ÚPRAVA ÚŘEDNÍCH HODINS účinností od 8. 4. 2021 je na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál provedena změna úředních hodin.
Úřední hodiny jsou pro všechny agendy:
pondělí a středa 8:00 – 17:00 hodin,
úterý a čtvrtek 8:00 – 14:00 hodin,
pátek 8:00 – 12:00 hodin.
I nadále upřednostňujeme bezkontaktní způsob podání (poštou, elektronicky). Při osobním kontaktu Vás žádáme o dodržování hygienických zásad a respektování pokynů našich zaměstnanců.
Sběrný box na budově úřadu bude zavedením rozšířených úředních hodin zrušen.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Úřední hodiny od 8.4.2021
1.4.2021 11:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Bruntal/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uredni-hodiny-od-8-4-2021rada/odborný rada – řízení o údajích SGI na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava Katastrálního úřadu pro Mo
1.4.2021 10:08 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Opava vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – řízení o údajích SGI na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava Katastrálního úřadu pro Morada/odborný rada – řízení o údajích SGI na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava Katastrálního úřadu pro Mo
1.4.2021 10:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Opavavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – řízení o údajích SGI na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
rada/odborný rada – řízení o údajích SGI na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava Katastrálního úřadu pro Mo
1.4.2021 10:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-–-rizeni-o-udajich-SGI-na-Katastvrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/vrchni-referent-rada-–-rizeni-o-oprave-chyby-v-SPIvrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:07 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Bruntál vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo vrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálníhovrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:07 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo vrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálníhovrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Bruntálvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
vrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
vrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
vrchní referent/rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:05 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/vrchni-referent-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatvrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:05 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Bruntál vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálníhovrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního
1.4.2021 10:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Bruntálvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Bruntál Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravsko
1.4.2021 10:02 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odbor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoodborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravsko
1.4.2021 10:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravsko
1.4.2021 10:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-vAgEagle™ Aerial Systems Announces Record Revenues for 2020
1.4.2021 3:14 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WICHITA, Kan., March 31, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- AgEagle Aerial Systems Inc. (NYSE American: UAVS) (“AgEagle” or the “Company”), an …Intermap Announces Filing of 2020 Annual Results
1.4.2021 3:14 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DENVER, March 31, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Intermap Technologies (TSX: IMP) (OTCQX: ITMSF) ("Intermap" or the "Company"), a global leader …OGC welcomes Chris Holmes as its inaugural Visiting Fellow
1.4.2021 0:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars
Chris Holmes will bring to OGC invaluable insight and perspective to the on-going development of the OGC API family of …
Veselé Velikonoce
1.4.2021 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad S každým příchodem jara přicházejí i tradiční svátky oslavující nový život a všechno s ním spojené. Velikonoce.Pro věřící se jedná o nejdůležitější svátky v roce, pro ostatní o milou tradici, která se předává z generace na generaci.
Veselé Velikonoce
1.4.2021 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad S každým příchodem jara přicházejí i tradiční svátky oslavující nový život a všechno s ním spojené. Velikonoce.Pro věřící se jedná o nejdůležitější svátky v roce, pro ostatní o milou tradici, která se předává z generace na generaci.
Mobility analytics from StreetLight Data available on HERE Marketplace
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Anonymized data from smartphones and navigation devices gives insights into traffic patterns and can help tackle transportation challenges …HawkEye 360 Announces Commissioning of Second Satellite Cluster
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Trio of satellites completes functional testing and starts commercial operationsHERNDON, Va., March 31, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — …
Fortem Technologies Demonstrates Integration with Forward Area Air Defense Command and Control System (FAAD C2)
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Pleasant Grove, Utah, March 31, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Fortem Technologies, a leader in airspace security and defense for detecting and defeating …ProStar Poised to Disrupt the Infrastructure Industry with the Release of a Revolutionary Technology
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GRAND JUNCTION, Colo., March 31, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — ProStar Holdings Inc ("ProStar®" or the "Company") (TSXV: MAPS) (FSE: …Autodesk Completes Acquisition of Innovyze, Provider of Smart Water Infrastructure Modeling, Simulation, and Predictive Technologies
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Accelerates Autodesk's digital twin development, advances the shared mission to help protect water resourcesSAN FRANCISCO, March 31, 2021 — …
SAM Announces Acquisition of R&S Digital Services
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAM Companies, the nation's leading provider of geospatial and construction services in North America, is pleased to announce it has completed the …Tangram Vision Raises Pre-Seed Funding Round to Enhance Sensors and Help Robots See the World
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Founded by computer vision veterans, Tangram Vision's mission is to make sensors simpler for robotics, drones, autonomous vehicles and factory …HCSS Offers Free Drone Flight Planner App With HCSS Aerial
31.3.2021 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HCSS Aerial: Drone Mission Works with Most Drones to Capture High-Resolution Images of Construction Job SitesSUGAR LAND, Texas, March 31, 2021 …
VRMesh 11.4 Adds Classification on Meshes and 2D Plan Extraction from Point Clouds
31.3.2021 18:42 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Bellevue, WA., Marth 31, 2021 - VirtualGrid is pleased to announce the availability of VRMesh v11.4, the latest version of its powerful point …buildingSMART vstupuje prostřednictvím czBIM do České republiky
31.3.2021 11:27 BIM NewsGlobální společenství, které řídí digitální transformaci stavebnictví uplatňováním otevřených standardů informačního modelování staveb (BIM) v celém životním cyklu staveb a infrastruktury, přichází do České republiky. Česko se tak přidává k více než dvaceti zemím, kde již buildingSMART působí, pobočku založila Odborná rada pro BIM (czBIM). Mezinárodní organizace buildingSMART tvořená pobočkami, členy, partnery a sponzory, zahrnujícími […]
The post buildingSMART vstupuje prostřednictvím czBIM do České republiky appeared first on BIM News.
Bentley Systems zve do soutěže Going Digital Awards in Infrastructure
31.3.2021 11:15 BIM NewsFirma Bentley Systems vyhlásila výzvu k podání nominací na 2021 Going Digital Awards in Infrastructure. Tento globální program ocenění, dříve známý jako Year in Infrastructure Awards, posuzovaný nezávislými porotami průmyslových odborníků, oceňuje infrastrukturní projekty za digitální inovace, které zlepšují realizaci projektů nebo technické parametry majetku. Uzávěrka nominací je 21. května 2021. Ocenění Going Digital Awards […]
The post Bentley Systems zve do soutěže Going Digital Awards in Infrastructure appeared first on BIM News.
BIM se bude učit na všech středních školách stavebního zaměření
31.3.2021 10:01 ZeměměřičOd září roku 2022 se na všech středních školách se stavebním zaměřením mají učit principy metody BIM. Ukládají to rámcové vzdělávací programy, platné od podzimu roku 2020. Změny čekají také studijní programy technických vysokých škol, které již informační modelování vyučují. V loňském průzkumu (PDF), uspořádaným Českou agenturou pro standardizaci a vyplněným 44 zástupci odborné veřejnosti, se […]
The post BIM se bude učit na všech středních školách stavebního zaměření appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Přednáška
31.3.2021 9:00 Geografický ústav MU
Zájemce z řad odborné i laické veřejnosti zveme na přednášku doc. RNDr. Petra Kubíčka, CSc. z Geografického ústavu PřF MU s názvem
Kartografie ve 3D – posun paradigmatu
Zájemce z řad odborné i laické veřejnosti zveme na přednášku doc. RNDr. Petra Kubíčka, CSc. z Geografického ústavu PřF MU s názvem Zájemce z řad odborné i laické veřejnosti zveme na přednášku doc. RNDr. Petra Kubíčka, CSc. z Geografického ústavu PřF MU s názvem Přednáška je součástí jmenovacího řízení doc. Kubíčka. Bude probíhat ve středu 31. března od 09:00 online v prostředí MS-Teams. Přednášky se můžete zúčastnit prostřednictvím tohoto odkazu: Klikněte sem a připojte se ke schůzce Rozšíření kartografické vizualizace a mapové tvorby o třetí rozměr sebou přináší řadu výzev. Prezentace se na počátku zaměří na podstatu trojrozměrného vnímání a následně rozebere hlavní kartografické a technologické výzvy související s využitím třetího rozměru obecně a bude představen koncept virtuálních geografických prostředí (VGE). Následně budou uvedeny hlavní směry výzkumu v dané oblasti a prezentovány vybrané empirické studie zaměřené na roli grafických proměnných ve 3D vizualizaci, vlivu míry realismu a interakce pro řešení prostorových úloh a využití VGE pro oblast navigace v interiéru budov.
Přednáška doc. RNDr. Petra Kubíčka, CSc.
31.3.2021 9:00
Geografický ústav MU
Kartografie ve 3D – posun paradigmatu
Přednáška doc. Petra Kubíčka pro veřejnost: Kartografie ve 3D – posun paradigmatu
31.3.2021 9:00
Geografický ústav MU
Kartografie ve 3D – posun paradigmatu
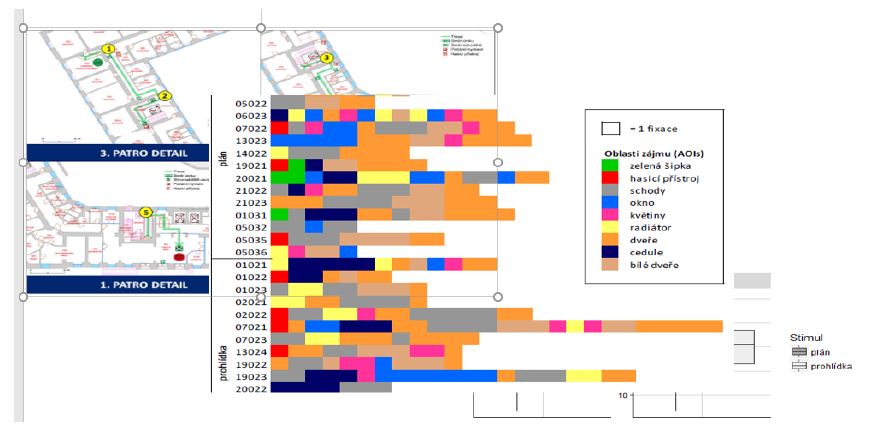
Oznámení o státní doktorské zkoušce a obhajobě disertační práce Mgr. Lenky Ondráčkové
31.3.2021 0:00 Geografický ústav MUAutoreferát (PDF)
Elistair, The Pioneer in Tethered UAVs, Announces a €5M Series B Round to Accelerate Its International Expansion
30.3.2021 22:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars LYON, France & BOSTON — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 30, 2021 —
Elistair, a market leader in tethered drones, has raised …
S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller Index Reports 11.2% Annual Home Price Gain to Start 2021
30.3.2021 22:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — S&P Dow Jones Indices (S&P DJI) today released the latest results for the S&P …PDFTron Acquires PDF3D, the World Leader in 3D PDF Conversion and Collaboration Technologies
30.3.2021 22:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VANCOUVER, BC, March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — PDFTron Systems Inc., the world's leading provider of document technology solutions for …Citadel Defense Secures New $5M Counter Drone Contract from U.S. Department of Defense
30.3.2021 18:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Titan has three years of mission effectiveness across multiple Combatant CommandsSAN DIEGO — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 30, 2021 …
Martin UAV Unveils V-BAT 128, Featuring Increased Payload, Endurance for Defense and Private-Sector Application
30.3.2021 18:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars PLANO, Texas, March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — Martin UAV, a leading advanced aviation technology manufacturer in the United …SkyX Expands into South America Amidst Growing Demand for Remote Monitoring Services
30.3.2021 18:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars TORONTO, March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — SkyX, a leader in aerial intelligence powered by autonomous long-range UAV solutions, is …Rhode Island Signs Participating Addendum with DroneUp Providing Public Sector Agencies Access to Drone Services
30.3.2021 18:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VIRGINIA BEACH, Va., March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — DroneUp, LLC and the State of Rhode Island have signed a Participating Addendum for …Střední školy budou BIM od podzimu 2022 učit povinně
30.3.2021 17:36 GeoBusinessOd září roku 2022 se na všech středních školách se stavebním zaměřením mají učit principy metody BIM. Ukládají to rámcové vzdělávací programy, platné od podzimu roku 2020. Změny čekají také studijní programy technických vysokých škol, které již informační modelování vyučují. Díky iniciativě skupiny EDU BIM a odboru Koncepce BIM České agentury pro standardizaci vzniká na […]
The post Střední školy budou BIM od podzimu 2022 učit povinně appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Utilis launches MasterPlan for water utility asset management
30.3.2021 16:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Pipe deficiency dataset is derived from direct satellite measurementsTEL AVIV, Israel, March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) —
TEL AVIV, …
Kinetica Offers Geospatial Visualization Within Tableau at Unlimited Scale
30.3.2021 16:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The Kinetica geospatial extension for Tableau lets users view all their data in real timeSAN FRANCISCO — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 30, …
Utility Study Demonstrates Benefits of Drones and IoT-Enabled Visual Software to Ensure Safer, More Reliable Power Grid
30.3.2021 16:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Cyberhawk drone-based inspections monitor over 11,500 transmission towers and nearly 150 substations across Scottish Utility NetworkDENVER, March …
ČÚZK ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 od 16
30.3.2021 14:26 GEUSware ČÚZK ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 a v neděli 4.4.2021 v průběhu dne zcela přeruší provoz Dálkového přístupu (DP) i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu (WSDP). Z tohoto důvodu budou v GEUSu nefunkční Podklady měření a Odesílání GP.rada / odborný rada v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru
30.3.2021 13:17 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - technický odbor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu v technickém odborurada / odborný rada v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru
30.3.2021 13:17 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralnihrada / odborný rada v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru
30.3.2021 13:17 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu v technickém odboru
Second Scout gets the go-ahead
30.3.2021 9:55 ESA Observing the Earth
Following the selection of the first Scout satellite mission last December, ESA has also given the greenlight to start negotiations with Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd in the UK to lead the development of the second Scout mission – HydroGNSS.
Bad Elf and Point One partner to provide Polaris GNSS corrections for Bad Elf Flex®
30.3.2021 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Scottsdale, AZ, USA – March 30, 2021 – Bad Elf, LLC and Point One Navigation, Inc. announce a strategic relationship to provide …Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 a v neděli 4.4.2021
30.3.2021 8:07 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/317008Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 a v neděli 4.4.2021
30.3.2021 8:07 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 a v neděli 4.4.2021 v průběhu dne bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. V rámci přerušení provozu nebudou instalovány žádné opravy ani nová funkčnost, odstávky jsou způsobeny pracemi na technologické infrastruktuře.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 a v neděli 4.4.2021
30.3.2021 8:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že ve čtvrtek 1.4.2021 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 a v neděli 4.4.2021 v průběhu dne bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. V rámci přerušení provozu nebudou instalovány žádné opravy ani nová funkčnost, odstávky jsou způsobeny pracemi na technologické infrastruktuře.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Velodyne Lidar Files Form S-1 Registration Statement to Register Existing Shares from the Previously Completed Merger Upon Release of the Lock-Up
30.3.2021 3:32 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Approximately Two-Thirds of Registered Shares Remain Locked-UpSAN JOSE, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 29, 2021 —
Velodyne …
CIOE-Intelligent Sensing Expo to promote industrial development
30.3.2021 3:32 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SHENZHEN, China, March 30, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — As one of the 6 expos in CIOE, Intelligent Sensing Expo focuses on new products, …SPÚ odvedl v roce 2020 do státního rozpočtu 549 miliónů za prodej pozemků
30.3.2021 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Praha, 30. března 2021 – Státní pozemkový úřad (SPÚ) v loňském roce odvedl z prodejů pozemků do státního rozpočtu ČR necelých 549 milionů korun.Ørsted and NOAA Sign Industry First Data Sharing Agreement
29.3.2021 22:05 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The historic agreement will lead to improved data collection in an effort to help save lives and increase America's coastal resiliencyBOSTON, March …
Kratos’ Autonomous Truck-Mounted Attenuator Named Infrastructure Game Changer by American Society of Civil Engineers
29.3.2021 20:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, March 29, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc. (NASDAQ: KTOS), a leading National Security …Maxar Awarded Contract to Support GEOINT Exploitation for U.S. Army and Combatant Commands
29.3.2021 20:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 29, 2021 —Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR), a trusted partner and innovator …
NV5 Acquires Geodynamics, Expanding Deep-Water Geospatial Capabilities
29.3.2021 20:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HOLLYWOOD, Fla., March 29, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- NV5 Global, Inc. (the “Company” or “NV5”) (Nasdaq: NVEE), a provider of compliance, …Nový stavební zákon se nelíbí městům, proto předkládají městské artikuly, zlepšující územní plánování
29.3.2021 19:37 GeoBusinessDo konce března 2021 je možné podávat pozměňovací návrhy k nové podobě stavebního zákona ve druhém čtení. Podle vedení českých měst zákon zásadním způsobem ovlivní kvalitu prostředí, ve kterém žijeme, ale také ekonomickou prosperitu celého Česka na několik desetiletí. Návrh připravilo Ministerstvo pro místní rozvoj ČR, podle zástupců velkých českých měst však nepřináší zlepšení v […]
The post Nový stavební zákon se nelíbí městům, proto předkládají městské artikuly, zlepšující územní plánování appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Modelování dopravy v digitálním dvojčeti chytrého města
29.3.2021 19:24 GeoBusinessV rámci Otevřeného jara se 6. dubna 2021 koná webinář o dopravním modelování. Pro přihlášené je účast na webináři zdarma. Webinář představí aktuální přístup k modelování dopravy v prostředí digitálního dvojčete chytrého města. Účastníkům budou nejprve názorně vysvětleny základní principy modelování dopravy, následovat bude představení webové aplikace pro dopravní modelování TraMod včetně živé ukázky. Na […]
The post Modelování dopravy v digitálním dvojčeti chytrého města appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Jak využít koncept mapových kompozic ve vzdělávání
29.3.2021 18:58 GeoBusinessDvanáctý webinář v rámci Otevřeného jara se koná 30. března od 13 hodin. Zdarma je webinář přístupný všem přihlášeným. Na webináři Viktorie Sloupová, Jan Macura a Otakar Čerba představí otevřené, především webové technologie, které umožňují interaktivní a atraktivní zařazení map do výuky. Postupně budou prezentovány ukázky tvorby jednoduchých map, jejich publikace na webu a především […]
The post Jak využít koncept mapových kompozic ve vzdělávání appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Uzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 15:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Dne 29.3.2021 započaly na přilehlých pozemcích Katastrálního úřadu pro Karlovarský kraj terénní úpravy.Menší parkoviště pro klienty Katastrálního pracoviště resp. Katastrálního úřadu na západní straně budovy je dočasně uzavřeno.
Pro parkování prosím použijte větší parkoviště na východní straně budovy (naproti OC Kaufland)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Uzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 15:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Karlovy-Vary/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uzavreni-mensiho-parkovisteUzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 15:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V rámci probíhajících terénních úprav je menší parkoviště pro klienty Katastrálního pracoviště resp. Katastrálního úřadu na západní straně budovy dočasně uzavřeno.Pro parkování prosím použijte větší parkoviště na východní straně budovy (naproti OC Kaufland)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Uzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 15:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karlovy Vary zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V rámci probíhajících terénních úprav je menší parkoviště pro klienty Katastrálního pracoviště resp. Katastrálního úřadu na západní straně budovy je dočasně uzavřeno.Pro parkování prosím použijte větší parkoviště na východní straně budovy (naproti OC Kaufland)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Uzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 14:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V rámci probíhajících terénních úprav je menší parkoviště pro klienty Katastrálního pracoviště resp. Katastrálního úřadu na západní straně budovy je dočasně uzavřeno.Pro parkování prosím použijte větší parkoviště na východní straně budovy (naproti OC Kaufland)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Uzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 14:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uzavreni-mensiho-parkovisteUzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 14:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Dne 29.3.2021 započaly na přilehlých pozemcích Katastrálního úřadu pro Karlovarský kraj terénní úpravy.Menší parkoviště pro klienty Katastrálního pracoviště resp. Katastrálního úřadu na západní straně budovy je dočasně uzavřeno.
Pro parkování prosím použijte větší parkoviště na východní straně budovy (naproti OC Kaufland)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Uzavření menšího parkoviště
29.3.2021 14:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V rámci probíhajících terénních úprav je menší parkoviště pro klienty Katastrálního pracoviště resp. Katastrálního úřadu na západní straně budovy dočasně uzavřeno.Pro parkování prosím použijte větší parkoviště na východní straně budovy (naproti OC Kaufland)
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN, poskytování info
29.3.2021 14:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Kroměřížvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN, poskytování informací PK v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Kroměříž
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN, poskytování info
29.3.2021 14:40 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Kroměříž vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN, poskytování infoOdborný referent - poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN, poskytování info
29.3.2021 14:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-poskytovani-informaci-KN,-poskyAgile governance needed for secure space systems
29.3.2021 11:58 European GNSS Agency
Security governance needs to be agile and reactive, European GNSS Agency (GSA) Head of Security Stefano Iannitti said at the virtual CYSAT conference, dedicated to cybersecurity for the space industry, which took place in Davos on 17-19 March. Iannitti went on to outline the main threats for a space system and the challenges faced in protecting both the services provided to users and the system itself.
Speaking about the GSA’s experience of space cyber security, Iannitti explained how the Agency monitors such challenges on a daily basis. “To manage cyber security, it is necessary for the right actor to have their hands on the system and to be able to react at the right time. The security governance aims at giving clear responsibility to each layer of the supply chain for that purpose. This governance also includes security assurance processes, internal audits, penetration tests and vulnerability management,” he said.
Evolving threat landscape
With almost two billion Galileo devices worldwide, one of the GSA’s key tasks is to protect the system, enabling it to achieve its full potential to boost innovation for the European economy and its citizens. The GSA Head of Security noted that, given the complexity of both the space segment and the ground segment, there is a wide range of security threats. “Different threats affect different segments and the threat landscape is constantly evolving,” he said.
Read this: Galileo Performance Workshop 2021: The highlights
“Security by design is a key concept,” Iannitti said, adding that this is being applied also in the development of the services provided by other components of the Space Programme, such as GOVSATCOM.
The fact that Galileo sites are spread around the world, often in remote locations, is also a challenge. “With stations spread across the globe, we need to ensure that these are not targets of malicious attacks,” he said, adding that it is necessary not only to protect critical infrastructure, but also the information that the sites contain.
And this: Galileo satellite performs collision avoidance manoeuvre
Iannitti stressed the importance of security intelligence: “You need to know your threats,” he said. He made reference to a recent Galileo satellite manoeuvre to avoid a collision, adding that it is important to monitor what there is in space that poses a threat. “The European Union understands this and has introduced the surveillance and tracking component in the space programme. This gives extra support in handling this type of event and in preventing potential collisions,” he said, adding that the introduction of standards would help everybody in the best management of space.
Comprehensive security coverage
The GSA is in charge of ensuring the security of the various components of the GNSS system and, as it transitions into the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), its mandate will expand to cover aspects of other components of the Programme, such as Copernicus along with GOVSATCOM, and potentially also Space Situational Awareness and other initiatives such as the secure connectivity and quantum computing infrastructure that the Union will want to introduce in the Programme. “These are critical systems for the Union and they will have to be protected, especially if they deliver critical governmental services,” he said.
The GSA currently covers all the phases of security provision. The Galileo Security Monitoring Centre is an integral part of the Galileo infrastructure. It monitors and takes action in relation to security threats, alerts and the operational status of systems components. Iannitti said that to close the loop, a security accreditation process is in place. This is provided by the Security Accreditation Board (SAB), which acts independently and is composed of representatives from the Member States, the Commission and the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy.
Regarding cooperation between EUSPA, other EU institutions and the European Space Agency (ESA), he said that different entities have different competences and missions. “EUSPA will be focused mainly on operations and service provision, and security, of course. For the development of the system we rely on ESA, and we work with all the institutions involved to manage the systems. These systems are of strategic importance to the Union and they also need political oversight,” he said.
For more information on security and the EU Space Programme, click here.
Agile governance needed for secure space systems
29.3.2021 11:58 European GNSS Agency
Security governance needs to be agile and reactive, European GNSS Agency (GSA) Head of Security Stefano Iannitti said at the virtual CYSAT conference, dedicated to cybersecurity for the space industry, which took place in Davos on 17-19 March. Iannitti went on to outline the main threats for a space system and the challenges faced in protecting both the services provided to users and the system itself.
Speaking about the GSA’s experience of space cyber security, Iannitti explained how the Agency monitors such challenges on a daily basis. “To manage cyber security, it is necessary for the right actor to have their hands on the system and to be able to react at the right time. The security governance aims at giving clear responsibility to each layer of the supply chain for that purpose. This governance also includes security assurance processes, internal audits, penetration tests and vulnerability management,” he said.
Evolving threat landscape
With almost two billion Galileo devices worldwide, one of the GSA’s key tasks is to protect the system, enabling it to achieve its full potential to boost innovation for the European economy and its citizens. The GSA Head of Security noted that, given the complexity of both the space segment and the ground segment, there is a wide range of security threats. “Different threats affect different segments and the threat landscape is constantly evolving,” he said.
Read this: Galileo Performance Workshop 2021: The highlights
“Security by design is a key concept,” Iannitti said, adding that this is being applied also in the development of the services provided by other components of the Space Programme, such as GOVSATCOM.
The fact that Galileo sites are spread around the world, often in remote locations, is also a challenge. “With stations spread across the globe, we need to ensure that these are not targets of malicious attacks,” he said, adding that it is necessary not only to protect critical infrastructure, but also the information that the sites contain.
And this: Galileo satellite performs collision avoidance manoeuvre
Iannitti stressed the importance of security intelligence: “You need to know your threats,” he said. He made reference to a recent Galileo satellite manoeuvre to avoid a collision, adding that it is important to monitor what there is in space that poses a threat. “The European Union understands this and has introduced the surveillance and tracking component in the space programme. This gives extra support in handling this type of event and in preventing potential collisions,” he said, adding that the introduction of standards would help everybody in the best management of space.
Comprehensive security coverage
The GSA is in charge of ensuring the security of the various components of the GNSS system and, as it transitions into the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), its mandate will expand to cover aspects of other components of the Programme, such as Copernicus along with GOVSATCOM, and potentially also Space Situational Awareness and other initiatives such as the secure connectivity and quantum computing infrastructure that the Union will want to introduce in the Programme. “These are critical systems for the Union and they will have to be protected, especially if they deliver critical governmental services,” he said.
The GSA currently covers all the phases of security provision. The Galileo Security Monitoring Centre is an integral part of the Galileo infrastructure. It monitors and takes action in relation to security threats, alerts and the operational status of systems components. Iannitti said that to close the loop, a security accreditation process is in place. This is provided by the Security Accreditation Board (SAB), which acts independently and is composed of representatives from the Member States, the Commission and the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy.
Regarding cooperation between EUSPA, other EU institutions and the European Space Agency (ESA), he said that different entities have different competences and missions. “EUSPA will be focused mainly on operations and service provision, and security, of course. For the development of the system we rely on ESA, and we work with all the institutions involved to manage the systems. These systems are of strategic importance to the Union and they also need political oversight,” he said.
For more information on security and the EU Space Programme, click here.
Measuring shoreline retreat
29.3.2021 11:45 ESA Observing the Earth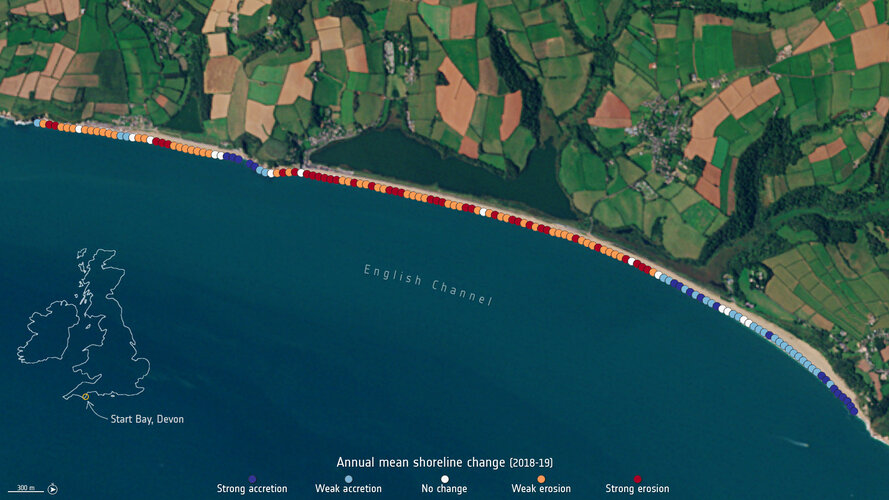
Climate change is having an undeniable influence on coastal areas. A substantial proportion of the world’s sandy coastlines are already eroding owing to increased storm surges, flooding and sea level rise. With our coastal environments in constant change, Earth observation satellites are being used to better strengthen our knowledge of changing coastlines.
Measuring shoreline retreat
29.3.2021 11:45 ESA Observing the Earth
Climate change is having an undeniable influence on coastal areas. A substantial proportion of the world’s sandy coastlines are already eroding owing to increased storm surges, flooding and sea level rise. With our coastal environments in constant change, Earth observation satellites are being used to better strengthen our knowledge of changing coastlines.
Již zítra začíná série webových seminářů
29.3.2021 8:55 ARCDATADovolujeme si vás pozvat na první z šestice webových seminářů, jejichž prostřednictvím vám v průběhu letošního jara přiblížíme svět ArcGIS Pro.
Tento seminář, který se bude věnovat přechodu z ArcMap do prostředí ArcGIS Pro, se uskuteční v úterý 30. března 2021 od 10.00 do 10.45. Další témata a jejich termíny naleznete v přehledu všech webových seminářů.
Pro sledování není zapotřebí instalovat žádný software, ani doplněk prohlížeče, stačí se pouze zaregistrovat na stránce webináře.Registrace i účast na semináři jsou zdarma, avšak registrace je nutná pro každý webový seminář zvlášť.
Výběrové řízení
29.3.2021 7:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z ZRVZ1001, oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem, Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město, v oboru služby 55. Zeměměřictví a katastr nemovitostí.Odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z ZRVZ1001
29.3.2021 7:27 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-zapisy-v-rizeniOdborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z ZRVZ1001
29.3.2021 7:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-městovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z ZRVZ1001
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z ZRVZ1001
29.3.2021 7:27 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z ZRVZ1001Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy BLUM do DAEX DESIGN
27.3.2021 21:38 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
nový převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN Vám ulehčí Vaší práci.
The post Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy BLUM do DAEX DESIGN appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Chráněno: Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN
27.3.2021 21:38 ŠPINAR - softwareStručný obsah příspěvku zde není uveden, protože je tento příspěvek chráněn heslem.
The post Chráněno: Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN
27.3.2021 21:38 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
nový převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN Vám ulehčí Vaší práci.
The post Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy BLUM do DAEX DESIGN
27.3.2021 21:38 ŠPINAR - software Vážení zákazníci,nový převodník Konfigurátoru korpusů od firmy Blum do DAEX DESIGN Vám ulehčí Vaší práci.
















