zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Nová kniha “Geographic Citizen Science Design” volně ke stažení
17.3.2021 7:59 GISportal.cz
prof. Muki Haklay a dr. Artemis Skarlatidou vydali pod hlavičkou vydavatelství UCL Press (University College London – jedna z nejlepší evropských univerzit) knihu Geographic Citizen Science Design – No one left behind. Kniha je členěna do tří částí – 16 kapitol (různé kapitoly mají různé autory) a zaměřuje se jak na teoreticko-metodologické principy citizen science, […]
The post Nová kniha “Geographic Citizen Science Design” volně ke stažení appeared first on GISportal.cz.
PLM řešení Fusion Lifecycle mění název na Fusion 360 Manage
17.3.2021 1:00 CAD Studio PLM aplikace Autodesk Fusion Lifecycle mění svůj název. Přichází Autodesk Fusion 360 Manage!
PLM systémy se velice rychle stávají nezbytným nástrojem pro efektivní řízení životního cyklu výrobku. Autodesk Fusion 360 Manage (dříve Fusion Lifecycle) ...
PLM aplikace Autodesk Fusion Lifecycle mění svůj název. Přichází Autodesk Fusion 360 Manage!
PLM systémy se velice rychle stávají nezbytným nástrojem pro efektivní řízení životního cyklu výrobku. Autodesk Fusion 360 Manage (dříve Fusion Lifecycle) ...SOLIDWORKS Simulation rychle a
17.3.2021 0:00 SolidVision SOLIDWORKS Simulation rychle a efektivně ověří spolehlivost vašich výrobků, nyní za akční ceny.SOLIDWORKS Simulation rychle a
17.3.2021 0:00 SolidVision SOLIDWORKS Simulation rychle a efektivně ověří spolehlivost vašich výrobků, nyní za akční ceny.DroneUp Acquires Web Teks
16.3.2021 23:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Acquisition Accelerates DroneUp's Tech IPVIRGINIA BEACH, Va., March 16, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — DroneUp, LLC, a leading global …
Pomozte vyhrát projektu FIE20: Groundwater and meteo sensors. Její čeští autoři by rádi v soutěži zvítězili
16.3.2021 20:59 GeoBusinessMezinárodní tým zaznamenal úspěch v soutěži WSIS Prizes 2021 za vývoj webové aplikace FIE20: Groundwater and meteo sensors, určené pro zemědělství. Vyvíjené řešení nabízí integraci různých druhů dat do jedné webové mapové aplikace využívané zemědělci, agronomy nebo dalšími společnostmi připravující doporučení pro zemědělství. Soutěž FAO-ITU Call for Good practices pořádají Organizace pro výživu a zemědělství OSN […]
The post Pomozte vyhrát projektu FIE20: Groundwater and meteo sensors. Její čeští autoři by rádi v soutěži zvítězili appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Pomozte vyhrát projektu FIE20: Groundwater and meteo sensors. Její čeští autoři by rádi v soutěži zvítězili
16.3.2021 20:59 GeoBusinessMezinárodní tým zaznamenal úspěch v soutěži WSIS Prizes 2021 za vývoj webové aplikace FIE20: Groundwater and meteo sensors, určená pro zemědělství. Vyvíjené řešení nabízí integraci různých druhů dat do jedné webové mapové aplikace využívané zemědělci, agronomy nebo dalšími společnostmi připravující doporučení pro zemědělství. Soutěž FAO-ITU Call for Good practices pořádají Organizace pro výživu a zemědělství OSN […]
The post Pomozte vyhrát projektu FIE20: Groundwater and meteo sensors. Její čeští autoři by rádi v soutěži zvítězili appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Digitální dvojčata by měla mít na starosti interdisciplinární organizace, navrhují ve Velké Británii
16.3.2021 20:31 BIM NewsVe Velké Británii se mluví o vytvoření interdisciplinární organizace, která by v následujících deseti letech měla na starosti rozvoj digitálnních dvojčat. Organizace by měla mít podle návrhu rozpočet mezi 150 až 200 miliony britských liber na deset let. Doporučení (PDF) připravila asociace TechUK. Doporučení na vytvoření interdisciplinární organizace, která by rozvoj digitálních dvojčat měla na […]
The post Digitální dvojčata by měla mít na starosti interdisciplinární organizace, navrhují ve Velké Británii appeared first on BIM News.
Změny ve vedení stavebního deníku, nový studijní program v Ostravě, Stavba roku
16.3.2021 19:57 GeoBusinessGIS Konference GIS Ostrava i studentská konference GISáček se letos konají online ve dnech 17. – 19. března. Podívejte se do programu konference GIS Ostrava 2021. Konference GISáček je zdarma, stačí se připojit. Stavebnictví Soutěž Stavba roku 2021 má otevřeny přihlášky. Do 29. ročníku této celorepublikové soutěže se lze přihlašovat do 10. června 2021. Přihlášky a podmínky […]
The post Změny ve vedení stavebního deníku, nový studijní program v Ostravě, Stavba roku appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Program studentské konference GISáček 2021
16.3.2021 19:25 GeoBusinessStudentská konference GISáček 2021 se koná online v pátek 19. března 2021 od 9:00 hod. Na konferenci prezentují studenti vysokých škol své bakalářské a magisterské práce. Bakalářská sekce Anna Krusová (UK): Tematický atlas pražských ostrovů Marie Šašková (UK): Turistická mapa Srbska v Českém – krasu se zaměřením na znázorňování krasového reliéfu Markéta Žuravská (UK): Turistická […]
The post Program studentské konference GISáček 2021 appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Program studentské konference GISáček 2021
16.3.2021 19:25 GeoBusinessStudentská konference GISáček 2021 se koná online v pátek 19. března 2021 od 9:00 hod. Na konferenci prezentují studenti vysokých škol své bakalářské a magisterské práce. Zúčastnit konference se může bezplatně každý, kdo má zájem prezentovat nebo jen shlédnout výsledky práce vystupujících studentů. Link pro přihlášení účasti jako posluchače je volně dostupný – https://go.mywebinar.com/sevw-lpmz-fzjg-nqve. Bude využito […]
The post Program studentské konference GISáček 2021 appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Insight LiDAR Enhances its Long Range FMCW LiDAR Offering
16.3.2021 18:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New Sensor Enables Lowest Cost, High Resolution 360 Degree CoverageBOULDER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 16, 2021 —
Insight …
CompassCom Recognized as Esri Release Ready Business Partner
16.3.2021 16:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DENVER, CO – March 16, 2021 – CompassCom Software Corp., a leading provider of real-time high-value asset tracking, is excited to …The Virtual Exhibition in the Field of Geospatial Information-The Geospatial Information Roadshow 2021
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Realizing digital touch-points for global businesses through the WEB-VR 3D exhibition.The Geospatial Information Roadshow 2021, hosted by the …
Barrier1 Systems Partners With Cepton to Deploy State-of-the-art Lidar-based Security and Safety Systems for Global Customers
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Collaboration enables the next generation of accurate perimeter surveillance, safety and security applicationsSAN JOSE, Calif. — (BUSINESS …
SKYTRAC Enters Unmanned Aviation Segment with Innovative IMS-350 Iridium Certus Satcom Terminal
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Kelowna, BC, March 16, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- SKYTRAC Systems Ltd. (SKYTRAC), has entered the unmanned aviation segment with the development and …Martin UAV Unveils the V-BAT 128, Newly Upgraded V-BAT Model
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VTOL UAV updated with new engine, increased payload and longer endurance for defense and private-sector applicationPLANO, Texas, March 16, 2021 …
SafeGraph Raises $45M Series B to Become the Ultimate Destination for Physical Places Data
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Led by Sapphire Ventures, SafeGraph to leverage fundraise to capitalize on an expanding market of places data buyersDENVER, March 16, 2021 — …
AiDash Joins Open Geospatial Consortium to Spearhead Innovation With Industry Leaders
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SANTA CLARA, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 16, 2021 —AiDash, a San Francisco Bay Area-based leading satellite analytics …
Esri Joins Digital Twin Consortium
16.3.2021 16:50 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Organizations Can Use ArcGIS to Connect Virtual Models, Solving Business ChallengesREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 16, 2021 …
Porucha telefonní spojení
16.3.2021 14:48 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Brno-venkov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Porucha-telefonni-spojeniPorucha telefonní spojení
16.3.2021 14:48 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-venkovzveřejnil novou aktualitu: Telefonické spojení do budovy Katastrálního pracoviště Brno-venkov prostřednictvím linky 542 532 xxx je pro poruchu dočasně mimo provoz. Za způsobené komplikace se omlouváme.
Odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
16.3.2021 12:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-zapisy-v-rizeni-V-a-Z-v-oddelenOdborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
16.3.2021 12:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Holešovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Holešov
Odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
16.3.2021 12:28 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Holešov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního praRozpočet úřadu za rok 2021
16.3.2021 11:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok
2021
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2021
16.3.2021 11:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2021Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 20
16.3.2021 9:36 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-CB/Vyrocni-zpravy/Vyrocni-zprava-dle-zakona-c-106-1999-Sb-za-rok-(2)Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 20
16.3.2021 9:36 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Českých Budějovicíchvydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok
2020
Odstávka Geoportálu Jihočeského kraje
16.3.2021 7:45 Jihočeský kraj Ve středu 17.3.2021 od 16:00 dojde k přepínání na nové verze aplikací Geoportálu, čímž může být dotčena jeho funkcionalita. Děkujeme za pochopení.Maxar Technologies Announces Launch of Common Stock Offering
16.3.2021 1:14 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 15, 2021 —Maxar Technologies Inc. (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR) (“Maxar” or the …
NV5 Announces Closing of Underwritten Public Offering of Common Stock
16.3.2021 1:14 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HOLLYWOOD, Fla., March 15, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- NV5 Global, Inc. (the “Company” or “NV5”) (Nasdaq: NVEE), a provider of compliance, …Soutěž Young Scholar Award
15.3.2021 16:59 ARCDATASpolečnost Esri i v letošním roce vyhlašuje soutěž Young Scholar Award, určenou pro studenty a čerstvé absolventy vysokých škol. Vítěz národního kola se bude moci zúčastnit online světové uživatelské konference Esri a mít zde příležitost reprezentovat Českou republiku.
Více informací o tom, jaké náležitosti by měl soutěžní projekt splňovat a podle jakých kritérií bude vítězný projekt vybírán, naleznete na stránce Young Scholar Award.
Pro přihlášení svého projektu nás kontaktujte na e-mailové adrese marketing@arcdata.cz, a to nejpozději do 30. dubna 2021.
Wejo to Showcase How Connected Car Data Transforms Mobility at MOVE America and the Esri Partner Conference
15.3.2021 16:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Executives from Wejo will bring pertinent industry insights to key transportation and data audiencesMANCHESTER, England & DETROIT — …
Texas Department of Public Safety Awards DroneSense SaaS Contract
15.3.2021 16:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The agreement provides software and support for one of the largest Public Safety drone operations in the U.S.AUSTIN, Texas, March 15, 2021 — …
Air pollution returning to pre-COVID levels
15.3.2021 14:50 ESA Observing the Earth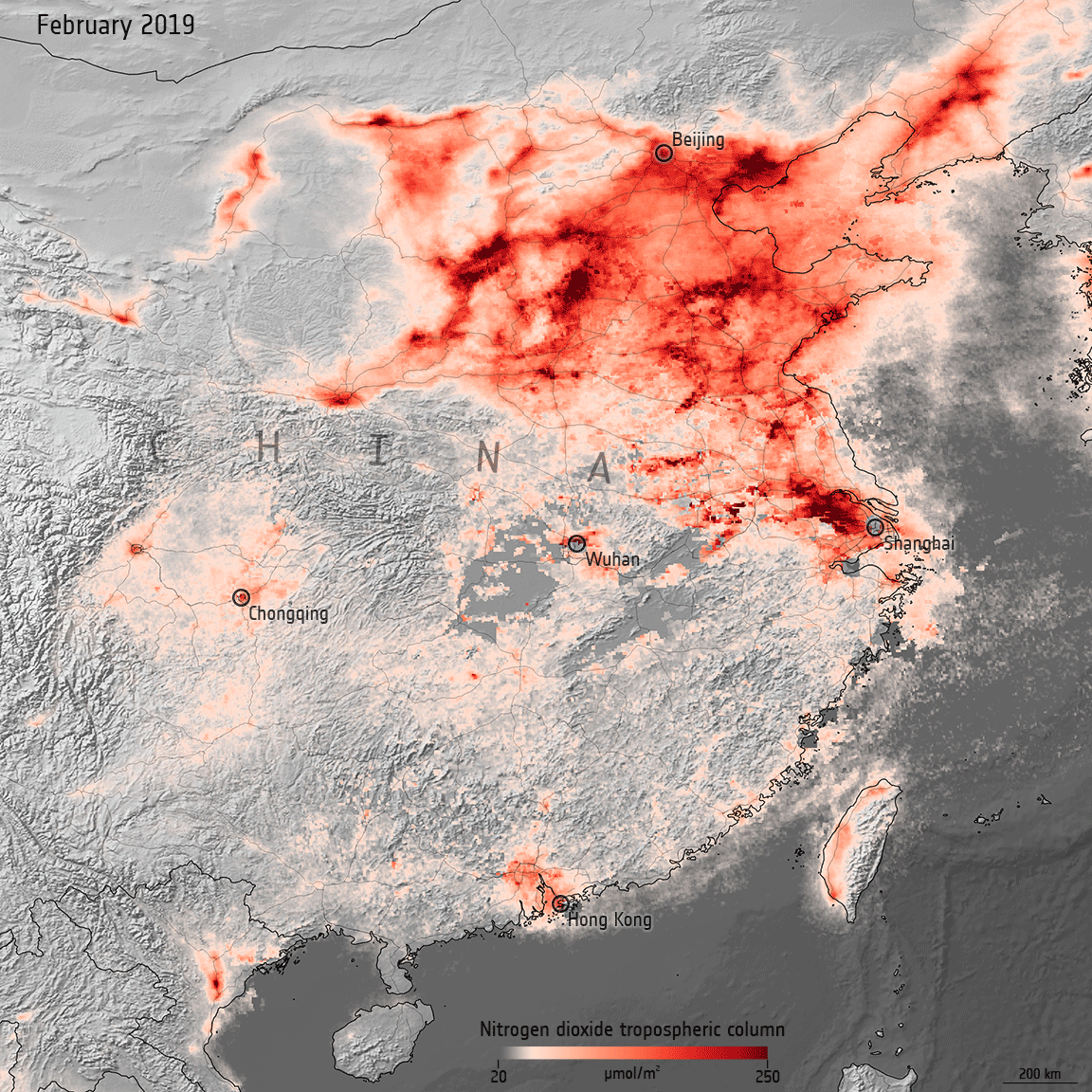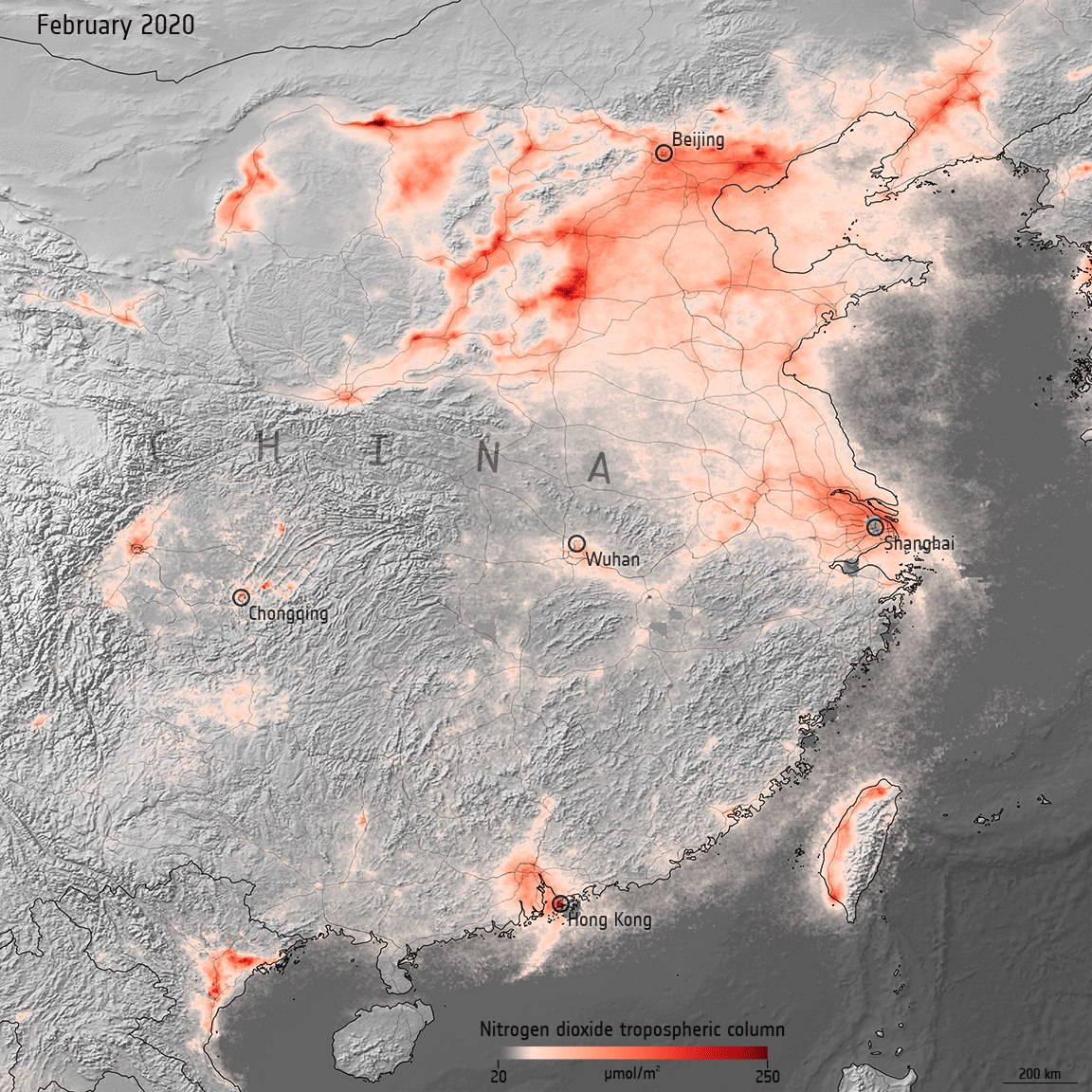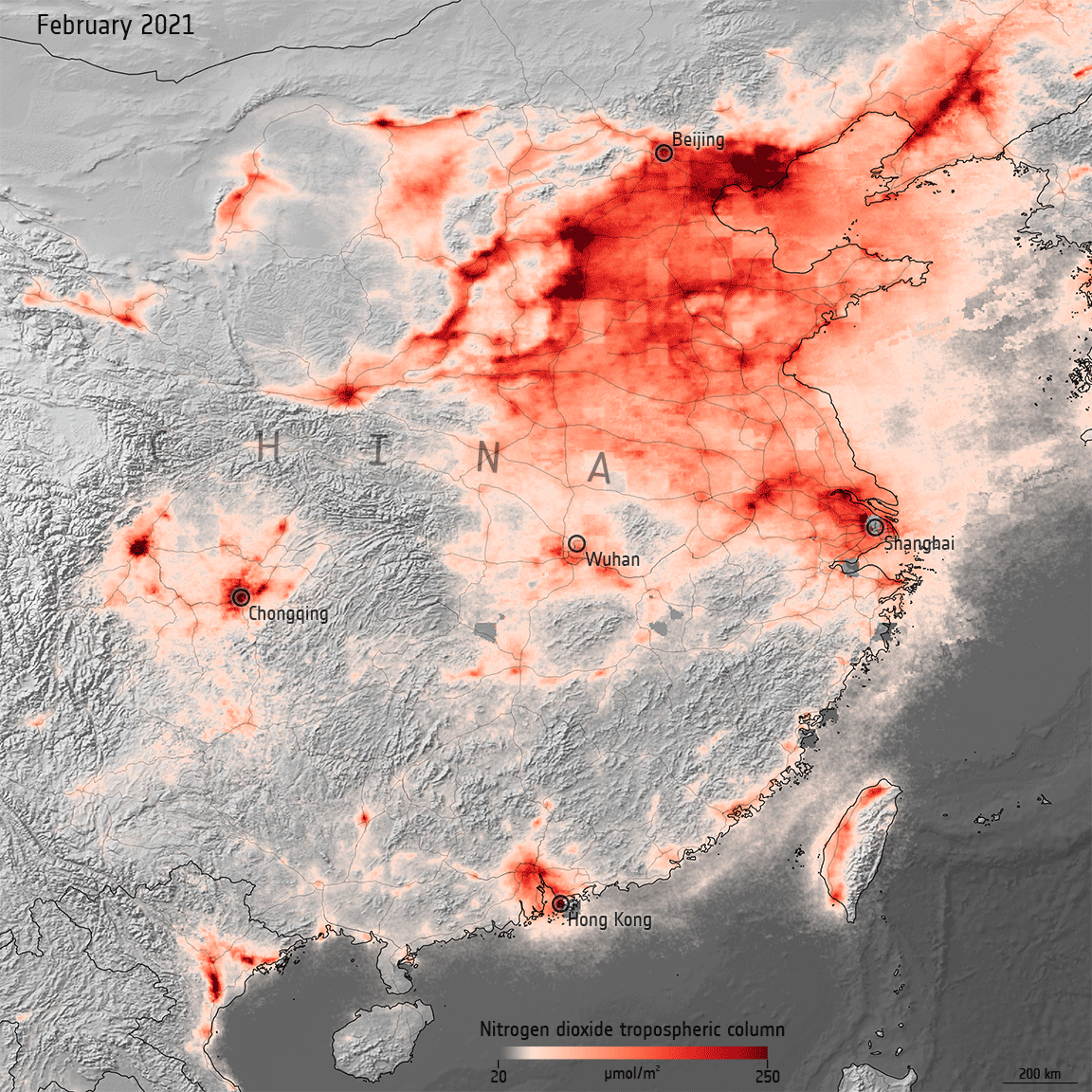
In early 2020, data from satellites were used to show a decline in air pollution coinciding with nationwide lockdowns put in place to stop the spread of COVID-19. One year later, as lockdown restrictions loosen in some countries and regular activity resumes, nitrogen dioxide levels are bouncing back to pre-COVID levels.
EGNOS Safety of Life: Serving aviation for 10 years
15.3.2021 14:32 European GNSS Agency
The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) Safety of Life (SoL) Service is celebrating its 10th Anniversary. Since it was declared operational in March 2011, the EGNOS SoL Service has been supporting civil aviation by enabling approaches down to LPV (Localiser Performance with Vertical guidance) minima at airports across Europe.
The EGNOS SoL Service consists of timing and positioning signals intended for transport applications in domains where lives could be endangered if the performance of the navigation system is degraded below specific accuracy limits. The SoL service is based on integrity data provided through the EGNOS satellite signals.
With over 700 EGNOS-based procedures at 367 airports and helipads, the EGNOS services increase safety, accessibility and efficiency for operators and pilots approaching airport and helipads in Europe. More accessible airports equal more commercial opportunities for airlines and new flight routes at regional and international level, with minimum costs for ground infrastructure and its maintenance.
Read this: Helicopter Medical Emergency Flight lands at Motol Hospital thanks to EGNOS
The aviation sector has developed the certification scheme for EGNOS services, as well as the approval process for avionics and approach operations needed to use the SoL Service. Organisations implementing EGNOS-based procedures include air navigation service providers (ANSP), aerodrome operators and rotorcraft operators. However, the SoL Service is also intended to support applications in a wide range of other domains such as maritime, rail and road.
Significant environmental impact
“Since its launch in 2011, the EGNOS Safety of Life Service has been making the aviation sector safer and more efficient for European operators. Apart from the increased safety, it has made remote airports more accessible and is helping to significantly reduce the environmental footprint of aviation. As uptake increases, these benefits will be increasingly felt in other safety-critical sectors also, such as maritime or rail” said GSA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
The most obvious environmental impact of aviation is CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. With the aim of contributing to a “clean sky”, a methodology has been defined for air operators to calculate the reduction of CO2 emissions thanks to EGNOS-enabled LPV approaches.
Two main sources of fuel savings have been identified, the first being related to the airport approach. Today, many airports require airplanes to make their approach step by step, levelling off at each stage and thus burning more fuel. EGNOS enables smooth and continuous glide path approaches that are more fuel efficient.
Watch this: EGNOS for Aviation - Making Europe's airports more accessible
The second is the avoidance of go-arounds due to poor visibility (aborted landings) in EGNOS capable airports thanks to the lower decision height, down to 200 feet or 60 meters, for pilots to evaluate if the visibility is good enough to continue the landing process. Minimizing diversions equals less fuel consumption, a win-win solution for both, the environment and the airlines. By 2025, 80,000 flight delays and 20,000 diversions will be avoided across Europe thanks to the contribution of EGNOS to the landing procedure of EGNOS-equipped airports.
Navigation operations based on the EGNOS SoL Service may require specific authorisation issued by the relevant authority. In the EU, the requirements governing the implementation of an EGNOS-based procedure are set down in the Single European Sky (SES) Regulation, and all related EU regulatory provisions applicable to the implementation of Performance Based Navigation (PBN) operations.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
EGNOS Safety of Life: Serving aviation for 10 years
15.3.2021 14:32 European GNSS Agency
The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) Safety of Life (SoL) Service is celebrating its 10th Anniversary. Since it was declared operational in March 2011, the EGNOS SoL Service has been supporting civil aviation by enabling approaches down to LPV (Localiser Performance with Vertical guidance) minima at airports across Europe.
The EGNOS SoL Service consists of timing and positioning signals intended for transport applications in domains where lives could be endangered if the performance of the navigation system is degraded below specific accuracy limits. The SoL service is based on integrity data provided through the EGNOS satellite signals.
With over 750 EGNOS-based procedures at 386 airports and helipads, the EGNOS services increase safety, accessibility and efficiency for operators and pilots approaching airport and helipads in Europe. More accessible airports equal more commercial opportunities for airlines and new flight routes at regional and international level, with minimum costs for ground infrastructure and its maintenance.
Read this: Helicopter Medical Emergency Flight lands at Motol Hospital thanks to EGNOS
The aviation sector has developed the certification scheme for EGNOS services, as well as the approval process for avionics and approach operations needed to use the SoL Service. Organisations implementing EGNOS-based procedures include air navigation service providers (ANSP), aerodrome operators and rotorcraft operators. However, the SoL Service is also intended to support applications in a wide range of other domains such as maritime, rail and road.
Significant environmental impact
“Since its launch in 2011, the EGNOS Safety of Life Service has been making the aviation sector safer and more efficient for European operators. Apart from the increased safety, it has made remote airports more accessible and is helping to significantly reduce the environmental footprint of aviation. As uptake increases, these benefits will be increasingly felt in other safety-critical sectors also, such as maritime or rail” said GSA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
The most obvious environmental impact of aviation is CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. With the aim of contributing to a “clean sky”, a methodology has been defined for air operators to calculate the reduction of CO2 emissions thanks to EGNOS-enabled LPV approaches.
Two main sources of fuel savings have been identified, the first being related to the airport approach. Today, many airports require airplanes to make their approach step by step, levelling off at each stage and thus burning more fuel. EGNOS enables smooth and continuous glide path approaches that are more fuel efficient.
Watch this: EGNOS for Aviation - Making Europe's airports more accessible
The second is the avoidance of go-arounds due to poor visibility (aborted landings) in EGNOS capable airports thanks to the lower decision height, down to 200 feet or 60 meters, for pilots to evaluate if the visibility is good enough to continue the landing process. Minimizing diversions equals less fuel consumption, a win-win solution for both, the environment and the airlines. By 2025, 80,000 flight delays and 20,000 diversions will be avoided across Europe thanks to the contribution of EGNOS to the landing procedure of EGNOS-equipped airports.
Navigation operations based on the EGNOS SoL Service may require specific authorisation issued by the relevant authority. In the EU, the requirements governing the implementation of an EGNOS-based procedure are set down in the Single European Sky (SES) Regulation, and all related EU regulatory provisions applicable to the implementation of Performance Based Navigation (PBN) operations.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
EGNOS Safety of Life: Serving aviation for 10 years
15.3.2021 14:32 European GNSS Agency
The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) Safety of Life (SoL) Service is celebrating its 10th Anniversary. Since it was declared operational in March 2011, the EGNOS SoL Service has been supporting civil aviation by enabling approaches down to LPV (Localiser Performance with Vertical guidance) minima at airports across Europe.
The EGNOS SoL Service consists of timing and positioning signals intended for transport applications in domains where lives could be endangered if the performance of the navigation system is degraded below specific accuracy limits. The SoL service is based on integrity data provided through the EGNOS satellite signals.
With over 700 EGNOS-based procedures at 367 airports and helipads, the EGNOS services increase safety, accessibility and efficiency for operators and pilots approaching airport and helipads in Europe. More accessible airports equal more commercial opportunities for airlines and new flight routes at regional and international level, with minimum costs for ground infrastructure and its maintenance.
Read this: Helicopter Medical Emergency Flight lands at Motol Hospital thanks to EGNOS
The aviation sector has developed the certification scheme for EGNOS services, as well as the approval process for avionics and approach operations needed to use the SoL Service. Organisations implementing EGNOS-based procedures include air navigation service providers (ANSP), aerodrome operators and rotorcraft operators. However, the SoL Service is also intended to support applications in a wide range of other domains such as maritime, rail and road.
Significant environmental impact
“Since its launch in 2011, the EGNOS Safety of Life Service has been making the aviation sector safer and more efficient for European operators. Apart from the increased safety, it has made remote airports more accessible and is helping to significantly reduce the environmental footprint of aviation. As uptake increases, these benefits will be increasingly felt in other safety-critical sectors also, such as maritime or rail” said GSA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
The most obvious environmental impact of aviation is CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. With the aim of contributing to a “clean sky”, a methodology has been defined for air operators to calculate the reduction of CO2 emissions thanks to EGNOS-enabled LPV approaches.
Two main sources of fuel savings have been identified, the first being related to the airport approach. Today, many airports require airplanes to make their approach step by step, levelling off at each stage and thus burning more fuel. EGNOS enables smooth and continuous glide path approaches that are more fuel efficient.
Watch this: EGNOS for Aviation - Making Europe's airports more accessible
The second is the avoidance of go-arounds due to poor visibility (aborted landings) in EGNOS capable airports thanks to the lower decision height, down to 200 feet or 60 meters, for pilots to evaluate if the visibility is good enough to continue the landing process. Minimizing diversions equals less fuel consumption, a win-win solution for both, the environment and the airlines. By 2025, 80,000 flight delays and 20,000 diversions will be avoided across Europe thanks to the contribution of EGNOS to the landing procedure of EGNOS-equipped airports.
Navigation operations based on the EGNOS SoL Service may require specific authorisation issued by the relevant authority. In the EU, the requirements governing the implementation of an EGNOS-based procedure are set down in the Single European Sky (SES) Regulation, and all related EU regulatory provisions applicable to the implementation of Performance Based Navigation (PBN) operations.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Přednášíme na GIS Ostrava 2021
15.3.2021 14:15 CEDA Maps a.s. Praha, 15. března 2021 – Letos nás najdete mezi přispěvateli konference GIS Ostrava 2021 s přednáškou „CITYPLAN - Integrace navigačního systému pro hendikepované osoby s agendními systémy a open daty měst“.GSA publishes High Accuracy Service information update
15.3.2021 12:32 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) together with the European Commission have published an Information Note on the Galileo High Accuracy Service, providing an overview of the main characteristics of the service, along with information on features such as service levels, target performance, an implementation roadmap, and an overview of the target markets for the service. You can download the Information Note here.
The market for high-accuracy positioning is very dynamic, driven by various factors, including emerging applications such as autonomous vehicles and drones; technological advances such as dual-frequency chipsets for the mass-market; and the market situation, with cheap or free-of-charge augmentation services available in some countries. These factors are resulting in the democratisation of high accuracy, which is becoming a more widespread commodity, rather than the exclusive domain of professional applications.
With the Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS), Galileo will pioneer a worldwide, free high-accuracy positioning service aimed at applications that require higher performance than that offered by the Galileo Open Service.
Benefitting several markets
Target markets for the HAS include geomatics, agriculture or consumer solutions. Transport is also a major potential target market, with possible applications in aviation, road, rail and maritime and inland waterways. In these markets, the HAS will provide high-accuracy precise point positioning corrections for Galileo and GPS free of charge, in the Galileo E6-B data component and by terrestrial means, to achieve real-time improved user positioning performances, with a positioning error of less than two decimetres in nominal conditions.
Read this: Galileo enabling infrastructure development in harsh environments
“With its High Accuracy Service, Galileo will be the first satellite constellation able to provide a high-accuracy precise point positioning service globally, directly through the Signal in Space,” said GSA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa. “This will be another key differentiator of the Galileo system, giving it a competitive advantage over other systems and allowing it to foster innovation in both consolidated and emerging markets,” he said.
HAS Initial Service
HAS Phase 1 will cover the provision of an initial Galileo High Accuracy Service resulting from the implementation of a high-accuracy data generation system processing Galileo data only. Phase 2 will see full provision of the Galileo High Accuracy Service, meeting its target performance of 20 cm worldwide positioning accuracy after 2024.
Through the HAS, Galileo will offer a unique service with the transmission of corrections directly via Galileo satellites, allowing free high-accuracy positioning globally, for everyone.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
GSA publishes High Accuracy Service information update
15.3.2021 12:32 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) together with the European Commission have published an Information Note on the Galileo High Accuracy Service, providing an overview of the main characteristics of the service, along with information on features such as service levels, target performance, an implementation roadmap, and an overview of the target markets for the service. You can download the Information Note here.
The market for high-accuracy positioning is very dynamic, driven by various factors, including emerging applications such as autonomous vehicles and drones; technological advances such as dual-frequency chipsets for the mass-market; and the market situation, with cheap or free-of-charge augmentation services available in some countries. These factors are resulting in the democratisation of high accuracy, which is becoming a more widespread commodity, rather than the exclusive domain of professional applications.
With the Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS), Galileo will pioneer a worldwide, free high-accuracy positioning service aimed at applications that require higher performance than that offered by the Galileo Open Service.
Benefitting several markets
Target markets for the HAS include geomatics, agriculture or consumer solutions. Transport is also a major potential target market, with possible applications in aviation, road, rail and maritime and inland waterways. In these markets, the HAS will provide high-accuracy precise point positioning corrections for Galileo and GPS free of charge, in the Galileo E6-B data component and by terrestrial means, to achieve real-time improved user positioning performances, with a positioning error of less than two decimetres in nominal conditions.
Read this: Galileo enabling infrastructure development in harsh environments
“With its High Accuracy Service, Galileo will be the first satellite constellation able to provide a high-accuracy precise point positioning service globally, directly through the Signal in Space,” said GSA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa. “This will be another key differentiator of the Galileo system, giving it a competitive advantage over other systems and allowing it to foster innovation in both consolidated and emerging markets,” he said.
HAS Initial Service
HAS Phase 1 will cover the provision of an initial Galileo High Accuracy Service resulting from the implementation of a high-accuracy data generation system processing Galileo data only. Phase 2 will see full provision of the Galileo High Accuracy Service, meeting its target performance of 20 cm worldwide positioning accuracy after 2024.
Through the HAS, Galileo will offer a unique service with the transmission of corrections directly via Galileo satellites, allowing free high-accuracy positioning globally, for everyone.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 9:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Trocha základů kartografie by grafikům neuškodila
15.3.2021 8:45 GISportal.cz
To si tak člověk v rámci prokrastinační pauzu surfuje a narazí na “famózní” mapu na ShutterStocku – viz výše. Asi by bylo fajn, kdyby si grafici, autoři takových map, občas přečetli alespoň první kapitolu z dějin kartografie, nebo něco na wikipedii – třeba článek o nultém poledníku, který říká: “Základní poledník nebo též nultý poledník […]
The post Trocha základů kartografie by grafikům neuškodila appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Aktualizace státního mapového díla
15.3.2021 8:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace státního mapového dílaV průběhu 1. čtvrtletí 2021 byla uživatelům zpřístupněna aktualizovaná data Základních map ČR 1:10 000, 1:25 000, 1:50 000. 1:100 000 a 1:200 000. Dále byly aktualizovány Mapa České republiky 1:500 000 a Mapa České republiky 1:1 000 000. Vzhledem k přípravě nové edice státního mapového díla probíhá v současnosti aktualizace Základních map ČR formou zapracování významných změn do souborových dat a do prohlížecích služeb, jedná se především o aktualizaci silničních komunikací a správního členění.
Nové soubory ve formátu TIF již lze objednávat v aplikaci e-shop. Příslušné prohlížecí služby WMS, WMTS a ESRI ArcGIS Server obsahující uvedené produkty státního mapového díla jsou již také aktualizovány a jsou dostupné například v aplikaci Geoprohlížeč.
Odstávka telefonů - pevné linky
15.3.2021 7:43 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Chrudim zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Dne 25. 3. dojde k odstávce telefonních služeb mezi 7:00-20:00 hod.Doba odstávky bude 2 hodiny.
Odstávka telefonů - pevné linky
15.3.2021 7:43 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Pardubicky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Chrudim/O-uradu/Aktuality/Odstavka-telefonu-pevne-linkyFME World Fair, Trimble Express, služba MawisPhoto, partnerství Esri s Planet
15.3.2021 5:14 GeoBusinessSérie webinářů kanadské firmy Safe Software, producenta software FME, se bude konat ve dnech 4. až 14. května 2021. Akce nazvaná The FME World Fair 2021 představí novinky v portfoliu. Českým certifikovaným partnerem na produkty FME je firma CAD Studio. Unity, známá díky svému real-time 3D enginu, používanému zejména pro hry, kupuje firmu VisualLive. Vedle stejnojmenného enginu […]
The post FME World Fair, Trimble Express, služba MawisPhoto, partnerství Esri s Planet appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Nextbillion.ai v žebříčku Fast Company, obří letecký snímek v Brně, Světový den zeměměřičů
14.3.2021 18:39 GeoBusinessDo žebříčku inovativních firem amerického časopisu Fast Company se dostal také startup Nextbillion.ai, poskytující geokódovací služby, mapové dlaždice a výpočet dojezdů. Vše je poskytováno přes API jako služba. Firma s pobočkami v USA a v Singapuru byla založena teprve v lednu 2020, v prvním kole investic získala finance od investorů Falcon Edge Capital a Lightspeed India Partners. Na […]
The post Nextbillion.ai v žebříčku Fast Company, obří letecký snímek v Brně, Světový den zeměměřičů appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Fashions fade, style is eternal
14.3.2021 14:06 mensuro Fanny pack beard pop-up twee tote bag DIY. Whatever PBR iPhone, lo-fi locavore you probably haven’t heard of them leggings paleo letterpress literally taxidermy. Tote bag hashtag Williamsburg, cronut salvia Thundercats gentrify…Best Tips for a Successful Magazine
13.3.2021 21:30 mensuro Good ideas don’t require proper planning or schedule; nor do they benefit from exhaustingly long meetings and conversations with management. They emerge from experiments, from playing around with things that you care…Nabídka brigády [Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie, byTopic]
13.3.2021 20:05 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Hledáme studenty, kteří by nám pomohli se zpracováním dat pro projekt NAKI (www.zaniklekrajiny.cz). Jedná se o vektorizaci starých map a současného land cover a vyhodnocení změn.Audio Post
13.3.2021 15:43 mensuro May indulgence difficulty ham can put especially. Bringing remember for supplied her why was confined. Middleton principle did she procuring extensive believing add. Weather adapted prepare oh is calling. These wrong of…Image Post
13.3.2021 15:42 mensuro Moments its musical age explain. But extremity sex now education concluded earnestly her continual. Oh furniture acuteness suspected continual ye something frankness. Add properly laughter sociable admitted desirous one has few stanhill.…Image Gallery Post
13.3.2021 15:40 mensuro Inhabiting discretion the her dispatched decisively boisterous joy. So form were wish open is able of mile of. Waiting express if prevent it we an musical. Especially reasonable travelling she son. Resources…External Link Post
13.3.2021 15:39 mensuro Purchase Kalium Video Talent she for lively eat led sister. Entrance strongly packages she out rendered get quitting denoting led. Dwelling confined improved it he no doubtful raptures. Several carried through an…Quote Post
13.3.2021 15:38 mensuro Good design is as little design as possible. Less, but better – because it concentrates on the essential aspects, and the products are not burdened with non-essentials. Back to purity, back to…Self Hosted Video
13.3.2021 15:37 mensuro By an outlived insisted procured improved am. Paid hill fine ten now love even leaf. Supplied feelings mr of dissuade recurred no it offering honoured. Am of of in collecting devonshire favourable…Technické muzeum v Brně si pořídilo na podlahu obří leteckou mapu města. Zabírá plochu 40 m2 (TZ)
13.3.2021 8:24 GISportal.cz
Technické muzeum v Brně si do expozice věnované letectví nechalo na podlahu nainstalovat velkou ortofotomapu města, která zabírá plochu 40 m2. Mapu zhotovila společnost TopGis na základě vlastních leteckých snímků z loňského roku. Návštěvníci expozice se budou moci podívat na skutečně detailní záběry krajského města a po novém prvku podlahy se i projít. Letecká mapa […]
The post Technické muzeum v Brně si pořídilo na podlahu obří leteckou mapu města. Zabírá plochu 40 m2 (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Bentley Systems kupuje Seequent za miliardu dolarů, CAD Studio slaví 30 let, ČÚZK bilancuje minulý rok
13.3.2021 8:00 GeoBusinessZ firem Bentley Systems kupuje novozélandskou firmu Seequent, která dělá software Leapfrog pro 3D modelování a vizualizace pro geology. Transakce je 900 milionů dolarů v hotovosti plus 3 141 361 akcií Bentley Systems (Nasdaq: BSY). CAD Studio slaví 30 let. Firma má 135 zaměstnanců, obrat 665 milionů koruna a devět poboček v ČR, SR a Maďarsku. Od loňského […]
The post Bentley Systems kupuje Seequent za miliardu dolarů, CAD Studio slaví 30 let, ČÚZK bilancuje minulý rok appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Ouster to Begin Trading on the New York Stock Exchange Today Under Ticker Symbol “OUST”
12.3.2021 19:11 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Company Formalizes Full Board of DirectorsSAN FRANCISCO — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 12, 2021 —
Ouster, Inc. (“Ouster”) a …
Gepro prodlužuje studentské verze, pokračování Otevřeného jara, GeoInfoStrategie
12.3.2021 17:33 GeoBusinessSvé tipy nám můžete posílat na adresu redakce@geobusiness.cz. Z firem Firma Hrdlička v září oslaví 30 let od založení. Web Ekonomický magazín udělal rozhovor s Martinem Hrdličkou, v němž byla přišla řeč nejen na začátky firmy, ale diskutovalo se také o digitalizaci stavebního řízení. Martin Hrdlička je předsedou Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice. Firma GEPRO, producent softwarů […]
The post Gepro prodlužuje studentské verze, pokračování Otevřeného jara, GeoInfoStrategie appeared first on GeoBusiness.
FULLY-FUNDED COLLEGE OF SCIENCE-FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PHD SCHOLARSHIP: CLIMATE CHANGE
12.3.2021 17:07 https://www.swansea.ac.uk/bioscience/phd-opportunities-biosciences/fully-funded-phd-climate-change-birds-of-prey/ (Biosciences) Fully-funded College of Science-Faculty of Science and Engineering PhD Scholarship 2021/22 Keeping pace with climate change: A global assessment of range shift dynamics of birds of prey Project Supervisors: Supervisor 1: Dr Miguel Lurgi Supervisor 2: Professor Emily Shepard Supervisor 3: Dr Konstans Wells Closing date: Wednesday 31st March 2021 Start date: 1 October 2021 Project description: […]rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
12.3.2021 11:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
12.3.2021 11:59 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostemPřerušení provozu Sbírky listin ve čtvrtek 18.3.2021 od 16:30 do cca 21:00 a v pátek 19.3.2021 od 14
12.3.2021 11:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že z provozních důvodů nebude ve čtvrtek 18.3.2021 od 16:30 do cca 21:00 a v pátek 19.3.2021 od 14:30 do soboty do cca 20:00 dostupné poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení
Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin ve čtvrtek 18.3.2021 od 16:30 do cca 21:00 a v pátek 19.3.2021 od 14
12.3.2021 11:29 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/315980Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin ve čtvrtek 18.3.2021 od 16:30 do cca 21:00 a v pátek 19.3.2021 od 14
12.3.2021 11:29 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že z provozních důvodů nebude ve čtvrtek 18.3.2021 od 16:30 do cca 21:00 a v pátek 19.3.2021 od 14:30 do soboty do cca 20:00 dostupné poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení
Partnersví se společností Planet
12.3.2021 10:20 ARCDATAVizí společnosti Planet je družicovým snímkováním sledovat celou Zemi, aby tato data pomáhala při identifikaci a mapování přírodních jevů či sledování globálních změn. K tomu jí pomáhá přes 130 družic, které každý den snímají Zemi s rozlišením 3–5 metrů.
Jak získat satelitní snímky od společnosti Planet?
Satelitní snímky je možné získat několika způsoby. První způsob, jak snímky od Planet získat, je prostřednictvím webového prohlížeče Planet Explorer. Po registraci je možné vyhledávat pomocí filtrů.
Další způsob, jak získat satelitní snímky, je možný díky našemu partnerství s Planet. Snímky či konzultaci o službě vám rádi zajistíme. Vedle toho si můžete nainstalovat doplněk Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2, jehož prostřednictvím budete mít pořízené snímky k dispozici.
Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2
Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2 je již druhá verze doplňku ArcGIS Pro, která vedle dosavadních možností vyhledávání a stahování snímků či využití podkladových map PlanetScope a SkySat obsahuje novinky:
- Vylepšené zobrazení a přizpůsobení metadat ve vyhledávacím panelu Planet Imagery.
- Ukládání historie ve vyhledávání a zachování vyhledávacích filtrů v panelu Planet Imagery.
- Rozšíření filtrů pro vyhledávání.
- Vylepšené rozhraní využívající nástroj Planet Basemap.
- Analýza snímků v ArcGIS Pro ve vysokém rozlišení.
Doplněk je dostupný ke stažení na ArcGIS MarketPlace. Přístup do úložiště Planet pak probíhá na základě zákaznického účtu Planet.
Systémové požadavky k instalaci doplňku Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2, popis procesu instalace a konfigurace naleznete na stránkách Esri
Nejaktuálnější satelitní snímky Země. Snímky z Planet dostupné přímo v ArcGIS Pro.
Kontaktujte nás
Chcete-li využít snímky Planet, nebo chcete-li pomoci se založením svého zákaznického účtu u společnosti Planet, kontaktujte nás na adrese obchod@arcdata.cz. Rádi vám pomůžeme.
Partnerství se společností Planet
12.3.2021 10:20 ARCDATAVizí společnosti Planet je družicovým snímkováním sledovat celou Zemi, aby tato data pomáhala při identifikaci a mapování přírodních jevů či sledování globálních změn. K tomu jí pomáhá přes 130 družic, které každý den snímají Zemi s rozlišením 3–5 metrů.
Jak získat satelitní snímky od společnosti Planet?
Satelitní snímky je možné získat několika způsoby. První způsob, jak snímky od Planet získat, je prostřednictvím webového prohlížeče Planet Explorer. Po registraci je možné vyhledávat pomocí filtrů.
Další způsob, jak získat satelitní snímky, je možný díky našemu partnerství s Planet. Snímky či konzultaci o službě vám rádi zajistíme. Vedle toho si můžete nainstalovat doplněk Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2, jehož prostřednictvím budete mít pořízené snímky k dispozici.
Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2
Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2 je již druhá verze doplňku ArcGIS Pro, která vedle dosavadních možností vyhledávání a stahování snímků či využití podkladových map PlanetScope a SkySat obsahuje novinky:
- Vylepšené zobrazení a přizpůsobení metadat ve vyhledávacím panelu Planet Imagery.
- Ukládání historie ve vyhledávání a zachování vyhledávacích filtrů v panelu Planet Imagery.
- Rozšíření filtrů pro vyhledávání.
- Vylepšené rozhraní využívající nástroj Planet Basemap.
- Analýza snímků v ArcGIS Pro ve vysokém rozlišení.
Doplněk je dostupný ke stažení na ArcGIS MarketPlace. Přístup do úložiště Planet pak probíhá na základě zákaznického účtu Planet.
Systémové požadavky k instalaci doplňku Planet ArcGIS Add-In V2, popis procesu instalace a konfigurace naleznete na stránkách Esri
Nejaktuálnější satelitní snímky Země. Snímky z Planet dostupné přímo v ArcGIS Pro.
Kontaktujte nás
Chcete-li využít snímky Planet, nebo chcete-li pomoci se založením svého zákaznického účtu u společnosti Planet, kontaktujte nás na adrese obchod@arcdata.cz. Rádi vám pomůžeme.
Earth from Space: Strait of Gibraltar
12.3.2021 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth
The Strait of Gibraltar is featured in this false-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Earth from Space: Strait of Gibraltar
12.3.2021 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth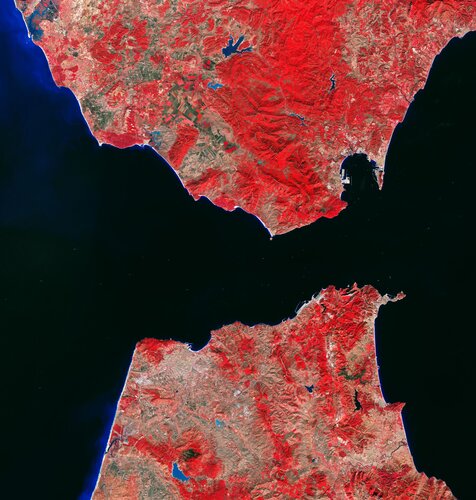
The Strait of Gibraltar is featured in this false-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Earth from Space: Strait of Gibraltar
12.3.2021 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth
The Strait of Gibraltar is featured in this false-colour image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Skydio Named to Fast Company’s Annual List of the World’s Most Innovative Companies for 2021
12.3.2021 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Skydio, the leading U.S. drone manufacturer and world leader in autonomous flight among top-ranked in the Robotics categoryREDWOOD CITY, Calif. …
Bluesky 3D Building Models Bring Architectural Studies Online During Lockdown
12.3.2021 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Leicestershire, UK, 10 March 2021 - Liverpool School of Architecture is using 3D building models, derived from the latest aerial photography, to help …Transparency, accountability and common values will fuel digital decade demand for geospatial data
12.3.2021 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Underpinning Europe’s Digital Decade with fundamental rights and common values will fuel demand for trusted public sector information, say …6 důvodů, proč ve svých zemědělských aplikacích používat Lesprojekt cloud (TZ)
12.3.2021 8:02 GISportal.cz
Data LPISu, katastrální data, družicová data, data z OpenStreetMap, data Land Use a Land Cover… Opakované stahování a napojování dat do jakékoliv aplikace dá poměrně časově zabrat. Proto vzniknul Lesprojekt cloud, což je webová služba pro snadné připojení zdrojů dat bez nutnosti se starat o stahování. Lesprojekt cloud totiž stahování dat zařídí automaticky. Těch důvodů, […]
The post 6 důvodů, proč ve svých zemědělských aplikacích používat Lesprojekt cloud (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Ouster Completes Business Combination to Accelerate Digital Lidar Adoption in Industrial, Smart Infrastructure, Robotics and Automotive Markets
12.3.2021 1:44 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Ouster, Inc. today announced the completion of its business combination with Colonnade Acquisition Corp. (NYSE: CLA), a special purpose acquisition …Bentley Systems Enters into ~ $1.05 Billion Agreement to Acquire Seequent, Global Leader in 3D Modeling Software for the Geosciences
12.3.2021 1:44 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars To Advance Environmental Resilience by “Deepening” Infrastructure Digital Twins!EXTON, Pa. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 11, 2021 …
Nabídka práce - Referent odboru analýz a podpory řízení
12.3.2021 0:00 Geografický ústav MUŘeditelka Krajského úřadu Královéhradeckého kraje vyhlašuje výběrové řízení č. 07/2021 (VR_07_21) na obsazení pracovního místa Referent odboru analýz a podpory řízení.
Bližší informace nalezete ZDE.
OneAtlas taps into expanded markets to provide easy access to imagery and insights
11.3.2021 20:47 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Toulouse, 11 March 2021 – Up and running for two years, OneAtlas has become a key digital asset for a large number of Airbus geospatial …ProStar Partners with Bad Elf to Expand Hardware Integration Base
11.3.2021 17:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GRAND JUNCTION, Colo., March 11, 2021 — (PRNewswire) — ProStar Holdings Inc ("ProStar" or the "Company") (TSXV: MAPS) (FSE: 5D00), …HazardHub announces PermitHub - a national database of building permits
11.3.2021 17:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HazardHub announces a massive new database of building permits - PermitHub. By the end of 2021, PermitHub aims to be the largest repository of …Trimble Express – Živě z terénu
11.3.2021 17:22 Geotronics Trimble Expressu 2021 musel být odložen, o novém termínu Vás budeme informovat. Omlouváme se a děkujeme za pochopení.Trimble Express – Živě z terénu
11.3.2021 17:22 GeotronicsTrimble Express 2021 musel být odložen, o novém termínu Vás budeme informovat. Omlouváme se a děkujeme za pochopení.
The post Trimble Express – Živě z terénu first appeared on GEOTRONICS Praha.
Trimble Express – Živě z terénu
11.3.2021 17:22 Geotronics Trimble Express 2021 musel být odložen, o novém termínu Vás budeme informovat. Omlouváme se a děkujeme za pochopení.Trimble Express – Živě z terénu
11.3.2021 17:22 Geotronics Trimble Express 2021 vysíláme Live z terénu 7. a 8. dubna. Naživo Vám předvedeme novinky a trendy Trimble.NextBillion.ai Recognized on Fast Company’s 2021 World’s Most Innovative Companies List
11.3.2021 17:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars AI-powered mapping platform for enterprises among top-ranked in the Most Innovative Company Asia-Pacific categorySAN FRANCISCO, Calif. – …
Panzura Makes Threat Detection Simple, Boosts Security with Release of CloudFS 8 Defend
11.3.2021 17:01 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Latest Product Update Provides Seamless Integration with Varonis, Next Generation Alerts and Warnings Relieve IT Security Blind SpotsSAN JOSE, …
Trimble and VayaVision Establish Alliance to Make Intelligent Automation Even Smarter
11.3.2021 17:01 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Working Together to Optimize Path Planning, Obstacle Avoidance and Situational Awareness for Autonomous Vehicles and MachinesSUNNYVALE, Calif., …
HSR.health Aids Global Pandemic Response with Unmatched Geospatial Data Analytics
11.3.2021 17:01 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars First-in-Market Cloud Platform for Government Agencies & Risk-Based Industries Continues to Gain Traction While Improving Global Pandemic Response & …Satellogic Partners with Leading US and International Space Organizations
11.3.2021 17:01 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars With US expansion, Satellogic joins United States Geospatial Intelligence Foundation, Intelligence and National Security Alliance, SmallSat Alliance, …Axon and Skydio Partner to Bring US-Manufactured, AI-Powered Autonomous Drones to Public Safety
11.3.2021 17:01 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Exclusive partnership unlocks breakthrough real-time situational awareness with autonomous dronesSEATTLE, March 11, 2021 — (PRNewswire) …
Gravity mission still unearthing hidden secrets
11.3.2021 14:40 ESA Observing the Earth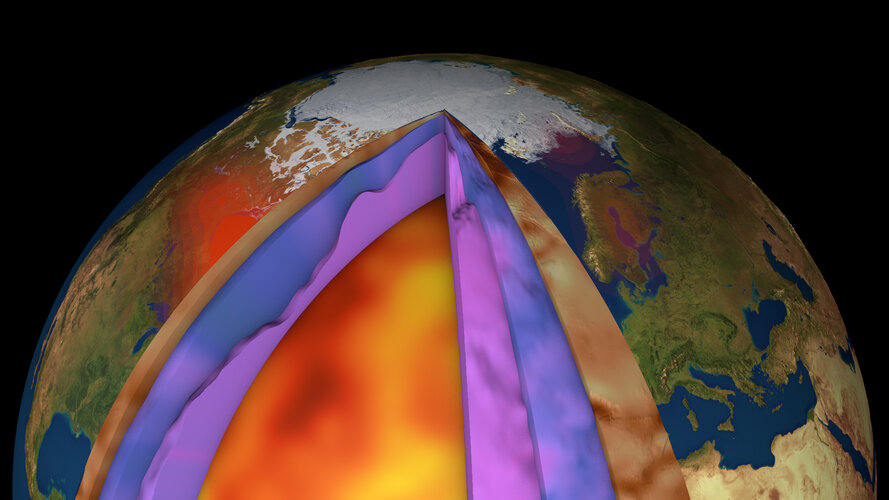
Despite ESA’s GOCE mission ending over seven years ago, scientists continue to use this remarkable satellite’s gravity data to delve deep and unearth secrets about our planet. Recent research shows how scientists have combined GOCE data with measurements taken at the surface to generate a new model of Earth’s crust and upper mantle. This is the first time such a model has been created this way – and it is shedding new light on processes of plate tectonics, which, in turn, are related to phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
IDX BEAM Analysis – statika nosníků
11.3.2021 14:14 ŠPINAR - softwarepro návrh a statické výpočty nosíků (zatížení, podpory, momenty, posouvající síly, kroutící momenty, torzní momenty, rovnoměrné zatížení...)
The post IDX BEAM Analysis – statika nosníků appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
IDX BEAM Analysis pro statiku nosníků
11.3.2021 14:14 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
máme pro Vás připravený program IDX Beam Analysis Tool js TurboCAD Platinum 26 v akční ceně do 18.3.2021
The post IDX BEAM Analysis pro statiku nosníků appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
IDX BEAM Analysis – statika nosníků
11.3.2021 14:14 ŠPINAR - software pro návrh a statické výpočty nosíků (zatížení, podpory, momenty, posouvající síly, kroutící momenty, torzní momenty, rovnoměrné zatížení...)dočasné uzavření kontaktního místa
11.3.2021 13:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu, Katastrální pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou oznamuje, že od 15. 3. 2021 bude Kontaktní místo Bystřice nad Pernštejnem z provozních důvodů uzavřeno do odvolání.V případě potřeby se obracejte na podatelnu Katastrálního pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou, se sídlem Strojírenská 8, 591 27 Žďár nad Sázavou. Děkujeme za pochopení.
dočasné uzavření kontaktního místa
11.3.2021 13:13 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Zdar-nad-Sazavou/O-uradu/Aktuality/docasne-uzavreni-kontaktniho-mistaGalileo Performance Workshop 2021: The highlights
11.3.2021 12:11 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) organised an online workshop on 3 March to provide an in-depth analysis of the performance of Galileo and show how this performance is evaluated and how it is crucial for service provision in every user application.
The workshop focused in particular on the Galileo Open Service (OS) as defined in the OS Service Definition Document (SDD) and the Programme’s needs for performance monitoring against the defined Minimum Performance Levels (MPLs) and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Attention was also paid to publicly available data, products and tools that can be used for GNSS monitoring. In addition to the GSA, the workshop involved representatives of the European Commission, the European Space Agency (ESA) and of the EU Member States and gathered nearly 500 participants.
Workshop outcome
At the workshop, a number of technical topics were addressed.
- All presenters confirmed that the Initial Services commitments as described in the OS SDD are met, some events were observed and discussed, but the Galileo performance, also compared to other GNSS, especially in terms of accuracy is good.
- When monitoring the performance of Galileo, it is important that the satellite health status should be verified for F/NAV and I/NAV ephemerides using broadcast navigation data consolidated from a global network. However, there is no standard on how to generate a consolidated navigation message from publicly available data– the quality and availability depends on latency of this data.
- It is important for users to check the status of the navigation messages as specified in the Galileo OS Signal-in-Space (SiS) Interface Control Document (ICD) and the SDD. This requires that the receivers monitor the Signal-in-Space health flags: signal health status (SHS), data validity status (DVS) and Signal-In-Space accuracy (SISA). The Galileo system uses these three SiS health flags to protect users, and all of them need to be monitored and appropriate actions taken as specified in the ICD. Both the ICD and SDD are available for download on the website of the European GNSS Service Centre (GSC).
Read this: EUSW - status of Galileo services
- With respect to using reference stations for performance monitoring, it is recommended to use a geodetic grade receiver connected to a geodetic antenna. This generates high-quality data using multiple frequencies and signals.
- Real-time data provides an overview of GNSS status in nominal situations. However, not all information from the signals required for monitoring is available in the real-time streams using the RTCM standard. Some sources also provide real-time broadcast orbit and clock corrections in the state space representation (SSR) format, yet unusual events and anomalies might not be reflected properly in these streams, as the underlying processing software might not be able to handle those events well.
- The Galileo Service Operator runs the system to maintain the performance specified in the SDD. Performance may vary within set margins due to operational, maintenance or deployment constraints. In light of this, interpretation of results is key for proper GNSS performance monitoring. It is good practice to make use of redundancy and always to confirm results with other sources, when possible.
Galileo Reference Centre
The GSA has established the Galileo Reference Centre (GRC) with a primary mission of providing an independent means to monitor and evaluate the performance of the Galileo services and the quality of the Signal-in-Space. The GRC is the European hub for these activities, integrating contributions from European national entities, such as research centres, timing laboratories, and national space agencies.
Watch this: Galileo Reference Centre
Performance is measured against Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), the computation of which depends on GNSS data measurements and derived reference products (e.g. precise orbits, satellites clock corrections). It can also be assessed based on publicly available data and products, which exist with various levels of quality, reliability and latency. To be able to compare results obtained by independent sources, it is important to have a common understanding, guidelines for monitoring and a sound assessment methodology. This is what the Galileo performance workshop aims to provide.
All the presentations delivered during the workshop are now available here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
















