zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Břeclav
17.5.2023 7:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vrchni-referent-rada-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-na-Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Břeclav
17.5.2023 7:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Břeclav vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti BřeclavRada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu 1
17.5.2023 7:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu 1
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu 1
17.5.2023 7:35 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odbor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu 1Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu 1
17.5.2023 7:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-vedouci-oddeleni-obnovy-katastÚspěchy na soutěži Gisáček 2023
17.5.2023 6:56 Katedra geoinformatiky UP Olomouc Musíme se pochlubit dalším úspěchem našich studentů, tentokrát na soutěži Gisáček 2023! V kategorii bakalářských prací se stal vítězem Martin Kukrál 😊 Magisterskou sekci ovládla Michaela Vojtěchovská a na druhém místě se umístil Michal Plánka🙃 Děkujeme a gratulujeme 🥳Úspěchy na soutěži Gisáček 2023
17.5.2023 6:56 Katedra geoinformatiky UP Olomouc Musíme se pochlubit dalším úspěchem našich studentů, tentokrát na soutěži Gisáček 2023! V kategorii bakalářských prací se stal vítězem Martin Kukrál 😊 Magisterskou sekci ovládla Michaela Vojtěchovská a na druhém místě se umístil Michal Plánka🙃 Děkujeme a gratulujeme 🥳Úspěchy na soutěži Gisáček 2023
17.5.2023 6:56 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucMusíme se pochlubit dalším úspěchem našich studentů, tentokrát na soutěži Gisáček 2023! V kategorii bakalářských prací se stal vítězem Martin Kukrál 😊 Magisterskou sekci ovládla Michaela Vojtěchovská a na druhém místě se umístil Michal Plánka🙃 Děkujeme a gratulujeme 🥳
The post Úspěchy na soutěži Gisáček 2023 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Tomáš Miniberger v Rozstřelu na iDNES.cz
17.5.2023 2:00 VARS.czGenerální ředitel VARS BRNO Tomáš Miniberger byl hostem pořadu Rozstřel na iDNES.cz. Okomentoval aktuální návrhy aktivistů požadujících snížení rychlosti v Praze a věnoval se i situaci okolo rekonstrukce Barrandovského mostu.
GISáček 2023 – výsledky studentské soutěže, pořádané od roku 1998
16.5.2023 14:01 GeoBusinessV Ostravě se 12. května sešli studenti a studentky ze všech vysokých škol a univerzit, kde se učí geoinformatika/geomatika, členové odborné komise a zástupci firem. Konal se 26. ročník studentské soutěže GISáček. Katedra geoinformatiky na VŠB – TU Ostrava tuto soutěž pořádá již od roku 1998. Pokud byste chtěli nahlédnout do výsledků předchozích ročníků, tak […]
The post GISáček 2023 – výsledky studentské soutěže, pořádané od roku 1998 appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Výběrové řízení na pozici rada / odborný rada - metodik KN v oddělení metodiky, kontroly a personal
16.5.2023 13:39 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Výběrové řízení na pozici rada / odborný rada - metodik KN v oddělení metodiky, kontroly a personalVýběrové řízení na pozici rada / odborný rada - metodik KN v oddělení metodiky, kontroly a personal
16.5.2023 13:39 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj kancelář ředitelevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Výběrové řízení na pozici rada / odborný rada - metodik KN v oddělení metodiky, kontroly a personalistiky kanceláře ředitele
Výběrové řízení na pozici rada / odborný rada - metodik KN v oddělení metodiky, kontroly a personal
16.5.2023 13:39 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vyberove-rizeni-na-pozici-rada-odborny-rada-metodiProdej 120 kusů betonových patek
16.5.2023 12:51 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Prodej-120-kusu-betonovych-patek-(2)Prodej 120 kusů betonových patek
16.5.2023 12:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Prodej 120 kusů betonových patek
Rada/odborný rada - inspektor - vedení SPI a SGI
16.5.2023 11:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Liberci/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-inspektor-vedeni-SPI-a-SGIobnovaRada/odborný rada - inspektor - vedení SPI a SGI
16.5.2023 11:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Libercivypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada - inspektor - vedení SPI a SGI
Rada/odborný rada - inspektor - vedení SPI a SGI
16.5.2023 11:07 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Liberci vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada - inspektor - vedení SPI a SGIRada/odborný rada - inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Liberci
16.5.2023 10:50 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Liberci vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada - inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v LiberciRada/odborný rada - inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Liberci
16.5.2023 10:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Libercivypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada - inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Liberci
Rada/odborný rada - inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Liberci
16.5.2023 10:50 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Liberci/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-inspektor-Zememerickeho-a-katastRada/odborný rada - inspektor Zeměměřického a katastrálního inspektorátu v Liberci
16.5.2023 10:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Libercivypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada - inspektor - obnova katastrálního operátu a revize katastru
GISáček 2023 (výsledky)
16.5.2023 9:27 GISportal.cz
12. května se na VŠB-TUO konala tradiční soutěž/konference GISáček, která je určená studentům vysokých škol, kteří zde mají možnost prezentovat výsledky svých odborných studentských prací. Každoročně se zde setkávají studenti z Česka i Slovenska, aby prezentovali širokou paletu využití geoinformatiky v jejich kvalifikačních pracích. Letos obě kategorie – bakalářskou i magisterskou/inženýrskou oponovali studenti z olomoucké geoinformatiky, […]
The post GISáček 2023 (výsledky) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
GISáček 2023 (výsledky)
16.5.2023 9:27 GISportal.cz
12. května se na VŠB-TUO konala tradiční soutěž/konference GISáček, která je určená studentům vysokých škol, kteří zde mají možnost prezentovat výsledky svých odborných studentských prací. Každoročně se zde setkávají studenti z Česka i Slovenska, aby prezentovali širokou paletu využití geoinformatiky v jejich kvalifikačních pracích. Letos obě kategorie – bakalářskou i magisterskou/inženýrskou oponovali studenti z olomoucké geoinformatiky, […]
The post GISáček 2023 (výsledky) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Coming Soon by Way of Redefining 3D Reconstruction, the Lixel X1 SLAM Scanner
16.5.2023 3:32 Satlab Geosolutions Get full details of Lixel X1 on 18 May 2023 at 10:00 AM (CET)Autodesk Fusion 360 v akci – získejte 3, zaplaťte 2
16.5.2023 0:00 Arkance SystemsAkce "Získejte 3, zaplaťte 2". Nové roční předplatné 3D CAD/CAM produktu s výraznou slevou. Až do 6. června 2023.
Zpráva Autodesk Fusion 360 v akci – získejte 3, zaplaťte 2 pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Autodesk Fusion 360 v akci – získejte 3, zaplaťte 2
16.5.2023 0:00 Arkance SystemsAkce "Zaplaťte 2 - získejte 3". Pořiďte si nové roční předplatné oblíbeného 3D CAD/CAM produktu s výraznou slevou. Až do do 6. června 2023.
Zpráva Autodesk Fusion 360 v akci – získejte 3, zaplaťte 2 pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Autodesk Fusion 360 v akci – získejte 3, zaplaťte 2
16.5.2023 0:00 Arkance SystemsAkce "Získejte 3, zaplaťte 2". Nové roční předplatné 3D CAD/CAM produktu s výraznou slevou. Až do 6. července 2023.
Zpráva Autodesk Fusion 360 v akci – získejte 3, zaplaťte 2 pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Safeguarding space infrastructure
15.5.2023 14:45 European GNSS Agency
Space traffic is a pressing issue. With over 20.000 satellites expected to be launched in the next decade, various orbits are becoming increasingly congested. The situation is especially pronounced in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
The abundance of satellites is not only responsible for "an unprecedented space traffic jam". It is also the cause of a large amount of space debris, or ‘’junk’’, which is increasing at an alarming rate. According to the Directorate General for Defence Industry and Space (DG DEFIS), over 1 million debris items larger than 1cm are currently orbiting the Earth.
When we talk about space debris, we often refer to large objects, such as dead satellites, that have either failed or not been moved to their designated ‘’graveyard orbit’’. But space debris can also be any manmade object in space, ranging from small cables and screws that have fallen off a rocket to actual rocket components. While some debris (in LEO) may re-enter the atmosphere after some years and burn up, large part will remain in orbit for hundreds, or even thousands of years.
Space debris can go on to cause further damage, potentially taking out functioning satellites. What’s more, the collision of space debris with satellites, operational or not, creates even more debris, thus further aggravating the problem.
In summer 2016, Copernicus Sentinel-1A satellite was hit by a millimetre-size particle in orbit causing only minor damage to one of the solar panels, fortunately not affecting the satellite’s performance.
The damages caused by larger pieces of debris to any navigation, communications and Earth Observation satellites could be irreversible and the repercussions will certainly affect us, end users down on Earth.

Before and after debris impacted the Sentinel-1A solar panel. Credits: European Space Agency (ESA)
Towards a unified approach in Space Traffic Management
As both space debris and congestion jeopardise the operation and security of the EU’s and Member States’ space assets, such as Galileo, Copernicus and EGNOS, the European Commission recently proposed an EU integrated approach to Space Traffic Management (EU STM). This holistic approach will secure long-term viability of space activities by ensuring that space remains a sustainable, safe and secure environment encompassing the means and the rules to access, conduct activities in, and return from outer space safely, sustainably and securely.
"It is of a geostrategic question to be able to monitor autonomously space and enhance our collective situational awareness of threats to European or national Space assets," remarked Commissioner for Internal Market Thierry Breton during the European Space Conference in 2023.
To ensure the adequate protection of its satellite infrastructure, the European Union has been relying on EU Space Surveillance and Tracking (EU SST) Partnership, which is the main operational pillar of STM.
The EU SST Partnership operates a network of ground-based sensors capable of surveying and tracking space objects, together with processing capabilities aiming to provide data, information and services on space objects that orbit the Earth.
Today, EU SST provides collision avoidance services to more than 390 satellites distributed in Low Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit and Geostationary Orbit using Member States’ civil and military assets that remain under the control of its Member States.
EUSPA to support the EU Space Traffic Management
As part of its expanded role in the Union Space Programme, and its expertise in service provision and security issues management, EUSPA will take responsibility for the Space Surveillance and Tracking (SST) service provision Front Desk as of July 1st, 2023.
"The EU SST Front Desk is a key interface for the delivery of SST information and services, including activities related to user coordination, service performance," says EUSPA Executive Director, Rodrigo da Costa. "Additionally, the SST Front Desk will be engaging with users and promoting the use of the SST services to further support the future of STM in the EU," he concludes.
The visit of the EU SST partnership Member States to EUSPA took place in this context, gathering all the representatives for a presentation of EUSPA and an exchange of views on future work.
"We are very pleased to visit EUSPA in Prague and we look forward to working with our future EU SST service provision front desk to support our growing user community" declared Pascal Faucher, Chairman, European Union Space Surveillance and Tracking Partnership, Defense and security, CNES. The responsibility is currently being transferred from the European Satellite Centre (SatCen), who currently operates the service, to EUSPA’s Galileo Security Monitoring Centre (GSMC) in Madrid.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Safeguarding space infrastructure
15.5.2023 14:45 European GNSS Agency
Space traffic is a pressing issue. With over 20.000 satellites expected to be launched in the next decade, various orbits are becoming increasingly congested. The situation is especially pronounced in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
The abundance of satellites is not only responsible for "an unprecedented space traffic jam". It is also the cause of a large amount of space debris, or ‘’junk’’, which is increasing at an alarming rate. According to the Directorate General for Defence Industry and Space (DG DEFIS), over 1 million debris items larger than 1cm are currently orbiting the Earth.
When we talk about space debris, we often refer to large objects, such as dead satellites, that have either failed or not been moved to their designated ‘’graveyard orbit’’. But space debris can also be any manmade object in space, ranging from small cables and screws that have fallen off a rocket to actual rocket components. While some debris (in LEO) may re-enter the atmosphere after some years and burn up, large part will remain in orbit for hundreds, or even thousands of years.
Space debris can go on to cause further damage, potentially taking out functioning satellites. What’s more, the collision of space debris with satellites, operational or not, creates even more debris, thus further aggravating the problem.
In summer 2016, Copernicus Sentinel-1A satellite was hit by a millimetre-size particle in orbit causing only minor damage to one of the solar panels, fortunately not affecting the satellite’s performance.
The damages caused by larger pieces of debris to any navigation, communications and Earth Observation satellites could be irreversible and the repercussions will certainly affect us, end users down on Earth.

Before and after debris impacted the Sentinel-1A solar panel. Credits: European Space Agency (ESA)
Towards a unified approach in Space Traffic Management
As both space debris and congestion jeopardise the operation and security of the EU’s and Member States’ space assets, such as Galileo, Copernicus and EGNOS, the European Commission recently proposed an EU integrated approach to Space Traffic Management (EU STM). This holistic approach will secure long-term viability of space activities by ensuring that space remains a sustainable, safe and secure environment encompassing the means and the rules to access, conduct activities in, and return from outer space safely, sustainably and securely.
"It is of a geostrategic question to be able to monitor autonomously space and enhance our collective situational awareness of threats to European or national Space assets," remarked Commissioner for Internal Market Thierry Breton during the European Space Conference in 2023.
To ensure the adequate protection of its satellite infrastructure, the European Union has been relying on EU Space Surveillance and Tracking (EU SST) Partnership, which is the main operational pillar of STM.
The EU SST Partnership operates a network of ground-based sensors capable of surveying and tracking space objects, together with processing capabilities aiming to provide data, information and services on space objects that orbit the Earth.
Today, EU SST provides collision avoidance services to more than 390 satellites distributed in Low Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit and Geostationary Orbit using Member States’ civil and military assets that remain under the control of its Member States.
EUSPA to support the EU Space Traffic Management
As part of its expanded role in the Union Space Programme, and its expertise in service provision and security issues management, EUSPA will take responsibility for the Space Surveillance and Tracking (SST) service provision Front Desk as of July 1st, 2023.
"The EU SST Front Desk is a key interface for the delivery of SST information and services, including activities related to user coordination, service performance," says EUSPA Executive Director, Rodrigo da Costa. "Additionally, the SST Front Desk will be engaging with users and promoting the use of the SST services to further support the future of STM in the EU," he concludes.
The visit of the EU SST partnership Member States to EUSPA took place in this context, gathering all the representatives for a presentation of EUSPA and an exchange of views on future work.
"We are very pleased to visit EUSPA in Prague and we look forward to working with our future EU SST service provision front desk to support our growing user community" declared Pascal Faucher, Chairman, European Union Space Surveillance and Tracking Partnership, Defense and security, CNES. The responsibility is currently being transferred from the European Satellite Centre (SatCen), who currently operates the service, to EUSPA’s Galileo Security Monitoring Centre (GSMC) in Madrid.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
20230515 - GaKO 5/2023
15.5.2023 13:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (5/2023) je k dispozici ke stažení.20230515 - GaKO 5/2023
15.5.2023 13:13 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (5/2023) je k dispozici ke stažení.20230515 - GaKO 5/2023
15.5.2023 13:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (5/2023) je k dispozici ke stažení.20230515 - GaKO 5/2023
15.5.2023 13:13 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (5/2023) je k dispozici ke stažení.
Nové číslo GaKO
15.5.2023 12:56
ÚGKK SR
Nové číslo časopisu Geodetického a Kartografického Obzoru 05/2023
Omezení provozu z důsledků přerušení elektřiny
15.5.2023 12:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vyškov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V DŮSLEDKU PŘERUŠENÍ DODÁVKY ELEKTŘINY BUDEPROVOZ KATASTRÁLNÍHO PRACOVIŠTĚ VYŠKOV DNE 31. 5. 2023
V DOBĚ OD 10:00 DO 12:00h
OMEZEN
Děkujeme za pochopení
Omezení provozu z důsledků přerušení elektřiny
15.5.2023 12:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Vyskov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Omezeni-provozu-z-dusledku-preruseni-elektrinyT-MAPY Semináře DTM - odborná setkání o Digitální technické mapě
15.5.2023 11:04 T-MAPYThe post T-MAPY Semináře DTM - odborná setkání o Digitální technické mapě appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
T-MAPY Semináře DTM - odborná setkání o Digitální technické mapě
15.5.2023 11:04 T-MAPYThe post T-MAPY Semináře DTM - odborná setkání o Digitální technické mapě appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
výběrové řízení na KP Jihlava
15.5.2023 11:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Jihlava zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada - oddělení aktualizace KN II Katastrálního pracoviště Jihlava na Katastrálním úřadu pro Vysočinu.výběrové řízení na KP Jihlava
15.5.2023 11:03 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/O-uradu/Aktuality/vyberove-rizeni-na-KP-Jihlava-(4)Odborný referentv oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č.3 na Technické sekci
15.5.2023 10:15 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj technická sekcevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referentv oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č.3 na Technické sekci
Odborný referentv oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č.3 na Technické sekci
15.5.2023 10:15 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referentv-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralniho-opOdborný referentv oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č.3 na Technické sekci
15.5.2023 10:15 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj technická sekce vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referentv oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č.3 na Technické sekciCivil Tools pro Autodesk Civil 3D – nová verze nadstavbové aplikace
15.5.2023 9:00 Arkance SystemsAplikace z vlastního vývoje nyní s podporou Autodesk Civil 3D 2024 a novou funkcí Filtr dle sad vlastností.
Zpráva Civil Tools pro Autodesk Civil 3D – nová verze nadstavbové aplikace pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
GaKO 5/2023
15.5.2023 0:01 GaKO GaKO 5/2023 ŘEZNÍČEK, J.: Výsledky přesných nivelací spojnic Základní geodynamické sítě ČR provedených v letech 2007 – 2021buildingSMART International Standards Summit, Rome, Italy 27 – 30 March 2023
13.5.2023 15:40 buildingSMART.orgThe buildingSMART International Standards Summit took place in Rome from March 27th to March 30th, 2023. The event brought together professionals from the international openBIM community to discuss and shape…
The post buildingSMART International Standards Summit, Rome, Italy 27 – 30 March 2023 appeared first on buildingSMART International.
Aktualizace podrobného popisu služeb k v. 1.4.3
13.5.2023 0:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální informuje, že k nainstalované nové verzi 1.4.3.1 IS DMVS na integračním prostředí INT1 byla v záložce Popis služeb aktualizována dokumentace Podrobného popisu služeb IS DMVS.On-line školení Trimble 3D Koridory
12.5.2023 15:33 GeotronicsGEODÉZIE - Připravili jsme pro Vás on-line školení Tvorba a využití 3D tras.
The post On-line školení Trimble 3D Koridory first appeared on GEOTRONICS Praha.
On-line školení Trimble 3D Koridory
12.5.2023 15:33 GeotronicsGEODÉZIE - Připravili jsme pro Vás on-line školení Tvorba a využití 3D tras.
The post On-line školení Trimble 3D Koridory first appeared on GEOTRONICS Praha.
DAEX DESIGN Standard v akční ceně
12.5.2023 15:20 ŠPINAR - software Vážení zákazníci, připravili jsme pro Vás DAEX DESIGN Standard pro výrobce a návrháře nábytku a interiérů v akční ceně s rozšiřujícími bonusy do 9. 9. 2023DAEX DESIGN Standard v akční ceně
12.5.2023 15:20 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci, připravili jsme pro Vás DAEX DESIGN Standard pro výrobce a návrháře nábytku a interiérů v akční ceně s rozšiřujícími bonusy do 9. 9. 2023
The post DAEX DESIGN Standard v akční ceně appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
rada/odborný rada - kontrola aktualizace - v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního p
12.5.2023 14:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-kontrola-aktualizace-v-oddeleni-rada/odborný rada - kontrola aktualizace - v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního p
12.5.2023 14:59 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Tábor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada - kontrola aktualizace - v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního prada/odborný rada - kontrola aktualizace - v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního p
12.5.2023 14:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Táborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada - kontrola aktualizace - v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Tábor (ID SM 30000315/30003939)
Online konference Autodesk LIVE 2024 – děkujeme za účast
12.5.2023 12:17 Arkance SystemsPro registrované účastníky i nové zájemce je nyní k dispozici kompletní archiv s videozáznamem všech prezentací.
Zpráva Online konference Autodesk LIVE 2024 – děkujeme za účast pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Here’s How SatLab Explored In Ocean Business 2023
12.5.2023 11:55 Satlab Geosolutions SatLab Integrated Marine System displayed comprehensive industrial solutions in Ocean Business 2023.Výsledky soutěže Mapa roku 2022
12.5.2023 10:25 GeoBusinessVe středu 3. května 2023 byly v Praze vyhlášeny výsledky 25. ročníku kartografické soutěže Mapa roku. Česká kartografická společnost, která je každoročním pořadatelem soutěže, prostřednictvím soutěže oceňuje kvalitní mapová díla, vytvořená a vydaná na území České republiky. Vítězové kategorií Kategorie Atlasy, soubory a edice map Česká geologická služba za dílo Geology, Soil Environment and Hydrogeology […]
The post Výsledky soutěže Mapa roku 2022 appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Earth from Space: Nishinoshima island, Japan
12.5.2023 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth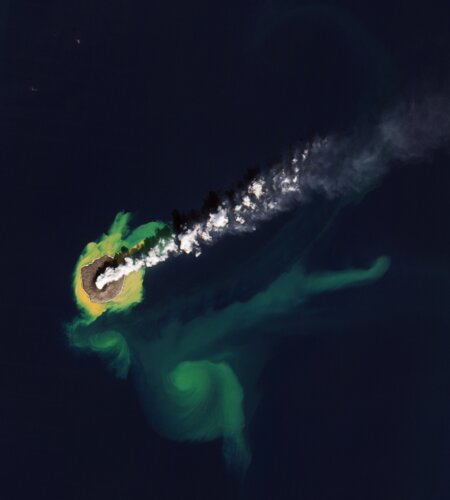 Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features the Japanese island of Nishinoshima, in the northwest Pacific Ocean.
Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features the Japanese island of Nishinoshima, in the northwest Pacific Ocean.
rada/odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Strakonice (ID SM 30000
12.5.2023 7:45 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Strakonice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Strakonice (ID SM 30000rada/odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Strakonice (ID SM 30000
12.5.2023 7:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-vedouci-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-rada/odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Strakonice (ID SM 30000
12.5.2023 7:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Strakonicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada - vedoucí oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Strakonice (ID SM 30000301/30003925)
APGEO - Pozvánka na 10. setkání geodetů Jihočeského kraje
12.5.2023 2:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice 10. setkání geodetů Jihočeského kraje se uskuteční 8. června 2023 v prostorách VŠTE v Českých Budějovicích.monitory HP Compaq LA1951g LCD
11.5.2023 14:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Nabidky-majetku/monitory-HP-Compaq-LA1951g-LCDmonitory HP Compaq LA1951g LCD
11.5.2023 14:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Havlíčkův Brod nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
monitory HP Compaq LA1951g LCD
Monitoring fluctuating forest carbon from space
11.5.2023 12:31 ESA Observing the Earth
Monitoring fluctuating forest carbon from space
20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
11.5.2023 9:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN"20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
11.5.2023 9:52 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(10)20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
11.5.2023 9:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(9)20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
11.5.2023 9:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN"Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
11.5.2023 9:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
11.5.2023 9:27 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN
11.5.2023 9:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN"20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení dokumentace KN
11.5.2023 9:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(5)dopis uozi
11.5.2023 9:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ve Sbírce zákonů byl zveřejněn zákon č. 88/2023 Sb., kterým se mění zákon č. 200/1994 Sb., o zeměměřictví.Novela zákona má mimo jiné dopad na činnosti úředně oprávněných zeměměřických inženýrů.
Viz odkaz dopis ÚOZI.
dopis uozi
11.5.2023 9:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/dopis-uoziKomunální veletrh v Olomouci
10.5.2023 18:42 TopGis Příští týden začíná Komunální veletrh v Olomouci, který je určený pro odborníky z řad měst a obcí včetně příspěvkových organizací a spolků. Neváhejte navštívit náš stánek, kde budete mít možnost seznámit se s nejnovějšími trendovými produkty a řešeními, které vám umožní efektivněji pracovat s daty, vizualizovat geografické informace a provádět komplexní analýzy pro lepší rozhodování.27. jednání KRS
10.5.2023 18:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 31. května 2023 proběhne distančně 27. jednání Koordinační rady správců DMVS a DTM.Surveying & Engineering
10.5.2023 16:44 Satlab Geosolutions Together with professional data processing and analysis software, SatLab’s advanced surveying products and industry solutions provide accurate measurements and positioning of physical features for civil engineering, land surveying, topographical surveying, hydrographic surveying, and mine surveying.Surveying & Engineering
10.5.2023 16:44 Satlab GeosolutionsTogether with professional data processing and analysis software, SatLab’s advanced surveying products and industry solutions provide accurate measurements and positioning of physical features for civil engineering, land surveying, topographical surveying, hydrographic surveying, and mine surveying.
The post Surveying & Engineering appeared first on Global Satellite Positioning Solutions | SatLab Geosolutions AB.
Komunální veletrh v Olomouci
10.5.2023 16:42 TopGisPříští týden začíná Komunální veletrh v Olomouci, který je určený pro odborníky z řad měst a obcí včetně příspěvkových organizací a spolků. Neváhejte navštívit náš stánek, kde budete mít možnost seznámit se s nejnovějšími trendovými produkty a řešeními, které vám umožní efektivněji pracovat s daty, vizualizovat geografické informace a provádět komplexní analýzy pro lepší ...
Článek Komunální veletrh v Olomouci se nejdříve objevil na TopGis, s.r.o..
Komunální veletrh v Olomouci
10.5.2023 16:42 TopGisPříští týden začíná Komunální veletrh v Olomouci, který je určený pro odborníky z řad měst a obcí včetně příspěvkových organizací a spolků. Neváhejte navštívit náš stánek, kde budete mít možnost seznámit se s nejnovějšími trendovými produkty a řešeními, které vám umožní efektivněji pracovat s daty, vizualizovat geografické informace a provádět komplexní analýzy pro lepší ...
Článek Komunální veletrh v Olomouci se nejdříve objevil na TopGis, s.r.o..
Komunální veletrh v Olomouci
10.5.2023 16:42 TopGisPříští týden začíná Komunální veletrh v Olomouci, který je určený pro odborníky z řad měst a obcí včetně příspěvkových organizací a spolků. Neváhejte navštívit náš stánek, kde budete mít možnost seznámit se s nejnovějšími trendovými produkty a řešeními, které vám umožní efektivněji pracovat s daty, vizualizovat geografické informace a provádět komplexní analýzy pro lepší ...
Článek Komunální veletrh v Olomouci se nejdříve objevil na TopGis, s.r.o..
Arkance Systems nově otevírá certifikační kurzy buildingSMART
10.5.2023 13:54 Arkance SystemsZkušení lektoři vám nabízí nový vzdělávací program, který vás připraví na certifikaci buildingSMART - Foundation - Basic.
Zpráva Arkance Systems nově otevírá certifikační kurzy buildingSMART pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Arkance Systems nově otevírá certifikační kurzy buildingSMART
10.5.2023 13:54 Arkance SystemsZkušení lektoři pro vás připravili novou nabídku vzdělávacího programu, který vás připraví na certifikaci buildingSMART - Foundation - Basic.
Zpráva Arkance Systems nově otevírá certifikační kurzy buildingSMART pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Pozvánka na mezinárodní DPZ školení
10.5.2023 7:52 GISportal.cz
Pozvánka na mezinárodní DPZ trénink Trans-Atlantic Training (TAT) 2023. „Remote sensing for environmental monitoring and modelling“, který se koná 27.června – 1. července 2023 v Praze a Brně a je společně organizován Univerzitou Karlovou, Masarykovou univerzitou, ESA a NASA. Hlavním cílem Trans-Atlantic Training jsou vzdělávací aktivity pro studenty a začínající vědce v oblasti dálkového průzkumu […]
The post Pozvánka na mezinárodní DPZ školení appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Pozvánka na mezinárodní DPZ školení
10.5.2023 7:52 GISportal.cz
Pozvánka na mezinárodní DPZ trénink Trans-Atlantic Training (TAT) 2023. „Remote sensing for environmental monitoring and modelling“, který se koná 27.června – 1. července 2023 v Praze a Brně a je společně organizován Univerzitou Karlovou, Masarykovou univerzitou, ESA a NASA. Hlavním cílem Trans-Atlantic Training jsou vzdělávací aktivity pro studenty a začínající vědce v oblasti dálkového průzkumu […]
The post Pozvánka na mezinárodní DPZ školení appeared first on GISportal.cz.
INT1 opět dostupné
10.5.2023 7:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníČeský úřad zeměměřický a katastrální informuje, že integrační prostředí INT1 IS DMVS je opět dostupné, instalace nové verze 1.4.3.1 informačního systému byla dokončena.
Pořádali jsem český stánek na největší světové akci na drony na Xponential 2023 v Denveru
9.5.2023 20:58 UAVATento týden se koná v Denveru v USA největší světová akce zaměřená na drony a autonomní systémy Xponential 2023, kde nemůžeme chybět s českým stánkem s Dronetag, UpVision, Workswell a Modelárna LIAZ. Současně jsme měli prezentaci v Solution Theatre, kde jsme představili český průmysl a výzkum s drony a české firmy Dronetag, LIAZ, UpVision a […]
The post Pořádali jsem český stánek na největší světové akci na drony na Xponential 2023 v Denveru appeared first on UAV Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl.
Lidaretto umožňuje geodetům udělat svoji práci rychleji, říká Erik Frohmann, tvůrce univerzálního skenovacího systému
9.5.2023 16:36 ZeměměřičNa základě svých vlastních zkušeností s měřením v terénu začala firma Geotech Bratislava před lety vyvíjet svůj vlastní skener Lidaretto. Ten má v sobě nejmodernější a nejpřesnější součástky, které jsou na trhu. Díky tomu má Lidaretto geodetickou přesnost. Dnes systém používají také čeští geodeti. A slova „lidar“ se lekat nemusíte – je to korektní název pro laserový skener. Erik […]
The post Lidaretto umožňuje geodetům udělat svoji práci rychleji, říká Erik Frohmann, tvůrce univerzálního skenovacího systému appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Geodeti chtějí zakázku udělat rychleji a levněji než jiná firma, říká Erik Frohmann, tvůrce systému Lidaretto
9.5.2023 16:36 ZeměměřičNa základě svých vlastních zkušeností s měřením v terénu začala firma Geotech Bratislava před lety vyvíjet svůj vlastní skener Lidaretto. Ten má v sobě nejmodernější a nejpřesnější součástky, které jsou na trhu. Díky tomu má Lidaretto geodetickou přesnost. Dnes systém používají také čeští geodeti. A slova „lidar“ se lekat nemusíte – je to korektní název pro laserový skener. Erik […]
The post Geodeti chtějí zakázku udělat rychleji a levněji než jiná firma, říká Erik Frohmann, tvůrce systému Lidaretto appeared first on Zeměměřič.
20230510 - volné místo - Odborný referent v OD katastru nemovitostí KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
9.5.2023 14:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Litomerice/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230510-volne-misto-Odborny-referent-v-OD-katastr20230510 - volné místo - Odborný referent v OD katastru nemovitostí KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
9.5.2023 14:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230510 - volné místo - Odborný referent v OD katastru nemovitostí KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
9.5.2023 14:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230510 - volné místo - Odborný referent v OD katastru nemovitostí KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
9.5.2023 14:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230510-volne-misto-Odborny-referent-v-OD-katastrHappy Europe Day!
9.5.2023 12:25 European GNSS Agency
Today, the EU and its citizens celebrate the signing of the Schuman Declaration, the historic agreement that laid the foundation for a united Europe and planted the seeds to what would evolve into the European Union.
A lot has been achieved in the seven decades since the declaration was signed on 9 May 1950. For example, we’ve established the freedom of movement for EU citizens, built one of the world’s biggest single markets and even won a Nobel Peace Prize. We continue to protect our citizens with robust consumer protection laws and are on our way to becoming the world’s first climate neutral continent.
We also built an independent space programme that is both competitive and innovative and that delivers real benefits to citizens and businesses alike. “The data and services provided by the EU Space Programme support EU interests and goals like the Green Deal and Digital Transformation and are indispensable to the daily lives of Europeans,” says EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
A comprehensive EU Space Programme
Over 4 billion people currently use Galileo, the world’s most precise positioning system, while many governments, national agencies, institutions, researchers and businesses are leveraging the information coming from Copernicus, the world’s best Earth Observation system.
The EU Space Programme also includes EGNOS, Europe's regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) that is used to improve the accuracy and reliability of GNSS positioning information. Originally designed to benefit aviation, EGNOS has revolutionised the way we fly – creating greater access to small and regional airports, increasing safety and facilitating more efficient and sustainable flight routes across Europe.
Rounding out the EU Space Programme are Space Situational Awareness (SSA), which provides comprehensive knowledge about space hazards, and the forthcoming GOVSATCOM, which aims to provide secure and cost-efficient communication capabilities to security and safety critical missions and operations.
The latest addition is IRIS2 (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity and Security by Satellite). The new satellite constellation will provide secure communication services to the EU and its Member States as well as broadband connectivity for European citizens, private companies and governmental authorities. Initial services are expected to launch next year, with full operational capability happening by 2027.
The link between space technology and user needs
Not only is Europe Day an opportunity to celebrate the achievement that is the EU Space Programme, it also coincides with EUSPA’s anniversary. Established two years ago as the European Union’s only agency dedicated to space, EUSPA serves as the essential link between space technology and user needs.
In addition to implementing the EU Space Programme, EUSPA is responsible for providing reliable, safe and secure space-related services and maximising their socio-economic benefits for all of society. By fostering the development of innovative and competitive upstream and downstream sectors and by engaging with the entire EU Space community, EUSPA helps drive innovation-based growth across the European economy. It also contributes to the safety of EU citizens, the security of the Union and its Member States and reinforces the EU’s strategic autonomy.
“At the heart of our work is a commitment to support an innovative and competitive EU space sector, ensuring that space continues to drive innovation-based growth in Europe and deliver services and applications that meet the challenges of both today and tomorrow,” adds da Costa.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Hydrography & Bathymetry
9.5.2023 10:44 Satlab GeosolutionsTaking advantage of the innovative underwater acoustic positioning systems and sonar technologies, SatLab’s marine products provide higher-resolution data for sand volume calculation, water flow measurement, flood assessments, safe navigation, and potential underwater project developments in terms of accuracy and reliability, and further to make contributions in water resources management, water ecological restoration and water environmental protection.
The post Hydrography & Bathymetry appeared first on Global Satellite Positioning Solutions | SatLab Geosolutions AB.
Hydrography & Bathymetry
9.5.2023 10:44 Satlab Geosolutions Taking advantage of the innovative underwater acoustic positioning systems and sonar technologies, SatLab’s marine products provide higher-resolution data for sand volume calculation, water flow measurement, flood assessments, safe navigation, and potential underwater project developments in terms of accuracy and reliability, and further to make contributions in water resources management, water ecological restoration and water environmental protection.20230509_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.5.2023 10:34 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Benesov/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(4)20230509_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.5.2023 10:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Benešov Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem"Autodesk Forma – cloudová aplikace s prvky AI nahrazuje Spacemaker
9.5.2023 10:21 Arkance SystemsPřichází nové cloudové řešení s automatizací, umělou inteligencí a dalšími funkcemi pro komplexní 3D BIM modelování chytrých měst.
Zpráva Autodesk Forma – cloudová aplikace s prvky AI nahrazuje Spacemaker pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Prodavač/ka v Obchodním oddělení
9.5.2023 9:16 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Prodavač/ka v Obchodním oddělení
Prodavač/ka v Obchodním oddělení
9.5.2023 9:16 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Prodavač/ka v Obchodním odděleníProdavač/ka v Obchodním oddělení
9.5.2023 9:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Volna-mista/DMS/Prodavac-ka-v-Obchodnim-oddeleniProdavač/ka v Obchodním oddělení
9.5.2023 9:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Prodavač/ka v Obchodním oddělení
Úspěch studentů na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023
9.5.2023 7:30 Katedra geoinformatiky UP Olomouc Gratulujeme našim studentům k excelentní reprezentaci na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023! Vyhráli a skvěle se umístili ve všech soutěžních kategoriích sekce Vědy o Zemi 🥳 Bakalářská kategorie: 1. Martin Kukrál (+2. místo v posterové sekci) 2. Jiří Vysloužil Magisterská kategorie: 1. Kateřina Bečicová 2. Michaela Vojtěchovská Doktorská kategorie: 1. Pavel Vyvlečka 2. Tereza Pohanková […]Úspěch studentů na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023
9.5.2023 7:30 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucGratulujeme našim studentům k excelentní reprezentaci na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023! Vyhráli a skvěle se umístili ve všech soutěžních kategoriích sekce Vědy o Zemi 🥳 Bakalářská kategorie: 1. Martin Kukrál (+2. místo v posterové sekci) 2. Jiří Vysloužil Magisterská kategorie: 1. Kateřina Bečicová 2. Michaela Vojtěchovská Doktorská kategorie: 1. Pavel Vyvlečka 2. Tereza Pohanková […]
The post Úspěch studentů na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Úspěch studentů na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023
9.5.2023 7:30 Katedra geoinformatiky UP Olomouc Gratulujeme našim studentům k excelentní reprezentaci na soutěži O cenu děkana 2023! Vyhráli a skvěle se umístili ve všech soutěžních kategoriích sekce Vědy o Zemi 🥳 Bakalářská kategorie: 1. Martin Kukrál (+2. místo v posterové sekci) 2. Jiří Vysloužil Magisterská kategorie: 1. Kateřina Bečicová 2. Michaela Vojtěchovská Doktorská kategorie: 1. Pavel Vyvlečka 2. Tereza Pohanková […]Geografické príspevky na eŠVK PriF UK 2023
8.5.2023 13:41 Geocommunity.skPríspevok Geografické príspevky na eŠVK PriF UK 2023 zobrazený najskôr GeoCommunity.sk.
Aeolus’ fiery demise to set standard for safe reentry
8.5.2023 13:08 ESA Observing the Earth
ESA’s wind mission, Aeolus, will soon be lowered in orbit leading to its fiery reentry and burn-up through Earth’s atmosphere. ESA’s efforts to ensure a safe return go well beyond international standards and place the Agency in the lead for space safety.
Vyhlášení soutěže mapa roku 2022 – výsledky a fotogalerie
7.5.2023 18:00 Česká kartografická společnostVe středu 3. května 2023 byly slavnostně vyhlášeny výsledky prestižní kartografické soutěže Mapa roku, letos 25. ročníku. Česká kartografická společnost oceňuje prostřednictvím soutěže kvalitní mapy a atlasy vydávané na území České republiky s celospolečenským přínosem. Ocenění MAPA ROKU 2022 obdržela v kategorii Atlasy, soubory a edice map Česká geologická služba za dílo Geology, Soil Environment and Hydrogeology of the Sidama […]
The post Vyhlášení soutěže mapa roku 2022 – výsledky a fotogalerie first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
Geografické príspevky na eŠVK PriF UK 2023
7.5.2023 13:41 Geocommunity.skPríspevok Geografické príspevky na eŠVK PriF UK 2023 zobrazený najskôr GeoCommunity.sk.
Electricity
7.5.2023 5:32 Satlab GeosolutionsBy integrating GNSS, cloud computing, big data, and LiDAR technologies, SatLab helps to achieve high precision time synchronization and ensure grid stability for intelligent grid infrastructure systems, eliminating the possibilities of safety hazards and unstable power control in remote control, monitoring, data collection, and other field operations.
The post Electricity appeared first on Global Satellite Positioning Solutions | SatLab Geosolutions AB.
Electricity
7.5.2023 5:32 Satlab Geosolutions By integrating GNSS, cloud computing, big data, and LiDAR technologies, SatLab helps to achieve high precision time synchronization and ensure grid stability for intelligent grid infrastructure systems, eliminating the possibilities of safety hazards and unstable power control in remote control, monitoring, data collection, and other field operations.DAEX DESIGN Standard pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy
5.5.2023 15:20 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci, připravili jsme pro Vás DAEX DESIGN Standard pro výrobce a návrháře nábytku a interiérů s rozšiřujícími bonusy do 21. 5. 2023
The post DAEX DESIGN Standard pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.



















