zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Termíny Leica Tour 2020
10.12.2019 10:15 ZeměměřičSpolečnost Gefos zve na svoji každoroční Leica Tour, tentokrát s číslovkou 2020. V pořadí již 21. ročník Leica Tour 2020 se bude konat v sedmi městech. Určitě si vyberete místo, které vám bude nejblíže. Ústí nad Labem: pondělí 9.3.2020, Clarion Congress Hotel, Špitálské nám. 3517 Karlovy Vary: úterý 10.3.2020, Hotel Dvorana, Chebská 44 České Budějovice: středa 11.3.2020, Clarion […]
The post Termíny Leica Tour 2020 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
PF 2020
10.12.2019 9:02 TopGis Příjemné prožití vánočních svátků a šťastný nový rok vám přeje tým TopGis.Corelogic Integrates Hover Property Measurement and 3D Technology into Underwriting Platform
10.12.2019 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The collaboration will increase customer satisfaction in the property underwriting process and allow carriers to better manage inspection …Setkání geodetů ve Zlínském kraji
10.12.2019 8:34 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Na konci listopadu se ve Zlíně uskutečnil již 3. ročník Setkání zeměměřičů Zlínského kraje. Akce se zúčastnilo 47 geodetů převážně ze Zlínského kraje, ale pozvání přijali i hosté z dalších částí republiky. Zaznělo celkem osm kvalitních příspěvků, APG byla mezi přednášejícími zastoupena Ing. Jiřím Bradáčem („Aktuálně DTM“) a Ing. Jaroslavem Cibulkou („Zprávy z dění APG“). Prestiž celé akci dodala i osobní […]APGEO - SETKÁNÍ GEODETŮ VE ZLÍNSKÉM KRAJI
10.12.2019 1:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Na konci listopadu se ve Zlíně uskutečnil již 3. ročník Setkání zeměměřičů Zlínského kraje. Akce se zúčastnilo 47 ...Rekordní sbírka pro Moment Charity Shops
10.12.2019 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Praha, 10. prosince 2019: Do letošní tradiční dobročinné sbírky, kterou pořádáme ve spolupráci s Moment Charity Shops se zapojili zaměstnanci našeho úřadu doslova s nadšením. Pro někoho nepotřebné věci MOMENT vrací zpět do života a výtěžek putuje na další dobročinné projekty. Jejich přehled naleznete na stránkách charity http://www.moment-ops.cz/komu-pomahame.html. Při předání sbírky si pracovníci Kanceláře ústředního ředitele trochu zaposilovali, ale stálo to za to. Ohodnoťte výsledek sami z přiložených fotografií. Děkujeme, jste skvělí!SkyWatch Selected to Build Advanced Autonomous Space Systems Using Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics for the Canadian Space Agency
9.12.2019 21:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars December 9, 2019 -- SkyWatch is excited to announce that the company was selected by the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) to complete Phase I of the …Fortem Technologies Selected by NATO For Defence Against Terrorism Program To Premiere Counter-UAV Solutions
9.12.2019 19:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Pleasant Grove, UT, Dec. 09, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Fortem Technologies, the leading provider of airspace defense solutions for a drone world, …Schmidt Ocean Institute Maps One Million Square Kilometers of Seafloor and Joins Monumental Mapping Initiative
9.12.2019 19:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Schmidt Ocean Institute, a non-profit dedicated to advancing the world's understanding of the ocean with cutting-edge science, reached a major …Radiant Earth Foundation Releases World’s First Open Repository for Geospatial Training Data
9.12.2019 16:51 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WASHINGTON, Dec. 09, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- To make geospatial information more accessible to data scientists who are working on global …Bentley Systems Wins Downstream Award for Digitalization
9.12.2019 16:43 Bentley Systems
Software Provider Helps Dow Chemical Company Implement AWP Best Practices Across the Organization
HOUSTON – Downstream Awards – 19 November 2019 – Bentley Systems, Incorporated, the leading global provider of comprehensive software and digital twin cloud services for advancing the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure, and Digital Construction Works (DCW), a Bentley Systems and Topcon Positioning Group joint venture providing digital automation, integration, and “twinning” services, around fit-for-purpose software and cloud services, announced that Bentley Systems was named a winner at the Downstream Awards. Bentley won in the Innovation in Downstream Digitalization category for Dow Chemical Company’s (Dow) use of its ConstructSim application.
The awards celebrate the best of the downstream industry and are organized by Petrochemical Update, a division of Reuters Events. Awards were announced in 11 categories, with winners chosen by a panel of 10 judges representing the industry.
Anne-Marie Walters, industry marketing director, oil and gas and manufacturing at Bentley Systems, said, “We are honored to have received this award, which recognizes Bentley as a provider of digital construction workflows, for the advancement of infrastructure projects, and specifically for Dow’s outstanding work of integrating advanced work packaging (AWP) into its global project methodology.”
“Dow is applying AWP as a program on capital projects of all sizes,” said Susan Brandt, vice president, business development at DCW. “After evaluating several other software packages, Dow selected Bentley’s ConstructSim to automate AWP on a programmatic basis. The team architected its methodology to make AWP via ConstructSim scalable, targeting its implementation on any project valued at more than USD 10 million.”
The implementation of AWP methods with ConstructSim helped Dow achieve amazing tool time results for piping and structural steel. Structural steel wrench time performance improved to 70% and piping wrench time performance rose to 63%, while the industry average wrench time is 37%. Other non-quantifiable benefits were the transparency of construction progress, as Dow was able to use the ConstructSim model in weekly construction status meetings.
“This award demonstrates how Bentley Systems is leading the way in the downstream industry. The entire team at Bentley Systems should be so proud to be acknowledged for their great success in 2019, and we are already looking forward to seeing how Bentley Systems, and all the other winners and finalists, continue to build on their success in 2020,” said Jonathan Witherspoon, sector head of Petrochemical Update.
About Digital Construction Works
Digital Construction Works: Company Launch Video
Founded in 2019, Digital Construction Works (DCW) provides digital automation, integration, and “twinning” services, around fit-for-purpose software and cloud services from Topcon Positioning Group, Bentley Systems, and other software vendors, to realize the breakthrough potential of constructioneering for industrializing construction. DCW is transforming the construction industry from its legacy document-centric paradigm and simplifying and enabling digital automated workflows and processes, technology integration, and digital twinning services for infrastructure. company. DCW is a Bentley Systems and Topcon Positioning Group joint venture www.digitalconstructionworks.com
About Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems is the leading global provider of software solutions to engineers, architects, geospatial professionals, constructors, and owner-operators for the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure, including public works, utilities, industrial plants, and digital cities. Bentley’s MicroStation-based open modeling applications, and its open simulation applications, accelerate design integration; its ProjectWise and SYNCHRO offerings accelerate project delivery; and its AssetWise offerings accelerate asset and network performance. Spanning infrastructure engineering, Bentley’s iTwin Services are fundamentally advancing BIM and GIS to 4D digital twins.
Bentley Systems employs more than 3,500 colleagues, generates annual revenues of $700 million in 170 countries, and has invested more than $1 billion in research, development, and acquisitions since 2014. From inception in 1984, the company has remained majority-owned by its five founding Bentley brothers. www.bentley.com
--
Bentley, the Bentley logo, Digital Construction Works (DCW), and ConstructSim are either registered or unregistered trademarks or service marks of Bentley Systems, Incorporated or one of its direct or indirect wholly owned subsidiaries. All other brands and product names are trademarks of their respective owners.
Pracovní nabídka [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
9.12.2019 14:25 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Knihovna geografie Přírodovědecké fakulty Univerzity Karlovypřijme pracovnici/pracovníka
na pozici knihovnice/knihovník-bibliograf.
ODSTÁVKA VÝDEJE A PŘÍJMU DAT ÚAP
9.12.2019 14:10 Plzeňský kraj Od středy 11.12.2019 do pátku 3.1.2020 dojde k odstávce systému Výdeje a příjmu dat ÚAP z tohoto Geoportálu. Důvodem bude přechod na novou verzi datového modelu dat ÚAP a úprava navazujících systémů.ODSTÁVKA VÝDEJE A PŘÍJMU DAT ÚAP
9.12.2019 14:10 Plzeňský kraj Od středy 11.12.2019 do pátku 13.11.2019 dojde k odstávce systému Výdeje a příjmu dat tohoto Geoportálu. Důvodem bude přechod na novou verzi datového modelu dat ÚAP a úprava navazujících systémů.Aktualizace dat ÚAP poskytovatelů České radiokomunikace a.s., ČEZ Distribuce a.s. a data vodovodů a kanalizací z aplikace PRVaK
9.12.2019 14:05 Plzeňský kraj V datech územně analytických podkladů Plzeňského kraje byla provedena kompletní aktualizace dat ve správě poskytovatelů České radiokomunikace a.s., ČEZ Distribuce a.s. a data aplikace Plán rozvoje vodovodů a kanalizací.Shaping the future of EGNSS research and innovation
9.12.2019 13:13 European GNSS Agency
Together with the European Commission, the European GNSS Agency (GSA) has been consulting with GNSS user communities to take their input into consideration when defining EGNSS downstream funding priorities in the new financial perspective. A recent report from the GSA summarises the results of these consultations and outlines future R&I priorities.
EGNSS downstream R&I should build on the positive momentum achieved in Horizon 2020, Fundamental Elements and earlier framework programmes by leveraging space data to build applications, receivers that integrate the various EU space programme services and stimulate entrepreneurship and job creation in Europe.
The GSA’s consultation with the GNSS user community during its User Consultation Platforms in 2017 and 2018 revealed that, to make the space sector competitive, R&I investment should be focused on the downstream domain, increasing the use of space signals and data, and leveraging the differentiators of the EU space programmes to improve the worldwide market share of EU industry and SMEs.
Read this: Horizon 2020 key to international cooperation for Galileo & EGNOS
After 2020, when the Galileo system is fully operational and the new version of EGNOS will start to be deployed, the primary goal will be to establish European GNSS as the leader in those markets and sectors that best exploit the unique differentiators of the systems. Steps should also be taken to complete market uptake in longer-term regulated market segments (e.g. rail, aviation and maritime). Also new funding tools should be introduced in order to cope with the new needs.
Key recommendations
The report makes a number of key recommendations, including on the need to secure the budget and scope related to EGNSS downstream in the Space Regulation and Horizon Europe. What’s more, to achieve the goals outlined above, the report recommends that the Horizon Europe budget be significantly increased compared to Horizon 2020. This increase will also allow for larger pilot projects and operational implementations of Galileo differentiators.
It is also recommended that the Fundamental Elements funding mechanism should fill the gaps in the development of EGNSS-enabled receivers and antennas and target the emerging Galileo differentiators as they become operational, so as to facilitate market readiness.
Finally, the report recommends the introduction of new funding tools to cope with new needs that cannot be covered by the Horizon 2020 and Fundamental Elements tools as used until now:
- Innovation Procurement for the public sector as a customer of Galileo;
- Centres of Excellence to leverage regional and national competences as examples and supporters for others;
- Space-based entrepreneurship to provide a dedicated funding tool for start-ups and SMEs (e.g. in the area of mass market);
- Venture Capital to scale-up our start-ups.
Next steps
In April 2019 the European Parliament and the Council reached a political agreement on key elements of the Horizon Europe proposal. According to this agreement, Horizon Europe will be structured in three Pillars: 1. Excellent Science; 2. Global Challenges and European Industrial Competitiveness; and 3. Innovative Europe.
And this: Latest updates to Reports on User Needs and Requirements released
Early involvement and exchanges with Member States and consultation with stakeholders and the public at large took place during the summer of 2019, to stimulate a co-design process towards the first Strategic Plan for the framework programme. This included a workshop held at GSA headquarters in Prague.
This Strategic Planning process will prepare the Strategic Plan for Horizon Europe for 2021-2024. The plan will facilitate the implementation of Horizon Europe, focusing on Pillar II, by setting out key strategic orientations for support to research and innovation. Drafting of the first Horizon Europe Work Programme on the basis of the Strategic Plan will take place during 2020, after which Horizon Europe will come into effect in 2021.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Shaping the future of EGNSS research and innovation
9.12.2019 13:13 European GNSS Agency
Together with the European Commission, the European GNSS Agency (GSA) has been consulting with GNSS user communities to take their input into consideration when defining EGNSS downstream funding priorities in the new financial perspective. A recent report from the GSA summarises the results of these consultations and outlines future R&I priorities.
EGNSS downstream R&I should build on the positive momentum achieved in Horizon 2020, Fundamental Elements and earlier framework programmes by leveraging space data to build applications, receivers that integrate the various EU space programme services and stimulate entrepreneurship and job creation in Europe.
The GSA’s consultation with the GNSS user community during its User Consultation Platforms in 2017 and 2018 revealed that, to make the space sector competitive, R&I investment should be focused on the downstream domain, increasing the use of space signals and data, and leveraging the differentiators of the EU space programmes to improve the worldwide market share of EU industry and SMEs.
Read this: Horizon 2020 key to international cooperation for Galileo & EGNOS
After 2020, when the Galileo system is fully operational and the new version of EGNOS will start to be deployed, the primary goal will be to establish European GNSS as the leader in those markets and sectors that best exploit the unique differentiators of the systems. Steps should also be taken to complete market uptake in longer-term regulated market segments (e.g. rail, aviation and maritime). Also new funding tools should be introduced in order to cope with the new needs.
Key recommendations
The report makes a number of key recommendations, including on the need to secure the budget and scope related to EGNSS downstream in the Space Regulation and Horizon Europe. What’s more, to achieve the goals outlined above, the report recommends that the Horizon Europe budget be significantly increased compared to Horizon 2020. This increase will also allow for larger pilot projects and operational implementations of Galileo differentiators.
It is also recommended that the Fundamental Elements funding mechanism should fill the gaps in the development of EGNSS-enabled receivers and antennas and target the emerging Galileo differentiators as they become operational, so as to facilitate market readiness.
Finally, the report recommends the introduction of new funding tools to cope with new needs that cannot be covered by the Horizon 2020 and Fundamental Elements tools as used until now:
- Innovation Procurement for the public sector as a customer of Galileo;
- Centres of Excellence to leverage regional and national competences as examples and supporters for others;
- Space-based entrepreneurship to provide a dedicated funding tool for start-ups and SMEs (e.g. in the area of mass market);
- Venture Capital to scale-up our start-ups.
Next steps
In April 2019 the European Parliament and the Council reached a political agreement on key elements of the Horizon Europe proposal. According to this agreement, Horizon Europe will be structured in three Pillars: 1. Excellent Science; 2. Global Challenges and European Industrial Competitiveness; and 3. Innovative Europe.
And this: Latest updates to Reports on User Needs and Requirements released
Early involvement and exchanges with Member States and consultation with stakeholders and the public at large took place during the summer of 2019, to stimulate a co-design process towards the first Strategic Plan for the framework programme. This included a workshop held at GSA headquarters in Prague.
This Strategic Planning process will prepare the Strategic Plan for Horizon Europe for 2021-2024. The plan will facilitate the implementation of Horizon Europe, focusing on Pillar II, by setting out key strategic orientations for support to research and innovation. Drafting of the first Horizon Europe Work Programme on the basis of the Strategic Plan will take place during 2020, after which Horizon Europe will come into effect in 2021.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Doktorské studium ve Španělsku
9.12.2019 12:44 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucPokud by někoho lákalo rozjet akademickou kariéru v nějakém klimaticky teplejším regionu, je tady nabídka PhD studia ve Španělsku: Universitat Oberta de Catalunya, fully accredited online university with headquarters in Barcelona (Spain), is looking for PhD candidates for Network and Information Technologies Doctoral Programme (see thesis proposal below) to start September 2020. Potential candidates may […]
The post Doktorské studium ve Španělsku appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Přihlašujte se na Spationomy 2.0
9.12.2019 12:39 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucJak jste se mohli dočíst v hromadném emailu, katedra pokračuje ve Spationomy, tentokrát máme upgrade na Spationomy 2.0, kde se zaměříme na „playful/serious learning/gamification“ aspekty spojující geoinformatiku se socioekonomickými tématy, konkrétně na tvorbu simulační hry. Deadline je v pátek 13.12. Tak do toho, ať při hraní simulačních her nedopadnete takto:
The post Přihlašujte se na Spationomy 2.0 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
20191209 Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
9.12.2019 12:36 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kladno Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN"20191209 Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
9.12.2019 12:36 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kladno/O-uradu/Aktuality/20190828-Odborny-rada-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-(4)Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
9.12.2019 12:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kladnovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
9.12.2019 12:34 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kladno vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KNVrchní referent / rada oddělení dokumentace KN
9.12.2019 12:34 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-(2)20191209 Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.12.2019 12:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kladno Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem"20191209 Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.12.2019 12:06 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kladno/O-uradu/Aktuality/20190828-Odborny-rada-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-(3)Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.12.2019 12:04 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kladnovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.12.2019 12:04 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kladno vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostemRada / odborný rada oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.12.2019 12:04 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-n-(4)Gratulujeme Dronetagu k vítězství v Galileo Masters 2019, firmě kterou mentoroval Jakub a s kterou spolupracujeme na e-identifikaci
9.12.2019 11:23 UpVisionGratulujeme Dronetagu k vítězství v Galileo Masters. 🙂 Je to už více než rok, kdy Jakub vymyslel challenge do Space hackathonu 2018 a mentoroval tým, který vyhrál a tvoří dnešní úspěšný Dronetag. Společně testujeme e-identifikaci pro drony a přístup do naší aplikace Maia. Vycházející hvězda kosmické scény. ⭐⭐⭐Před pár dny se na European Space Weeku ve finských […]
The post Gratulujeme Dronetagu k vítězství v Galileo Masters 2019, firmě kterou mentoroval Jakub a s kterou spolupracujeme na e-identifikaci appeared first on Upvision.
Ph.D. and Postdoctoral research positions at the UCSB Geography Department
9.12.2019 9:42 Two postdoctoral research fellow positions at the University of California Santa BarbaraThe MOVE Laboratory (http://move.geog.ucsb.edu) at the Geography Department at UC Santa Barbara is seeking applications for two postdoctoral research fellowswith an anticipated start date as early as 15 January 2020. Candidates are expected to hold a Ph.D. in GIScience, Geography, Cartography, Computer Science, or Data Science. The successful […]Tenure Track Faculty Position at University of Wyoming: Assistant Professor in Geospatial Data Science and Computation
9.12.2019 9:41 Tenure Track Faculty Position: Assistant Professor in Geospatial Data Science and Computation To Apply:https://uwyo.taleo.net/careersection/00_ex/jobdetail.ftl?job=19004680&lang=en The Wyoming Geographic Information Science Center (WyGISC) at the University of Wyoming (UW) invites applications for a tenure track Assistant Professor position in Geospatial Data Science and Computation with expertise in Geospatial Informatics and an anticipated start date of August 2020. […]Lecturer/Senior Lecturer in Geospatial Science at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand
9.12.2019 9:40 https://jobs.canterbury.ac.nz/jobdetails?jobmc=1676UCGIS Lecturer/ Senior Lecturer in Geospatial ScienceSchool of Earth and Environment – Te Kura AronukurangiCollege of Science – Te Rāngai PūtaiaoUniversity of Canterbury – Te Whare Wānanga o WaitahaChristchurch, New Zealand Full-time at 37.5 hours per week (1.0 FTE) Continuing (i.e. permanent) position What You Will Do We invite applications for a Lecturer/ Senior Lecturer […]Tenure track Faculty Position in Remote Sensing and Geospatial Image Processing at the Wyoming Geographic Information Science Center, University of Wyoming
9.12.2019 9:38 Tenure track Faculty Position in Remote Sensing and Geospatial Image Processing at the Wyoming Geographic Information Science Center, University of Wyoming. To apply and for more details, visit: https://uwyo.taleo.net/careersection/00_ex/jobdetail.ftl?job=19004679&lang=en The Wyoming Geographic Information Science Center (WyGISC) at the University of Wyoming invites applications for a tenure track faculty position in remote sensing and geospatial image […]Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Děčín na Katastr
9.12.2019 8:17 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemoOdborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Děčín na Katastr
9.12.2019 8:17 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Děčín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Děčín na KatastrOdborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Děčín na Katastr
9.12.2019 8:17 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Děčínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Děčín na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
VÚV TGM - OpenGIS WFS - ISVS
9.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Výzkumný ústav vodohospodářský TGM, v.v.i., poskytuje přístup k prostorovým datům vybraných evidencí ISVS voda prostřednictvím stahovací služby (WFS).Studijní pobyty v Indii
9.12.2019 0:00 Geografický ústav MUČást studia můžete strávit nejen v Číně, ale i v Indii. V tomto případě jde o program meziuniverzitní mobility, který je administrovaný přímo na Geografickém ústavu, a výběrové řízení vyžaduje méně formalit a je kratší. Jde o prestižní státní univerzitu s netradičním jménem Tata Institute of Social Sciences v Mumbaí (známé též pod koloniálním názvem Bombaj). Více informací naleznete zde.
Termín uzávěrky přihlášek: 10. únor 2020
IWCE announces agenda and opens registration for its 44th annual conference for critical communications industry
6.12.2019 20:27 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars ATLANTA, Dec 3rd, 2019, IWCE the leading annual event for critical communications technology professionals, today unveiled its full program for its …Satellites key to '10 Insights in Climate Science' report
6.12.2019 16:04 ESA Observing the Earth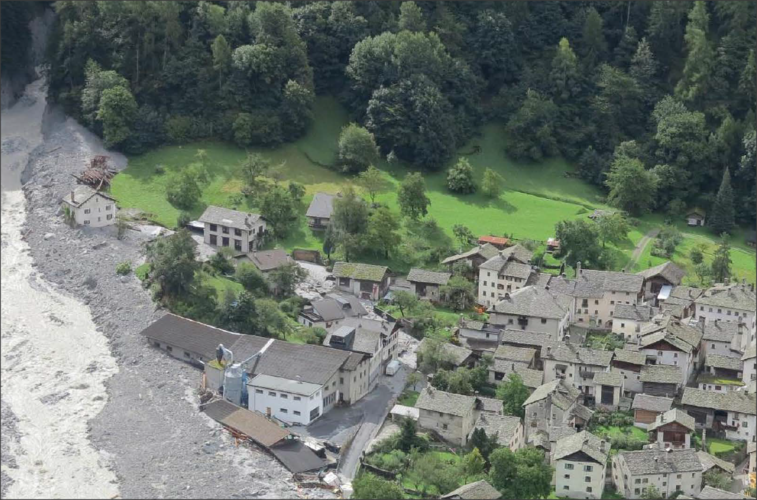
A new easy-to-read guide, ‘10 New Insights in Climate Science’ has been presented to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’s Executive Secretary, Patricia Espinosa, at the COP25 climate conference.
New biomass map to take stock of the world’s carbon
6.12.2019 15:30 ESA Observing the Earth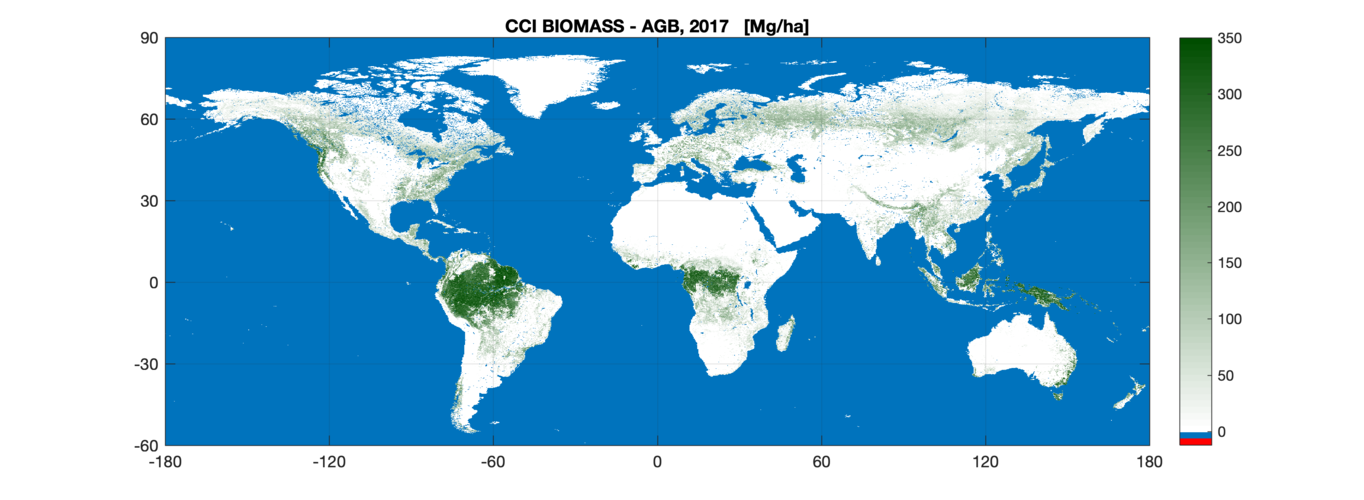
The first of a series of global maps aimed at quantifying change in carbon stored as biomass across the world’s forests and shrublands has been released today by ESA’s Climate Change Initiative at COP25 – the United Nation Climate Change Conference currently taking place in Madrid.
Nové číslo GaKO
6.12.2019 14:00
ÚGKK SR
Nové číslo časopisu Geodetického a Kartografického Obzoru 12/2019
20191206-GaKO-12-2019
6.12.2019 13:58 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Aktuální číslo Geodetického a kartografického obzoru (12/2019) je k dispozici ke stažení.GaKO 12/2019
6.12.2019 12:42 GaKO GaKO 12/2019 RADĚJ, K.–LECHNER, J.–DRBAL, A.: Výzkumný ústav geodetický, topografický a kartografický, v. v. i. – 65 let jeho existence IMRIŠEK, M.: Implementácia navigačného družicového systému Galileo do spracovania Európskej permanentnej sieteGaKO 12/2019
6.12.2019 12:42 GaKO GaKO 12/2019 RADĚJ, K.–LECHNER, J.–DRBAL, A.: Výzkumný ústav geodetický, topografický a kartografický, v. v. i. – 65 let jeho existence IMRIŠEK, M.: Implementácia navigačného družicového systému Galileo do spracovania Európskej permanentnej sieteGaKO 12/2019
6.12.2019 12:42 GaKO GaKO 12/2019 RADĚJ, K.–LECHNER, J.–DRBAL, A.: Výzkumný ústav geodetický, topografický a kartografický, v. v. i. – 65 let jeho existence IMRIŠEK, M.: Implementácia navigačného družicového systému Galileo do spracovania Európskej permanentnej sieteGaKO 12/2019
6.12.2019 12:38 GaKO GaKO 12/2019 RADĚJ, K.–LECHNER, J.–DRBAL, A.: Výzkumný ústav geodetický, topografický a kartografický, v. v. i. – 65 let jeho existence IMRIŠEK, M.: Implementácia navigačného družicového systému Galileo do spracovania Európskej permanentnej sietePerformance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
6.12.2019 12:23 European GNSS Agency
The Aeroficial Intelligence system leverages Galileo positioning and EGNOS augmentation in data-driven solutions that increase operational efficiency and considerably reduce fuel consumption in the aviation industry. In this way, it addresses a pressing challenge in an industry that is set to see the world’s aircraft fleet more than double in the next 20 years.
Galileo-Copernicus Synergy Challenge
In addition to the overall prize, 26 more prizes were awarded at this year’s Galileo Masters, including the Galileo-Copernicus Synergy Challenge. This award went to Xylene, an app that revolutionises the way timber is supplied to the market. The concept behind the Xylene app is to document every step of the timber supply chain, from the forest to the final product. This unique Source-2-Store process not only enables supply chain tracking, but also validates the origin of the wood as certified or not.
Read this: uMaze takes Accuracy Matters prize in Galileo Innovation Challenge
By automatically registering GNSS position and consignment volume data, matching this with the individual process steps and generating real-time reports in the event of violations, the app prevents illegal wood from entering the supply chain and reduces fraud. The end customer, in addition to each partner along the supply chain, can visualise the entire supply chain using QR codes. Leveraging Galileo positioning and Copernicus imagery, the app offers the best combination of reliability, feasibility and cost.
Promoting innovation
“Promoting innovation has always been a key goal for the GSA. During our 11 years of partnership with the Galileo Masters, the competition has been an important generator of new market-driven applications and services based on Galileo’s differentiators, and this year has been no different,” said GSA Executive Director Carlo des Dorides. “I would like to congratulate all of the participants in this year’s competition and particularly the winners for their innovative use of Galileo,” he said.
Idea of the year
In the ‘Idea of the Year’ category, the winner was CX-GEODRON – a radar-based drone payload for underground detection. The CX-Geodron project is developing a drone payload based on radar equipment and post-processing techniques for geo-referenced data to complement, and sometimes replace, LiDAR laser technologies and take the next step in underground detection applications.
And this: First Galileo-enabled autonomous vehicle successfully demonstrated
The use of drones in non-destructive inspection applications has proven feasible and effective, making this a field with very important growth potential. The accuracy, stability, and flight time of drone platforms have significantly improved and the feasibility of using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems in different applications related to terrestrial observation has been demonstrated. What’s more, the detection of buried objects is also continuing to improve with regard to resolution and depth.
Start-up of the Year
The winner in the ‘Start-up of the Year’ category - PODIS (POst DIstress Signal) - is a client-server IoT solution-as-a-service for automatic crash notification (ACN). The solution’s unique selling point is its patented underlying methodology for filtering out false alarms. Other ACN systems try to filter out false alarms on the client side, which is difficult due to varying vehicle behaviour, while PODIS does this on the server side.
In this way, PODIS maximises the use of the “golden hour”. This is a trauma term that refers to the first hour from the moment a car accident occurs. The goal of trauma professionals is to get injured people to a hospital within one hour to increase their chances of survival.
The Galileo Masters annually awards the best services, products, and business ideas using satellite navigation in everyday life, fostering the development of market-driven applications and identifying the most outstanding business cases related to GNSS, in line with the EU Space Strategy.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Performance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
6.12.2019 12:23 European GNSS Agency
The Aeroficial Intelligence system leverages Galileo positioning and EGNOS augmentation in data-driven solutions that increase operational efficiency and considerably reduce fuel consumption in the aviation industry. In this way, it addresses a pressing challenge in an industry that is set to see the world’s aircraft fleet more than double in the next 20 years.
Galileo-Copernicus Synergy Challenge
In addition to the overall prize, 26 more prizes were awarded at this year’s Galileo Masters, including the Galileo-Copernicus Synergy Challenge. This award went to Xylene, an app that revolutionises the way timber is supplied to the market. The concept behind the Xylene app is to document every step of the timber supply chain, from the forest to the final product. This unique Source-2-Store process not only enables supply chain tracking, but also validates the origin of the wood as certified or not.
Read this: uMaze takes Accuracy Matters prize in Galileo Innovation Challenge
By automatically registering GNSS position and consignment volume data, matching this with the individual process steps and generating real-time reports in the event of violations, the app prevents illegal wood from entering the supply chain and reduces fraud. The end customer, in addition to each partner along the supply chain, can visualise the entire supply chain using QR codes. Leveraging Galileo positioning and Copernicus imagery, the app offers the best combination of reliability, feasibility and cost.
Promoting innovation
“Promoting innovation has always been a key goal for the GSA. During our 11 years of partnership with the Galileo Masters, the competition has been an important generator of new market-driven applications and services based on Galileo’s differentiators, and this year has been no different,” said GSA Executive Director Carlo des Dorides. “I would like to congratulate all of the participants in this year’s competition and particularly the winners for their innovative use of Galileo,” he said.
Idea of the year
In the ‘Idea of the Year’ category, the winner was CX-GEODRON – a radar-based drone payload for underground detection. The CX-Geodron project is developing a drone payload based on radar equipment and post-processing techniques for geo-referenced data to complement, and sometimes replace, LiDAR laser technologies and take the next step in underground detection applications.
And this: First Galileo-enabled autonomous vehicle successfully demonstrated
The use of drones in non-destructive inspection applications has proven feasible and effective, making this a field with very important growth potential. The accuracy, stability, and flight time of drone platforms have significantly improved and the feasibility of using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems in different applications related to terrestrial observation has been demonstrated. What’s more, the detection of buried objects is also continuing to improve with regard to resolution and depth.
Start-up of the Year
The winner in the ‘Start-up of the Year’ category - PODIS (POst DIstress Signal) - is a client-server IoT solution-as-a-service for automatic crash notification (ACN). The solution’s unique selling point is its patented underlying methodology for filtering out false alarms. Other ACN systems try to filter out false alarms on the client side, which is difficult due to varying vehicle behaviour, while PODIS does this on the server side.
In this way, PODIS maximises the use of the “golden hour”. This is a trauma term that refers to the first hour from the moment a car accident occurs. The goal of trauma professionals is to get injured people to a hospital within one hour to increase their chances of survival.
The Galileo Masters annually awards the best services, products, and business ideas using satellite navigation in everyday life, fostering the development of market-driven applications and identifying the most outstanding business cases related to GNSS, in line with the EU Space Strategy.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Performance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
6.12.2019 12:23 European GNSS Agency
Performance Cockpit, a business intelligence system from the start-up Aeroficial Intelligence, was named the 2019 Overall Winner of the Galileo Masters international innovation competition during its awards ceremony, held as part of European Space Week on 4 December in Helsinki, Finland.
The Aeroficial Intelligence system leverages Galileo positioning and EGNOS augmentation in data-driven solutions that increase operational efficiency and considerably reduce fuel consumption in the aviation industry. In this way, it addresses a pressing challenge in an industry that is set to see the world’s aircraft fleet more than double in the next 20 years.
Galileo-Copernicus Synergy Challenge
In addition to the overall prize, 26 more prizes were awarded at this year’s Galileo Masters, including the Galileo-Copernicus Synergy Challenge. This award went to Xylene, an app that revolutionises the way timber is supplied to the market. The concept behind the Xylene app is to document every step of the timber supply chain, from the forest to the final product. This unique Source-2-Store process not only enables supply chain tracking, but also validates the origin of the wood as certified or not.
Read this: uMaze takes Accuracy Matters prize in Galileo Innovation Challenge
By automatically registering GNSS position and consignment volume data, matching this with the individual process steps and generating real-time reports in the event of violations, the app prevents illegal wood from entering the supply chain and reduces fraud. The end customer, in addition to each partner along the supply chain, can visualise the entire supply chain using QR codes. Leveraging Galileo positioning and Copernicus imagery, the app offers the best combination of reliability, feasibility and cost.
Promoting innovation
“Promoting innovation has always been a key goal for the GSA. During our 11 years of partnership with the Galileo Masters, the competition has been an important generator of new market-driven applications and services based on Galileo’s differentiators, and this year has been no different,” said GSA Executive Director Carlo des Dorides. “I would like to congratulate all of the participants in this year’s competition and particularly the winners for their innovative use of Galileo,” he said.
Idea of the year
In the ‘Idea of the Year’ category, the winner was CX-GEODRON – a radar-based drone payload for underground detection. The CX-Geodron project is developing a drone payload based on radar equipment and post-processing techniques for geo-referenced data to complement, and sometimes replace, LiDAR laser technologies and take the next step in underground detection applications.
And this: First Galileo-enabled autonomous vehicle successfully demonstrated
The use of drones in non-destructive inspection applications has proven feasible and effective, making this a field with very important growth potential. The accuracy, stability, and flight time of drone platforms have significantly improved and the feasibility of using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems in different applications related to terrestrial observation has been demonstrated. What’s more, the detection of buried objects is also continuing to improve with regard to resolution and depth.
Start-up of the Year
The winner in the ‘Start-up of the Year’ category - PODIS (POst DIstress Signal) - is a client-server IoT solution-as-a-service for automatic crash notification (ACN). The solution’s unique selling point is its patented underlying methodology for filtering out false alarms. Other ACN systems try to filter out false alarms on the client side, which is difficult due to varying vehicle behaviour, while PODIS does this on the server side.
In this way, PODIS maximises the use of the “golden hour”. This is a trauma term that refers to the first hour from the moment a car accident occurs. The goal of trauma professionals is to get injured people to a hospital within one hour to increase their chances of survival.
The Galileo Masters annually awards the best services, products, and business ideas using satellite navigation in everyday life, fostering the development of market-driven applications and identifying the most outstanding business cases related to GNSS, in line with the EU Space Strategy.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Omezení provozu 31.12.2019
6.12.2019 11:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Dovolujeme si upozornit, že v úterý dne 31.12.2019 budou všechna katastrální pracoviště Katastrálního úřadu pro Jihočeský kraj otevřena pro veřejnost pouze v době od 8:00 do 13:00 hodin.Děkujeme za pochopení.
Ing. Jiří Vrána
ředitel úřadu
Omezení provozu 31.12.2019
6.12.2019 11:56 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Omezeni-provozu-31-12-2019Účastnili jsme se Amsterdam Drone Week a hlavně EASA High Level Conference on Drones 2019
6.12.2019 11:19 UpVisionNáročný týden v Amsterdamu je u konce. 🙂 Účastnili jsme se ještě Amsterdam Drone Week a hlavně EASA High Level Conference on Drones 2019. Na fotce je Jakub s projektovým manažerem EASA, který má na starost novou U-Space regulaci, kterou společně dlouhodobě konzultujeme. Náročný týden v Amsterdamu je u konce. 🙂 Účastnili jsme se ještě Amsterdam Drone Week […]
The post Účastnili jsme se Amsterdam Drone Week a hlavně EASA High Level Conference on Drones 2019 appeared first on Upvision.
Referent v oddělení aktualizace KN
6.12.2019 10:40 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Referent v oddělení aktualizace KNReferent v oddělení aktualizace KN
6.12.2019 10:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Referent-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-KNReferent v oddělení aktualizace KN
6.12.2019 10:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Referent v oddělení aktualizace KN
Provoz 31.12.2019
6.12.2019 10:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Děkujeme za pochopení
Provoz 31.12.2019
6.12.2019 10:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Vážení klienti,
dne 31.12.2019 budou úřední hodiny 8:00 – 13:00 hod.
Úřední hodiny Katastrálního pracoviště Jičín budou 8:00 – 11:00 hod.
Děkujeme za pochopení
Provoz 31.12.2019
6.12.2019 10:21 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Děkujeme za pochopení
Provoz 31.12.2019
6.12.2019 10:21 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Provoz-31-12-2019Mato Grosso, Brazil
6.12.2019 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth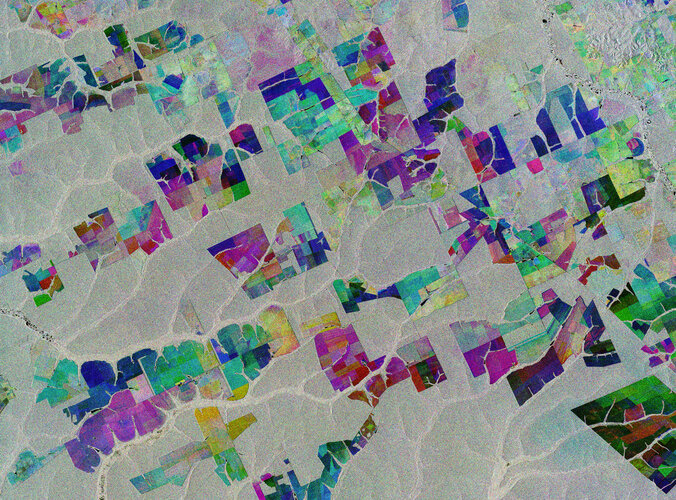 Image:
Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission takes us over part of the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso deep in the Amazon interior.
This image combines three separate radar images from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission taken about two years apart to show change in crops and land cover over time.
Unlike images from satellites carrying optical or ‘camera-like’ instruments, images acquired with imaging radar are interpreted by studying the intensity of the backscatter radar signal, which is related to the roughness of the ground.
Here, the first image, from 2 May 2015, is picked out in blue; the second, from 16 March 2017, picks out changes in green; and the third from 18 March 2019 in red; areas in grey depict little or no change between 2015 and 2019.
Ironically, Mato Grosso means ‘great woods’, but, as these coloured rectangular shapes portray, much of the tropical forest has been cut down and given over to farming. While this image only shows a small area, Mato Grosso is one of Brazil’s top cattle-producing and crop-producing states, with the main crops including corn, soya and wheat.
However, although the state has one of the highest historical rates of deforestation in Amazonian Brazil, deforestation is slowing and Mato Grosso is now said to be a global leader in climate-change solutions.
As an advanced radar mission, Copernicus Sentinel-1 can image the surface of Earth through cloud and rain and regardless of whether it is day or night. This makes it ideal for monitoring areas that tend to be covered by cloud such as rainforests.
This image is also featured on the Earth from Space video programme.
Mapová aplikace ÚAP - aktualizace
6.12.2019 10:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Územně analytické podklady byla aktualizována k 6.12.2019.Earth from Space: Mato Grosso
6.12.2019 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:02:33
Video:
00:02:33
In this week's edition of the Earth from Space programme, the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission takes us over part of the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso deep in the Amazon interior.
See also Mato Grosso, Brazil to download the image.
DigEplan Integrates Electronic Plan Review to Cityworks Platform
6.12.2019 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars December 04, 2019 -- DigEplan, a leading integrated electronic plan review solution, and GIS-centric public asset management solution firm, Cityworks …Map of the Month: Online & brick-and-mortar purchasing power for toys & hobbies, Germany 2019
6.12.2019 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GfK's Map of the Month for December illustrates the 2019 regional distribution of purchasing power for toys and hobbies via online and …Astronaut assistant CIMON-2 is on its way to the International Space Station
6.12.2019 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Human-machine interaction and artificial intelligence in spaceNew technology demonstrator with improved ‘sense of direction’ and …Cena za nejlepší mapu putuje do Olomouce
6.12.2019 8:59 GISportal.cz
Kartografický časopis Journal of Maps udělil cenu Best Map Award za rok 2019 Jiřímu Pánkovi a Bohumilu Ptáčkovi, autorům článku Mapping citizens’ emotions: participatory planning support system in Olomouc, Czech Republic. Cena je udělována od roku 2008 a nejedná se o čistě ocenění nejlepší mapy, či akademického článku, ale spíše o kombinaci excelentních výsledků v obou oblastech. Letošní […]
The post Cena za nejlepší mapu putuje do Olomouce appeared first on GISportal.cz.
INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
6.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 02. 12. 2019 je to 96,63% území České republiky, t.j. 76 208,84km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Katastrální mapa ve formátech DGN a DXF poskytovaná v e-shopu
6.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě je poskytována zdarma ve formátu DGN a DXF a obsahuje prvky Digitální katastrální mapy (DKM) a Katastrální mapy digitalizované (KMD), tedy bodová pole, budovy, další prvky mapy, hranice parcel, katastrální hranice, parcely katastru nemovitostí, prvky orientační mapy a hranice věcného břemene. Z důvodu použití formátu DGN produkt neobsahuje značky na liniích a oblouky jsou nahrazeny lomenými čárami. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě k 02. 12. 2019 pokrývá 96,63% území České republiky, t.j. 76 208,84km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě poskytovaná v e-shopu
6.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě je poskytována za úplatu a obsahuje analogovou mapu s kompletní kresbou. Analogová mapa pokrývá 3,20 % území České republiky, což je 2 522,72km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.INSPIRE téma Parcely (CP)
6.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze katastrální území (pro celou Českou Republiku) a parcely a jejich hranice z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 02. 12. 2019 je to 96,63% území České republiky, t.j. 76 208,84km2). Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Parcely ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Adresy (AD)
6.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma adresy (AD). Vychází především z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze adresní místa a jejich komponenty, kterými jsou stát, obec, část obce, městský obvod v Praze (MOP), městký obvod/městská část (MO/MČ), ulice a pošta a to na území celé České Republiky. Obsahují rozvněž geometrii, která určuje definiční bod adresního místa. V datové sadě nění uvedeno 1,28%, t.j. 37566 adresních míst (k 02. 12. 2019), protože neobsahují definiční bod, podle kterého by je bylo možné prostorově určit. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech a ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních a INSPIRE Data Specification on Addresses v 3.0.1 z 26.4.2010. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Adresy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Budovy (BU)
6.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma budovy (BU). Data pochází částečně z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech, a částečně z ISKN (Informační systém katastru nemovistostí). Zdrojem informací o budovách v ISKN je objekt Stavba, v RÚIAN je to Stavební objekt. Většina Staveb je zároveň Stavebními objekty, ale jsou případy, kdy tomu tak není. Kromě Budov datová sada obsahuje i části budov, které jsou pro potřeby INSPIRE vyjádřeny vchody z RÚIAN. Vchody obsahují informace o počtu podlaží, technickoekonomických atributech apod. Datová sada pokrývá celé území české republiky. V datové sadě není uvedeno 1,16%, t.j. 48688 budov (k 02. 12. 2019), protože neobsahují definiční bod ani polygon. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech, ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních, v zákoně 256/2013 Sb., o katastru nemovitostí, v katastrální vyhlášce č. 357/2013 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Buildings v 3.0 z 13.12.2013. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Budovy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.SAIC Announces Third Quarter of Fiscal Year 2020 Results
6.12.2019 0:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Revenues: $1.6 billion; 38% revenue growthDiluted earnings per share: $0.94; Adjusted diluted earnings per share(1): $1.39
Adjusted EBITDA(1) as …
Nabídka práce - Správce prostorových dat
6.12.2019 0:00 Geografický ústav MUOdbor dopravy Magistrátu města Brna hledá pracovníka na pozici Správce prostorových dat (Brno).
Bližší informace naleznete ZDE.
Stipendium ke studiu v Čínské lidové republice v akademickém roce 2020/2021
6.12.2019 0:00 Geografický ústav MUČínská vláda nabízí v rámci iniciativy 17+1 českým zájemcům 40 stipendijních míst ke studiu bakalářských, magisterských i doktorských studijních programů v ČLR počínaje akademickým rokem 2020/2021, jakož i ke studijním či výzkumným stážím v ČLR v délce jednoho až dvou semestrů v akademickém roce 2020/2021.
Zájemci doručí požadované dokumenty ve stanoveném termínu na Odbor mezinárodních vztahů MŠMT.Termín pro odevzdání přihlášek je 13. ledna 2020 do 15 hodin.
Podrobné informace naleznete ZDE.
New 35-year satellite data record charts sea-temperature change
5.12.2019 17:47 ESA Observing the Earth
Four trillion satellite measurements, taken over four decades from 1981 to 2018, have been merged to create a continuous global record and will help to understand the science behind Earth’s climate.
A paper published recently in Nature Scientific Data describes how this new dataset of global sea-surface temperature is one of the longest satellite climate data records available. The dataset will play a key role in evaluating global models used to predict how our oceans will influence future climate change.
35-year data record charts sea-temperature change
5.12.2019 17:47 ESA Observing the Earth
Four trillion satellite measurements, taken over four decades from 1981 to 2018, have been merged to create a continuous global record that will help to understand the science behind Earth’s climate.
A paper published recently in Nature Scientific Data describes how this new dataset of global sea-surface temperature is one of the longest satellite climate data records available. The dataset will play a key role in evaluating global models used to predict how our oceans will influence future climate change.
35-year data record charts sea temperature change
5.12.2019 17:47 ESA Observing the Earth
Four trillion satellite measurements, taken over four decades from 1981 to 2018, have been merged to create a continuous global record that will help to understand the science behind Earth’s climate.
A paper published recently in Nature Scientific Data describes how this new dataset of global sea-surface temperature is one of the longest satellite climate data records available. The dataset will play a key role in evaluating global models used to predict how our oceans will influence future climate change.
Unicorn bude pro CETIN zavádět software pro projektování a plánování optické kabeláže
5.12.2019 16:42 GeoBusiness Společnost Česká telekomunikační infrastruktura (CETIN), která provozuje telekomunikační sítě a datová centra oddělené od operátora O2, si ve výběrovém řízení vybrala společnost Unicorn, aby do jejích GISů a systémů pro podporu provozu zavedla software nizozemské firmy Geostruct. Řešení od Geostructu bude umožňovat plánování a projektování FTTx sítí ve všech lokalitách. „Dodávaný software podporuje kompletně celý […]Unicorn bude pro CETIN zajišťovat projektování a plánování optické kabeláže
5.12.2019 16:42 GeoBusiness Společnost Česká telekomunikační infrastruktura (CETIN), která provozuje telekomunikační sítě a datová centra oddělené od operátora O2, si ve výběrovém řízení vybrala společnost Unicorn, aby do jejích GISů a systémů pro podporu provozu zavedla software nizozemské firmy Geostruct. Řešení od Geostructu bude umožňovat plánování a projektování FTTx sítí ve všech lokalitách. „Dodávaný software podporuje kompletně celý […]Dedrone Counter-Drone Technology Achieves Approval by the UK Centre for the Protection of National Infrastructure (CPNI)
5.12.2019 16:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars UK Centre for Protection of National Infrastructure (CPNI) approves Dedrone Technology for sUAS detectionLONDON and SAN FRANCISCO, Dec. 5, 2019 …
rideOS adds Mapping and Automotive Technologies Industry Leaders, Brian McClendon & Ralf Lenninger, to Advisory Board
5.12.2019 16:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN FRANCISCO, Dec. 05, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- rideOS, a technology platform designed to accelerate the safe, global rollout of next-generation …Clark Regional Waste Water District and FLO Analytics Leverage Flowfinity to Achieve GIS-Centric Digital Transformation Project
5.12.2019 16:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VANCOUVER, British Columbia, Dec. 5, 2019 — (PRNewswire) — Flowfinity Wireless Inc. today published a case study outlining how …Pozvánka na seminář Družicové metody v geodézii a katastru
5.12.2019 16:18 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČU Seminář Družicové metody v geodézii a katastru se bude konat ve čtvrtek 30. ledna 2020 na VUT v Brně. Jedná se již o 23. ročník této akce. Podrobnosti naleznete na http://geodesy.fce.vutbr.cz/konference/gnss-seminar/, kde je možno se i přihlásit.Cartotrophy 2019
5.12.2019 15:00 Geografický ústav MUV pondělí 5. prosince 2019 se na Geografickém ústavu uskuteční již 14. ročník šifrovací hry s geograficko-kartografickým nádechem - Cartotrophy. Letos ve znamení virtuální reality.
Podrobné informace o hře a odkaz na registraci naleznete na http://www.geogr.muni.cz/cartotrophy. Možnost přihlášení vyprší 1. prosince 2019 v 18:00, tak neváhejte.
Těší se na vás organizační tým.
Sentinel-6 Mission
5.12.2019 14:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:05:20
Video:
00:05:20
In a cleanroom in Ottobrunn, Germany, the latest Copernicus Sentinel satellite is ready for final testing before it is packed up and shipped to the US for liftoff next year. Designed and built to chart changing sea level, it is the first of two identical Sentinel-6 satellites that will be launched consecutively to continue the time series of sea-level measurements. This new mission builds on heritage from previous ocean topography satellites, including the French–US Topex-Poseidon and Jason missions, previous ESA missions such as the ERS satellites, Envisat and CryoSat, as well as Copernicus Sentinel-3. With millions of people around the world at risk from rising seas, it is essential to continue measuring the changing height of the sea surface so that decision-makers are equipped to take appropriate mitigating action – as is being currently highlighted at the COP-25 Climate Change Conference in Spain.
Sentinel-6: charting sea level
5.12.2019 14:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:05:20
Video:
00:05:20
In a cleanroom in Ottobrunn, Germany, the latest Copernicus Sentinel satellite is ready for final testing before it is packed up and shipped to the US for liftoff next year. Designed and built to chart changing sea level, it is the first of two identical Sentinel-6 satellites that will be launched consecutively to continue the time series of sea-level measurements. This new mission builds on heritage from previous ocean topography satellites, including the French–US Topex-Poseidon and Jason missions, previous ESA missions such as the ERS satellites, Envisat and CryoSat, as well as Copernicus Sentinel-3. With millions of people around the world at risk from rising seas, it is essential to continue measuring the changing height of the sea surface so that decision-makers are equipped to take appropriate mitigating action – as is being currently highlighted at the COP-25 Climate Change Conference in Spain.
Capella Space Appoints RSI as Marketing Partner in India
5.12.2019 11:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN FRANCISCO and HYDERABAD, December 4, 2019 — Capella Space, an information services company providing Earth observation data on demand, …New 2019 CRESTA zones offer universal standard for global risk management
5.12.2019 11:42 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GfK’s new CRESTA zones provide a worldwide cartographic standard for the aggregation and exchange of risk insightsBruchsal, Germany, …
Universidad del Valle de Guatemala is ready to deploy Guatemala’s first satellite under UNOOSA-JAXA KiboCUBE Programme
5.12.2019 11:29 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VIENNA/TOKYO, 4 December (UN Information Service) – The team from Universidad del Valle de Guatemala have completed the development of their …Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
5.12.2019 11:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
5.12.2019 11:29 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hodonín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti HodonínVrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
5.12.2019 11:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hodonínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
5.12.2019 11:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vrchni-referent-rada-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-naVrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
5.12.2019 11:29 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení dokumentace KN na katastrálním pracovišti HodonínGreen City Watch grabs top prize at Copernicus Masters
5.12.2019 11:20 ESA Observing the Earth
Green City Watch won this year’s Copernicus Masters competition in a ceremony held yesterday at the European Space Week in Helsinki, Finland. Using Copernicus Sentinel satellite data, this application combines big data from space with artificial intelligence to measure the quality of green urban spaces.
Plánovaná odstávka - Výpadek sítě
5.12.2019 10:00 Středočeský kraj Z důvodu výměny infrastrukturních prvků dojde termínu od 06.12. 14:00 do 08.12. do 23:59 k výpadku sítě, tj. k výpadku webových stránek úřadu a dalších informačních systémů provozovaných v síti Krajského úřadu Středočeského kraje.Zkrácení úředních hodin 31.12.2019
5.12.2019 9:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Pardubicky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Zkraceni-urednich-hodin-31-12-2019Zkrácení úředních hodin 31.12.2019
5.12.2019 9:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zkrácení úředních hodin 31.12.2019 VÁŽENÍ KLIENTI,V ÚTERÝ DNE 31. 12. 2019 BUDOU ÚŘEDNÍ HODINY POUZE V DOBĚ OD 8:00 DO 12:00 HODIN.
DĚKUJEME ZA POCHOPENÍ.
Geoobchod zve na setkání uživatelů GNSS techniky 2020
5.12.2019 7:19 ZeměměřičSpolečnost Geoobchod zve na setkání uživatelů GNSS techniky, které se uskuteční ve dnech 14. a 15. ledna 2020 v Koutech u Ledče nad Sázavou. Pozvánka na setkání Letos se chceme zaměřit na podrobné informace o fungování všech satelitních systémů, které u nás můžete využívat a na jejich výhody, nevýhody a hlavně možnosti. Internetové připojení se stále vyvíjí a vy potřebujete vědět, jaké máte možnosti v terénu, […]
The post Geoobchod zve na setkání uživatelů GNSS techniky 2020 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
EUGEO 2021
5.12.2019 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace 8th EUGEO CongressPřírodovědecká fakulta Univerzity Karlovy a Česká Geografická společnost ve spolupráci s Asociací geografických společností v Evropě organizuje 8th EUGEO Congress on the Geography of Europe v Praze. Kongres se uskuteční od 28. Června do 1. Července 2021. Hlavní téma kongresu je "Sustainable geographies in the heart of Europe", odkazující na vášeň
Poslanci schválili vznik Portálu stavebníka, standard BIM, digitální stavební deník a novelu zeměměřického zákona
5.12.2019 6:00 GeoBusiness Poslanecká sněmovna dne 4. prosince 2019 schválila novelu zákona o zeměměřictví a o změně a doplnění některých zákonů, souvisejících s jeho zavedením. Předlohu zákona nyní dostanou k projednání senátoři. Digitalizace by od července 2023 měla zkracovat a zjednodušovat stavební řízení všem účastníkům. Vzniknout má elektronický informační systém pro vyřizování všech záležitostí, které se týkají stavebního […]Drone Aviation and LTE Advanced / 5G-NR Wireless Technology Provider ComSovereign Announce Merger
5.12.2019 1:26 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Combined Organization to Focus on Penetration of 5G Systems to New and Existing Global Carrier Customer Base for Fixed Infrastructure and Aerial …Srážkoodtoková data
5.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Vybraná, veřejně přístupná, část dat z databází ČHMÚ určená pro studijní účely.V hydrologické části je umístěno 10 stanic povrchových vod na větších povodích s průměrnými denními průtoky od začátku pozorování a 3 stanice na malých povodích v Jizerských horách s průměrnými denními průtoky, hodinovými průtoky, měřením sněhu, denními úhrny srážek a hodinovými úhrny srážek od roku 2002.V klimatologické části jsou umístěny 3 stanice s denními úhrny srážek a teplotami od roku 2002.Stahovací služba - srážkoodtoková data
5.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Vybraná, veřejně přístupná, část dat z databází ČHMÚ určená pro studijní účely.V hydrologické části je umístěno 10 stanic povrchových vod na větších povodích s průměrnými denními průtoky od začátku pozorování a 3 stanice na malých povodích v Jizerských horách s průměrnými denními průtoky, hodinovými průtoky, měřením sněhu, denními úhrny srážek a hodinovými úhrny srážek od roku 2002.V klimatologické části jsou umístěny 3 stanice s denními úhrny srážek a teplotami od roku 2002.Stránka existuje i v angličtině.Geoelektrika – Vertikální elektrické sondování (VES)
5.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Databáze obsahuje situaci měřících stanovišť vertikálního elektrického profilování a měřené sondážní křivky.Petrofyzika
5.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Databáze obsahuje soubor laboratorních měření komplexu fyzikálních vlastností hornin, který lze rozdělit na dvě skupiny: 1) skalární parametry - hustotní parametry (mineralogická a objemová hustota), pórovitost, střední magnetická susceptibilita a parametry přirozené radioaktivity (U, Th, K, celková aktivita gama),2) parametry směrově závislé - remanentní magnetizace, hodnoty šíření elastických vln, elektrické vlastnosti a vyzvaná polarizace. Databáze se člení na 2 subregistry – fyzikální vlastnosti vzorků z povrchu (20371 ks) a vzorků z vrtných jader z 550 vrtů.Gravimetrie
5.12.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Databáze obsahuje data z gravimetrického mapování ČR v měřítkách 1 : 200 000 z let 1957-1960 (pokryto 100% území – ca 23tis tíhových bodů). Od roku 1960 začalo systematické mapování v měřítku 1 : 25 000, které pokrývá téměř 70% rozlohy republiky. Ke konci roku 2018 je v databázi využíváno pouze ca 4 tisíce bodů (3992) z původního mapování 1 : 200 000 a 304199 tisíc bodů z měření 1 : 25 000, které stará měření 1 : 200 000 na příslušných mapách postupně nahrazují.Nexit Launches as the Next Generation in Mobile Mapping With $10 Million in Funding
4.12.2019 23:47 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars All-in-One Road Trip App Launches During Peak Holiday Travel Season, Providing Drivers with Unmatched Navigation & Search FeaturesNEW YORK …
Poslanecká sněmovna schválila novelu zeměměřického zákona
4.12.2019 23:28 ZeměměřičPoslanecká sněmovna dne 4. prosince 2019 schválila novelu zákona o zeměměřictví a o změně a doplnění některých zákonů, souvisejících s jeho zavedením. Předlohu zákona nyní dostanou k projednání senátoři. Digitalizace by od července 2023 měla zkracovat a zjednodušovat stavební řízení všem účastníkům. Vzniknout má elektronický informační systém pro vyřizování všech záležitostí, které se týkají stavebního řízení. Povolovací řízení se má vést prostřednictvím tzv. Portálu […]
The post Poslanecká sněmovna schválila novelu zeměměřického zákona appeared first on Zeměměřič.
MGISS Appoints Mike Cooper to Expand Geospatial Business
4.12.2019 16:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars December 04, 2019 -- Mike Cooper has joined the management team at MGISS, a specialist in the use of geospatial technology in the utility, …The Latest RoboSense LiDAR Perception Solution Will Support Robo Taxi Development
4.12.2019 16:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars A Developed And Complete RS-Fusion-P5 Was Launched In Markets Outside ChinaSHENZHEN, China — (BUSINESS WIRE) — December 4, 2019 …