zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Open position at Lund University
5.11.2019 11:30 There is an open position at Lund University, Sweden, to employ a researcher who is expert in Spatiotemporal analysis and machine learning. https://lu.varbi.com/en/what:job/jobID:297623/type:job/where:4/apply:1Pozvánka na stánok Geotronics Slovakia
5.11.2019 11:23 Geotronics.skPríspevok Pozvánka na stánok Geotronics Slovakia zobrazený najskôr Geotronics Slovakia.
STOP-STAV na části k.ú. Horní Branná
5.11.2019 11:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Semily STOP-STAV k .ú. Horní Branná Dne 4. 11. 2019 byl na části kat. území Horní Branná vyhlášen STOP- stav pro všechny zápisy do katastru (vklady a záznamy) a rezervace nových parcelních čísel do doby zplatnění obnoveného katastrálního operátu mapováním. Geodetickou veřejnost tímto upozorňujeme na nemožnost rezervace nových parcelních čísel a žádáme je, aby danému STOP-stavu přizpůsobili plánované, nebo rozpracované zakázky v tomto k. ú.STOP-STAV na části k.ú. Horní Branná
5.11.2019 11:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Semily/O-uradu/Aktuality/STOP-STAV-na-casti-k-u-Horni-BrannaFinal EGNSS calls open under Horizon 2020
5.11.2019 11:05 European GNSS Agency
The new Horizon EGNSS market uptake 2019-2020 Call, with a total budget of EUR 21 million, opened on 5 November. Dealing with the development of new innovative applications fostering digitisation, smart mobility, societal resilience and environmental protection and with a brand new topic tailored to public authorities, these is the last Horizon 2020 Call before the launch of its successor framework programme – Horizon Europe. The deadline for submissions is 5 March 2020.
The specific challenge of the ‘GNSS applications fostering green, safe and smart mobility’ topic (LC-SPACE-EGNSS-1-2019-2020) is to develop innovative EGNSS-based applications that lead to low-emission, safer, more secure, lower cost and higher performance mobility. The topic also targets transport solutions that respond to the increased mobility needs of people and goods while improving the continuity of transport services in aviation, rail, road and maritime.
The ‘EGNSS applications fostering digitisation’ topic (DT-SPACE-EGNSS-2-2019-2020) aims at fostering the adoption of EGNOS and Galileo in mass markets and ensuring that users reap the benefits of these programmes. To achieve this, the topic targets applications that make the best use of innovative EGNSS features such as better multipath resistance and authentication, in addition to applications that contribute to the competitiveness of the EGNSS industry in mobile applications, with special focus on the innovative role of SMEs.
Read this: GNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
The third topic in the new call targets ‘EGNSS applications fostering societal resilience and protecting the environment’ (SU-SPACE-EGNSS-3-2019-2020). It aims to develop innovative EGNSS applications in agriculture, mapping and surveying, timing and synchronisation and not only, which will support societal resilience, safeguard the wellbeing of EU citizens, improve emergency and disaster management as a response to climate related, natural and man-made disasters and ensure green growth.
Pre-commercial procurement
Finally, there is a brand new pilot topic ‘EGNSS applications for public authorities' (SPACE-EGNSS-5-2020) with the objective to launch demand-driven actions by public authorities and customise EGNSS applications to their needs. Proposals should build on the procurement needs of the public authorities, should support EGNSS market uptake across Europe and demonstrate the sustainability of solutions beyond the lifespan of the proposed project.
And this: Galileo Innovators – take up the challenge!
Possible innovation procurement applications include EGNSS for mobility as a service, cooperative ITS, public transport and smart cities, implementation of Performance Based Navigation procedures, integration of EGNSS into U-Space for drones, and others. The European GNSS Agency (GSA) organised a series of webinars in September to explore the potential for pre-commercial procurement in four market segments: aviation, maritime, rail, and timing and synchronisation.
Horizon 2020 Space Info Days and Brokerage Event
In an effort to inform a wide range of stakeholders about the upcoming funding opportunities, the GSA together with the European Commission and the Horizon 2020 Space NCP Network (COSMOS2020plus) jointly hosted the Horizon 2020 Space Info Days and Brokerage event at the GSA’s headquarters in Prague, in September. The event’s first day aimed at informing about the last H2020 Space Calls and other space business while the second day was devoted to public consultation on the new Framework Programme for Research and Innovation “Horizon Europe”.
Over the two day event, more than 150 participants from 28 countries were updated on the status of Galileo and Copernicus and on the synergies arising from these two flagship programmes. In addition, the participants had the opportunity to network and meet potential partners
To view presentations from the Horizon 2020 Info Day, click here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Final EGNSS calls open under Horizon 2020
5.11.2019 11:05 European GNSS Agency
Four new innovation actions, with a total budget of EUR 21 million, opened under the Horizon 2020 call ‘EGNSS market uptake 2019-2020’ on November 5. Dealing with EGNSS applications for pre-commercial procurement and fostering digitisation, smart mobility, societal resilience and environmental protection, these are the last Horizon 2020 calls before the launch of its successor framework programme – Horizon Europe. The deadline for submissions is 5 March 2020.
Among the four new actions, the ‘EGNSS applications fostering digitisation’ topic (DT-SPACE-EGNSS-2-2019-2020) aims at fostering the adoption of EGNSS (EGNOS and Galileo) in mass markets and ensuring that users reap the benefits of these programmes. To achieve this, the topic targets applications that make the best use of innovative EGNSS features such as better multipath resistance and authentication, in addition to applications that contribute to the competitiveness of the EGNSS industry in mobile applications, with special focus on the innovative role of SMEs.
The specific challenge of the ‘GNSS applications fostering green, safe and smart mobility’ topic (LC-SPACE-EGNSS-1-2019-2020) is to develop innovative EGNSS-based applications that lead to low-emission, safer, more secure, lower cost and higher performance mobility. The topic also targets transport solutions that respond to the increased mobility needs of people and goods while improving the continuity of transport services.
Read this: GNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
Pre-commercial procurement
The third topic in the new call targets ‘EGNSS applications for public authorities' (SPACE-EGNSS-5-2020). The objective is to launch demand-driven actions by public authorities aimed at customising EGNSS applications to their needs. Proposals should build on the procurement needs of the participating organisations, should support EGNSS market uptake across Europe and demonstrate the sustainability of solutions beyond the lifespan of the proposed project.
Possible innovation procurement applications include EGNSS for mobility as a service, cooperative ITS, public transport and smart cities, implementation of Performance Based Navigation procedures, integration of EGNSS into U-Space for drones, and others. The European GNSS Agency (GSA) organised a series of webinars in September to explore the potential for pre-commercial procurement in four market segments: aviation, maritime, rail, and timing and synchronisation.
And this: Galileo Innovators – take up the challenge!
Innovative applications
Finally, the ‘EGNSS applications fostering societal resilience and protecting the environment’ topic (SU-SPACE-EGNSS-3-2019-2020) aims to develop innovative EGNSS applications to support societal resilience, safeguard the wellbeing of EU citizens, improve emergency and disaster management as a response to climate related, natural and man-made disasters and ensure green growth.
In an effort to inform a wide range of stakeholders about the upcoming funding opportunities, the GSA and the Horizon 2020 Space NCP Network (COSMOS2020plus) jointly hosted the Horizon 2020 Space Information Day and Brokerage Event at the GSA’s headquarters in Prague, in September. The event presented funding opportunities in Horizon 2020 Space and provided first-hand information on the final Horizon 2020 Space Calls, with a special focus on the EGNSS/GALILEO Call.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Final EGNSS calls open under Horizon 2020
5.11.2019 11:05 European GNSS Agency
The new Horizon EGNSS market uptake 2019-2020 Call, with a total budget of EUR 21 million, opened on 5 November. Dealing with the development of new innovative applications fostering digitisation, smart mobility, societal resilience and environmental protection and with a brand new topic tailored to public authorities, these is the last Horizon 2020 Call before the launch of its successor framework programme – Horizon Europe. The deadline for submissions is 5 March 2020.
The specific challenge of the ‘GNSS applications fostering green, safe and smart mobility’ topic (LC-SPACE-EGNSS-1-2019-2020) is to develop innovative EGNSS-based applications that lead to low-emission, safer, more secure, lower cost and higher performance mobility. The topic also targets transport solutions that respond to the increased mobility needs of people and goods while improving the continuity of transport services in aviation, rail, road and maritime.
The ‘EGNSS applications fostering digitisation’ topic (DT-SPACE-EGNSS-2-2019-2020) aims at fostering the adoption of EGNOS and Galileo in mass markets and ensuring that users reap the benefits of these programmes. To achieve this, the topic targets applications that make the best use of innovative EGNSS features such as better multipath resistance and authentication, in addition to applications that contribute to the competitiveness of the EGNSS industry in mobile applications, with special focus on the innovative role of SMEs.
The third topic in the new call targets ‘EGNSS applications fostering societal resilience and protecting the environment’ (SU-SPACE-EGNSS-3-2019-2020). It aims to develop innovative EGNSS applications in agriculture, mapping and surveying, timing and synchronisation and not only, which will support societal resilience, safeguard the wellbeing of EU citizens, improve emergency and disaster management as a response to climate related, natural and man-made disasters and ensure green growth.
Read this: GNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
Pre-commercial procurement
Finally, there is a brand new pilot topic ‘EGNSS applications for public authorities' (SPACE-EGNSS-5-2020) with the objective to launch demand-driven actions by public authorities and customise EGNSS applications to their needs. Proposals should build on the procurement needs of the public authorities, should support EGNSS market uptake across Europe and demonstrate the sustainability of solutions beyond the lifespan of the proposed project.
Possible innovation procurement applications include EGNSS for mobility as a service, cooperative ITS, public transport and smart cities, implementation of Performance Based Navigation procedures, integration of EGNSS into U-Space for drones, and others. The European GNSS Agency (GSA) organised a series of webinars in September to explore the potential for pre-commercial procurement in four market segments: aviation, maritime, rail, and timing and synchronisation.
And this: Galileo Innovators – take up the challenge!
Horizon 2020 Space Info Days and Brokerage Event
In an effort to inform a wide range of stakeholders about the upcoming funding opportunities, the GSA together with the European Commission and the Horizon 2020 Space NCP Network (COSMOS2020plus) jointly hosted the Horizon 2020 Space Info Days and Brokerage event at the GSA’s headquarters in Prague, in September. The event’s first day aimed at informing about the last H2020 Space Calls and other space business while the second day was devoted to public consultation on the new Framework Programme for Research and Innovation “Horizon Europe”.
Over the two day event, more than 150 participants from 28 countries were updated on the status of Galileo and Copernicus and on the synergies arising from these two flagship programmes. In addition, the participants had the opportunity to network and meet potential partners.
To view presentations from the Horizon 2020 Info Day, click here
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Final EGNSS calls open under Horizon 2020
5.11.2019 11:05 European GNSS Agency
Four new innovation actions, with a total budget of EUR 21 million, opened under the Horizon 2020 call ‘EGNSS market uptake 2019-2020’ on November 5. Dealing with EGNSS applications for pre-commercial procurement and fostering digitisation, smart mobility, societal resilience and environmental protection, these are the last Horizon 2020 calls before the launch of its successor framework programme – Horizon Europe. The deadline for submissions is 5 March 2020.
Among the four new actions, the ‘EGNSS applications fostering digitisation’ topic (DT-SPACE-EGNSS-2-2019-2020) aims at fostering the adoption of EGNSS (EGNOS and Galileo) in mass markets and ensuring that users reap the benefits of these programmes. To achieve this, the topic targets applications that make the best use of innovative EGNSS features such as better multipath resistance and authentication, in addition to applications that contribute to the competitiveness of the EGNSS industry in mobile applications, with special focus on the innovative role of SMEs.
The specific challenge of the ‘GNSS applications fostering green, safe and smart mobility’ topic (LC-SPACE-EGNSS-1-2019-2020) is to develop innovative EGNSS-based applications that lead to low-emission, safer, more secure, lower cost and higher performance mobility. The topic also targets transport solutions that respond to the increased mobility needs of people and goods while improving the continuity of transport services.
Read this: GNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
Pre-commercial procurement
The third topic in the new call targets ‘EGNSS applications for public authorities' (SPACE-EGNSS-5-2020). The objective is to launch demand-driven actions by public authorities aimed at customising EGNSS applications to their needs. Proposals should build on the procurement needs of the participating organisations, should support EGNSS market uptake across Europe and demonstrate the sustainability of solutions beyond the lifespan of the proposed project.
Possible innovation procurement applications include EGNSS for mobility as a service, cooperative ITS, public transport and smart cities, implementation of Performance Based Navigation procedures, integration of EGNSS into U-Space for drones, and others. The European GNSS Agency (GSA) organised a series of webinars in September to explore the potential for pre-commercial procurement in four market segments: aviation, maritime, rail, and timing and synchronisation.
And this: Galileo Innovators – take up the challenge!
Innovative applications
Finally, the ‘EGNSS applications fostering societal resilience and protecting the environment’ topic (SU-SPACE-EGNSS-3-2019-2020) aims to develop innovative EGNSS applications to support societal resilience, safeguard the wellbeing of EU citizens, improve emergency and disaster management as a response to climate related, natural and man-made disasters and ensure green growth.
In an effort to inform a wide range of stakeholders about the upcoming funding opportunities, the GSA and the Horizon 2020 Space NCP Network (COSMOS2020plus) jointly hosted the Horizon 2020 Space Information Day and Brokerage Event at the GSA’s headquarters in Prague, in September. The event presented funding opportunities in Horizon 2020 Space and provided first-hand information on the final Horizon 2020 Space Calls, with a special focus on the EGNSS/GALILEO Call.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Final EGNSS calls open under Horizon 2020
5.11.2019 11:05 European GNSS Agency
The new Horizon EGNSS market uptake 2019-2020 Call, with a total budget of EUR 21 million, opened on 5 November. Dealing with the development of new innovative applications fostering digitisation, smart mobility, societal resilience and environmental protection and with a brand new topic tailored to public authorities, this is the last Horizon 2020 Call before the launch of its successor framework programme – Horizon Europe. The deadline for submissions is 5 March 2020.
The specific challenge of the ‘GNSS applications fostering green, safe and smart mobility’ topic (LC-SPACE-EGNSS-1-2019-2020) is to develop innovative EGNSS-based applications that lead to low-emission, safer, more secure, lower cost and higher performance mobility. The topic also targets transport solutions that respond to the increased mobility needs of people and goods while improving the continuity of transport services in aviation, rail, road and maritime.
The ‘EGNSS applications fostering digitisation’ topic (DT-SPACE-EGNSS-2-2019-2020) aims at fostering the adoption of EGNOS and Galileo in mass markets and ensuring that users reap the benefits of these programmes. To achieve this, the topic targets applications that make the best use of innovative EGNSS features such as better multipath resistance and authentication, in addition to applications that contribute to the competitiveness of the EGNSS industry in mobile applications, with special focus on the innovative role of SMEs.
Read this: GNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
The third topic in the new call targets ‘EGNSS applications fostering societal resilience and protecting the environment’ (SU-SPACE-EGNSS-3-2019-2020). It aims to develop innovative EGNSS applications in agriculture, mapping and surveying, timing and synchronisation and not only, which will support societal resilience, safeguard the wellbeing of EU citizens, improve emergency and disaster management as a response to climate related, natural and man-made disasters and ensure green growth.
Pre-commercial procurement
Finally, there is a brand new pilot topic ‘EGNSS applications for public authorities' (SPACE-EGNSS-5-2020) with the objective to launch demand-driven actions by public authorities and customise EGNSS applications to their needs. Proposals should build on the procurement needs of the public authorities, should support EGNSS market uptake across Europe and demonstrate the sustainability of solutions beyond the lifespan of the proposed project.
And this: Galileo Innovators – take up the challenge!
Possible innovation procurement applications include EGNSS for mobility as a service, cooperative ITS, public transport and smart cities, implementation of Performance Based Navigation procedures, integration of EGNSS into U-Space for drones, and others. The European GNSS Agency (GSA) organised a series of webinars in September to explore the potential for pre-commercial procurement in four market segments: aviation, maritime, rail, and timing and synchronisation.
Horizon 2020 Space Info Days and Brokerage Event
In an effort to inform a wide range of stakeholders about the upcoming funding opportunities, the GSA together with the European Commission and the Horizon 2020 Space NCP Network (COSMOS2020plus) jointly hosted the Horizon 2020 Space Info Days and Brokerage event at the GSA’s headquarters in Prague, in September. The event’s first day aimed at informing about the last H2020 Space Calls and other space business while the second day was devoted to public consultation on the new Framework Programme for Research and Innovation “Horizon Europe”.
Over the two day event, more than 150 participants from 28 countries were updated on the status of Galileo and Copernicus and on the synergies arising from these two flagship programmes. In addition, the participants had the opportunity to network and meet potential partners
To view presentations from the Horizon 2020 Info Day, click here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov
5.11.2019 11:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-pravni-vztahy-k-nemoviodborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov
5.11.2019 11:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti PelhřimovOdborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signed
5.11.2019 10:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-oddeleni-pravni-vztahy-k-nemovitoOdborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signed
5.11.2019 10:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signed
Odborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signed
5.11.2019 10:18 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signedOdborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signed
5.11.2019 10:11 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu, Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent-oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Pelhřimov_signedMapová aplikace ÚAP - aktualizace
5.11.2019 10:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Územně analytické podklady byla aktualizována k 5.11.2019.Výběrové řízení na pozici Geograf/ka v Sekretariátu Názvoslovné komise ČÚZK v Praze
5.11.2019 9:51 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČUGeograf/ka v Sekretariátu Názvoslovné komise ČÚZK v Praze
Popis pozice:
- Posuzování a ověřování kvality výsledků zeměměřických činností při standardizaci
a aktualizaci jmen nesídelních geografických objektů z území České republiky spravovaných
v celostátní databázi geografických dat Geonames a prováděni dalších obdobných
systémových zeměměřických prací při standardizaci a aktualizaci geografických jmen
ve veřejném zájmu.
- Podílení se na vizualizaci názvoslovných dat z území mimo ČR, standardizovaných
Názvoslovnou komisí z databáze.
- řešení problémů uživatelů, příprava návodů.
IT znalosti a dovednosti:
- základy práce v Microstation, ArcGIS nebo jiném SW na tvorbu GIS
- znalost prostředí Windows a běžných kancelářských programů.
Další požadavky:
- minimálně VOŠ nebo vysokoškolské vzdělání v bakalářském studijním programu, výhodou
zaměření na kartografii, geomatiku, geografii, databáze, příp. onomastiku
- vynikající znalost českého jazyka, němčina nebo angličtina vítána
- komunikativnost slovem i písmem
Praxe:
Není nutná.
Nabízíme:
- pracovní poměr na plný či zkrácený úvazek na dobu určitou (zástup za prac. na rodičovské
dovolené),
- práci ve státní správě s garancí dodržování zákonů a etického kodexu v pracovně-právních
vztazích,
zajímavou a tvůrčí práci s možností dalšího profesního rozvoje,
- odměňování v souladu dle zákona 234/2014 Sb., o platových poměrech státních
zaměstnanců, platová třída 10, platový stupeň dle zápočtu praxe, s možností osobního
ohodnocení v závislosti na úspěších plnění pracovních úkolů,
- systém zaměstnaneckých a sociálních výhod (5 týdnů dovolené, FKSP, pružná pracovní
doba, závodní stravování)
Požadované dokumenty:
- motivační dopis,
- strukturovaný profesní životopis s popisem dosavadní odborné praxe,
- kopie dokladu o nejvyšším dosaženém vzdělání.
Předpokládaný termín nástupu: 1. prosince 2019 nebo dle dohody
Dokumenty zasílejte na: irena.svehlova@cuzk.cz, do 30. 11. 2019
Bližší informace k pracovní náplni a odborným požadavkům poskytne:
pí Irena Švehlová, prom. fil., e-mail:irena.svehlova@cuzk.cz
KÚ-3779-2019-vyhlášení výběrového řízení_signed
5.11.2019 9:21 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/KU-3779-2019-vyhlaseni-vyberoveho-rizeni_signedKÚ-3779-2019-vyhlášení výběrového řízení_signed
5.11.2019 9:21 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo KÚ-3779-2019-vyhlášení výběrového řízení_signedKÚ-3779-2019-vyhlášení výběrového řízení_signed
5.11.2019 9:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
KÚ-3779-2019-vyhlášení výběrového řízení_signed
OGC Pilot Initiative seeks to mature standards-based “Applications to the Data” architecture; funding available for participants
5.11.2019 8:20 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The Earth Observations Applications Pilot will evaluate the maturity of specifications developed to achieve a paradigm shift in Earth Observation - …New global CEO for technology innovator Maptek
5.11.2019 7:32 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Maptek has announced Eduardo Coloma as the new global CEO to lead the business at an exciting time for mining. Coloma is well known in the …ŘSD připravuje výměnný formát záborového elaborátu, podílí se na něm Hrdlička a GMtech
5.11.2019 6:29 ZeměměřičSpolečnost Hrdlička byla před časem oslovena Ředitelstvím silnic a dálnic ČR (ŘSD) na společné tvorbě výměnného formátu záborových elaborátů, uváděného pod zkratkou VFZE. Tento výměnný formát bude závazný a definovaný v datovém předpisu C3 pro tvorbu digitálního záborového elaborátu. Ředitelství silnic a dálnic je v České republice jedním z nejvýznamnějších investorů v investiční výstavbě a zároveň majoritním objednatelem projektů silničních staveb. Své požadavky […]
The post ŘSD připravuje výměnný formát záborového elaborátu, podílí se na něm Hrdlička a GMtech appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Maxar Technologies Reports Third Quarter 2019 Results
4.11.2019 22:51 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — November 4, 2019 —Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR) (“Maxar” or the …
USGIF to Host 2019 GEOINT Community Week Events
4.11.2019 19:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Foundation to hold a variety of opportunities for learning, discussion, and networking
Herndon, Virginia (November 4, 2019)—The United …
GC Pilot Initiative seeks to mature standards-based “Applications to the Data” architecture; funding available for participants
4.11.2019 18:58 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The Earth Observations Applications Pilot will evaluate the maturity of specifications developed to achieve a paradigm shift in Earth Observation - …Nejbližší zkoušky ÚOZI budou v druhé polovině listopadu
4.11.2019 17:23 ZeměměřičNejbližší termín zkoušek odborné způsobilosti k udělení úředního oprávnění pro ověřování výsledků zeměměřických činností se koná 20. listopadu 2019 v Praze v budově ČÚZK. Bližší informace o zkouškách odborné způsobilosti podá personální odbor ČÚZK (Ing. Lucie Chromá), e-mail: lucie.chroma@cuzk.cz; tel.: 28404 1261. Podmínky pro udělení úředního oprávnění pro ověřování výsledků zeměměřických činností (dále jen „úřední oprávnění“) a náležitosti žádosti o udělení úředního oprávnění […]
The post Nejbližší zkoušky ÚOZI budou v druhé polovině listopadu appeared first on Zeměměřič.
rada/odborný rada – inspektor
4.11.2019 17:16 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Pardubicích vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – inspektorrada/odborný rada – inspektor
4.11.2019 17:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Pardubicíchvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – inspektor
rada/odborný rada – inspektor
4.11.2019 17:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Pardubicic/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-–-inspektorVZ: Komplexní pozemkové úpravy Oldřiš u Hlinska
4.11.2019 17:08 ZeměměřičPředmětem plnění veřejné zakázky malého rozsahu na služby je zpracování návrhu komplexních pozemkových úprav (dále jen „KoPÚ“) v katastrálním území Oldřiš u Hlinska, včetně nezbytných geodetických prací v třídě přesnosti určené pro obnovu katastru nemovitostí vyhláškou č. 357/2013 Sb., o katastru nemovitostí (katastrální vyhláška), ve znění pozdějších předpisů (dále jen „katastrální vyhláška“). Návrh KoPÚ bude zpracován tak, aby jej bylo […]
The post VZ: Komplexní pozemkové úpravy Oldřiš u Hlinska appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Booz Allen and Orbital Insight Announce Strategic Alliance to Help US Government Meet National Security Challenges
4.11.2019 16:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Booz Allen to launch Modzy Platform, deploying Orbital Insight’s AI for the intelligence community ROSSLYN, Va., Nov. 04, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) …ESIP Develops Earth Science Data Operational Readiness Levels to Empower Disaster Responders
4.11.2019 16:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars CANBERRA, Australia, Nov. 04, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- GEO Week 2019 -- Earth Science Information Partners (ESIP), the global community …Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin v sobotu 9.11.2019 od 8:00 do cca 12:00
4.11.2019 14:35 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že z provozních důvodů nebude v sobotu 9.11.2019 od 8:00 do cca 12:00 dostupné poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin v sobotu 9.11.2019 od 8:00 do cca 12:00
4.11.2019 14:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že z provozních důvodů nebude v sobotu 9.11.2019 od 8:00 do cca 12:00 dostupné poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin v sobotu 9.11.2019 od 8:00 do cca 12:00
4.11.2019 14:35 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/272091Odborný / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutn
4.11.2019 14:26 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště TrutnOdborný / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutn
4.11.2019 14:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-kOdborný / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutn
4.11.2019 14:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
20191105-statistické údaje za 3.čtvrtletí
4.11.2019 14:19 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zveřejněny statistické údaje za 3. čtvrtletí roku 2019 o vybraných transakcích s nemovitostmi evidovanými v KN.Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
4.11.2019 14:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nRada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
4.11.2019 14:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
4.11.2019 14:18 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov20191104-termín zkoušek ÚOZI
4.11.2019 14:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zkoušky ÚOZI se budou konat dne 20. listopadu 2019.Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrových řízení na služební místa:
4.11.2019 13:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:
Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrových řízení na služební místa:
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – vedení katastrální mapy na Katastrálním pracovišti Karviná
Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrových řízení na služební místa:
4.11.2019 13:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Rada/odborný rada - řízení o údajích SGI na Katastrálním pracovišti Opava Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj,
Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrových řízení na služební místa:
4.11.2019 13:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Odborný referent - obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj,
Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrových řízení na služební místa:
4.11.2019 13:37 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Oznameni-o-vyhlaseni-vyberovych-rizeni-na-sluzebniOznámení o vyhlášení výběrových řízení na služební místa:
4.11.2019 13:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Odborný referent - obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
Odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Morav
4.11.2019 13:04 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odbor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro MoravOdborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Morav
4.11.2019 13:04 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
Odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Morav
4.11.2019 13:04 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-68Odborný referent/vrchní referent – vedení katastrální mapy na Katastrálním pracovišti Karviná
4.11.2019 12:23 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Karviná vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent – vedení katastrální mapy na Katastrálním pracovišti KarvináOdborný referent/vrchní referent – vedení katastrální mapy na Katastrálním pracovišti Karviná
4.11.2019 12:23 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-vedeni-katastraOdborný referent/vrchní referent – vedení katastrální mapy na Katastrálním pracovišti Karviná
4.11.2019 12:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Karvinávypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent – vedení katastrální mapy na Katastrálním pracovišti Karviná
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN
4.11.2019 12:20 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místek vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent - poskytování informací KNOdborný referent - poskytování informací KN
4.11.2019 12:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-poskytovani-informaci-KNOdborný referent - poskytování informací KN
4.11.2019 12:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místekvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN
4.11.2019 12:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místekvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN
4.11.2019 12:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místekvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent - poskytování informací KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
4.11.2019 12:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místekvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
4.11.2019 12:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-nRada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-Místek
4.11.2019 12:16 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Frýdek-Místek vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu na Katastrálním pracovišti Frýdek-MístekGNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
4.11.2019 11:42 European GNSS Agency
Connected and Automated Mobility is poised to transform the movement of people and goods, vehicle ownership and mobility services. Recent technological leaps are rapidly bringing us closer to this new frontier, making transportation safer, more accessible and sustainable. At the ITS World Congress in Singapore, European GNSS Agency (GSA) Executive Director Carlo des Dorides stressed the central role of GNSS in the Connected and Automated Mobility ecosystem.
Positioning is needed everywhere, but it is the area of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAV) that presents the highest challenges in term of performance. Speaking at a congress plenary session on Advancing Connected and Automated Mobility Deployment on 22 October, the GSA Executive Director said that, thanks to new powerful GNSS signals, such as those provided by the Galileo High Accuracy Service, the industry would be able to offer decimetre-level absolute positioning at a low cost, functioning seamlessly in challenging environments such as deep urban canyons and in low visibility weather conditions.
Paradigm change
With regard to mobility, he noted that Mobility as a Service, for example, would bring about a paradigm change in transportation, made possible by the simultaneous availability of multiple technologies, including satellite-enabled location based services. “Moreover, autonomous vehicles will soon be a reality and we are already working to demonstrate the great potential of EGNOS and Galileo in this area, together with other on-board sensors,” he said, adding that Galileo is the only constellation that will provide authentication of the satellite navigation signal.
Read this: Save the Date: Live demo of first Galileo-enabled autonomous vehicle
“In ITS, Horizon 2020 is helping to showcase the full potential of advanced satellite positioning for autonomous vehicles, based on integrated solutions that need to start from low-level signal processing to high-level data fusion in order to get a continuous and reliable positioning,” he said. He also noted that the GSA´s Fundamental Elements programme was funding the development of an E-GNSS engine to provide precise location to critical applications and to a set of diverse in-vehicle applications that improve passenger comfort and make mobility smarter.
Two pillars
At Galileo Mobility Night, a panel discussion at the ITS World Congress organised by GNSS.asia later the same day, des Dorides told participants that GNSS is currently structured around two pillars - the multi-constellation concept and the multi-frequency concept. “Recent developments in technology mean that our devices and handsets can be compatible with three or ever four constellations, which means that our smartphones can choose the best combination of satellites to compute our positioning,” he said.
And this: European GNSS supports smarter mobility
Stressing that Galileo is the only GNSS constellation in which all satellites have multi-frequency capability, he went on to say that multi-frequency means better accuracy, as using two frequencies makes it easier to correct ionospheric errors and mitigate multipath reflections in urban canyons.
Also speaking at Galileo Mobility Night, Dr Johanna Tzanidaki from ERTICO-ITS Europe outlined some of the areas where Galileo’s accuracy is critical. These include automated driving, urban air mobility (drones), logistics, road pricing and congestion charging. “Galileo is also very important in the development of HD maps, and HD maps are the key to automated and autonomous driving, she said.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
GNSS and mobility: innovation in motion at ITS Singapore
4.11.2019 11:42 European GNSS Agency
Connected and Automated Mobility is poised to transform the movement of people and goods, vehicle ownership and mobility services. Recent technological leaps are rapidly bringing us closer to this new frontier, making transportation safer, more accessible and sustainable. At the ITS World Congress in Singapore, European GNSS Agency (GSA) Executive Director Carlo des Dorides stressed the central role of GNSS in the Connected and Automated Mobility ecosystem.
Positioning is needed everywhere, but it is the area of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAV) that presents the highest challenges in term of performance. Speaking at a congress plenary session on Advancing Connected and Automated Mobility Deployment on 22 October, the GSA Executive Director said that, thanks to new powerful GNSS signals, such as those provided by the Galileo High Accuracy Service, the industry would be able to offer decimetre-level absolute positioning at a low cost, functioning seamlessly in challenging environments such as deep urban canyons and in low visibility weather conditions.
Paradigm change
With regard to mobility, he noted that Mobility as a Service, for example, would bring about a paradigm change in transportation, made possible by the simultaneous availability of multiple technologies, including satellite-enabled location based services. “Moreover, autonomous vehicles will soon be a reality and we are already working to demonstrate the great potential of EGNOS and Galileo in this area, together with other on-board sensors,” he said, adding that Galileo is the only constellation that will provide authentication of the satellite navigation signal.
Read this: Save the Date: Live demo of first Galileo-enabled autonomous vehicle
“In ITS, Horizon 2020 is helping to showcase the full potential of advanced satellite positioning for autonomous vehicles, based on integrated solutions that need to start from low-level signal processing to high-level data fusion in order to get a continuous and reliable positioning,” he said. He also noted that the GSA´s Fundamental Elements programme was funding the development of an E-GNSS engine to provide precise location to critical applications and to a set of diverse in-vehicle applications that improve passenger comfort and make mobility smarter.
Two pillars
At Galileo Mobility Night, a panel discussion at the ITS World Congress organised by GNSS.asia later the same day, des Dorides told participants that GNSS is currently structured around two pillars - the multi-constellation concept and the multi-frequency concept. “Recent developments in technology mean that our devices and handsets can be compatible with three or ever four constellations, which means that our smartphones can choose the best combination of satellites to compute our positioning,” he said.
And this: European GNSS supports smarter mobility
Stressing that Galileo is the only GNSS constellation in which all satellites have multi-frequency capability, he went on to say that multi-frequency means better accuracy, as using two frequencies makes it easier to correct ionospheric errors and mitigate multipath reflections in urban canyons.
Also speaking at Galileo Mobility Night, Dr Johanna Tzanidaki from ERTICO-ITS Europe outlined some of the areas where Galileo’s accuracy is critical. These include automated driving, urban air mobility (drones), logistics, road pricing and congestion charging. “Galileo is also very important in the development of HD maps, and HD maps are the key to automated and autonomous driving, she said.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Geograf/ka Praha
4.11.2019 11:01 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Geograf/ka Praha
Geograf/ka Praha
4.11.2019 11:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Geograf/ka Praha
Geograf/ka Praha
4.11.2019 11:01 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Geograf/ka Prahaodborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Morav
4.11.2019 10:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-68odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Morav
4.11.2019 10:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odbor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravodborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Morav
4.11.2019 10:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent – obnova katastrálního operátu 68 v technickém odboru Katastrálního úřadu pro Moravskoslezský kraj
GEOSMART 2020
4.11.2019 10:24 Satlab GeosolutionsThis year’s GEOSMART will be held in HICC HYDERABAD, INDIA, from 3-5 December 2019. Satlab will showcase the full line of GNSS and Optical products and share the Smart Monitoring Solution, which providing monitoring professionals with the flexibility to swiftly analyze and understand complex projects with the highest accuracy and reliability. Click here to join […]
The post GEOSMART 2020 appeared first on Satlab – Global Satellite Positioning Solutions.
GEOSMART 2020
4.11.2019 10:24 Satlab GeosolutionsThis year’s GEOSMART will be held in HICC HYDERABAD, INDIA, from 3-5 December 2019. Satlab will showcase the full line of GNSS and Optical products and share the Smart Monitoring Solution, which providing monitoring professionals with the flexibility to swiftly analyze and understand complex projects with the highest accuracy and reliability. Click here to join […]
The post GEOSMART 2020 appeared first on SatLab – Global Satellite Positioning Solutions.
Revealing interior temperature of Antarctic ice sheet
4.11.2019 10:20 ESA Observing the Earth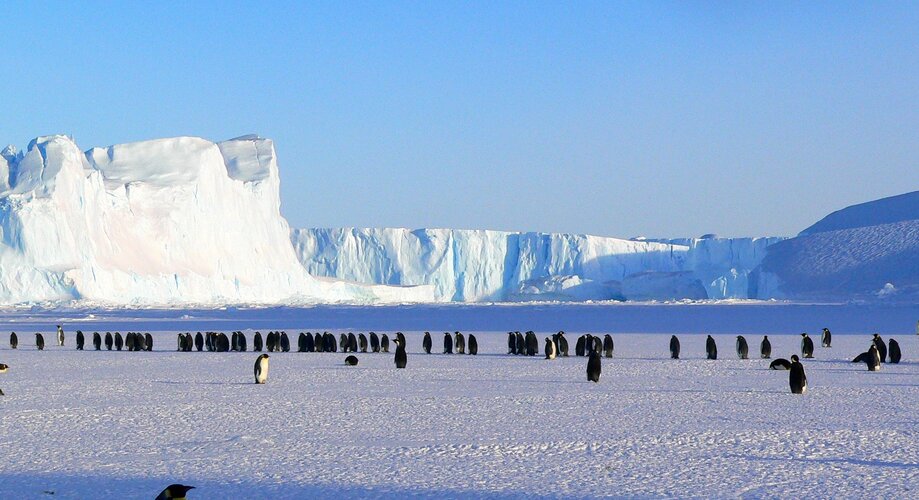
As ESA’s SMOS satellite celebrates 10 years in orbit, yet another result has been added to its list of successes. This remarkable satellite mission has shown that it can be used to measure how the temperature of the Antarctic ice sheet changes with depth – and it’s much warmer deep down.
Mapová aplikace ÚPD - nové dokumentace
4.11.2019 9:00 Jihočeský kraj V mapové aplikaci Územně plánovací dokumentace obcí byla aktualizována územně plánovací dokumentace obcí v ORP Prachatice – Netolice; ORP Český Krumlov – Vyšší Brod; ORP České Budějovice – Zliv, Hluboká nad Vltavou a Srubec.Koncem listopadu se opět setkají zeměměřiči, působící ve Zlínském kraji
3.11.2019 23:18 ZeměměřičSetkání zeměměřičů Zlínského kraje se po roce uskuteční opět ve Zlíně. Páteční odpolední program je plný zajímavých přednášek. Kdy: pátek 29. listopadu 2019 Kde: Centroprojekt Zlín Čas: 13:00 až 20:00 hod. Referáty, které jsou na programu setkání Aktuálně DTM, Ing. Bradáč DTM Zlínský kraj, Mgr. Křeková Legalizace staveb a jiné nešvary z pohledu stavebního úřadu, Ing. Skácel Vystoupení zástupce […]
The post Koncem listopadu se opět setkají zeměměřiči, působící ve Zlínském kraji appeared first on Zeměměřič.
CHC Navigation Introduces New GNSS RTK Tablet
3.11.2019 11:16 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Portable and versatile, the LT700H RTK tablet brings accuracy at your fingertips.Shanghai, China – November 1st, 2019 - CHC Navigation, today …
Brněnský listopadový Missing maps mapathon na konferenci OpenAlt
2.11.2019 15:00 Geografický ústav MUBrněnský listopadový Missing maps mapathon na konferenci OpenAlt
Po roce se opět koná v Brně konference OpenAlt (https://openalt.cz/2019) a opět se na ní uskuteční i mapathon.
Přijďte podpořit práci Lékařů bez hranic tím, že pomůžete do otevřené mapy světa OpenStreetMap zmapovat místa ohrožená humanitárními krizemi.
Když už budete na mapathonu, proč se nepodívat i na další přednášky konference? Účast na OpenAlt je bezplatná. Na konferenci je množství přednášek z oboru otevřených dat, OpenStreetMap a svobodného sotftware. Program je k prozkoumání zde: https://openalt.cz/2019/program.php
Kdy a kde to bude?
sobota 2. listopadu od 15:00 do 18:00
Fakulta informačních technologií
Vysoké učení technické v Brně
Božetěchova 1/2, 61266 Brno
Přesné místo mapathonu: https://www.openstreetmap.org/way/44684868.
Registrace: https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/brnensky-listopadovy-missing-maps-mapathon-na-konferenci-openalt-tickets-77722075821.
Co se na setkání bude dít?
Na mapathonu budeme společně podle satelitních snímků vytvářet v OpenStreetMap mapu jednoho z míst, na kterém působí Lékaři bez hranic.
Pokud nemáte zkušenosti, nevadí. Všechno se na místě naučíte a po krátkém školení už budete moci sami mapovat. Pokud máte zkušenosti, tím lépe. Budeme pracovat ve třech skupinách:
- Skupina začátečníků bude při školení získávat první zkušenosti s editací OpenStreetMap
- Zkušenější mapéři se budou mít možnost naučit program JOSM – volně dostupný pokročilý editor pro OpenStreetMap
- Ti, kteří už umí alespoň základy JOSM, se mohou vyškolit na validátory, kteří kontrolují výsledky práce dalších mapérů. Vyškolení co největšího počtu validátorů je aktuálně ten nejdůležitější úkol mapathonů po celém světě. Jsou nedostatkoví a vážení, tak se přidejte.
Samozřejmě, zváni jsou i zkušení uživatelé, kteří už žádné školení nepotřebují a chtějí jen nerušeně mapovat či validovat.
Pokud již patříte mezi zkušené a chtěli byste se přidat do organizačního týmu, tak se na tom na mapathonu rádi domluvíme.
Mám si něco připravit?
Protože se mapathon koná v rámci konference, tak velice doporučujeme zaregistrovat se na mapathon (ale také na samotnou konferenci (https://openalt.cz/2019/form_registrace.php). Organizátoři chtějí mít přibližný přehled o počtu návštěvníků konference. Děkujeme.
Pokud ještě nemáte účet na OpenStreetMap, vytvořte si ho zde: https://www.openstreetmap.org/user/new.
Pokud chcete být ve skupině pokročilých mapérů učících se JOSM, je vhodné mít na počítači předem nainstalován program JOSM. Je volně ke stažení na adrese https://josm.openstreetmap.de. Program vyžaduje nainstalovaný programovací jazyk Java.
Pokud chcete být ve skupině validátorů, je výhodou již alespoň základní znalost editoru JOSM. Ideální je proto nejdříve absolvovat mapathon ve skupině JOSM a na následujícím mapathonu přejít k validátorům.
Těší se na Vás organizační tým conference OpenAlt a organizační tým brněnských mapathonů.
Daniel, Radim, Katka, Jakub, Jakub, Michal, Tomáš.
Bližší informace: Radim Štampach (stampach@mail.muni.cz)Eos Releases Underground Infrastructure Mapping Solution for Collector for ArcGIS
1.11.2019 22:16 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Eos Locate™ for Collector for ArcGIS enables utilities to map buried assets with submeter or centimeter accuracy
OCTOBER 29, …
Autodesk Extends Invitation to Join Financial Results Conference Call
1.11.2019 18:40 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Third Quarter Fiscal 2020 Financial Results Conference Call to be Held Tuesday, November 26, 2:00 p.m. Pacific TimeSAN RAFAEL, Calif., Nov. 1, 2019 …
Carlson Offers End-of-Year Savings on Hardware and Software
1.11.2019 18:11 Carlson Software MAYSVILLE, Kentucky, U.S.A. (October 2019) — From now until December 31, 2019, industry professionals have the opportunity to purchase the latest versions of popular Carlson products and bundles through special End-of-Year pricing. The Carlson Pick 4 Suite, which allows customers to pick 4 modules: Survey, Civil, GIS, Hydrology, CADnet, or Point Cloud Basic is available […]Carlson Offers End-of-Year Savings on Hardware and Software
1.11.2019 18:11 Carlson Software MAYSVILLE, Kentucky, U.S.A. (October 2019) — Carlson has released special End-of-Year pricing on hardware and software. From now until December 31, 2019, industry professionals have the opportunity to purchase the latest versions of popular Carlson products and bundles. The Carlson Pick 4 Suite, which allows customers to pick 4 modules: Survey, Civil, GIS, Hydrology, CADnet, […]Pozvánka na konferenci JUNIORSTAV 2020
1.11.2019 13:58 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČU Dovolujeme si vás pozvat na konferenci JUNIORSTAV 2020. Termín registrace konference JUNIORSTAV byl prodloužen do 10. 11. 2019 (ačkoliv web konference zatím tvrdí něco jiného). Přihlášení je možné na http://www.juniorstav.cz/cs/registrace/V rámci pokračující spolupráce s časopisem GaKO bude autorům nejzajímavějších příspěvků sekce 8. Geodézie, kartografie a geoinformatika nabídnuta možnost publikace v tomto časopise.
Inspektor/inspektorka
1.11.2019 13:56 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-CB/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Inspektor-inspektorkaInspektor/inspektorka
1.11.2019 13:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Českých Budějovicíchvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Inspektor/inspektorka
Inspektor/inspektorka
1.11.2019 13:56 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Českých Budějovicích vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Inspektor/inspektorkaObjednávky knih [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
1.11.2019 13:40 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Nejpozdější termín pro objednávky knih je 15.11.2019The Handheld Fast And Professional 3d Mapping System With High Resolution 5k Images
1.11.2019 12:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars November 01, 2019 -- HERON LITE is appreciated in the market to be best solution for fast 3D surveying and mapping of indoor buildings, small …Christian U. Haas appointed as CEO of PTV Group
1.11.2019 11:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Executive Board of the Karlsruhe based software company is complete / Management to accelerate the company’s growthKarlsruhe, October 31, …
BIM historických objektů
1.11.2019 11:21 Konference BIM OpenJak přistupovat na BIM u historických budov a jak se vytváří 3D informační modely historických objektů. Záznam z konference BIM Open, která se konala 17.9.2019 v Ostravě. Prezentuje Bohumil Michalík ze společnosti G4D.
The post BIM historických objektů appeared first on BIM Open.
Aktualizace datového skladu ÚAP
1.11.2019 11:00 Ústecký krajOd 1. listopadu bude probíhat aktualizace datového skladu Geoportálu územně analytických podkladů na novou verzi datového modelu. Žádáme všechny pořizovatele, aby po tuto dobu nenahrávali žádné aktualizace. Modul pro aktualizaci dat bude po dobu migrace mimo provoz. Konec migrace a opětovné uvedení do provozu bude oznámeno stejným způsobem. Výdej dat bude po dobu migrace funkční.
CG/LA Announces New National Infrastructure Performance Council
1.11.2019 10:29 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Spearheaded by founding members Maurice R. “Hank” Greenberg and David Petraeus, new initiative will bring together accomplished business, …GIC Collects Imagery over Kincade Fire in Sonoma County
1.11.2019 10:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars IMAGES AVAILABLE TO EMERGENCY PERSONNEL, GIC MEMBER INSURERS, AND THE MEDIADES PLAINES, Ill., Oct. 31, 2019 — The Kincade Fire has now …
Halloween crack
1.11.2019 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth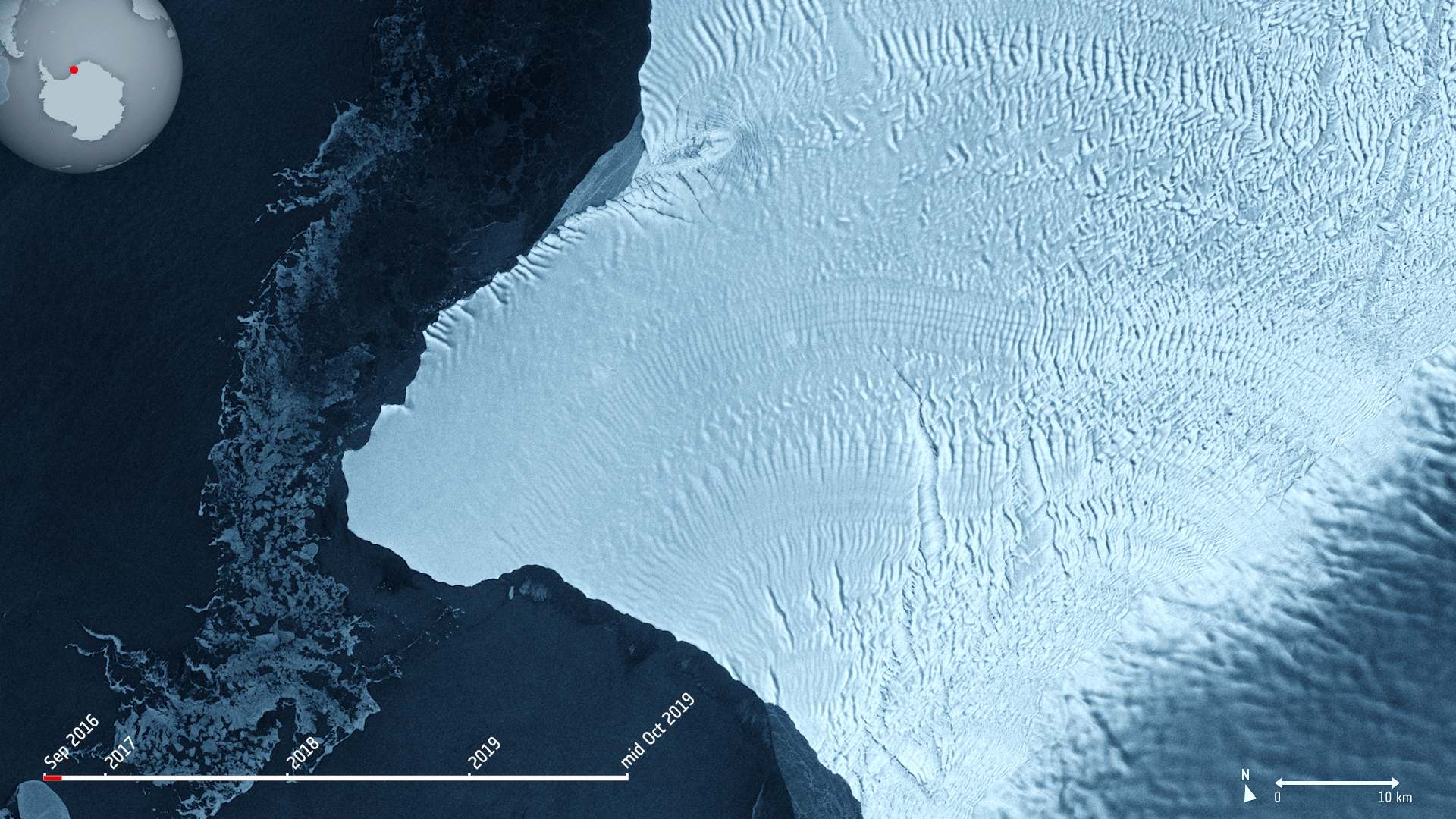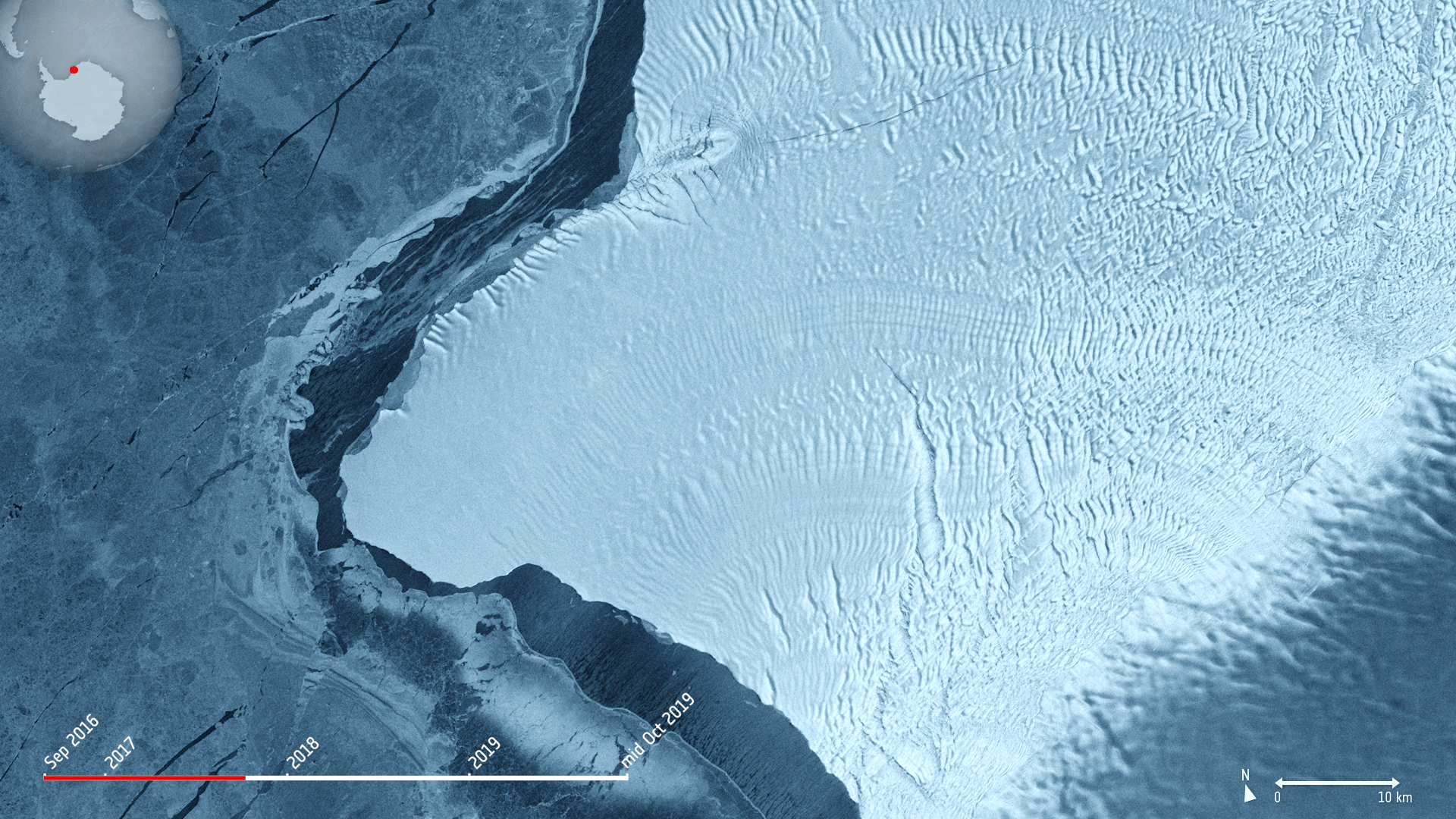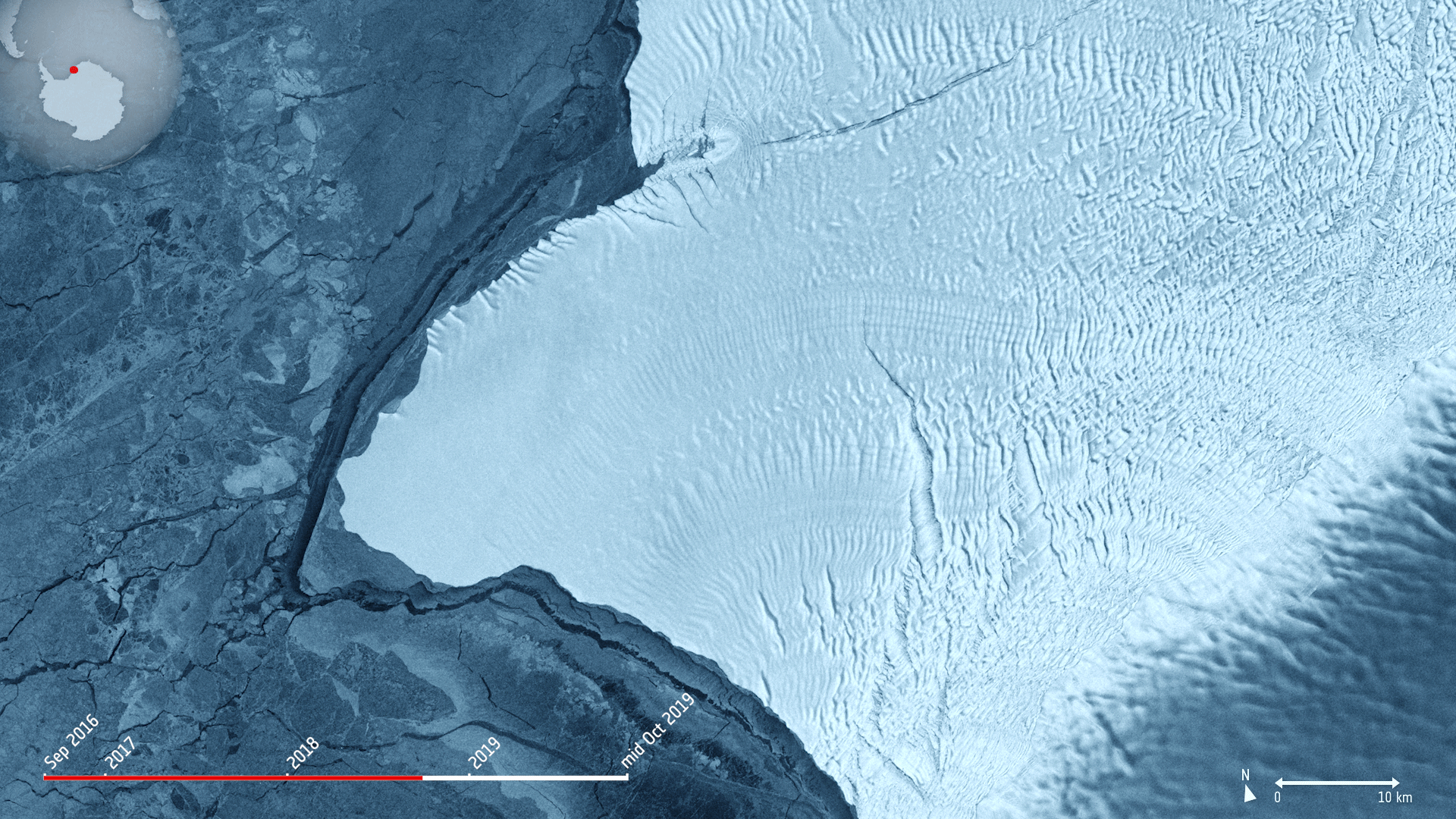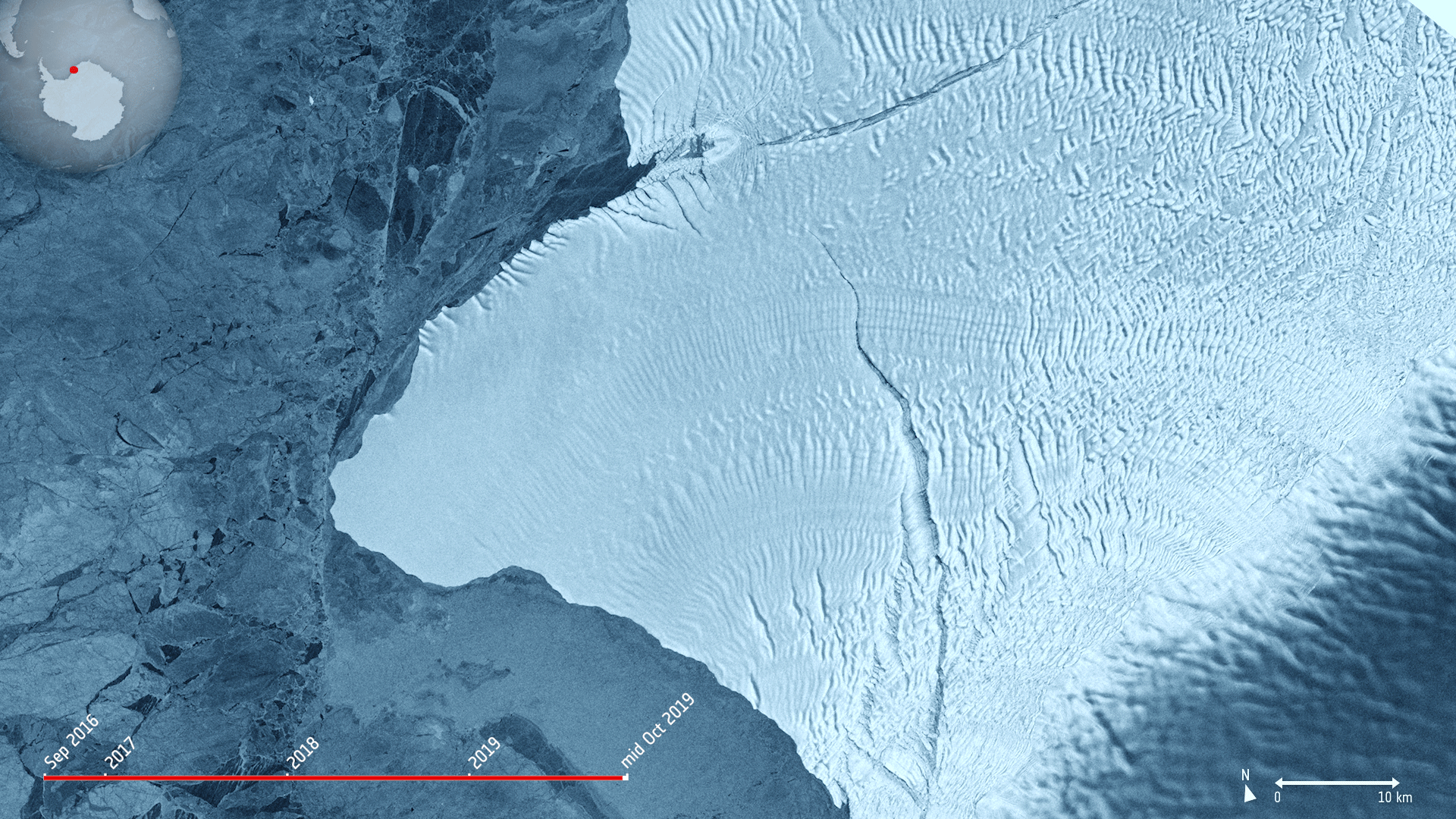 Image:
Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission takes us over cracks in the Brunt ice shelf, which lies in the Weddell Sea sector of Antarctica.
Using radar images from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission, the animation shows the evolution of two ice fractures from September 2016 until mid-October 2019. The large chasm running northwards is called Chasm 1, while the split extending eastwards is referred to as the Halloween Crack.
First spotted on 31 October 2016, the Halloween crack runs from an area known as McDonald Ice Rumples – which is where the underside of the floating ice sheet is grounded on the shallow seabed. This pinning point slows the flow of ice and crumples the ice surface into waves.
Chasm 1 on the other hand has been in place for over 25 years. It was previously stable for many years, but in 2012, it was noticed that the dormant crack started extending northwards.
Now, Chasm 1 and Halloween crack are only separated by a few kilometres. When they meet, an iceberg about the size of Greater London will break off. The two lengthening fractures have been set to intersect for years – it’s only a matter of time for the two to meet.
The Brunt shelf has been monitored by glaciologists for decades and is constantly changing. Early maps from the 1970s indicate that the ice shelf used to be a mass of small icebergs welded together by sea ice.
Calving is a natural process of the life cycle of ice shelves. Although the iceberg is of a considerable size, it will not be the largest of icebergs to calve in Antarctica. In 2017, a chunk of Larsen C broke off spawning one of the largest icebergs on record and changing the outline of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Ice shelf movement is very unpredictable. Routine monitoring from satellites offer unprecedented views of events happening in remote regions, and show how ice shelves are responding to changes in ice dynamics, air and ocean temperatures.
As an advanced radar mission, Copernicus Sentinel-1 can image the surface of Earth through cloud and rain and regardless of whether it is day or night. This makes it an ideal mission for monitoring the polar regions, which are in darkness during the winter months and for monitoring tropical forests, which are typically shrouded by cloud.
This image is also featured on the Earth from Space video programme.
Earth from Space: Halloween crack
1.11.2019 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:02:57
Video:
00:02:57
In this week's edition of the Earth from Space programme, the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission takes us over cracks in the Brunt ice shelf, which lies in the Weddell Sea sector of Antarctica.
See also Halloween crack to download the image.
Pozvánka na seminář pro zpracovatele geografických dat pro CETIN
1.11.2019 9:27 Ve spolupráci s odbory dokumentace CETIN, a. s. si Vás dovolujeme pozvat na seminář, jehož hlavním tématem bude nová revize metodiky dokumentace a její dopady do softwaru ProGEO a MTel lite. Metodika bude účinná od ledna roku 2020.ČSGK bude mít sjezd a ples v Ostravě
1.11.2019 8:55 ZeměměřičČeský svaz geodetů a kartografů zve na svůj 12. sjezd. Setkání členů se bude konat v sobotu 8. února 2020 od 13 hod. v Ostravě v Nové aule VŠB – TU Ostrava. V ten samý den se večer od 19 hod. uskuteční také 12. ples zeměměřičů, na který vás ČSGK srdečně zve. Vstupenku na ples si můžete objednat na webu HGF VŠB-TU […]
The post ČSGK bude mít sjezd a ples v Ostravě appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Budovy v Brně, aneb Kancelář architekta opět boduje!
1.11.2019 8:39 GISportal.cz
Webová aplikace Budovy v Brně prezentuje výsledky průzkumu stavebních objektů na území města Brna z roku 2018. Jedná se o první část celoměstského průzkumu, která zaujímá oblast historického centra a navazující část centra širšího. V rámci průzkumu byly zjišťovány především informace o podlažnosti a funkčním využití budov. Sesbíraná data vstupují do následných prostorových analýz, která […]
The post Budovy v Brně, aneb Kancelář architekta opět boduje! appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Tunisia Automates Census Work with Web, Mobile, and Enterprise GIS (ArcNews Online)
1.11.2019 8:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsTrimble Announces CEO Succession
31.10.2019 22:22 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Rob Painter, Current CFO, to Become New CEOSUNNYVALE, Calif., Oct. 30, 2019 — (PRNewswire) — Trimble (NASDAQ: TRMB) announced …
FARO Reports Third Quarter 2019 Financial Results
31.10.2019 22:22 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars LAKE MARY, Fla., Oct. 30, 2019 — (PRNewswire) — FARO® (NASDAQ: FARO), the world's most trusted source for 3D measurement and imaging …Trimble Reports Third Quarter 2019 Results
31.10.2019 22:22 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars - Earnings per share in line with guidanceSUNNYVALE, Calif., Oct. 30, 2019 — (PRNewswire) — Trimble Inc. (NASDAQ: TRMB) today …
Blockchain Transaction System and Drone-Powered Precision Agriculture Highlight Celexus R&D
31.10.2019 22:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars PHOENIX, Oct. 31, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Celexus, Inc. (OTCQB: CXUS) announced today its new research and development division. In …Catalyst Analytic Technologies Takes Flight
31.10.2019 22:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Catalyst Analytic Technologies has launched as a woman owned and operated consulting and services organization (DBE/SBE) specializing in the …Swift UAV Services Team Assists Bahamian Ministry Support Efforts
31.10.2019 22:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Conducting 98 Day and Night Missions, Providing Real-Time Situational Maps to Key OfficialsSAN CLEMENTE, Calif., Oct. 31, 2019 — (PRNewswire) …
Soar Adds China Siwei to Its Growing List of Satellite Imagery Partners
31.10.2019 22:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN FRANCISCO — (BUSINESS WIRE) — October 31, 2019 —Digital mapping and imagery company Soar has announced a strategic …
Satnav in the landscape harnessed for global error mapping
31.10.2019 15:01 ESA Navigation
There are more than five billion satnav devices on Earth. Along with smartphones and mobile receivers, this figure includes networks of fixed receiver stations, used to improve accuracy. An ESA-led project will harness these networks to provide an ongoing overview of satnav performance from the global to national and regional scale.
Satnav in the landscape harnessed for global error mapping
31.10.2019 15:01 ESA Navigation
There are at the moment more than five billion satnav devices on Earth. Along with smartphones and mobile receivers, this figure includes networks of fixed receiver stations, used to boost service accuracy. A new ESA-led project will harness these networks to provide an ongoing overview of satnav performance from the global to national to regional scale.
5G - a huge potential market for GNSS
31.10.2019 14:55 European GNSS Agency
5G will deliver high-speed, low-latency broadband connectivity that will open the door to a new generation of applications, according to the GNSS Market Report from the European GNSS Agency (GSA), published earlier this month.
The market reports predicts that several mobile 5G commercial launches will take place over the next three years in North America, Asia-Pacific and Europe, with 1.2 billion 5G connections expected in 2025 according to the GSM Association (GSMA). In anticipation of this 5G growth, receiver manufacturers are developing and launching hardware that can meet the increased requirements of the future networks. One such launch is the new GNM181 receiver module from Meinberg, which hit the market at the start of October this year.
Stringent timing requirements
With nanosecond-level timing accuracy, the new Meinberg GNM181 multi-band GNSS receiver module not only meets the most stringent 5G timing requirements, it provides a differential timing mode for highly accurate local timing and built-in security for highest robustness against malicious attacks.
This robustness is particularly relevant for 5G, as the 5G timing and synchronisation function may require more precision and more robustness than 4G, and will face more deployment challenges, such as a large number of sites in difficult locations. Thanks to its multi-constellation capacity (Galileo, GPS, BeiDou, and GLONASS), the receiver is ideal for global deployments and is unaffected by ionospheric errors, with automatic ionospheric correction.
Read this: Demetra delivers dividends for ELPROMA
The variety of inputs and outputs means that the combined GNSS receiver is suitable for a broad range of applications, including time and frequency synchronisation tasks and the measurement of asynchronous time events.
“The strength of Galileo’s signal and its advanced code modulations mean that Galileo is better at mitigating multipath effects. This will be critical for urban 5G networks. The latest offering from Meinberg shows that the industry understands Galileo’s benefits, such as high accuracy timing, and is eager to pass them on to customers,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani.
Robust dual frequency
According to the GNSS Market Report, the availability of accurate, cost effective and robust, dual-frequency GNSS systems, in particular Galileo, will be critical in providing business opportunities within the 5G market. The GNM181 receiver ticks this box also, offering dual frequency support for GPS (L1, L2), Galileo (E1, E5), GLONASS (L1OF, L2OF) and Beidou (B1l, B2l) with a new multi-band antenna.
And this: NaviSoC: leveraging Galileo’s dual-frequency precision for the mass market
The module is fully compatible with Meinberg’s Intelligent Modular Synchronisation (IMS) product family, which means that the GNM181 clock module can be installed in any clock slot on all IMS systems. Users can easily add the GNM181 as a second, redundant clock module to their already deployed IMS systems or field-replace their current IMS clock modules with the new GNM181 multiband receiver board.
The modular approach of the IMS platform allows field replacement and hot-swap capabilities for modules and power supplies. This concept makes the platforms future-proof and expandable by making it possible to add or replace modules when new technologies or interfaces are required.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
31.10.2019 12:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
oznameni_o_vyhlaseni_vyberoveho_rizeni_2019_PV právník
31.10.2019 12:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/oznameni_o_vyhlaseni_vyberoveho_rizeni_2019_PV-prarada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
31.10.2019 12:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Prostějovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu

















