zprávy
zdroje zpráv:20240415- GaKO 4/24
15.4.2024 10:03 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (4/2024) je k dispozici ke stažení.202407129-GaKO 7-8/24
15.4.2024 10:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (7-8/2024) je k dispozici ke stažení.20240515-GaKO 5/24
15.4.2024 10:03 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (5/2024) je k dispozici ke stažení.202407129-GaKO 7/24
15.4.2024 10:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (7/2024) je k dispozici ke stažení.
Nové číslo GaKO
15.4.2024 10:00
ÚGKK SR
Nové číslo časopisu Geodetického a Kartografického Obzoru 04/2024
20240415-VŘ KP Prachatice
15.4.2024 8:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnízveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa ředitele/ ředitelky Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice.
20240415-VŘ KP Prachatice
15.4.2024 8:51 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa ředitele/ ředitelky Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice.20240415-VŘ KP Prachatice
15.4.2024 8:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa ředitele/ ředitelky Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice.20240415-VŘ KP Prachatice
15.4.2024 8:51 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa ředitele/ ředitelky Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice.GaKO 4/2024
15.4.2024 0:01 GaKO GaKO 4/2024 WEIGEL, J.: Ellipsa – speciální případ křivky vejcové – zajímavé křivky profesora MarkaNabídka studentských brigád ve společnosti GRAPO s.r.o.
14.4.2024 19:50 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucNabízíme způsob, jak si přivydělat během studia, aniž by to ovlivnilo Vaše studijní povinnosti. 1) Brigáda ve výrobě reklamy: Zahrnuje drobné manuální práce s občasným použitím ručního nářadí (vrtačky, nýtovačky), kompletaci světelných i nesvětelných nápisů, lepení desek, nátěr polystyrenů a osazování LEDkami. Všechny dovednosti poskytneme a proškolíme. Budete pracovat v týmovém prostředí, ve kterém kolegové […]
The post Nabídka studentských brigád ve společnosti GRAPO s.r.o. first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
DAEX DESIGN Plus 24 v akci
12.4.2024 19:32 ŠPINAR - softwareDAEX DESIGN pro truhlaře, výrobce nábytku a návrháře interiérů v akční nabídce!
The post DAEX DESIGN Plus 24 v akci appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
rada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
12.4.2024 17:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/rada-odborny-rada-–-kontrola-listin-urcenych-k-zaprada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
12.4.2024 17:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:rada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
rada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
12.4.2024 17:54 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisurada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
12.4.2024 17:54 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-–-kontrola-listin-urcenych-k-zaprada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
12.4.2024 17:54 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – kontrola listin určených k zápisu
Simulation for Industrial Systems Part 1-Transcript
12.4.2024 17:19 Siemens Industry SoftwareVictoria Carlos: Hi everyone, and welcome back to our Smart Manufacturing Podcast series. I’m your host, Victoria Carlos, a thought…

The “definition of openBIM-based Workflows and Exchanges for Electric Power Transmission and Distribution” Activity Proposal is now out for review by the Standards Committee.
12.4.2024 16:10 buildingSMART.orgVote closing date: 10 May 2024Report: Link The “openBIM-based Workflows and Exchanges for Electric Power Transmission and Distribution” Activity Proposal addresses examining the requirements of high-voltage electrical power transmission and…
The post The “definition of openBIM-based Workflows and Exchanges for Electric Power Transmission and Distribution” Activity Proposal is now out for review by the Standards Committee. appeared first on buildingSMART International.
EarthCARE mission card with tagline
12.4.2024 15:10 ESA Observing the Earth
EarthCARE: cloud and aerosol mission
EarthCARE mission card for portal
12.4.2024 15:10 ESA Observing the Earth
EarthCARE - ESA's cloud and aerosol mission
Konference DigiGeo Liberec 2024 (pozvánka)
12.4.2024 13:35 GISportal.cz
Katedra geoinformatiky a didaktiky informatiky TU Liberec zve na konferenci DigiGeo 2024, která se uskuteční čtvrtek 6. 6. a pátek 7. 6. 2024 O čem DigiGeo Liberec 2024 bude? Dvoudenní setkání stovky zájemců především o geografické vzdělávání a jeho podporu digitálními technologiemi. Přednášky na téma dobré učitelské praxe. Dílny s praktickými ukázkami. Setkávání, síťování, odborné […]
The post Konference DigiGeo Liberec 2024 (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Konference DigiGeo Liberec 2024 (pozvánka)
12.4.2024 13:35 GISportal.cz
Katedra geoinformatiky a didaktiky informatiky TU Liberec zve na konferenci DigiGeo 2024. O čem DigiGeo Liberec 2024 bude? Dvoudenní setkání stovky zájemců především o geografické vzdělávání a jeho podporu digitálními technologiemi. Přednášky na téma dobré učitelské praxe. Dílny s praktickými ukázkami. Setkávání, síťování, odborné diskuse. Inspirace. A jaká témata otevřeme? Geotechnologie v terénní geografické výuce. […]
The post Konference DigiGeo Liberec 2024 (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Konference DigiGeo Liberec 2024 (pozvánka)
12.4.2024 13:35 GISportal.cz
Katedra geoinformatiky a didaktiky informatiky TU Liberec zve na konferenci DigiGeo 2024, která se uskuteční čtvrtek 6. 6. a pátek 7. 6. 2024 O čem DigiGeo Liberec 2024 bude? Dvoudenní setkání stovky zájemců především o geografické vzdělávání a jeho podporu digitálními technologiemi. Přednášky na téma dobré učitelské praxe. Dílny s praktickými ukázkami. Setkávání, síťování, odborné […]
The post Konference DigiGeo Liberec 2024 (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Letní teambuilding se konal tentokrát na Slapech
12.4.2024 12:54 Hrdlička Tradiční letní teambuilding jsme letos uspořádali v Nové Živohošti na Slapech.ředitel/ka odboru – rada/odborný rada – ředitel/ka Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice (ID SM 300002
12.4.2024 12:41 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Prachaticevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
ředitel/ka odboru – rada/odborný rada – ředitel/ka Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice (ID SM 30000250/30003874)
ředitel/ka odboru – rada/odborný rada – ředitel/ka Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice (ID SM 300002
12.4.2024 12:41 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Prachatice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo ředitel/ka odboru – rada/odborný rada – ředitel/ka Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice (ID SM 300002ředitel/ka odboru – rada/odborný rada – ředitel/ka Katastrálního pracoviště Prachatice (ID SM 300002
12.4.2024 12:41 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/reditel-ka-odboru-–-rada-odborny-rada-–-reditel-kaLetní teambuilding se konal tentokrát na Slapech
12.4.2024 11:57 Hrdlička Tradiční letní teambuilding jsme letos uspořádali v Nové Živohošti na Slapech.ředitel/ka odboru GI KN – rada/odborný rada Katastrálního pracoviště České Budějovice (ID SM 3000012
12.4.2024 10:58 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/reditel-ka-odboru-GI-KN-–-rada-odborny-rada-Katastředitel/ka odboru GI KN – rada/odborný rada Katastrálního pracoviště České Budějovice (ID SM 3000012
12.4.2024 10:58 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště České Budějovice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo ředitel/ka odboru GI KN – rada/odborný rada Katastrálního pracoviště České Budějovice (ID SM 3000012ředitel/ka odboru GI KN – rada/odborný rada Katastrálního pracoviště České Budějovice (ID SM 3000012
12.4.2024 10:58 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště České Budějovicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
ředitel/ka odboru GI KN – rada/odborný rada Katastrálního pracoviště České Budějovice (ID SM 30000122/30003746)
Chceme pomáhat a pomáháme Ukrajině
12.4.2024 10:57 Hrdlička Prostřednictvím naší neziskové organizace Horizont HG 2014, z.ú kupujeme drony.Chceme pomáhat a pomáháme Ukrajině
12.4.2024 10:55 Hrdlička Prostřednictvím naší neziskové organizace Horizont HG 2014, z.ú kupujeme drony.Dronedge 2024 – 9. ročník konference Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl
12.4.2024 10:09 UAVA Přijměte pozvání na letošní již 9. ročník konference Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl – Dronedge 2024. Datum: 11.9.2024 Místo: kino Dlabačov, Praha 6 Registrace bude spuštěnana přelomu červen/červenec 2024.Earth from Space: The Ebro Delta
12.4.2024 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth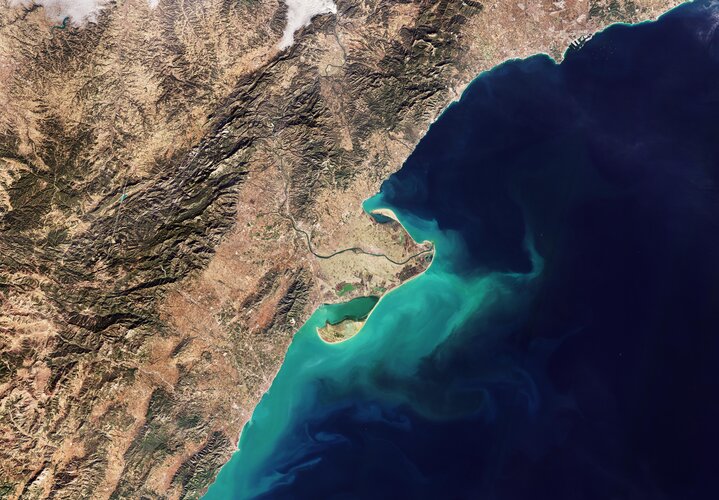 Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image shows the delta of the Ebro River on the northeast coast of Spain.
Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image shows the delta of the Ebro River on the northeast coast of Spain.
EuroCarto 2024 – prodloužený deadline
11.4.2024 19:48 Česká kartografická společnostDeadline pro zasílání abstraktů na konferenci EuroCarto 2024 byl prodloužen do 24. dubna. Pro více informací navštivte https://eurocarto2024.org/.
The post EuroCarto 2024 – prodloužený deadline first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
Mapa roku 2023 [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
11.4.2024 11:10 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Slavnostní vyhlášení výsledků soutěže proběhne ve čtvrtek 9. května 2024.Pracovní nabídka: Editor dat Digitální Technické Mapy Moravskoslezské kraje
11.4.2024 9:03 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucMoravskoslezské datové centrum, které je příspěvkovou organizací Moravskoslezského kraje nabízí pozici: Editor dat Digitální Technické Mapy Moravskoslezské kraje (DTM MSK) Odkaz na nabídku: https://www.msdc.cz/kariera/
The post Pracovní nabídka: Editor dat Digitální Technické Mapy Moravskoslezské kraje first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Map-Oriented Dashboards Online—From Minor Method to GIScience Trend
11.4.2024 9:02 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucKapitola v nové knize od Springeru hodnotí mapové dashboardy Prestižní vydavatelství Springer vydalo zbrusu novou knihu Advances in Geoinformatics Technologies (https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-50848-6) jejíž součástí je kapitola Map-Oriented Dashboards Online—From Minor Method to GIScience Trend. Dr. Nétek z naší katedry v ní rozebírá aspekty a popularitu mapových dashboardů. Kapitolu si můžete přečíst zde: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379441928_Map-Oriented_Dashboards_Online-From_Minor_Method_to_GIScience_Trend.
The post Map-Oriented Dashboards Online—From Minor Method to GIScience Trend first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Map-Oriented Dashboards Online—From Minor Method to GIScience Trend
11.4.2024 9:02 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucKapitola v nové knize od Springeru hodnotí mapové dashboardy Prestižní vydavatelství Springer vydalo zbrusu novou knihu Advances in Geoinformatics Technologies (https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-50848-6) jejíž součástí je kapitola Map-Oriented Dashboards Online—From Minor Method to GIScience Trend. Dr. Nétek z naší katedry v ní rozebírá aspekty a popularitu mapových dashboardů. Kapitolu si můžete přečíst zde: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379441928_Map-Oriented_Dashboards_Online-From_Minor_Method_to_GIScience_Trend. — New book […]
The post Map-Oriented Dashboards Online—From Minor Method to GIScience Trend first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Nová verze WSGP
11.4.2024 8:27 GEPROČÚZK připravuje nasazení nové verze webové služby dálkového přístupu pro vyhotovitele a ověřovatele geometrických plánů (WSGP). Nová verze WSGP 2.10 má být nasazena v pátek 26.4. 2024. Provoz služby stávající verze WSGP 2.9 bude nasazením nové verze ukončen. Přechodné období, během něhož by fungovaly současně obě verze, nebude. Systém KOKEŠ verze 16 bude na tuto připravovanou změnu […]
Článek Nová verze WSGP se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
16. jednání TPS
10.4.2024 19:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 25. dubna 2024 proběhne distančně 16. jednání Technické pracovní skupiny Koordinační rady správců DMVS a DTM.Aktualizace Metodiky pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS
10.4.2024 19:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V záložce Metodika byl aktualizován dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíAktualizace Metodiky pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS
10.4.2024 19:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V záložce Metodika byl aktualizován dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíAktualizace Metodiky pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS
10.4.2024 19:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V záložce Metodika byl aktualizován dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíAktualizace Metodiky pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS
10.4.2024 19:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V záložce Metodika byl aktualizován dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování ZPS DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíPředstavení FARO Orbis – ohlédnutí
10.4.2024 15:48 3gon Ve dnech 26. – 27. 3. 2024 se konala živá premiéra prvního hybridního skeneru na světě FARO Orbis a my20240411 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v odd.právních vztahů KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro Ústec. kraj
10.4.2024 14:54 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20240411 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v odd.právních vztahů KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro Ústec. kraj
10.4.2024 14:54 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Litomerice/O-uradu/Aktuality/20240411-volne-misto-Rada-odborny-rada-v-odd-pravn20240411 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v odd.právních vztahů KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro Ústec. kraj
10.4.2024 14:54 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20240411 - volné místo - Rada/odborný rada v odd.právních vztahů KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro Ústec. kraj
10.4.2024 14:54 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20240411-volne-misto-Rada-odborny-rada-v-odd-pravnRada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na
10.4.2024 14:52 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice naRada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na
10.4.2024 14:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na
10.4.2024 14:52 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemAliance a KOTRA pořádali roundtable s korejským velvyslancem
10.4.2024 13:41 UAVA Aliance a KOTRA včera pořádali roundtable s korejským velvyslancem na ambasádě v Praze k rozvíjející se spolupráci v oblasti dronů mezi českými a korejskými firmami a ohledně podpůrných aktivit. Současně jsme informovali o úspěšné české účasti a stánku na Korea Drone Show 2024. #drony #inovaceAliance a KOTRA pořádali roundtable s korejským velvyslancem
10.4.2024 13:41 UAVA Aliance a KOTRA včera pořádali roundtable s korejským velvyslancem na ambasádě v Praze k rozvíjející se spolupráci v oblasti dronů mezi českými a korejskými firmami a ohledně podpůrných aktivit. Současně jsme informovali o úspěšné české účasti a stánku na Korea Drone Show 2024. #drony #inovace20240410_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
10.4.2024 10:49 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-vychod/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(3)20240410_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
10.4.2024 10:49 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I. V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I."20240410_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN
10.4.2024 9:49 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN"20240410_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN
10.4.2024 9:49 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-vychod/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230724_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-aktu-(2)ARKANCE a její dceřiná společnost U.S. CAD kupují společnost CADD Microsystems
10.4.2024 9:46 Arkance SystemsVýznamná akvizice CADD Microsystems - americké softwarové firmy z Virginie, platinového partnera Autodesku a Bluebeam
Zpráva ARKANCE a její dceřiná společnost U.S. CAD kupují společnost CADD Microsystems pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Pozvánka na konferenci ARKANCE LIVE 2025
9.4.2024 13:00 Arkance SystemsNejnovější CAD/CAM, BIM a GIS/FM technologie a novinky Autodesku budou prezentovány na tradiční jarní online konferenci
Zpráva Pozvánka na konferenci ARKANCE LIVE 2025 pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Pozvánka na konferenci ARKANCE LIVE 2025
9.4.2024 13:00 Arkance SystemsNejnovější CAD/CAM, BIM a GIS/FM novinky z vlastního vývoje ARKANCE a novinky Autodesku 2025 na tradiční online konferenci
Zpráva Pozvánka na konferenci ARKANCE LIVE 2025 pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
20240409 - VŘ Agenda VZ a smluv
9.4.2024 12:53 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa odborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv.20240409 - VŘ Agenda VZ a smluv
9.4.2024 12:53 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2024/20240409-VR-Agenda-VZ-a-smluv20240409 - VŘ Agenda VZ a smluv
9.4.2024 12:53 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa odborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv.Odborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv odboru informatiky
9.4.2024 12:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnívypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv odboru informatiky
Odborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv odboru informatiky
9.4.2024 12:37 ČÚZK /Urady/Cesky-urad-zememericky-a-katastralni/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-rada-Agenda-VZ-a-smluv-odboru-informatikyOdborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv odboru informatiky
9.4.2024 12:37 ČÚZK - volná místa Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada - Agenda VZ a smluv odboru informatikyKonference GIS Esri v ČR (save the date)
9.4.2024 11:23 GISportal.cz
Konference GIS Esri je největším oborovým setkáním geoinformatiků v Česku a již více než třicet let seznamuje účastníky s novinkami v oblasti GIS a s aktuálními projekty ve veřejném i soukromém sektoru. I v letošním roce se konference bude konat v Kongresovém centru Praha, ve dnech 6. a 7. listopadu 2024. Více informací budeme přinášet […]
The post Konference GIS Esri v ČR (save the date) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Konference GIS Esri v ČR (save the date)
9.4.2024 11:23 GISportal.cz
Konference GIS Esri je největším oborovým setkáním geoinformatiků v Česku a již více než třicet let seznamuje účastníky s novinkami v oblasti GIS a s aktuálními projekty ve veřejném i soukromém sektoru. I v letošním roce se konference bude konat v Kongresovém centru Praha, ve dnech 6. a 7. listopadu 2024. Více informací budeme přinášet […]
The post Konference GIS Esri v ČR (save the date) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Nominace MR2023
9.4.2024 11:10 Česká kartografická společnostNOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU 2023 Odborná komise České kartografické společnosti na svém zasedání zhodnotila všechny přihlášené produkty a nominovala kartografické produkty na ocenění Mapa roku 2023 v pěti soutěžních kategoriích. Přehled nominovaných produktů je uveden na stránkách soutěže MAPA ROKU. Slavnostní vyhlášení výsledků soutěže proběhne ve čtvrtek 9. května 2024 v atriu Armádního muzea Žižkov od 13 […]
The post Nominace MR2023 first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
NOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU
9.4.2024 11:10 Česká kartografická společnostNOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU 2023 Odborná komise České kartografické společnosti na svém zasedání zhodnotila všechny přihlášené produkty a nominovala kartografické produkty na ocenění Mapa roku 2023 v pěti soutěžních kategoriích. Přehled nominovaných produktů je uveden na stránkách soutěže MAPA ROKU. Slavnostní vyhlášení výsledků soutěže proběhne ve čtvrtek 9. května 2024 v atriu Armádního muzea Žižkov od 13 […]
The post first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
NOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU 2023
9.4.2024 11:10 Česká kartografická společnostOdborná komise České kartografické společnosti na svém zasedání zhodnotila všechny přihlášené produkty a nominovala kartografické produkty na ocenění Mapa roku 2023 v pěti soutěžních kategoriích. Přehled nominovaných produktů je uveden na stránkách soutěže MAPA ROKU. Slavnostní vyhlášení výsledků soutěže proběhne ve čtvrtek 9. května 2024 v atriu Armádního muzea Žižkov od 13 hodin – více o vyhlášení zde. Zváni […]
The post NOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU 2023 first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
NOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU 2023
9.4.2024 11:10 Česká kartografická společnostOdborná komise České kartografické společnosti na svém zasedání zhodnotila všechny přihlášené produkty a nominovala kartografické produkty na ocenění Mapa roku 2023 v pěti soutěžních kategoriích. Přehled nominovaných produktů je uveden na stránkách soutěže MAPA ROKU. Slavnostní vyhlášení výsledků soutěže proběhne ve čtvrtek 9. května 2024 v atriu Armádního muzea Žižkov od 13 hodin – více o vyhlášení zde. Zváni […]
The post NOMINACE NA OCENĚNÍ MAPA ROKU 2023 first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
Total solar eclipse seen from space
9.4.2024 11:00 ESA Observing the Earth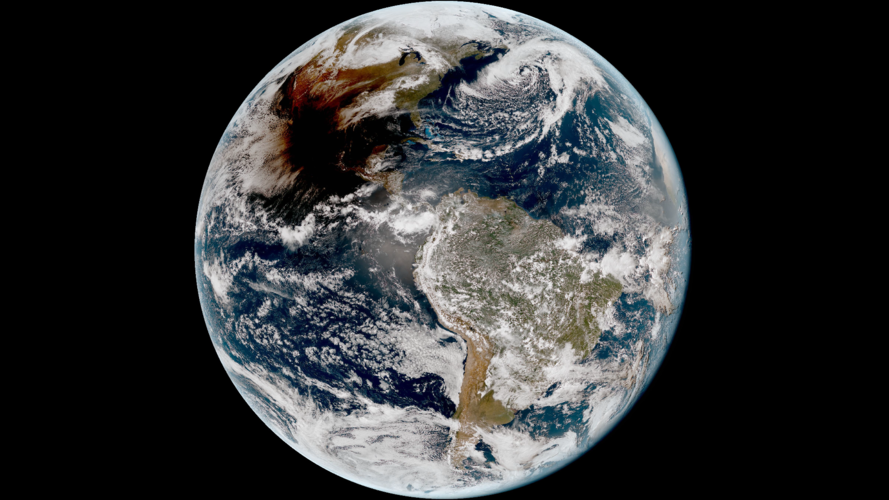 Video:
00:00:07
Video:
00:00:07
A total solar eclipse swept across North America yesterday, blocking out the Sun momentarily with parts of the continent plunged into darkness. Geostationary satellites orbiting 36 000 km away captured images of the rare celestial event.
These images, captured by the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-16), captured the moon’s shadow moving across North America from approximately 16:00 to 23:00 CEST (15:00 to 22:00 BST.)
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth and, for a short period, blocks the face of the Sun, save for a visible ring of light, known as the Sun’s corona.
The track of the moon’s shadow across Earth’s surface, called the path of totality, spanned across the North American continent – from Mexico to the very eastern tip of Canada.
The GOES series is a collaborative development and acquisition effort between National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and NASA. The GOES-16 (GOES-East) satellite, the first of the series, provides continuous imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth's western hemisphere and monitors space weather.
The Copernicus Sentinel-3 mission also captured images of the eclipse with its Sea and Land Surface Temperature Radiometer (SLSTR).
The eclipse also acts as a laboratory for researching what happens to weather when the Moon’s shadow passes over. The shadow makes air temperatures drop and can cause clouds to evolve in different ways. Data from GOES, Sentinel-3 and other satellites are now being used to explore these effects.
rada/odborný rada - inspektor
9.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Plzni/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-inspektorrada/odborný rada - inspektor
9.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Plzni vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada - inspektorrada/odborný rada - inspektor
9.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Plznivypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada - inspektor
Mapová aplikace ÚPD - nové dokumentace
9.4.2024 10:10 Jihočeský krajV mapové aplikaci Územně plánovací dokumentace obcí byla aktualizována ÚPD obcí ORP Třeboň - Nová Ves nad Lužnicí, ORP Č. Krumlov - Černá v Pošumaví, Věžovatá Pláně, ORP Milevsko - Vlksice, ORP Tábor - Chotoviny.
Our Ocean from Space: a journey into Earth's marine ecosystems
9.4.2024 10:06 ESA Observing the Earth
GISáček 2024
9.4.2024 8:04 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucGISáček – hlaste se na tradiční studentskou konferenci v oblasti geoinformatiky! Katedra geoinformatiky VŠB-TU Ostrava zve na tradiční studentskou konferenci GISáček, která je určená studentům vysokých škol, kteří zde mají možnost prezentovat výsledky svých odborných studentských prací v oblasti geoinformatiky. ️ Kdy: 15.5.2024 Kde: VŠB-TUO, Ostrava, Poruba, 17.listopadu 2172/15 (Universitní Aula, místnost UA178 (Rektorský salónek) […]
The post GISáček 2024 first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK /Zememerictvi/Zememericke-cinnosti/Aktuality-pro-zememerice/2024/Zmena-nazvu-textoveho-souboru-overeniZměna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. Obnovení provozu předpokládáme v cca 18:30 hodin. U této verze nedochází ke změnám webových služeb.
Dokumenty sbírky listin poskytované přes Dálkový přístup nebudou dostupné od pátku 12.4.2024 od 15:30 do soboty 13. 4. 2024 do cca 18:00.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/412673Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. Obnovení provozu předpokládáme v cca 18:30 hodin. U této verze nedochází ke změnám webových služeb.
Dokumenty sbírky listin poskytované přes Dálkový přístup nebudou dostupné od pátku 12.4.2024 od 15:30 do soboty 13. 4. 2024 do cca 18:00.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. Obnovení provozu předpokládáme v cca 18:30 hodin. U této verze nedochází ke změnám webových služeb.
Dokumenty sbírky listin poskytované přes Dálkový přístup nebudou dostupné od pátku 12.4.2024 od 15:30 do soboty 13. 4. 2024 do cca 18:00.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
World Beacon Day – Galileo continues to help save lives
8.4.2024 12:24 European GNSS AgencyWorld Beacon Day or #406 day is a day to honour the search and rescue teams that are helping save thousands of lives every year. 406 Day marks the 6 April as a reference to the 406 MHz frequency of the beacons used by the SAR teams in their missions. These beacons are integrated into the COSPAS-SARSAT system and are helping to save 2,000 lives per year.
What is COSPAS-SARSAT?
Galileo SAR system is integrated into the COSPAS-SARSAT programme - a satellite-based SAR distress alert detection and information distribution system. The system finds distress signals from radio beacons that comply with COSPAS-SARSAT specifications and standards and provides the information to search and rescue teams.
How does Galileo play a role?
Galileo has proven a valuable resource when it comes to these rescue missions.
Thanks to the SAR transponder which seamlessly integrates into the satellite constellation, Galileo has revolutionised the detection and location process of distress beacons, significantly reducing response times and enhancing survival probabilities.
By locating the 406 MHz signals transmitted from the beacons, the System pinpoints the distress position and timely expedites the location data to relevant authorities significantly augmenting the likelihood of survival for those in perilous situations.
Central to Galileo’s innovation is the Return Link Service (RLS), a ground-breaking feature that provides 406 users with a vital confirmation and reassurance that its distress transmission has been received within a remarkable 10-to-20-minute timeframe.
Galileo’s SAR technology has not only revolutionized SAR operations but has also become a beacon of hope for individuals facing emergencies in remote or hazardous environments. With each successful mission, Galileo reaffirms its status as an indispensable asset, transcending boundaries and saving lives with unparalleled efficiency.
Galileo SAR Fully Operational Capability (FOC)
Galileo's Search and Rescue Service is set for a remarkable leap forward with the imminent declaration of its Full Operational Capability (FOC). This milestone promises to elevate safety and support in SAR operations, reaffirming Galileo's dedication to worldwide SAR endeavours.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 AdeonZaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 Adeon
Zaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 Adeon
Zaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 Adeon
Zaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
20240408_Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
8.4.2024 10:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Pribram/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230910_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-prav-(4)20240408_Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
8.4.2024 10:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN"Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
8.4.2024 10:34 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KNRada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
8.4.2024 10:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbramvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/rada-odborny-rada-–-navrh-zapisu,-kontrola-a-z-(1)rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-rada-–-opravy-chyb-v-KN-(1)odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-rada-–-vedouci-pravniho-oddeleni-VIodborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:27 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatněnírada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění

















