zprávy
zdroje zpráv:rada/odborný rada - inspektor
9.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Plzni/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-inspektorrada/odborný rada - inspektor
9.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Plzni vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada - inspektorrada/odborný rada - inspektor
9.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Plznivypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada - inspektor
Mapová aplikace ÚPD - nové dokumentace
9.4.2024 10:10 Jihočeský krajV mapové aplikaci Územně plánovací dokumentace obcí byla aktualizována ÚPD obcí ORP Třeboň - Nová Ves nad Lužnicí, ORP Č. Krumlov - Černá v Pošumaví, Věžovatá Pláně, ORP Milevsko - Vlksice, ORP Tábor - Chotoviny.
Our Ocean from Space: a journey into Earth's marine ecosystems
9.4.2024 10:06 ESA Observing the Earth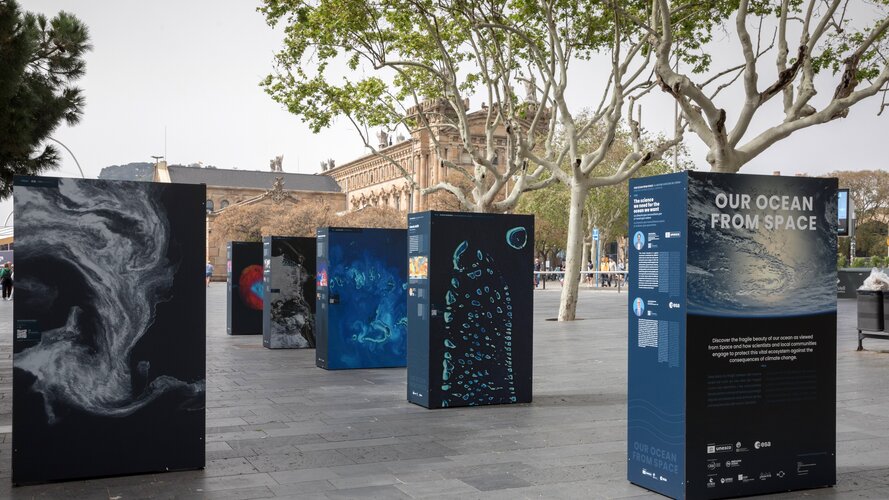
GISáček 2024
9.4.2024 8:04 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucGISáček – hlaste se na tradiční studentskou konferenci v oblasti geoinformatiky! Katedra geoinformatiky VŠB-TU Ostrava zve na tradiční studentskou konferenci GISáček, která je určená studentům vysokých škol, kteří zde mají možnost prezentovat výsledky svých odborných studentských prací v oblasti geoinformatiky. ️ Kdy: 15.5.2024 Kde: VŠB-TUO, Ostrava, Poruba, 17.listopadu 2172/15 (Universitní Aula, místnost UA178 (Rektorský salónek) […]
The post GISáček 2024 first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK /Zememerictvi/Zememericke-cinnosti/Aktuality-pro-zememerice/2024/Zmena-nazvu-textoveho-souboru-overeniZměna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Změna názvu textového souboru ověření
8.4.2024 15:34 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Upozorňujeme, že dnem 27. dubna 2024 dojde ke změně názvu textového souboru podle § 18 odst. 4 vyhlášky č. 31/1995 Sb., kterou se provádí zákon o zeměměřictví, z "Overeni_UOZI" a příponu *.txt na název "Overeni" a příponu *.txt. Bližší informace naleznete zde.Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. Obnovení provozu předpokládáme v cca 18:30 hodin. U této verze nedochází ke změnám webových služeb.
Dokumenty sbírky listin poskytované přes Dálkový přístup nebudou dostupné od pátku 12.4.2024 od 15:30 do soboty 13. 4. 2024 do cca 18:00.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/412673Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. Obnovení provozu předpokládáme v cca 18:30 hodin. U této verze nedochází ke změnám webových služeb.
Dokumenty sbírky listin poskytované přes Dálkový přístup nebudou dostupné od pátku 12.4.2024 od 15:30 do soboty 13. 4. 2024 do cca 18:00.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 do cca 18:30 (Dokumenty sbírky listin z DP od
8.4.2024 14:04 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 12.4.2024 od 16:30 bude z provozních důvodů zcela přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu i Webových služeb dálkového přístupu. Obnovení provozu předpokládáme v cca 18:30 hodin. U této verze nedochází ke změnám webových služeb.
Dokumenty sbírky listin poskytované přes Dálkový přístup nebudou dostupné od pátku 12.4.2024 od 15:30 do soboty 13. 4. 2024 do cca 18:00.
Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
World Beacon Day – Galileo continues to help save lives
8.4.2024 12:24 European GNSS AgencyWorld Beacon Day or #406 day is a day to honour the search and rescue teams that are helping save thousands of lives every year. 406 Day marks the 6 April as a reference to the 406 MHz frequency of the beacons used by the SAR teams in their missions. These beacons are integrated into the COSPAS-SARSAT system and are helping to save 2,000 lives per year.
What is COSPAS-SARSAT?
Galileo SAR system is integrated into the COSPAS-SARSAT programme - a satellite-based SAR distress alert detection and information distribution system. The system finds distress signals from radio beacons that comply with COSPAS-SARSAT specifications and standards and provides the information to search and rescue teams.
How does Galileo play a role?
Galileo has proven a valuable resource when it comes to these rescue missions.
Thanks to the SAR transponder which seamlessly integrates into the satellite constellation, Galileo has revolutionised the detection and location process of distress beacons, significantly reducing response times and enhancing survival probabilities.
By locating the 406 MHz signals transmitted from the beacons, the System pinpoints the distress position and timely expedites the location data to relevant authorities significantly augmenting the likelihood of survival for those in perilous situations.
Central to Galileo’s innovation is the Return Link Service (RLS), a ground-breaking feature that provides 406 users with a vital confirmation and reassurance that its distress transmission has been received within a remarkable 10-to-20-minute timeframe.
Galileo’s SAR technology has not only revolutionized SAR operations but has also become a beacon of hope for individuals facing emergencies in remote or hazardous environments. With each successful mission, Galileo reaffirms its status as an indispensable asset, transcending boundaries and saving lives with unparalleled efficiency.
Galileo SAR Fully Operational Capability (FOC)
Galileo's Search and Rescue Service is set for a remarkable leap forward with the imminent declaration of its Full Operational Capability (FOC). This milestone promises to elevate safety and support in SAR operations, reaffirming Galileo's dedication to worldwide SAR endeavours.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 AdeonZaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 Adeon
Zaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 Adeon
Zaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025
8.4.2024 11:44 Adeon
Zaregistrujte se na naši tradiční roadshow strojírenských technologií, na které vám předvedeme letošní novinky v Autodesk produktech pro konstruktéry a výrobu.
The post Roadshow strojírenských technologií řady 2025 appeared first on Adeon CZ.
20240408_Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
8.4.2024 10:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Pribram/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230910_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-prav-(4)20240408_Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
8.4.2024 10:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN"Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
8.4.2024 10:34 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KNRada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
8.4.2024 10:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbramvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/rada-odborny-rada-–-navrh-zapisu,-kontrola-a-z-(1)rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-rada-–-opravy-chyb-v-KN-(1)odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-rada-–-vedouci-pravniho-oddeleni-VIodborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka úřadu vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na pozici:odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:27 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatněnírada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
rada/odborný rada – návrh zápisu, kontrola a zplatnění
8.4.2024 10:27 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-–-navrh-zapisu,-kontrola-a-z-(2)odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:26 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada – opravy chyb v KNodborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
odborný rada – opravy chyb v KN
8.4.2024 10:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-rada-–-opravy-chyb-v-KN-(1)odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:24 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:24 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-rada-–-vedouci-pravniho-oddeleni-VIodborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
8.4.2024 10:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada – vedoucí právního oddělení VI.
Zkrácení otevírací doby [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
8.4.2024 10:00 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK V pondělí 8. dubna 2024 bude Knihovna geografie z technických důvodů otevřena pouze do 16:00.Výběrové řízení na KP Jihlava
8.4.2024 9:56 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vyberove-rizeni-na-KP-JihlavaVýběrové řízení na KP Jihlava
8.4.2024 9:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Jihlava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný referent/vrchní referent – oddělení aktualizace KN I Katastrálního pracoviště Jihlava.Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Holešov
8.4.2024 9:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Holešovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Holešov
Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Holešov
8.4.2024 9:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Holešov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště HolešovRada / odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Holešov
8.4.2024 9:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-vedouci-oddeleni-aktualizace-aNávrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
8.4.2024 9:40 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské MeziříčíNávrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
8.4.2024 9:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Meziříčívypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
Návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
8.4.2024 9:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Navrh-zapisu-v-katastru-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-KN-Návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
8.4.2024 9:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Meziříčívypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent - návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
Návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Valašské Meziříčí
8.4.2024 9:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Navrh-zapisu-v-katastru-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-KNodborný referent - vrchní referent - aktualizace KN I KP Jihlava
8.4.2024 9:38 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Jihlava vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent - vrchní referent - aktualizace KN I KP Jihlavaodborný referent - vrchní referent - aktualizace KN I KP Jihlava
8.4.2024 9:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-aktualizace-KN-I-odborný referent - vrchní referent - aktualizace KN I KP Jihlava
8.4.2024 9:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Jihlavavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent - vrchní referent - aktualizace KN I KP Jihlava
Vrchní referent / rada – správa dokumentace katastru v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracovi
8.4.2024 9:32 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada – správa dokumentace katastru v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviVrchní referent / rada – správa dokumentace katastru v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracovi
8.4.2024 9:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada – správa dokumentace katastru v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Zlín
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
8.4.2024 9:22 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-poskytovani-infOdborný referent / vrchní referent – poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
8.4.2024 9:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Uherské Hradištěvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN, poskytování informací s PK v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Uherské Hradiště
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KN
8.4.2024 9:22 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Uherské Hradiště vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent – poskytování informací KN, poskytování podkladů, nahlížení do KNZahájení projektu COMUNIDAD, který sbližuje Evropu a Latinskou Ameriku! (TZ)
8.4.2024 8:14 GISportal.cz
S podporou programu Horizont Evropa (grantová dohoda: 101131859) byl zahájen nový projekt COMUNIDAD, jehož cílem je vytvořit společenství zainteresovaných stran, které se bude věnovat využívání dat programu Copernicus. Projekt se zaměřuje na společný vývoj algoritmů, služeb a produktů přizpůsobených potřebám místních uživatelů, čímž se zvýší kvalita globálních produktů programu Copernicus. Iniciativa bude rovněž zkoumat kombinované […]
The post Zahájení projektu COMUNIDAD, který sbližuje Evropu a Latinskou Ameriku! (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Zahájení projektu COMUNIDAD, který sbližuje Evropu a Latinskou Ameriku! (TZ)
8.4.2024 8:14 GISportal.cz
S podporou programu Horizont Evropa (grantová dohoda: 101131859) byl zahájen nový projekt COMUNIDAD, jehož cílem je vytvořit společenství zainteresovaných stran, které se bude věnovat využívání dat programu Copernicus. Projekt se zaměřuje na společný vývoj algoritmů, služeb a produktů přizpůsobených potřebám místních uživatelů, čímž se zvýší kvalita globálních produktů programu Copernicus. Iniciativa bude rovněž zkoumat kombinované […]
The post Zahájení projektu COMUNIDAD, který sbližuje Evropu a Latinskou Ameriku! (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
20240408-Statistické údaje
8.4.2024 7:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zveřejněny statistické údaje za 1. čtvrtletí roku 2024 o vybraných transakcích s nemovitostmi evidovanými v KN.20240408-Statistické údaje
8.4.2024 7:18 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Zveřejněny statistické údaje za 1. čtvrtletí roku 2024 o vybraných transakcích s nemovitostmi evidovanými v KN.Příklady a individuální školení pro zvýšení kvality Vašich vizualizací v DAEX DESIGN 24
7.4.2024 22:12 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
dovolujeme si vám nabídnout příklady a individuální školení pro zvýšení kvality vizualizací v programu DAEX DESIGN 24.
The post Příklady a individuální školení pro zvýšení kvality Vašich vizualizací v DAEX DESIGN 24 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Novinka – Příklady a individuální školení pro zvýšení kvality Vašich vizualizací v DAEX DESIGN 24
7.4.2024 22:12 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
dovolujeme si vám nabídnout příklady a individuální školení pro zvýšení kvality vizualizací v programu DAEX DESIGN 24.
The post Novinka – Příklady a individuální školení pro zvýšení kvality Vašich vizualizací v DAEX DESIGN 24 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Krátka správa č. 19/2024
5.4.2024 14:52 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 19/2024 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 18/2024
5.4.2024 14:48 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 18/2024 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
EGNOS offers increased resiliency against peak solar flares
5.4.2024 12:56 European GNSS Agency
Have trouble telling your north from your south? You’re not alone. It turns out, the sun seems to get things mixed up too.
That’s because every 11 or so years, the sun’s magnetic field flips, causing its north and south poles to switch places. This process is called the solar cycle, and we’re currently in the early stages of Solar Cycle 25.
Solar cycles are marked by a significant increase of activity on the sun’s surface. Sometimes this activity can result in solar flares, which are large eruptions that blast energy and material into space.
When a flare reaches Earth, it can impact everything from radio communications to electricity grids. It can even cause issues with satellite signals, including the GNSS signals we use for location, positioning and timing services.
The good news is that there are services that can detect incoming solar flares. For example, on 23 March, the Space Weather Prediction Center, part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), issued a severe geomagnetic storm alert about the detection of a strong solar flare.
When that solar flare hit on 24 March, it caused satellite anomalies and periods of GPS degradation.
However, thanks to EGNOS, most of us probably didn’t even notice.
EGNOS, Europe's regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS), helps improve the performance of GNSS systems like GPS and Galileo. It does this by using GNSS measurements taken by accurately located reference stations deployed across Europe. All measured GNSS errors are transferred to a central computing centre where differential corrections and integrity messages are calculated. These calculations are then broadcast over the covered area using geostationary satellites that serve as an augmentation, or overlay, to the original GNSS message.
As a result, EGNOS improves the accuracy and reliability of GNSS positioning information – even during such anomalies as a solar flare. In fact, during the 24 March solar flare event, EGNOS recorded good performance. EGNOS Safety-of-life Service performance dropped slightly in the far north of Finland and Norway, down to 98%. Users in the area were more likely to notice the aurora borealis lighting up the sky than any issue with their positioning information.
Just as Solar Cycle 25 continues to ramp up, so too does EGNOS. The latest system upgrade offers increased resilience against peak solar activity, amongst other advanced functionalities.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
EGNOS Safety-of-Life service offers increased resiliency against peak solar flares
5.4.2024 12:56 European GNSS Agency
Have trouble telling your north from your south? You’re not alone. It turns out, the sun seems to get things mixed up too.
That’s because every 11 or so years, the sun’s magnetic field flips, causing its north and south poles to switch places. This process is called the solar cycle, and we’re currently in the early stages of Solar Cycle 25.
Solar cycles are marked by a significant increase of activity on the sun’s surface. Sometimes this activity can result in solar flares, which are large eruptions that blast energy and material into space.
When a flare reaches Earth, it can impact everything from radio communications to electricity grids. It can even cause issues with satellite signals, including the GNSS signals we use for location, positioning and timing services.
The good news is that there are services that can detect incoming solar flares. For example, on 23 March, the Space Weather Prediction Center, part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), issued a severe geomagnetic storm alert about the detection of a strong solar flare.
When that solar flare hit on 24 March, it caused satellite anomalies and periods of GPS degradation.
However, thanks to EGNOS, most of us probably didn’t even notice.
EGNOS, Europe's regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS), helps improve the performance of GNSS systems like GPS and soon Galileo. It does this by using GNSS measurements taken by accurately located reference stations deployed across Europe. All measured GNSS errors are transferred to a central computing centre where differential corrections and integrity messages are calculated. These calculations are then broadcast over the covered area using geostationary satellites that serve as an augmentation, or overlay, to the original GNSS message.
As a result, EGNOS improves the accuracy and reliability of GNSS positioning information – even during such anomalies as a solar flare. In fact, during the 24 March solar flare event, EGNOS recorded good performance. EGNOS Safety-of-life Service performance dropped slightly in the far north of Finland and Norway, down to 98%. Users in the area were more likely to notice the aurora borealis lighting up the sky than any issue with their positioning information.
Just as Solar Cycle 25 continues to ramp up, so too does EGNOS. The latest system upgrade offers increased resilience against peak solar activity, amongst other advanced functionalities.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion
5.4.2024 12:53 AdeonSpolečnost Autodesk představuje inovativní funkci v softwaru Autodesk Fusion, která umožňuje uživatelům aktivně bojovat proti změně klimatu a vyrábět udržitelněji. […]
The post Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion
5.4.2024 12:53 Adeon
Společnost Autodesk představuje inovativní funkci v softwaru Autodesk Fusion, která umožňuje uživatelům aktivně bojovat proti změně klimatu a vyrábět udržitelněji. […]
The post Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion
5.4.2024 12:53 Adeon
Společnost Autodesk představuje inovativní funkci v softwaru Autodesk Fusion, která umožňuje uživatelům aktivně bojovat proti změně klimatu a vyrábět udržitelněji. […]
The post Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion
5.4.2024 12:53 Adeon
Společnost Autodesk představuje inovativní funkci v softwaru Autodesk Fusion, která umožňuje uživatelům aktivně bojovat proti změně klimatu a vyrábět udržitelněji. […]
The post Udělejte krok k zelenější budoucnosti s Autodesk Fusion appeared first on Adeon CZ.
odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro
5.4.2024 12:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralni-(1)odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro
5.4.2024 12:02 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj technický útvar vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu proodborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro
5.4.2024 12:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj technický útvarvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro
5.4.2024 11:29 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu proodborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro
5.4.2024 11:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Trutnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu technického útvaru Katastrálního úřadu pro
5.4.2024 11:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralniho-oEarth from Space: Victoria, Australia
5.4.2024 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth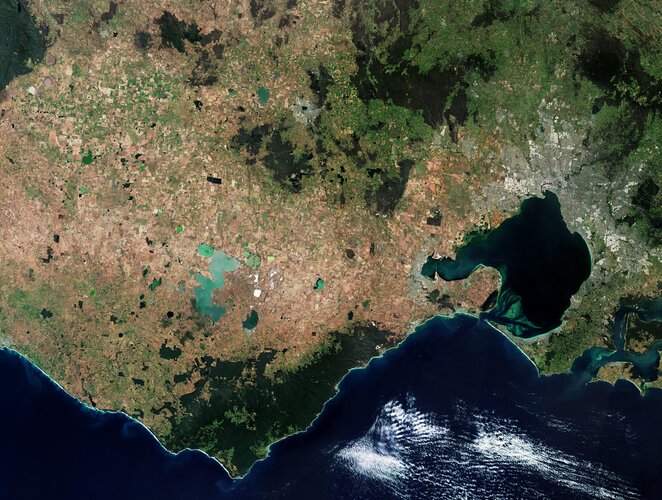 Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features part of Victoria, a state in southeast Australia.
Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features part of Victoria, a state in southeast Australia.
Krátka správa č. 17/2024
5.4.2024 9:29 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 17/2024 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Výsledky volební členské schůze CAGI
5.4.2024 8:27 GISportal.cz
V úterý 26. března 2024 se na Novotného lávce v Praze uskutečnila volební členská schůze České asociace pro geoinformace (CAGI). Ta v rámci svého programu zvolila nové předsednictvo a rovněž kontrolní komisi na období 2024-2027. Nově zvolené předsednictvo následně zvolilo předsedu, 1. a 2. místopředsedu a výkonný výbor. Jmenovitě vypadá vedení CAGI pro období 2024-2027 následovně: Předseda: doc. […]
The post Výsledky volební členské schůze CAGI appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Výsledky volební členské schůze CAGI
5.4.2024 8:27 GISportal.cz
V úterý 26. března 2024 se na Novotného lávce v Praze uskutečnila volební členská schůze České asociace pro geoinformace (CAGI). Ta v rámci svého programu zvolila nové předsednictvo a rovněž kontrolní komisi na období 2024-2027. Nově zvolené předsednictvo následně zvolilo předsedu, 1. a 2. místopředsedu a výkonný výbor. Jmenovitě vypadá vedení CAGI pro období 2024-2027 následovně: Předseda: doc. […]
The post Výsledky volební členské schůze CAGI appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Aliance byla partnerem konference DroneCon 2024 na ČVUT CIIRC
4.4.2024 17:37 UAVA Aliance byla partnerem konference DroneCon 2024, která se konala dnes 4.4.2024 na ČVUT CIIRC. Účastnili jsme se aktivně panelové diskuze především na téma pokročilého využití dronů, zavádění U-space, testovacího prostoru a jak rozvolnit létání BVLOS.Aliance byla partnerem konference DroneCon 2024 na ČVUT CIIRC
4.4.2024 17:37 UAVA Aliance byla partnerem konference DroneCon 2024, která se konala dnes 4.4.2024 na ČVUT CIIRC. Účastnili jsme se aktivně panelové diskuze především na téma pokročilého využití dronů, zavádění U-space, testovacího prostoru a jak rozvolnit létání BVLOS.odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Jičín
4.4.2024 14:49 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-rada-vedouci-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-(1)odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Jičín
4.4.2024 14:49 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jičínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Jičín
odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Jičín
4.4.2024 14:49 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jičín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště JičínEUSPA funded research projects take flight
4.4.2024 14:14 European GNSS Agency
Innovative Air Mobility (IAM) is an air-based transport system that integrates new aircraft designs and technologies, including drones, Urban Air Mobility (UAM) concepts and eVTOLs, into today’s airspace operations. In doing so, it will revolutionise how we move people and goods while also making transport more efficient and effective. According to EASA, IAM is defined as “the safe, secure and sustainable air mobility of passengers and cargo enabled by new-generation technologies integrated into a multimodal transportation system”.
Through such funding initiatives as Horizon Europe and Fundamental Elements, EUSPA is supporting numerous research and development projects working within the IAM sector as well as aerial operations (e.g. surveillance, inspections, mapping, telecommunications networking, etc.).
One of those initiatives is the DEGREE project. Funded under the Fundamental Elements mechanism, the project is developing a cutting-edge Galileo dual-frequency GNSS receiver. By leveraging the unique features of Galileo, the receiver will help Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) safely integrate into non-segregated airspace and into U-space, the EU’s UAS Traffic Management (UTM) system.
The DEGREE receiver is unique in that it leverages the Galileo Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) service to detect certain types of spoofing attacks.
“OSNMA stands as a formidable defence against the tampering and spoofing of navigation data, which is essential to the safe integration of UAS into the airspace,” explains DEGREE project manager Sergi Dueñas Pedrosa.
While the OSNMA provides defence against some spoofing attacks, the project’s use of the Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS) enhances the receiver’s ability to operate in situations where high positioning accuracy is required.
According to Dueñas Pedrosa, the integration of Galileo’s OSNMA and HAS services into the GNSS receivers takes the operational capabilities of a UAS platform to a whole new level both within Europe and beyond. “These services not only provide navigation-level authentication and better accuracy, they also provide confidence and assurance that the navigation system integrated into a customer’s platform can handle the stringent requirements for such critical operations as emergency management or the transport of medical goods,” he says.
Earlier this year, the project successfully conducted flight tests to validate the performance of its GNSS receiver.
Helping drones safely navigate low altitude airspace
Also working on the GNSS receiver front is the GEODESY project. The Fundamental Elements supported project has developed a multi-constellation, multi-frequency Galileo GNSS receiver that will help drones safely navigate the low altitude airspace that defines most urban areas.
The receiver, which uses both the Galileo OSNMA and HAS, is designed to achieve robust navigation performance, as well as critical technical and operational requirements.
The project also added integrity features into the navigation system.
That system was recently tested on two drones, one fixed-wing and one rotary-wing, at the ATLAS experimental flight centre, during which the GNSS receiver was able to achieve such key operations as automatic take-offs and landings.
Addressing IAM’s safety and security issues
Addressing the safety and security of IAM applications that rely on Position Navigation and Time (PNT) technologies powered by EGNSS is GAUSSIAN. The Horizon Europe funded project aims to demonstrate how combining the authenticated Galileo signals with integrated GNSS/INS platforms will result in greater robustness against spoofing attempts and the better continuity and availability of PNT data in constrained environments.
“GAUSSIAN wants to mitigate some of the security risks and concerns that originate from the real needs of flight operators, and we want to do so by leveraging advances in existing PNT technologies,” explains GAUSSIAN project coordinator Daniele Stopponi.
The project also intends to use the Precise Point Positioning (PPP)-RTK corrections provided by the Galileo HAS to help improve PNT data accuracy.
“Starting with existing concepts, prototypes and components developed by different companies, we are focused on creating new integrated and certified products for the rapidly evolving advanced air mobility market,” adds Stopponi.
Thanks to the work being done by GAUSSIAN, along with that of the DEGREE and GEODESY projects, IAM and aerial operations are on track to not only take off, but to do so in a way that will make air transport safer, quieter and more sustainable.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
EUSPA funded research projects take flight
4.4.2024 14:14 European GNSS Agency
Innovative Air Mobility (IAM) is an air-based transport system that integrates new aircraft designs and technologies, including drones, Urban Air Mobility (UAM) concepts and eVTOLs, into today’s airspace operations. In doing so, it will revolutionise how we move people and goods while also making transport more efficient and effective. According to EASA, IAM is defined as “the safe, secure and sustainable air mobility of passengers and cargo enabled by new-generation technologies integrated into a multimodal transportation system”.
Through such funding initiatives as Horizon Europe and Fundamental Elements, EUSPA is supporting numerous research and development projects working within the IAM sector as well as aerial operations (e.g. surveillance, inspections, mapping, telecommunications networking, etc.).
One of those initiatives is the DEGREE project. Funded under the Fundamental Elements mechanism, the project is developing a cutting-edge Galileo dual-frequency GNSS receiver. By leveraging the unique features of Galileo, the receiver will help Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) safely integrate into non-segregated airspace and into U-space, the EU’s UAS Traffic Management (UTM) system.
The DEGREE receiver is unique in that it leverages the Galileo Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) service to detect certain types of spoofing attacks.
“OSNMA stands as a formidable defence against the tampering and spoofing of navigation data, which is essential to the safe integration of UAS into the airspace,” explains DEGREE project manager Sergi Dueñas Pedrosa.
While the OSNMA provides defence against some spoofing attacks, the project’s use of the Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS) enhances the receiver’s ability to operate in situations where high positioning accuracy is required.
According to Dueñas Pedrosa, the integration of Galileo’s OSNMA and HAS services into the GNSS receivers takes the operational capabilities of a UAS platform to a whole new level both within Europe and beyond. “These services not only provide navigation-level authentication and better accuracy, they also provide confidence and assurance that the navigation system integrated into a customer’s platform can handle the stringent requirements for such critical operations as emergency management or the transport of medical goods,” he says.
Earlier this year, the project successfully conducted flight tests to validate the performance of its GNSS receiver.
Helping drones safely navigate low altitude airspace
Also working on the GNSS receiver front is the GEODESY project. The Fundamental Elements supported project has developed a multi-constellation, multi-frequency Galileo GNSS receiver that will help drones safely navigate the low altitude airspace that defines most urban areas.
Learn how GEODESY supports drones achieving robuts navigation performances.
The receiver, which uses both the Galileo OSNMA and HAS, is designed to achieve robust navigation performance, as well as critical technical and operational requirements.
The project also added integrity features into the navigation system.
That system was recently tested on two drones, one fixed-wing and one rotary-wing, at the ATLAS experimental flight centre, during which the GNSS receiver was able to achieve such key operations as automatic take-offs and landings.
Addressing IAM’s safety and security issues
Addressing the safety and security of IAM applications that rely on Position Navigation and Time (PNT) technologies powered by EGNSS is GAUSSIAN. The Horizon Europe funded project aims to demonstrate how combining the authenticated Galileo signals with integrated GNSS/INS platforms will result in greater robustness against spoofing attempts and the better continuity and availability of PNT data in constrained environments.
“GAUSSIAN wants to mitigate some of the security risks and concerns that originate from the real needs of flight operators, and we want to do so by leveraging advances in existing PNT technologies,” explains GAUSSIAN project coordinator Daniele Stopponi.
The project also intends to use the Precise Point Positioning (PPP)-RTK corrections provided by the Galileo HAS to help improve PNT data accuracy.
“Starting with existing concepts, prototypes and components developed by different companies, we are focused on creating new integrated and certified products for the rapidly evolving advanced air mobility market,” adds Stopponi.
Thanks to the work being done by GAUSSIAN, along with that of the DEGREE and GEODESY projects, IAM and aerial operations are on track to not only take off, but to do so in a way that will make air transport safer, quieter and more sustainable.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
20240405 - volné místo – Vedoucí OPV k nemovitostem KP Žatec na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
4.4.2024 14:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Žatec zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa představeného - Vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20240405 - volné místo – Vedoucí OPV k nemovitostem KP Žatec na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
4.4.2024 14:11 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Zatec/O-uradu/Aktuality/20240405-volne-misto-–-Vedouci-OPV-k-nemovitostem20240405 - volné místo – Vedoucí OPV k nemovitostem KP Žatec na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
4.4.2024 14:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20240405-volne-misto-–-Vedouci-OPV-k-nemovitostem20240405 - volné místo – Vedoucí OPV k nemovitostem KP Žatec na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
4.4.2024 14:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Žatec zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa představeného - Vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký krajVedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřadu
4.4.2024 14:03 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vedouci-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemovitostem-KaVedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřadu
4.4.2024 14:03 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Žatec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřaduVedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřadu
4.4.2024 14:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Žatecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vedoucí oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Žatec na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Moravian Geographical Report [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
4.4.2024 13:30 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Vyšlo první číslo ročníku 2024.All eyes on the Arctic Weather Satellite
4.4.2024 11:50 ESA Observing the Earth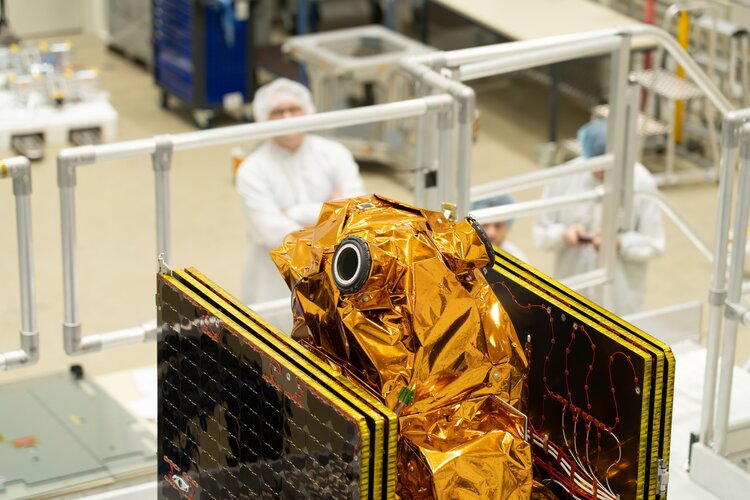
ESA’s new Arctic Weather Satellite has taken centre stage at OHB’s facilities in Stockholm, Sweden, before the spacecraft is packed up and shipped to California, US, for a launch currently scheduled for June.
Embracing the New Space approach to demonstrate new concepts in a cost-effective and timely manner, the Arctic Weather Satellite has been designed to show how it can improve weather forecasts in the Arctic.
Vše o produktech Autodesk 2025: Průvodce novinkami
4.4.2024 9:19 Adeon
S příchodem nového roku přináší Autodesk řadu aktualizací pro své klíčové produkty, otevírající dveře k novým možnostem ve světě designu, […]
The post Vše o produktech Autodesk 2025: Průvodce novinkami appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Vše o produktech Autodesk 2025: Průvodce novinkami
4.4.2024 9:19 Adeon
S příchodem nového roku přináší Autodesk řadu aktualizací pro své klíčové produkty, otevírající dveře k novým možnostem ve světě designu, […]
The post Vše o produktech Autodesk 2025: Průvodce novinkami appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Vše o produktech Autodesk 2025: Průvodce novinkami
4.4.2024 9:19 AdeonS příchodem nového roku přináší Autodesk řadu aktualizací pro své klíčové produkty, otevírající dveře k novým možnostem ve světě designu, […]
The post Vše o produktech Autodesk 2025: Průvodce novinkami appeared first on Adeon CZ.
GISáček 2024
4.4.2024 8:36 GISportal.cz
Katedra geoinformatiky VŠB-TU Ostrava zve na tradiční studentskou konferenci GISáček, která je určená studentům vysokých škol, kteří zde mají možnost prezentovat výsledky svých odborných studentských prací. Vstup je zdarma jak pro vystupující, tak pro posluchače. Studentská konference je soutěžní, je otevřená pro všechny studenty bakalářských a magisterských programů všech vysokých škol v České a Slovenské […]
The post GISáček 2024 appeared first on GISportal.cz.
GISáček 2024
4.4.2024 8:36 GISportal.cz
Katedra geoinformatiky VŠB-TU Ostrava zve na tradiční studentskou konferenci GISáček, která je určená studentům vysokých škol, kteří zde mají možnost prezentovat výsledky svých odborných studentských prací. Vstup je zdarma jak pro vystupující, tak pro posluchače. Studentská konference je soutěžní, je otevřená pro všechny studenty bakalářských a magisterských programů všech vysokých škol v České a Slovenské […]
The post GISáček 2024 appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Okno do praxe 2024
4.4.2024 8:15 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucHledáte svou cestu v budoucí kariéře? Navštivte veletrh pracovních příležitostí Okno do praxe, který pro vás pořádá Přírodovědecká fakulta a Kariérní centrum UP! 9. dubna 2024 10:00 – 15:00 Přírodovědecká fakulta Seznamte se s potenciálními zaměstnavateli a získejte výhody, které vám otevřou dveře na trhu práce. Mezi vystavovateli je hned několik IT i GIS firem […]
The post Okno do praxe 2024 first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Seznam k. ú. s probíhající obnovou operátu a revizemi katastru v působnosti KP Opava 2024
4.4.2024 8:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Opava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální pracoviště Opava informuje vlastníky a jiné oprávněné a zároveň odbornou veřejnost, že v rámci jeho územní působnosti probíhá obnova operátu novým mapováním a je prováděna revize údajů katastru nemovitostí.Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající obnovou katastrálního operátu novým mapováním v roce 2024:
Jakartovice,
Košetice ve Slezsku,
Leskovec u Vítkova,
Malé Heraltice,
Skrochovice,
Štítina.
Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající revizí údajů katastru v roce 2024:
Bohuslavice u Hlučína,
Hněvošice,
Jezdkovice,
Ludgeřovice,
Suché Lazce,
Šilheřovice,
Závada u Hlučína.
Podrobnosti k jednotlivým činnostem jsou uvedeny v oznámeních na úředních deskách obecního úřadu a katastrálního pracoviště.
Seznam k. ú. s probíhající obnovou operátu a revizemi katastru v působnosti KP Opava 2024
4.4.2024 8:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Opava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální pracoviště Opava informuje vlastníky a jiné oprávněné a zároveň odbornou veřejnost, že v rámci jeho územní působnosti probíhá obnova operátu novým mapováním a je prováděna revize údajů katastru nemovitostí.Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající obnovou katastrálního operátu novým mapováním v roce 2024:
Jakartovice,
Košetice ve Slezsku,
Leskovec u Vítkova,
Malé Heraltice,
Skrochovice,
Štítina.
Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající revizí údajů katastru v roce 2024:
Bohuslavice u Hlučína,
Hněvošice,
Ludgeřovice,
Opava-Město,
Služovice,
Suché Lazce,
Šilheřovice,
Závada u Hlučína.
Podrobnosti k jednotlivým činnostem jsou uvedeny v oznámeních na úředních deskách obecního úřadu a katastrálního pracoviště.
Seznam k. ú. s probíhající obnovou operátu a revizemi katastru v působnosti KP Opava 2024
4.4.2024 8:11 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Opava/O-uradu/Aktuality/Seznam-k-u-s-probihajici-obnovou-operatu-a-revizemSeznam k. ú. s probíhající obnovou operátu a revizemi katastru v působnosti KP Opava 2024
4.4.2024 8:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Opava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální pracoviště Opava informuje vlastníky a jiné oprávněné a zároveň odbornou veřejnost, že v rámci jeho územní působnosti probíhá obnova operátu novým mapováním a je prováděna revize údajů katastru nemovitostí.Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající obnovou katastrálního operátu novým mapováním v roce 2024:
Jakartovice,
Košetice ve Slezsku,
Leskovec u Vítkova,
Malé Heraltice,
Skrochovice,
Štítina.
Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající revizí údajů katastru v roce 2024:
Bohuslavice u Hlučína,
Hněvošice,
Kylešovice,
Ludgeřovice,
Opava-Město,
Služovice,
Suché Lazce,
Závada u Hlučína.
Podrobnosti k jednotlivým činnostem jsou uvedeny v oznámeních na úředních deskách obecního úřadu a katastrálního pracoviště.
Seznam k. ú. s probíhající obnovou operátu a revizemi katastru v působnosti KP Opava 2024
4.4.2024 8:11 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Opava/O-uradu/Aktuality/Seznam-k-u-s-probihajici-obnovou-operatu-a-revizemSeznam k. ú. s probíhající obnovou operátu a revizemi katastru v působnosti KP Opava 2024
4.4.2024 8:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Opava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální pracoviště Opava informuje vlastníky a jiné oprávněné a zároveň odbornou veřejnost, že v rámci jeho územní působnosti probíhá obnova operátu novým mapováním a je prováděna revize údajů katastru nemovitostí.Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající obnovou katastrálního operátu novým mapováním v roce 2024:
Jakartovice,
Košetice ve Slezsku,
Malé Heraltice,
Skrochovice,
Štítina.
Seznam katastrálních území s probíhající revizí údajů katastru v roce 2024:
Bohuslavice u Hlučína,
Hlučín,
Jelenice,
Jilešovice,
Kylešovice,
Ludgeřovice,
Opava-Město,
Služovice,
Suché Lazce,
Závada u Hlučína.
Podrobnosti k jednotlivým činnostem jsou uvedeny v oznámeních na úředních deskách obecního úřadu a katastrálního pracoviště.
ISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1
3.4.2024 20:49 Společnost pro fotogrammetrii a dálkový průzkumISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1
The post ISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1 appeared first on SFDP.
ISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1
3.4.2024 20:49 Společnost pro fotogrammetrii a dálkový průzkum ISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1ISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1
3.4.2024 20:49 Společnost pro fotogrammetrii a dálkový průzkum ISPRS e-bulletin: 2024 – Issue No.1Saharan dust plume
3.4.2024 15:40 ESA Observing the Earth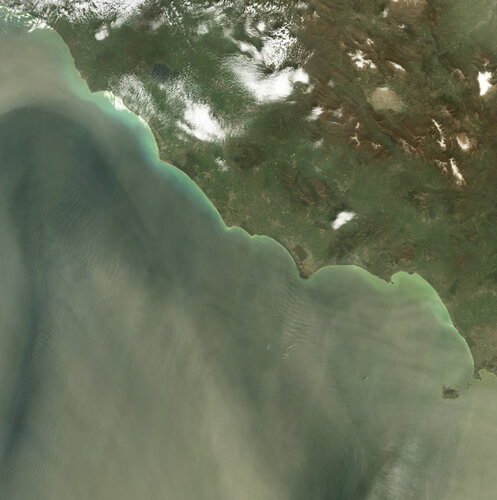 Image:
Images from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission show a large dust storm originating from the Sahara Desert that has engulfed skies across the central Mediterranean Basin.
Image:
Images from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission show a large dust storm originating from the Sahara Desert that has engulfed skies across the central Mediterranean Basin.
Uzavření budovy na celý den v úterý 16.dubna
3.4.2024 13:36 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucZ důvodu servisních prací na přípojce vodovodu dojde v úterý 16. 4. 2024 k uzavření naší budovy a tedy i katedry po celý den. Veškerá výuka bude převedena do online formy. Organizační podrobnosti sdělí příslušný vyučující.
The post Uzavření budovy na celý den v úterý 16.dubna first appeared on Katedra geoinformatiky.















