zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Výběrové řízení na pozici referent majetkové správy Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
26.5.2023 10:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Volna-mista/DMS/Vyberove-rizeni-na-pozici-referent-majetkove-spravVýběrové řízení na pozici referent majetkové správy Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
26.5.2023 10:47 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Výběrové řízení na pozici referent majetkové správy Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký krajEarth from Space: São Paulo, Brazil
26.5.2023 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Image:
This radar image from Copernicus Sentinel-1 shows the city of São Paulo and part of the homonymous state in southeast Brazil.
Image:
This radar image from Copernicus Sentinel-1 shows the city of São Paulo and part of the homonymous state in southeast Brazil.
Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023
25.5.2023 11:57 GEPRO29. ročník konference 20. a 21. září 2023 | Praha, hotel Olšanka Jménem společností GEPRO a ATLAS, ve spolupráci se společností EuroGV, vás srdečně zveme na 29. ročník konference Setkání uživatelů produktů a služeb společností GEPRO a ATLAS, který se bude konat ve dnech 20. a 21. září 2023 v hotelu Olšanka v Praze. Tato …
Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023 Pokračovat ve čtení »
Článek Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023 se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023
25.5.2023 11:57 GEPRO29. ročník konference 20. a 21. září 2023 | Praha, hotel Olšanka Jménem společností GEPRO a ATLAS, ve spolupráci se společností EuroGV, vás srdečně zveme na 29. ročník konference Setkání uživatelů produktů a služeb společností GEPRO a ATLAS, který se bude konat ve dnech 20. a 21. září 2023 v hotelu Olšanka v Praze. Tato …
Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023 Pokračovat ve čtení »
Článek Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023 se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023
25.5.2023 11:57 GEPRO29. ročník konference 20. a 21. září 2023 | Praha, hotel Olšanka Jménem společností GEPRO a ATLAS, ve spolupráci se společností EuroGV, vás srdečně zveme na 29. ročník konference Setkání uživatelů produktů a služeb společností GEPRO a ATLAS, který se bude konat ve dnech 20. a 21. září 2023 v hotelu Olšanka v Praze. Tato […]
Článek Konference GEPRO & ATLAS 2023 se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
20230526 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Chomutov na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
25.5.2023 11:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Chomutov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Chomutov na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230526 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Chomutov na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
25.5.2023 11:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Chomutov/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230526-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-v-O20230526 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Chomutov na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
25.5.2023 11:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Chomutov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Chomutov na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230526 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Chomutov na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
25.5.2023 11:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230526-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-v-OOdborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastr
25.5.2023 11:43 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Chomutovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Chomutov na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastr
25.5.2023 11:43 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-ak-(2)Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastr
25.5.2023 11:43 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Chomutov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí KatastrAn improved view of global sea ice
25.5.2023 8:55 ESA Observing the Earth
Earth’s declining ice is without a doubt one of the clearest signs of climate change. A new high-resolution sea-ice concentration data record has just been released as part of ESA’s Climate Change Initiative – providing new insights of sea ice concentration across the globe.
Představili jsme český průmysl a výzkum s drony na Korea Drone UAM Expo 2023
24.5.2023 20:41 UAVATento týden jsme představili český průmysl a výzkum s drony na Korea Drone UAM Expo 2023, který se konal v Incheonu. Korea na této akci ukázala, že patří mezi lídry v průmyslu a výzkumu s drony, kde vystavovalo spousta výrobců korejských dronů různých typů a dalších souvisejících řešení pro potřebnou implementaci Urban Air Mobility. Kromě […]
The post Představili jsme český průmysl a výzkum s drony na Korea Drone UAM Expo 2023 appeared first on UAV Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl.
Tristan McDonnell podcast conversation
24.5.2023 20:00 buildingSMART.orgTristan McDonnell served for many years on the buildingSMART International Infrastructure Room. We discuss this as well as his responsibilities being a Director at ARUP. We recall the experiences developing…
The post Tristan McDonnell podcast conversation appeared first on buildingSMART International.
Alex Plenty podcast conversation
24.5.2023 20:00 buildingSMART.orgAlex Plenty has recently been elected to the buildingSMART International Building Domain Steering Committee. He discusses how openBIM standards are needed to improve buildings and infrastructure from the perspective of…
The post Alex Plenty podcast conversation appeared first on buildingSMART International.
Metodika pro geodety k aktualizaci DTM
24.5.2023 18:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do nové záložky Metodika byl přidán dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování základní prostorové situace DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíMetodika pro geodety k aktualizaci DTM
24.5.2023 18:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do nové záložky Metodika byl přidán dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování základní prostorové situace DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíMetodika pro geodety k aktualizaci DTM
24.5.2023 18:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do nové záložky Metodika byl přidán dokument Metodika pro geodetické zaměřování základní prostorové situace DTM kraje a pro práci s dokumentacíAnd the winners for ‘Best Prototype’ are…
24.5.2023 16:26 European GNSS Agency
#myEUspace, EUSPA’s signature competition, developed under the CASSINI Entrepreneurship Initiative, challenges innovators to develop game-changing solutions that leverage EU Space data from Galileo, Europe’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), and/or Copernicus, the European Earth Observation programme.
This year’s competition is unique in that it is divided into three different prize tracks (Ideas, Prototypes and Commercial Products), with each track consisting of three different innovation areas:
- Space My Life: Consumer solutions in focus areas such as health, citizen safety and security, gaming and entertainment, sports and fitness, tourism.
- Our Green Planet: Innovative solutions addressing conservation of ecosystems, green mobility, sustainable agriculture, management of energy and resources.
- Dive in Deep Tech: Innovative solutions combining EU space data with deep technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Quantum technologies, Blockchain, Metaverse and Extended Reality.
This evolution aimed at encouraging more innovators to apply – which is exactly what it did. Following a first track that saw 92 ideas submitted, the competition’s second track – for Best Prototypes – received 95 submissions from 25 countries of the European Economic Area.
After carefully evaluating each prototype and assessing their technology maturity, the #myEUspace competition jury has made its decision. “With this second track geared towards tested prototypes and beta versions ready to be brought to market, the jury paid particular attention to overall innovativeness, market potential, feasibility and relevance to the EU Space Programme,” says Justyna Redelkiewicz, Market and Downstream Innovation - Consumer Entrepreneurship and Environment Manager at EUSPA.
Without further ado, the 10 winners of the #myEUspace competition’s ‘Best Prototypes’ track are:
- CoCuRA Eco: Machine learning techniques to identify organic cotton
- OverView: Online platform to access and visualise environmental data
- Spillalert: Intuitive web interface for oil spills and blackwater tank detection
- Plantiverse: Green area monitoring and management platform
- Artificial Brain Tech: Quantum optimised scheduling of Earth Observation satellites
- Avalanche Monitoring: Monitoring avalanches with satellites and seismic sensors
- Climate AI for Web3: Real-world portable climate API for virtual worlds powered by AI and satellite data
- WaveOut: Augmented reality navigation app that guides by sound
- AeroVR: Virtual reality solution that simulates real UAV flights and operations
- Artur (Nav-X): Smartphone app using augmented reality to digitally explore tourist destinations
Submissions for the ‘Commercial Products’ track, the competition’s third and final track, are currently being evaluated.
Organised by EUSPA as part of the European Commission’s CASSINI – Space Entrepreneurship Initiative, the #myEUspace competition is open to teams from all EU Member States plus Switzerland, Norway and Iceland and has a total prize of nearly EUR 1 million.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Fighting wildfires in France from space | FIRE Preview
24.5.2023 16:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:12:42
Video:
00:12:42
Enjoy a sneak peek of ESA’s new documentary that looks at fire in all its fury - and how satellite technology is helping to mitigate this consequence of climate change. Join us on this journey as we meet the firefighter who fought one of the largest wildfires in his career, climate scientists working with satellite data, and the people on the frontline using these data to aid those affected. The full documentary will be released this summer.
Nová smernica
24.5.2023 16:00
ÚGKK SR
V sekcii Technické predpisy a iné akty riadenia je zverejnená Smernica na postup pri zápise, zmene a výmaze vecného bremena v súbore popisných informácií katastra nehnuteľností č. SM_UGKK SR_15/2023.
Fighting wildfires in France | FIRE Preview
24.5.2023 16:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:12:42
Video:
00:12:42
Enjoy a sneak peek of ESA’s new documentary that looks at fire in all its fury - and how satellite technology is helping to mitigate this consequence of climate change. Join us on this journey as we meet the firefighter who fought one of the largest wildfires in his career, climate scientists working with satellite data, and the people on the frontline using these data to aid those affected. The full documentary will be released this summer.
Fighting wildfires in France | FIRE Preview
24.5.2023 16:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:12:42
Video:
00:12:42
Enjoy a sneak peek of ESA’s new documentary that looks at fire in all its fury - and how satellite technology is helping to mitigate this consequence of climate change. Join us on this journey as we meet the firefighter who fought one of the largest wildfires in his career, climate scientists working with satellite data, and the people on the frontline using these data to aid those affected. The full documentary will be released this summer.
Fighting wildfires in France | FIRE Preview
24.5.2023 16:00 ESA Observing the Earth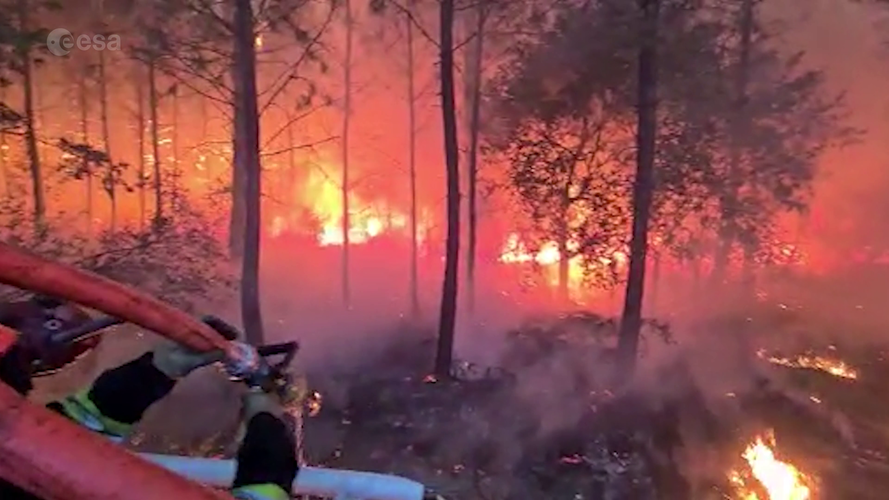 Video:
00:12:42
Video:
00:12:42
Enjoy a sneak peek of ESA’s new documentary that looks at fire in all its fury - and how satellite technology is helping to mitigate this consequence of climate change. Join us on this journey as we meet the firefighter who fought one of the largest wildfires in his career, climate scientists working with satellite data, and the people on the frontline using these data to aid those affected. The full documentary will be released this summer.
Webinář o správě Autodesk účtu, druhů licencí a jejich správném užívání
24.5.2023 15:04 Adeon
Společnost Adeon CZ srdečně zve všechny zájemce na exkluzivní webinář, který se zaměří na Autodesk Account, jeho spravování spolu se […]
The post Webinář o správě Autodesk účtu, druhů licencí a jejich správném užívání appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Webinář o správě Autodesk účtu, druhů licencí a jejich správném užívání
24.5.2023 15:04 Adeon
Společnost Adeon CZ srdečně zve všechny zájemce na exkluzivní webinář, který se zaměří na Autodesk Account, jeho spravování spolu se […]
The post Webinář o správě Autodesk účtu, druhů licencí a jejich správném užívání appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního
24.5.2023 9:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Zlín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN KatastrálníhoOdborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního
24.5.2023 9:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Zlínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Zlín
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního
24.5.2023 9:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-navrh-zapis-(1)Satellites provide crucial insights into Arctic amplification
24.5.2023 9:45 ESA Observing the Earth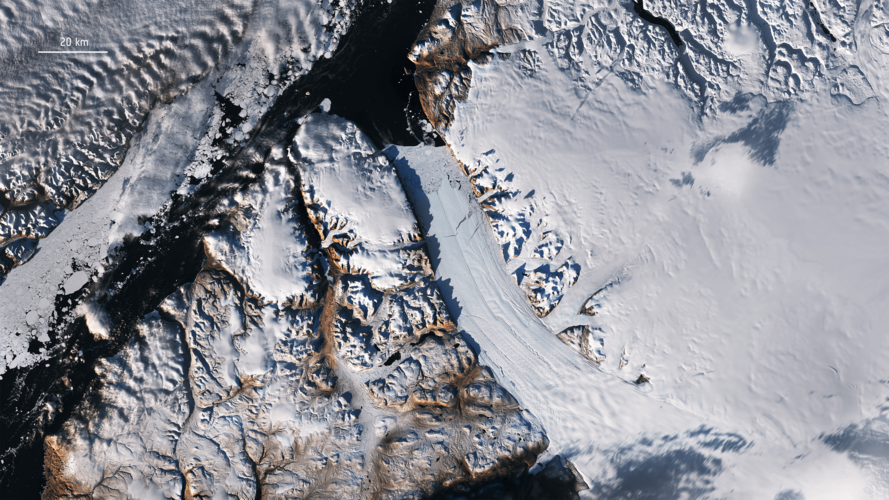
The Arctic, once again at the forefront of climate change, is experiencing disproportionately higher temperature increases compared to the rest of the planet, triggering a series of cascading effects known as Arctic amplification. As concerns continue to grow, satellites developed by ESA have become indispensable tools in understanding and addressing the complex dynamics at play and the far-reaching consequences for the environment and human societies.
Satellites provide crucial insights into Arctic amplification
24.5.2023 9:45 ESA Observing the Earth
The Arctic, once again at the forefront of climate change, is experiencing disproportionately higher temperature increases compared to the rest of the planet, triggering a series of cascading effects known as Arctic amplification.
As concerns continue to grow, satellites developed by ESA have become indispensable tools in understanding and addressing the complex dynamics at play and the far-reaching consequences for the environment and human societies.
Krátka správa č. 24/2023
24.5.2023 9:19 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 24/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 23/2023
24.5.2023 9:15 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 23/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Join us for the first Galileo HAS Days!
23.5.2023 12:41 European GNSS Agency
Scheduled for 28-29 June 2023, this event is an opportunity for the Galileo HAS user community, industry stakeholders, application developers and international experts to know more about the Galileo HAS Service (in operation since January 2023). In addition, it will be a great opportunity for all attendees to come together to discuss and share their expectations on the HAS service challenges and benefits.
During two days, participants will have the opportunity to learn more about the latest status of Galileo HAS service, including current performance, evolution plans and key user applications and to network. There will be also dedicated user sessions in parallel where participants could rotate, including live demonstrations allowing participants to experiment the Galileo HAS capabilities. In addition, participants will have also the chance to visit the European GNSS Service Centre (GSC) premises, the single interface between the Galileo system and the users. The GSC is a centre of expertise, knowledge sharing, custom performance assessment, information dissemination and support to the provision of value-added services enabled by the Galileo services. For the particular case of Galileo HAS, the GSC hosts the High Accuracy Data Generator (HADG), which computes the HAS orbit and clock corrections as well as the signal biases which are broadcast through the Galileo constellation and over the internet.
This first edition of the Galileo HAS Days will be held as a hybrid event, meaning you can join either online or physically in INTA (Torrejón de Ardoz, Madrid - Spain).
The draft agenda is available here.
Registration for the event is open until 16 June 2023 for those willing to attend onsite. Join us here!
For more information on Galileo HAS, please refer to the service documentation available online.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
ESA receives Space for Climate Protection Award
23.5.2023 12:20 ESA Observing the Earth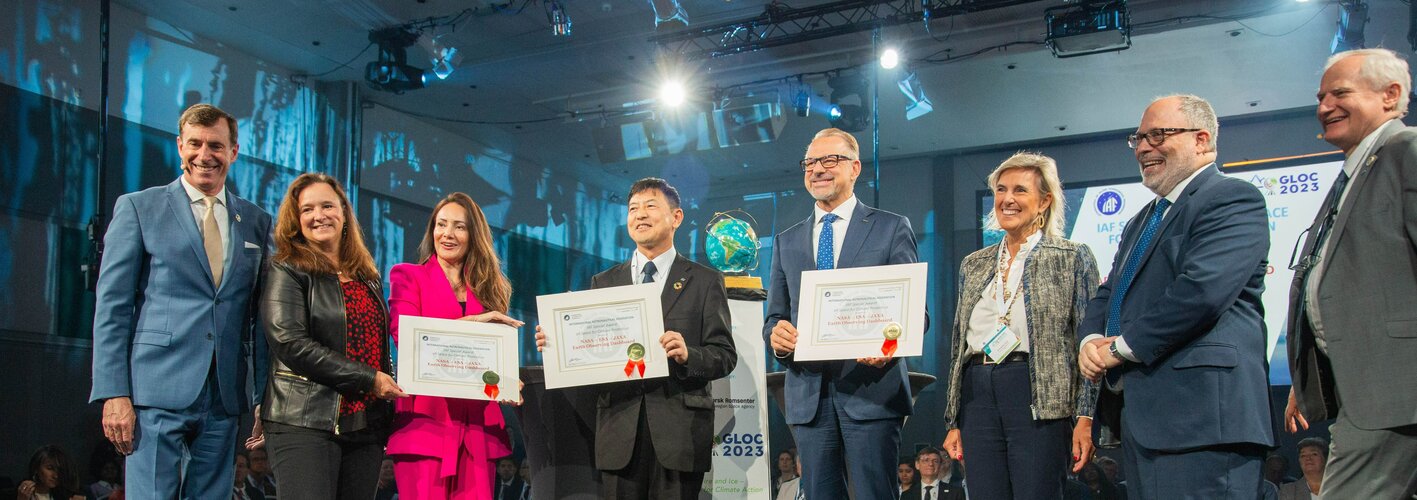
ESA has been presented the ‘Space for Climate Protection’ Special Award by the International Astronautical Federation during the Global Space Conference on Climate Change – currently taking place in Oslo, Norway.
Stav pořizování dat ZPS
23.5.2023 11:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do záložky Podklady IS DTM byl pro případné využití přidán adresář s tabulkami popisující aktuálním stav pořizování dat základní prostorové situace (ZPS) DTM v jednotlivých krajích.20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
23.5.2023 11:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN"20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
23.5.2023 11:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Beroun/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(10)20230511_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
23.5.2023 11:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Beroun/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(10)Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
23.5.2023 11:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-a-dokOdborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
23.5.2023 11:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Berounvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
23.5.2023 11:08 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Beroun vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KNAnnual global ice loss simulated over Oslo
23.5.2023 9:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:01:20
Video:
00:01:20
Satellites play a vital role in monitoring the rapid changes taking place in the Arctic. Tracking ice lost from the world’s glaciers, ice sheets and frozen land shows that Earth is losing ice at an accelerating rate.
Using information from ESA’s ERS, Envisat and CryoSat satellites as well as the Copernicus Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 missions, research led by Tom Slater of the University of Leeds, found that the rate at which Earth has lost ice has increased markedly within the past three decades. Currently, more than a trillion tonnes of ice is lost each year.
To put this into perspective, this is equivalent to an ice cube measuring 10x10x10 km over Oslo’s skyline. Putting it another way, the amount of ice loss globally is equivalent to 12 000 times the annual water use of the Norwegian capital.
The sooner Earth’s temperature is stabilised, the more manageable the impacts of ice loss will be.
Continuity in satellite data is the key to predicting future ice losses, and to assist in mitigating the threats posed by sea-level rise, shrinking high mountain glaciers and further climate feedbacks. The Copernicus Expansion missions, CRISTAL, CIMR and ROSE-L have been designed to fill the gaps in current Sentinel capabilities for comprehensive monitoring of changes in the global ice cover.
Watch now: Global Space Conference on Climate Change
23.5.2023 8:53 ESA Observing the Earth
Watch now: Global Space Conference on Climate Change
20230523_Odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Rakovnik/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230111_Odborny-rada-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-(1)20230523_Odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rakovník Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem"Odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:43 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rakovníkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:43 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rakovník vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem20230523_rada/odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rakovník Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: rada/odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa rada/odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem"20230523_rada/odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:22 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Rakovnik/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(3)Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:21 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rakovník vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostemRada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
23.5.2023 8:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rakovníkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
ISSS 2023 - Český zavináč za rok 2023
23.5.2023 7:00 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální byl do rukou předsedy oceněn cenou Český zavináč za rok 2023 "za přínos v elektronizaci veřejné správy v České republice, zejména pak za rozvoj a digitalizaci katastru nemovitostí, který je svým rozsahem služeb unikátní i v celoevropském měřítku". Cena byla slavnostně udělena v průběhu mezinárodní konference ISSS 2023.ISSS 2023 - Český zavináč za rok 2023
23.5.2023 7:00 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální byl do rukou předsedy oceněn cenou Český zavináč za rok 2023 "za přínos v elektronizaci veřejné správy v České republice, zejména pak za rozvoj a digitalizaci katastru nemovitostí, který je svým rozsahem služeb unikátní i v celoevropském měřítku". Cena byla slavnostně udělena v průběhu mezinárodní konference ISSS 2023.ISSS 2023 - Český zavináč za rok 2023
23.5.2023 7:00 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2023/ISSS-2023-Cesky-zavinac-za-rok-2023ISSS 2023 - Český zavináč za rok 2023
23.5.2023 7:00 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální byl do rukou předsedy oceněn cenou Český zavináč za rok 2023 "za přínos v elektronizaci veřejné správy v České republice, zejména pak za rozvoj a digitalizaci katastru nemovitostí, který je svým rozsahem služeb unikátní i v celoevropském měřítku". Cena byla slavnostně udělena v průběhu mezinárodní konference ISSS 2023.ISSS 2023 - Český zavináč za rok 2023
23.5.2023 7:00 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální byl do rukou předsedy oceněn cenou Český zavináč za rok 2023 "za přínos v elektronizaci veřejné správy v České republice, zejména pak za rozvoj a digitalizaci katastru nemovitostí, který je svým rozsahem služeb unikátní i v celoevropském měřítku". Cena byla slavnostně udělena v průběhu mezinárodní konference ISSS 2023.odborný referent/vrchní referent – poskytování informací a nahlížení do KN
22.5.2023 18:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent/vrchní referent – poskytování informací a nahlížení do KN
odborný referent/vrchní referent – poskytování informací a nahlížení do KN
22.5.2023 18:27 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-poskytovani-infodborný referent/vrchní referent – poskytování informací a nahlížení do KN
22.5.2023 18:27 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent/vrchní referent – poskytování informací a nahlížení do KNKrajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty
22.5.2023 14:40 Adeon
Společnost Adeon CZ srdečně zve všechny zájemce na exkluzivní webinář, který se zaměří na produkt Autodesk Revit, přesněji doplněk Enviroment […]
The post Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty
22.5.2023 14:40 Adeon
Společnost Adeon CZ srdečně zve všechny zájemce na exkluzivní webinář, který se zaměří na produktAutodesk Revit, přesněji doplněk Enviroment od […]
The post Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty
22.5.2023 14:40 Adeon
Společnost Adeon CZ srdečně zve všechny zájemce na exkluzivní webinář, který se zaměří na produkt Autodesk Revit, přesněji doplněk Enviroment […]
The post Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty
22.5.2023 14:40 Adeon
Společnost Adeon CZ srdečně zve všechny zájemce na exkluzivní webinář, který se zaměří na produktAutodesk Revit, přesněji doplněk Enviroment od […]
The post Krajina a BIM jednoduše – webinář nejen pro zahradní architekty appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Tři Fusiony za cenu dvou
22.5.2023 11:21 Adeon
Autodesk ohlásil jarní akci pro nové licence aplikace Fusion 360. V rámci akce lze pořídit 3 nové licence za cenu […]
The post Tři Fusiony za cenu dvou appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Tři Fusiony za cenu dvou
22.5.2023 11:21 Adeon
Autodesk ohlásil jarní akci pro nové licence aplikace Fusion 360. V rámci akce lze pořídit 3 nové licence za cenu […]
The post Tři Fusiony za cenu dvou appeared first on Adeon CZ.
Využití GIS a družicových dat k řešení lokálních problémů kolem nás (pozvánka)
22.5.2023 9:18 GISportal.cz
Máte zájem přispět k řešení lokálních problémů a výzev v místě, kde žijete? Zapojte se do hackathonu Copernicus Academy CZ „Využití GIS a družicových dat k řešení lokálních problémů kolem nás“, který se uskuteční v Kampusu Hybernská v Praze během víkendu 3. – 4. června 2023. S využitím geoinformačních systémů (GIS) a družicových dat budeme […]
The post Využití GIS a družicových dat k řešení lokálních problémů kolem nás (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Využití GIS a družicových dat k řešení lokálních problémů kolem nás (pozvánka)
22.5.2023 9:18 GISportal.cz
Máte zájem přispět k řešení lokálních problémů a výzev v místě, kde žijete? Zapojte se do hackathonu Copernicus Academy CZ „Využití GIS a družicových dat k řešení lokálních problémů kolem nás“, který se uskuteční v Kampusu Hybernská v Praze během víkendu 3. – 4. června 2023. S využitím geoinformačních systémů (GIS) a družicových dat budeme […]
The post Využití GIS a družicových dat k řešení lokálních problémů kolem nás (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Vrchním ministerským radou v oddělení pořizování a územně správním MMR? Zní to dobře? Čtěte dál...
22.5.2023 8:37 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČUOZNÁMENÍ O VYHLÁŠENÍ VÝBĚROVÉHO ŘÍZENÍ na služební místo vrchního ministerského rady v oddělení pořizování a územně správní, v odboru územního plánování
Co nabízíme: Možnost podílet se na tvorbě koncepce územního plánování v ČR. Rozmanitou činnost v oblasti digitalizace územního plánování. Možnost podílet se na zavádění inovativních řešení v územních plánování. Možnost profesního růstu zejména v oblasti digitalizace veřejné správy. Odměňování ve 14. platové třídě (tarifní plat od 34.840 Kč do 51.530 Kč podle délky Vaší započitatelné praxe) a osobní příplatek na základě Vašeho individuálního výkonu. Benefity naleznete na: https://www.mmr.cz/cs/kariera/benefity.
Co očekáváme: Dosažené vzdělání v magisterském studijním programu. Na služebním místě budete vykonávat službu v oboru 41. Bydlení, územní plánování a stavební řád. Bližší informace jsou uvedeny v oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení. Předpokládaný nástup v červenci 2023.
Datum vystavení 16. 05. 2023
Datum platnosti 07. 06. 2023
Doba trvání Na dobu neurčitou
Smluvní vztah Služební poměr
Veškeré informace na https://www.mmr.cz/cs/kariera/pracovni-prilezitosti/vrchni-ministersky-rada-v-oddeleni-porizovani-(8)
Otevírací doba knihovny v letním zkouškovém období [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
22.5.2023 0:00 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK V letním zkouškovém období (22. května - 30. června 2023) se otevírací doba mění jen nepatrně, ve čtvrtek je otevřeno pouze do 12:00, jinak vše zůstává stejné (Po až St 9-18, Čt 9-12 a Pá 9-15 h).Mapwidget je nový pythonový balíček pro interaktivní 3D mapy v Jupyteru
21.5.2023 21:49 GeoBusinessQiusheng Wu (@giswqs) oznámil vydání nového pythonového balíčku. Nazval jej mapwidget. Slouží k tvorbě interaktivních 3D map v prostředí Jupyter. Použity jsou javascriptové knihovny jako CesiumJS, Mapbox, MapLibre, Leaflet a OpenLayers. Mapwidget je k dispozici na Githubu.
The post Mapwidget je nový pythonový balíček pro interaktivní 3D mapy v Jupyteru appeared first on GeoBusiness.
DAEX DESIGN Start pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy
20.5.2023 17:57 ŠPINAR - software Vážení zákazníci, připravili jsme pro Vás DAEX DESIGN Start pro výrobce a návrháře nábytku a interiérů s rozšiřujícími bonusy do 28. 5. 2023Schválení dokumentace nové verze JVF DTM
19.5.2023 22:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální informuje, že dokumentace k nové verzi JVF DTM 1.4.2.2 byla dne 5. května 2023 schválena Koordinační radou správců DMVS a DTM.3D dlaždice budou součástí QGISu, Emma Hain a Lutra Consulting mají grant od Cesium
19.5.2023 20:38 GeoBusinessFirma Cesium, stojící za vývojem stejnojmenného 3D enginu Cesium.js, který ve svých projektech používají i komerční firmy jako Bentley Systems, se začátkem dubna 2023 rozhodla, že věnuje nějaké finance (milion dolarů) zpět do open sourceové komunity. Iniciativa nazvaná Cesium Grants ocenila – teď v polovině května – první čtyři týmy/projekty. Jeden z týmů tvoří Emma […]
The post 3D dlaždice budou součástí QGISu, Emma Hain a Lutra Consulting mají grant od Cesium appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Search and Rescue Exercise in Cyprus highlights the role of the EU Space Programme in maritime operations
19.5.2023 16:20 European GNSS Agency
EUSPA, together with Eurisy, recently co-organised a workshop on Satellite-based Services for Disaster Risk Management. Held in Nicosia, Cyprus, the workshop brought together national and regional stakeholders to discuss how satellite-based services can support disaster risk management and search and rescue operations.
The workshop was hosted by Cyprus, in cooperation with the Department of Electronic Communications, Deputy Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digital Policy and EURISY.
The event kicked-off with a number of keynote speakers, including from Deputy Minister of Research, Innovation and Digital Policy Philippos HADJIZACHARIAS stated that "investing in Space means investing in the future". "Space is seen as a driver of innovation, growth and competitiveness and a key factor in accelerating the twin digital and green transitions and promoting societal well-being. The vast amounts of information provided by satellite systems can be used in a variety of sectors, and one of them is Disaster Risk Management," he said.
“While Galileo, EGNOS, Copernicus and GOVSATCOM are powerful tools in their own right, the Emergency Management and Disaster Response sector stands to benefit the most when these solutions are used in synergy,” added EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa. “That’s why, as a user-oriented agency, EUSPA closely follows this market’s needs and works to shape and deliver new space-enabled services accordingly.”
Supporting a range of disaster scenarios
Speakers also provided insight on how the various components of the EU Space Programme can be used to support a wide range of disaster scenarios – including fighting wildfires. For instance, fire departments and decision makers are using Copernicus data to help mitigate the risk of fires before they happen and to battle them when they do. They’re also replacing their ground-based systems and use of rotorcraft with drones equipped with a range of sensors for capturing data. Such systems are particularly beneficial in rural and remote areas, where Earth Observation-equipped drones guided by the precise positioning offered by GNSS can provide wildfire fighters with another layer of information – and protection.
The use of European GNSS is also helping save lives. Take for example the European 112-emergency number. Thanks to the inclusion of Galileo signals in most mobile phones, when someone places an emergency call, the emergency responder will receive their location information with an accuracy down to just a few metres. This level of accuracy has had a major impact in terms of response times, ultimately allowing for quicker intervention in emergency situations where every second counts – resulting in more lives being saved.
Last but not least is the forthcoming GOVSATCOM, which provide secure, cost-efficient communication capabilities to security and safety-critical missions, operations and infrastructure. “Galileo provides information about where you are, Copernicus provides information about what is around you and GOVSATCOM provides resilient, secure and high-availability connectivity to the disaster area in order to coordinate the rescue teams and get real-time on-site information. Thus, GOVSATCOM complements the existing space-based tools provided by the EU Space Programme to support disaster risk management,” said Georgios Synnefakis, EUSPA GOVSATCOM programme manager.

EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa presenting the EU Space Programme at the Satellite-based Services for Disaster Risk Management
The policy perspective
The programme concluded with a high-level policy panel moderated by EUSPA, where decision-makers were invited to shed light on the national and European policy framework, as well as share their perspectives on the future of risk assessment and management.
Galileo Search and Rescue in action
Parallel to the Eurisy workshop, the Cypriot authorities organised a Search and Rescue exercise as part of the larger ARGONAUT 2023 military exercise in presence of Minister of Defense, Michalis Giorgallas. In the exercise, several EU and NATO Member States participated, including Greece, France, the US, Israel, Italy and Cyprus.
The scenario involved a passenger ship traveling from the Middle East Region towards the Republic of Cyprus when it sent out a MAYDAY alert.
A Galileo-enabled EPIRB equipped with the ground-breaking Galileo Return Link Service (RLS) was successfully activated to notify the authorities.
The emergency signal was picked up by the Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre (MRCC) in just under 2 minutes, confirming once again Galileo's excellent performance.
“With the EU recognising European Maritime Day this week, this demonstration shows how the EU Space Programme provides European maritime operators, seafarers and national authorities with the tools they need to enhance safety at sea, optimise navigation performance and protect our oceans,” said da Costa, who watched the exercise live from the Joined Rescue Coordination Center.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Earth from Space: Oslo, Norway
19.5.2023 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth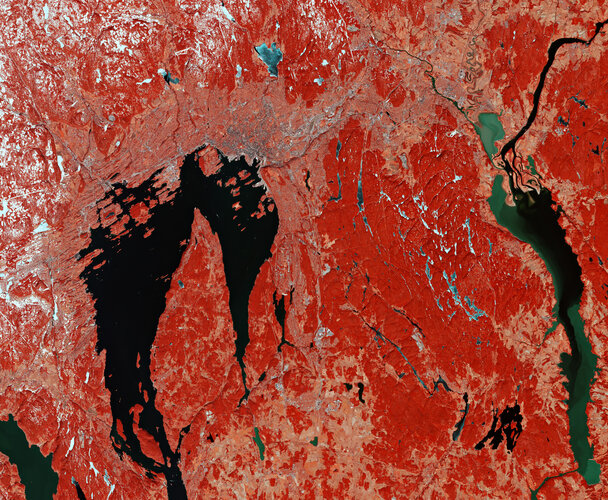 Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Oslo, Norway’s capital and largest city, and host of the 2023 Global Space Conference on Climate Change, taking place on 23–25 May.
Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Oslo, Norway’s capital and largest city, and host of the 2023 Global Space Conference on Climate Change, taking place on 23–25 May.
Odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Zlín
19.5.2023 9:25 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Zlín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště ZlínOdborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Zlín
19.5.2023 9:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-–-navrh-zapisu-v-katastru-v-oddelOdborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Zlín
19.5.2023 9:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Zlínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Zlín
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního
19.5.2023 9:15 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Vsetínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Vsetín
Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního
19.5.2023 9:15 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Vsetín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN KatastrálníhoOdborný referent / vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního
19.5.2023 9:15 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-navrh-zapisu-v-20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:56 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Usti-nad-Labem/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230519-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-(2)20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230519-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-(2)20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký krajOdborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastr
19.5.2023 6:53 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí KatastrOdborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastr
19.5.2023 6:53 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-ak-(1)Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastr
19.5.2023 6:53 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labemvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Usti-nad-Labem/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230519-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-(1)20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:37 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230519-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-(1)20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OAaD KP Ústí n.L. na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OD katastru nemovit. KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:22 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Litomerice/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230519-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-v-O20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OD katastru nemovit. KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OD katastru nemovit. KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:22 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230519-volne-misto-–-Odborny-vrchni-referent-v-O20230519 - volné místo – Odborný/vrchní referent v OD katastru nemovit. KP Litoměřice na KÚ pro ÚK
19.5.2023 6:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného místa - Odborný/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký krajOdborný / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litom
19.5.2023 6:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litom
19.5.2023 6:18 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště LitomOdborný / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Litom
19.5.2023 6:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-katDAEX DESIGN Start pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy
18.5.2023 17:57 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci, připravili jsme pro Vás DAEX DESIGN Start pro výrobce a návrháře nábytku a interiérů s rozšiřujícími bonusy do 28. 5. 2023
The post DAEX DESIGN Start pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
DAEX DESIGN Start pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy
18.5.2023 17:57 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci, připravili jsme pro Vás DAEX DESIGN Standard pro výrobce a návrháře nábytku a interiérů s rozšiřujícími bonusy do 21. 5. 2023
The post DAEX DESIGN Start pro truhláře a nábytkáře s akčními bonusy appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
rada / odborný rada – interní audit v Katastrálním úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
18.5.2023 12:47 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada – interní audit v Katastrálním úřadu pro Liberecký krajrada / odborný rada – interní audit v Katastrálním úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
18.5.2023 12:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/rada-odborny-rada-–-interni-audit-v-Katastralnim-urada / odborný rada – interní audit v Katastrálním úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
18.5.2023 12:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada – interní audit v Katastrálním úřadu pro Liberecký kraj
Odstávka mapových aplikací Geoportálu a výdeje dat
18.5.2023 12:40 Jihočeský krajV pátek 19.5.2023 od 17:00 budou z technických důvodů nedostupné mapové aplikace Geoportálu a ve večerních hodinách budou dostupné na nových URL adresách.
rnrnOmlouváme se za komplikace
Odstávka mapových aplikací Geoportálu a výdeje dat
18.5.2023 10:55 Jihočeský krajV pátek 19.3.2023 od 17:00 budou z technických důvodů nedostupné mapové aplikace Geoportálu a ve večerních hodinách budou dostupné na nových URL adresách.
rnrnOmlouváme se za komplikace
Zkušenosti z leteckého snímkování a leteckého laserového skenování pro potřeby DTM ČR
18.5.2023 9:52 GeoBusinessZdeněk Klusoň z brněnské firmy Primis vystoupil na konferenci „GIS Esri v ČR 2022“ s referátem o snímkovacích pracech pro Digitální technickou mapu ČR. Firma Primis se specializuje na snímkování a laserové skenování z leteckých prostředků. V referátu Zdeněk Klusoň popisuje zkušenosti a poznatky z realizace leteckého snímkování a laserového skenování pro potřeby DTM ČR. […]
The post Zkušenosti z leteckého snímkování a leteckého laserového skenování pro potřeby DTM ČR appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2024 (první info)
18.5.2023 8:23 GISportal.cz
Organizační tým ARCDATA PRAHA si Vás dovolujeme pozvat na letošní ročník Konference GIS Esri v ČR, která se bude konat 8. a 9. listopadu 2023. Tentokrát se opět sejdeme v Kongresovém centru Praha. Největší setkání geoinformatiků v Česku proběhne opět kombinovanou formou – můžete dorazit osobně, nebo si celou konferenci následně pustit ze záznamu. Ať si […]
The post Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2024 (první info) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2024 (první info)
18.5.2023 8:23 GISportal.cz
Organizační tým ARCDATA PRAHA si Vás dovolujeme pozvat na letošní ročník Konference GIS Esri v ČR, která se bude konat 8. a 9. listopadu 2023. Tentokrát se opět sejdeme v Kongresovém centru Praha. Největší setkání geoinformatiků v Česku proběhne opět kombinovanou formou – můžete dorazit osobně, nebo si celou konferenci následně pustit ze záznamu. Ať si […]
The post Konference GIS Esri v ČR 2024 (první info) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Our oceans are in hot water
17.5.2023 16:30 ESA Observing the Earth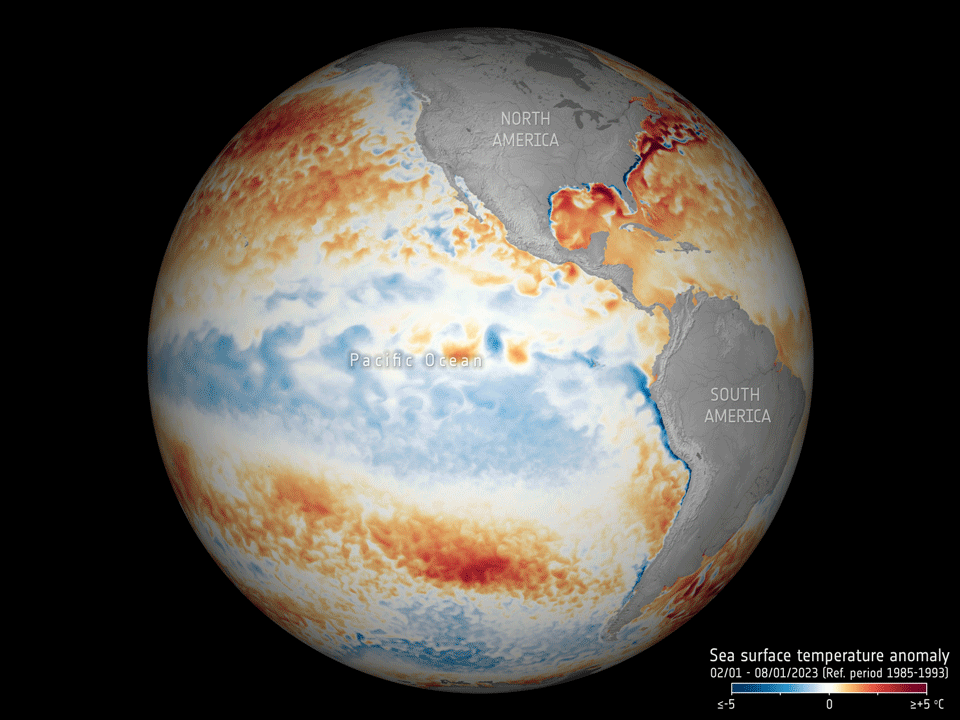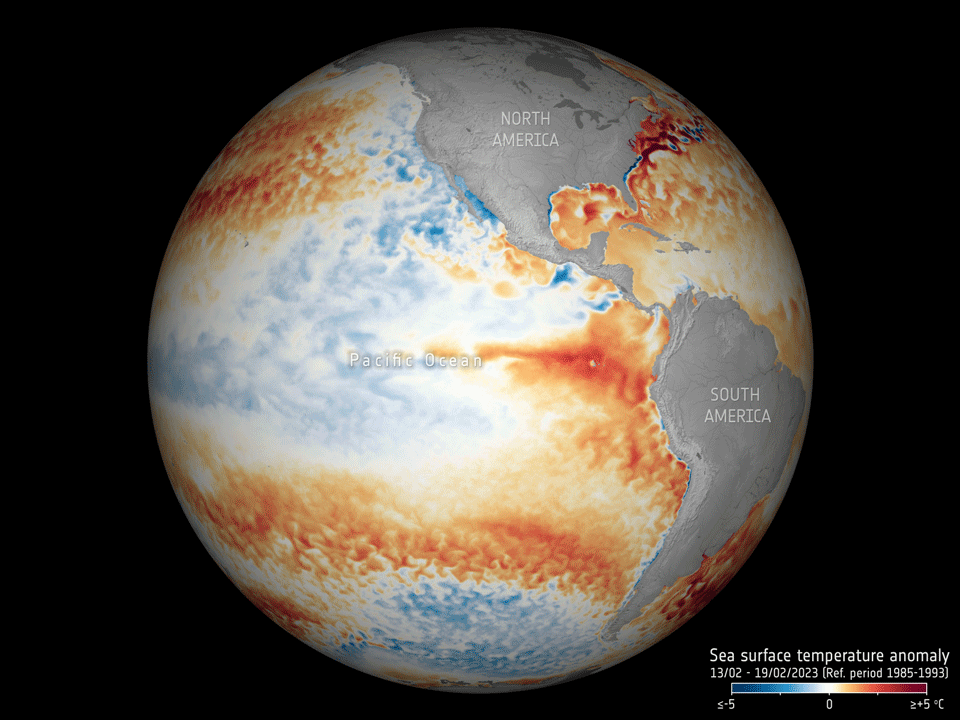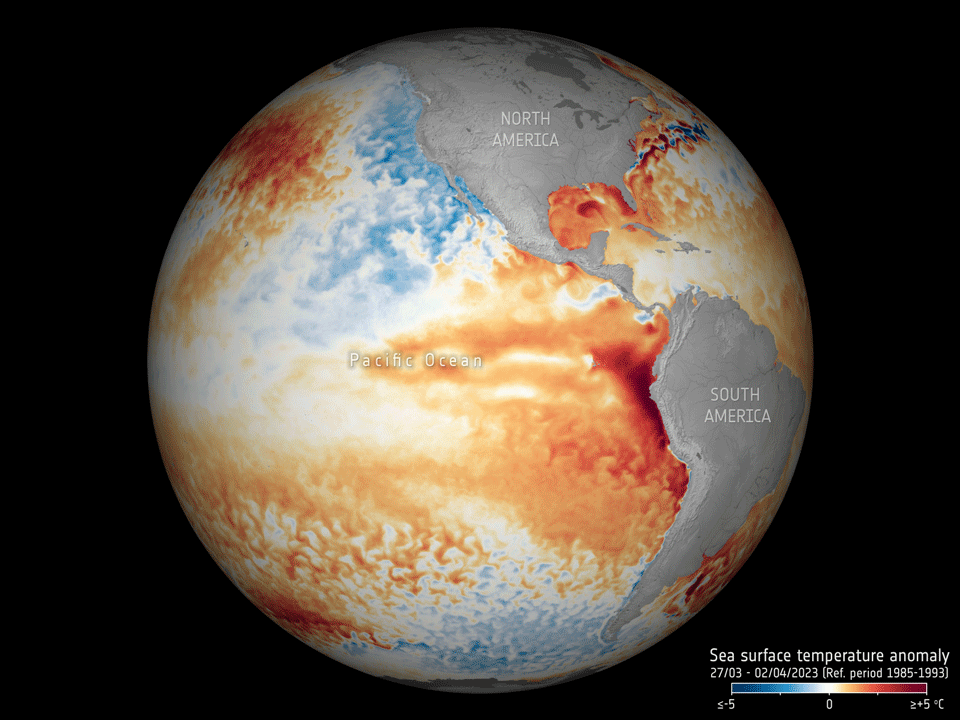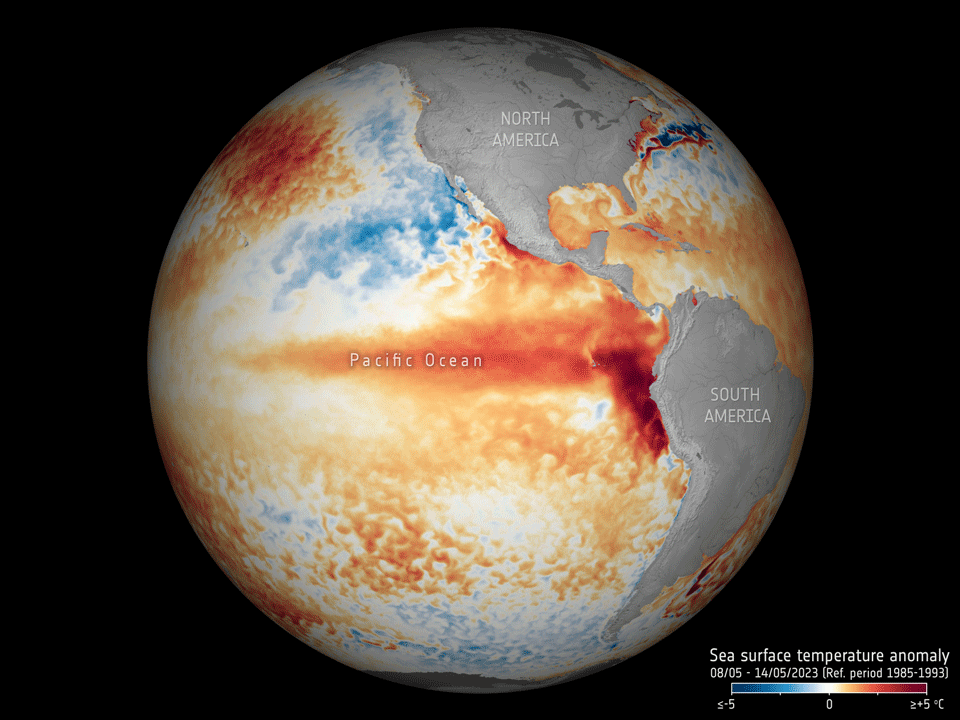
Adding to the grim list of record ice losses, record air temperatures and record droughts, which have all hit the headlines recently, the temperature of the surface waters of our oceans is also at an all-time high. With an El Niño looming, concerns are that we will soon be facing even worse extremes. Satellites orbiting overhead are being used to carefully track the patterns that lead up to El Niño to further understand and predict the consequences of this cyclic phenomenon against the backdrop of climate change.
Our oceans are in hot water
17.5.2023 16:30 ESA Observing the Earth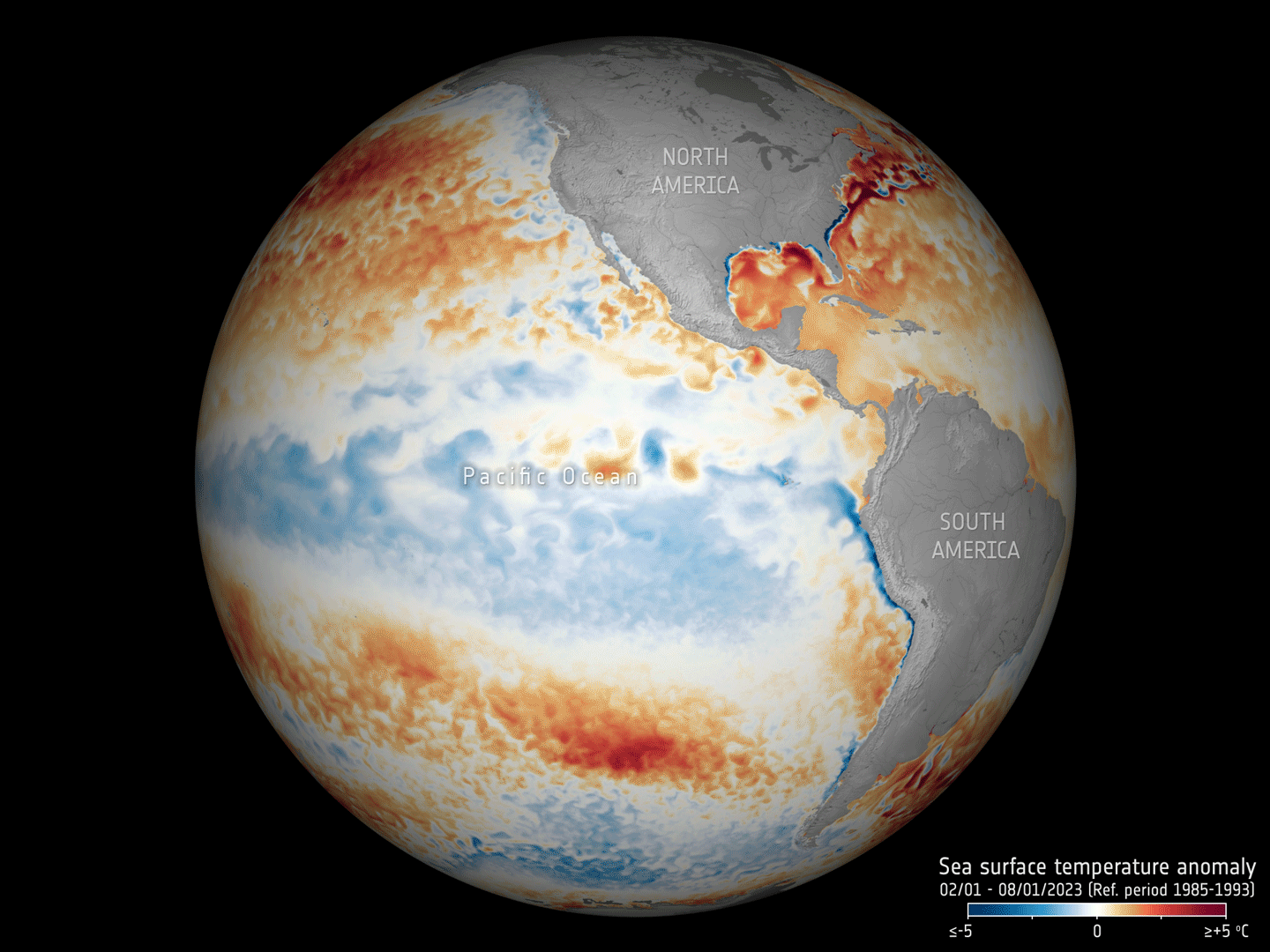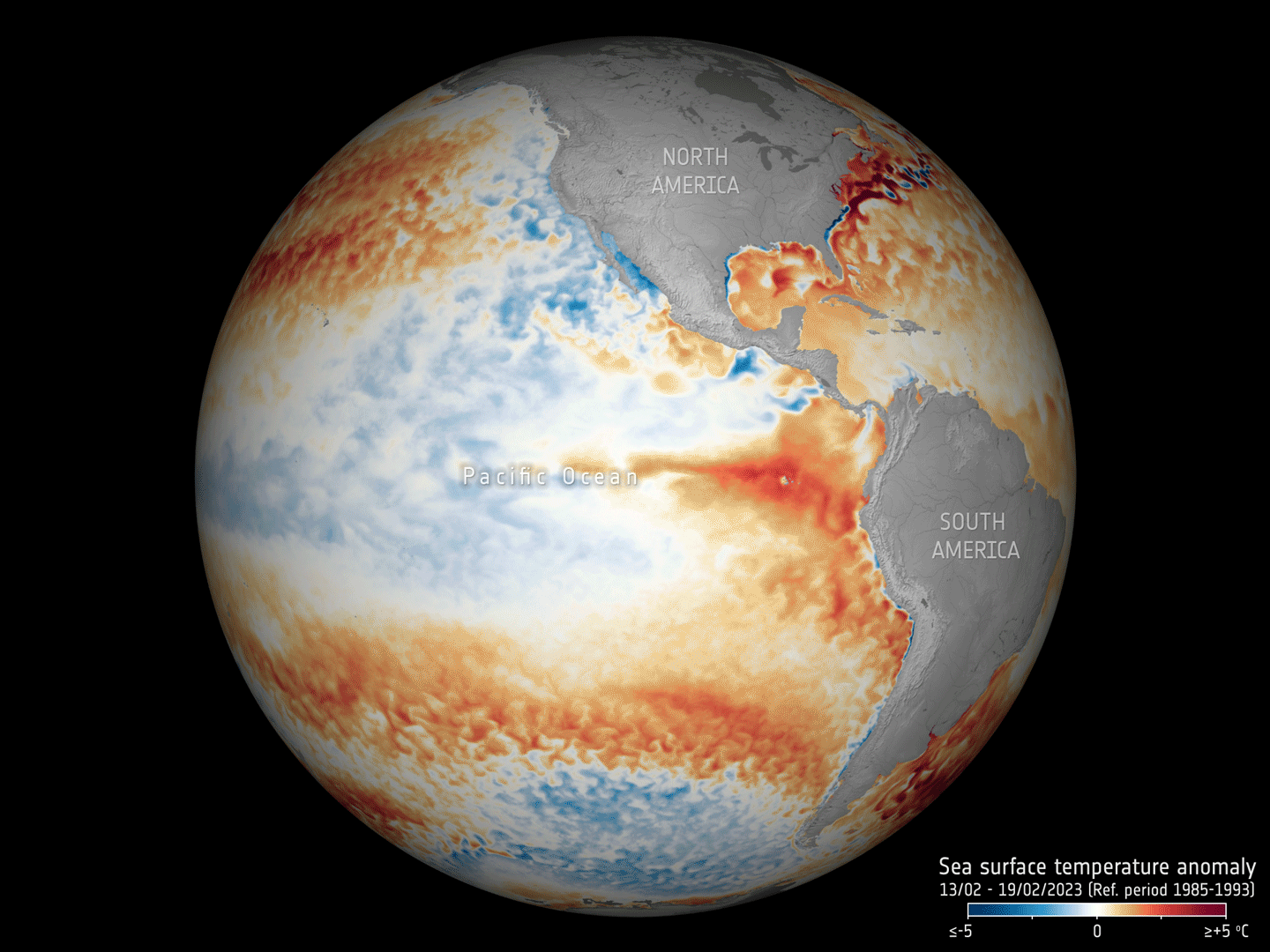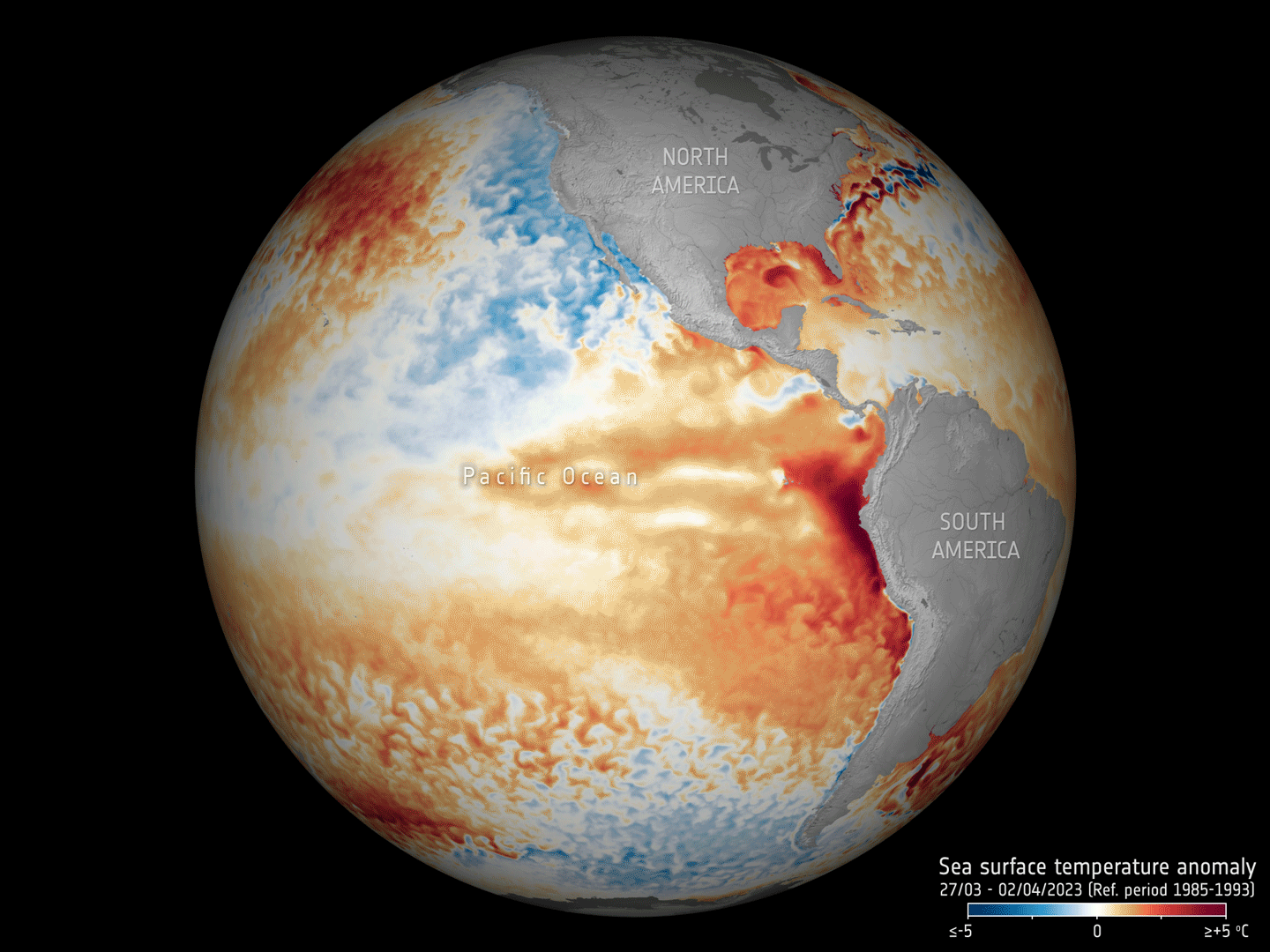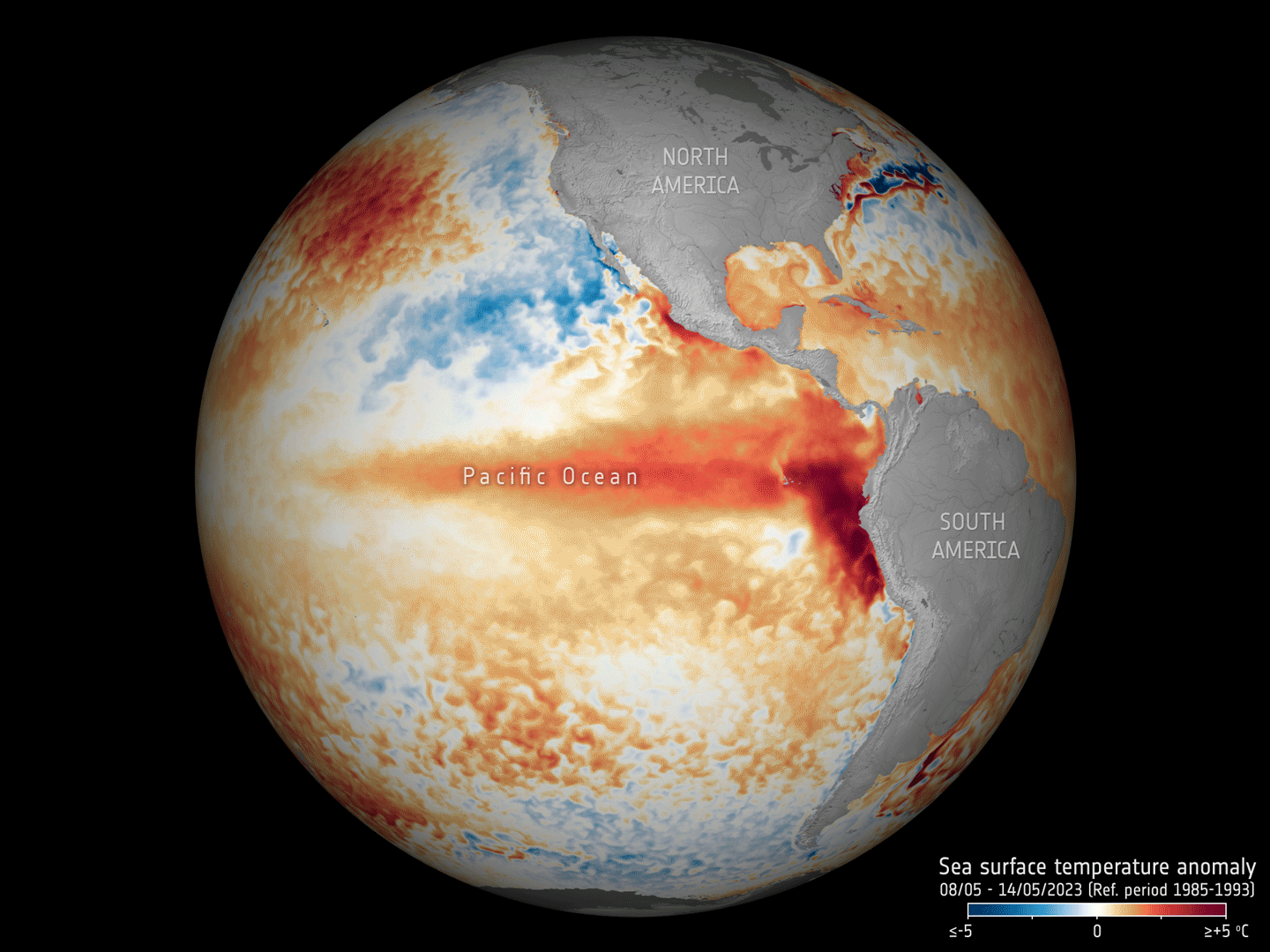
Adding to the grim list of record ice losses, record air temperatures and record droughts, which have all hit the headlines recently, the temperature of the surface waters of our oceans is also at an all-time high. With an El Niño looming, concerns are that we will soon be facing even worse extremes. Satellites orbiting overhead are being used to carefully track the patterns that lead up to El Niño to further understand and predict the consequences of this cyclic phenomenon against the backdrop of climate change.
Geodetem nejefektivnějšího povrchového dolu světa?
17.5.2023 13:29 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČUSpolečnost EXACT nabízí práci ve světově nejefektivnějším povrchovém dole Boliden [www.boliden.com , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EGI0dN012Qk ].
Povrchový důl je velký zážitek. Jsou tam ty největší stavební stroje. Exact Group tam má skoro 10 geodetů (Švédi, Češi, Slováci), takže je to jednodušší do začátku pro toho, kdo by si chtěl vyzkoušet pracovat v zahraničí. Teď na projektu plánují víc geodetů, než se čekalo a jako vždy rychle. Naše práce je převážně s GPS pro kontrolu kubatur zemních prací tam, kde buduje zázemí, odkaliště, infrastruktura, apod. 14 dní práce 12h, 14dní volno na projektovou smlouvu (jen na projekt květen – listopad/prosinec) s motivačním čistým příjmem 60.000,- kč/měsíc + ubytování + letenky.).
Geodet musí umět dobře anglicky, být komunikativní, pracovat samostatně, přizpůsobit se Švédskému systému práce. Není to pro každého. Je to pro toho, kdo chce něco zažít, prozkoumat možnosti a má motivaci překročit hranice „známého“. Toto je ideální start. Zde bude v Českém kolektivu, pracovat samostatně se Švédy.)
V případě, že máte o pozici zájem pošlete CV na e-mail: czech.office@teamexact.com
Technická odstávka ESKN
17.5.2023 12:45
ÚGKK SR
Úrad geodézie, kartografie a katastra SR v snahe vylepšiť svoje služby pre konzumentov bude realizovať aktualizáciu informačných systémov. Z tohto dôvodu je potrebné kvôli lepšej funkčnosti portálov ESKN urobiť TECHNICKÚ ODSTÁVKU. Dňa 19.05.2023 (piatok) od 18:00 do 21.05.2023 do 18:00 bude technická odstávka elektronických služieb katastra nehnuteľností, nakoľko bude realizovaná aktualizácia infraštruktúry systému elektronických služieb katastra nehnuteľností.
#PortálESKN #od:19.05.2023@18:00 #do:21.05.2023@18:00
Výběrové řízení
17.5.2023 11:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě, ve znění pozdějších předpisů, vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV0603, na Katastrálním úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj, oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem, na Katastrálním pracovišti Klatovy, se služebním působištěm v Klatovech.Na služebním místě je státní služba vykonávána v oboru služby 55. Zeměměřictví a katastr nemovitostí.
Služební místo je zařazeno podle přílohy č. 1 k zákonu o státní službě do 12. platové třídy.
Služba na služebním místě bude vykonávána ve služebním poměru na dobu neurčitou.
Předpokládaným dnem nástupu do služby na služebním místě je 1. srpen 2023 nebo dle dohody.
Posuzovány budou žádosti o přijetí do služebního poměru a zařazení na služební místo nebo žádosti o zařazení na služební místo podané ve lhůtě do 15. června 2023.
Výběrové řízení
17.5.2023 11:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě, ve znění pozdějších předpisů, vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV0603, na Katastrálním úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj, oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem, na Katastrálním pracovišti Klatovy, se služebním působištěm v Klatovech.Na služebním místě je státní služba vykonávána v oboru služby 55. Zeměměřictví a katastr nemovitostí.
Služební místo je zařazeno podle přílohy č. 1 k zákonu o státní službě do 12. platové třídy.
Služba na služebním místě bude vykonávána ve služebním poměru na dobu neurčitou.
Předpokládaným dnem nástupu do služby na služebním místě je 1. srpen 2023 nebo dle dohody.
Posuzovány budou žádosti o přijetí do služebního poměru a zařazení na služební místo nebo žádosti o zařazení na služební místo podané ve lhůtě do 15. června 2023.
















