zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Bentley and Trimble launch new Hololens 2 products
11.3.2019 14:26 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Extranet Evolution, UK
Read the articleWelcome to the future
11.3.2019 14:19 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
AEC Magazine, UK
Read the articleMicrosoft targets construction with new HoloLens
11.3.2019 14:09 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
New Civil Engineer, UK
Read the article20190311 Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
11.3.2019 13:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik "20190311 Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
11.3.2019 13:23 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Pribram/O-uradu/Aktuality/20161013Rada-odborny-rada-–-informatik-(2)(ID SM 30003687) odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy
11.3.2019 13:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj - odbor obnovy katastrálního operátuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
(ID SM 30003687) odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu (3040) na Katastrálním úřadu pro Jihočeský kraj
(ID SM 30003687) odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy
11.3.2019 13:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-ref-v-ref_obnova(ID SM 30003687) odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy
11.3.2019 13:14 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj - odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo (ID SM 30003687) odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovyVrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
11.3.2019 13:13 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-–-spravce-informacnich-a-komuVrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
11.3.2019 13:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbramvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatik
11.3.2019 13:13 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií – informatikPracovní příležitosti v Agentuře pro evropský GNSS (GSA)
11.3.2019 12:57 Český Kosmický PortálVyužijte příležitost a staňte se zaměstnancem Agentury pro Evropský GNSS (GSA), sídlící od r. 2012 v pražských Holešovicích. Na webových stránkách GSA v sekci Job opportunities naleznete podrobné informace o volných pracovních místech.
Mikronosiče pomohou růstu evropské ekonomiky
11.3.2019 12:10 Český Kosmický PortálRozkvétající trh s malými družicemi je za poptávkou po nových způsobe dopravy do vesmíru. Aktuální studie proveditelnosti podporovaná ESA studovala nově nabízené služby mikronosičů a vytváření nových obchodních příležitostí.
Mikronosiče pomohou růstu evropské ekonomiky
11.3.2019 12:10 Český Kosmický PortálRozkvétající trh s malými družicemi je za poptávkou po nových způsobe dopravy do vesmíru. Aktuální studie proveditelnosti podporovaná ESA studovala nově nabízené služby mikronosičů a vytváření nových obchodních příležitostí.
Working towards AI and Earth observation
11.3.2019 11:46 ESA Observing the Earth
Satellites observing and measuring our planet deliver a huge amount of data that not only helps understand how our world is changing, but also benefits society by feeding into a myriad of everyday applications. Taking this to the next level, ESA is exploring how even more could be gained from these valuable data by using artificial intelligence (AI).
Rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV1002
11.3.2019 11:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-–-rozhodovani-o-povoleni-vkladuRada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV1002
11.3.2019 11:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-městovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV1002
Rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV1002
11.3.2019 11:02 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu RPV1002Rada/odborný rada v oddělení obnovy a revize KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno-venkov
11.3.2019 10:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-venkovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada v oddělení obnovy a revize KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno-venkov
Rada/odborný rada v oddělení obnovy a revize KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno-venkov
11.3.2019 10:52 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-obnovy-a-revize-KN-naRada/odborný rada v oddělení obnovy a revize KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno-venkov
11.3.2019 10:52 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-venkov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada v oddělení obnovy a revize KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno-venkov20190304-Zkoušky ÚOZI
11.3.2019 9:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zkoušky ÚOZI se budou konat 20. a 21. března 2019.20190304-Zkoušky ÚOZI
11.3.2019 9:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zkoušky ÚOZI se budou konat dne 20. a 21. března 2019.Soutěž o nejlepší mapu na geografické téma
11.3.2019 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformaceOrganizátoři Zeměpisné olympiády ve spolupráci s Českou kartografickou společností vyhlašují doplňkovou soutěž O nejlepší mapu na geografické téma.
Každý účastník 21. ročníku Zeměpisné olympiády se může soutěže zúčastnit odevzdáním vlastnoručně vytvořené mapy na libovolné geografické téma.
Autoři nejlepších map budou odměněni Českou
Geologická mapa 1 : 25 000
11.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Aplikace mapového serveru zobrazuje výsledky geologického mapování České republiky v měřítku 1 : 25 000 (GEOČR25), které probíhá od roku 1999 po současnost. Jedná se o zakryté geologické mapy, další navazující speciální mapy (Nerostných surovin, Geofaktorů životního prostředí), které jsou konstruovány od roku 2008, jsou zatim k dispozici ke stažení v souborech PDF.Geologická mapa 1 : 25 000 (GEOČR25)
11.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE ArcGIS Server služba zobrazuje výsledky geologického mapování v měřítku 1 : 25 000, které probíhá od roku 1999 po současnost. Jedná se o zakryté geologické mapy, další navazující speciální mapy (Nerostných surovin, Geofaktorů životního prostředí), které jsou konstruovány od roku 2008, jsou zatim k dispozici ke stažení v souborech PDF.Přehled geologického mapování 1 : 25 000 (GEOČR25)
11.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE ArcGIS Server služba zobrazuje přehled geologického mapování v měřítku 1 : 25 000 (GEOČR25), které probíhá od roku 1999 po současnost.BIM pro stavby dopravní infrastruktury
10.3.2019 22:26 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Zasedání pracovní skupiny pro inženýrskou geodézii se zúčastnil Ivo Vykydal, ředitel odboru kanceláře ředitele SFDI, který představil plán digitalizace a zavádění BIM pro stavby dopravní infrastruktury. Diskutován byl návrh předpisu pro informační modelování staveb pro infrastrukturní stavby – Datový standard – pro PDPS. Lukáš Kutil informoval, že návrh předpisu byl členy pracovní skupiny doplněn o tři zásadní […]'PCI Geomatics Offers Service Pack Update for Geomatica and GXL 2018" by Susan Smith
10.3.2019 9:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsVÚGTK nabízí volné pozice v oblasti GNSS
10.3.2019 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Výzkumný ústav geodetický, topografický a kartografický nabízí dvě volná místa v oblasti globálních navigačních satelitních systémů:Pozice pro analýzy a využití dat z Globálních Navigačních Družicových Systémů (GNSS):Požadujeme:• vysokoškolské vzdělání v oblasti přírodních či technických věd• znalost programování v prostředí Linux• zájem oAPGEO - BIM PRO STAVBY DOPRAVNÍ INFRASTRUKTURY
10.3.2019 1:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Zasedání pracovní skupiny pro inženýrskou geodézii se zúčastnil Ivo Vykydal, ředitel odboru kanceláře ředitele SFDI ...Nedostupnost aplikace DP přes IPv6
9.3.2019 16:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Z technických důvodů není aplikace dálkového přístupu do katastru nemovitostí dostupná přes IPv6.Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Nedostupnost aplikace DP přes IPv6
9.3.2019 16:25 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Z technických důvodů není aplikace dálkového přístupu do katastru nemovitostí dostupná přes IPv6.Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Nedostupnost aplikace DP přes IPv6
9.3.2019 16:25 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/250884Flirtey and City of Reno receive FAA approval for drone delivery beyond visual line of sight
9.3.2019 0:16 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars RENO, Nev., March 8, 2019 — (PRNewswire) — Flirtey has received approval from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to conduct …Výroční členská schůze 2019
8.3.2019 21:00 Spolek zeměměřičů Brno aktualizace 29. 3. 2019 Výbor Spolku zeměměřičů Brno Vás srdečně zve na ČLENSKOU SCHŮZI 28. března 2019 v 15:30 Schůze se bude konat v konferenčním sále Katastrálního pracoviště Brno – venkov, Úzká 6, Brno Program: 1. Zpráva o činnosti a hospodaření v roce 2018 2. Zpráva revizní komise 3. Návrh... Read more »Výroční členská schůze 2019
8.3.2019 21:00 Spolek zeměměřičů Brno Výbor Spolku zeměměřičů Brno Vás srdečně zve na ČLENSKOU SCHŮZI 28. března 2019 v 15:30 Schůze se bude konat v konferenčním sále Katastrálního pracoviště Brno – venkov, Úzká 6, Brno Program: 1. Zpráva o činnosti a hospodaření v roce 2018 2. Zpráva revizní komise 3. Návrh činnosti a hospodaření na... Read more »24. mezinárodní slovensko-polsko-české geodetické dny
8.3.2019 20:43 Spolek zeměměřičů Brno hotel TATRA****, Námestie 1. mája 5, 811 06 Bratislava – Staré Mesto 6. – 8. června 2018 Podrobnosti včetně on-line přihlášky jsou dostupné zde Účast a přihlášení členů SZB bude projednána na výroční schůzi 28. 3. 2018. Odborné sekce Aktuálne informácie o činnosti v rezortoch od národných autorít Kataster nehnuteľností... Read more »25. mezinárodní slovensko-polsko-české geodetické dny
8.3.2019 20:43 Spolek zeměměřičů Brno hotel TATRA****, Námestie 1. mája 5, 811 06 Bratislava – Staré Mesto 6. – 8. června 2018 Podrobnosti včetně on-line přihlášky jsou dostupné zde Účast a přihlášení členů SZB bude projednána na výroční schůzi 28. 3. 2018. Odborné sekce Aktuálne informácie o činnosti v rezortoch od národných autorít Kataster nehnuteľností... Read more »Microsoft launches HoloLens 2 to enhance mixed reality
8.3.2019 19:59 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
AEC Magazine, UK
Read the articleMicrosoft’s HoloLens 2 mixed-reality headset: better specs, comfort, enterprise features
8.3.2019 19:53 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Spar3D, USA
Read the articleRoadmap for Upgrading to MicroStation CONNECT Edition
8.3.2019 19:43 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Microstation Connections, USA
Read the articleSimple Quantities in the MicroStation CONNECT Edition
8.3.2019 19:34 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Microstation Connections, USA
Read the articleBentley Systems is Associate Sponsor at Geospatial World Forum 2019
8.3.2019 18:48 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Amsterdam: Geospatial Media and Communications is pleased to introduce Bentley Systems as the Associate Sponsor for Geospatial World Forum 2019. The …Esri Partners with 3LOG Systems to Bring the Power of Location Intelligence to Forestry Management
8.3.2019 18:47 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Log Inventory Solution Will Integrate with Esri's GIS Software toImprove Efficiency
REDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — …
Esri Recognizes Women’s Contributions to GIS in New Book
8.3.2019 18:47 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 23 Stories of Extraordinary Women Improving the WorldREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 8, 2019 —
Esri,
…
ESA joins with business to invent the future of navigation
8.3.2019 16:57 ESA Navigation
The only thing more remarkable than how all of us are walking around with space-grade navigation capability and atomic clock timing precision in our pockets is how much we take all of this for granted. Satellite navigation has changed our lives, triggering a quiet revolution in our society and economy.
ESA joins with business to invent the future of navigation
8.3.2019 16:57 ESA Navigation
The only thing more remarkable than how all of us are walking around with space-grade navigation capability and atomic clock timing precision in our pockets is how much we take all of this for granted. Satellite navigation has changed our lives, triggering a quiet revolution in our society and economy.
ESA joins with business to invent the future of navigation
8.3.2019 16:57 ESA Navigation
The only thing more remarkable than how all of us are walking around with space-grade navigation capability and atomic clock timing precision in our pockets is how much we take all of this for granted. Satellite navigation has changed our lives, triggering a quiet revolution in our society and economy.
New observations for the new economy
8.3.2019 15:41 ESA Observing the Earth
We all listen to weather forecasts and know they rely on satellite data. What may not be so obvious is that many other aspects of our lives depend on robust satellite data, from growing crops to tackling the major issue of climate change. The socio-economic benefits of Earth observation are huge, and increasing. In Europe, ESA, Eumetsat and the EU work closely together, in long-term partnerships, to make sure these benefits are delivered.
New observations for the new economy
8.3.2019 15:41 ESA Observing the Earth
We all listen to weather forecasts and know they rely on satellite data. What may not be so obvious is that many other aspects of our lives depend on robust satellite data, from growing crops to tackling the major issue of climate change. The socio-economic benefits of Earth observation are huge, and increasing. In Europe, ESA, Eumetsat and the EU work closely together, in long-term partnerships, to make sure these benefits are delivered.
Aktualizace dat ÚAP poskytovatelů ČEPS, České radiokomunikace a SŽDC
8.3.2019 15:00 Plzeňský kraj V datech územně analytických podkladů Plzeňského kraje byla provedena kompletní aktualizace dat ve správě poskytovatelů ČEPS a.s., České radiokomunikace a.s. a SŽDC s.o.Aktualizace dat ÚAP poskytovatelů ČEPS, České radiokomunikace a SŽDC
8.3.2019 15:00 Plzeňský kraj V datech územně analytických podkladů Plzeňského kraje byla provedena kompletní aktualizace dat ve správě poskytovatelů ČEPS, a.s., České radiokomunikace a.s. a SŽDC, s.o.obsah>Nabídky pozic ve Výzkumném ústavu geodetickém, topografickém a kartografickém
8.3.2019 14:59 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČU Výzkumný ústav geodetický, topografický a kartografický nabízí hned dvě pozice najednou.Pozice pro analýzy a využití dat z Globálních Navigačních Družicových Systémů (GNSS):
Požadujeme:
• vysokoškolské vzdělání v oblasti přírodních či technických věd
• znalost programování v prostředí Linux
• zájem o vědeckou činnost a osobní růst
• samostatnost a spolehlivost
• schopnost týmové práce
• schopnost komunikace v anglickém jazyce
Za výhody považujeme:
• orientace v problematice GNSS
• znalost objektového programování
• znalost základů statistiky
• zkušenost s vizualizací dat
• zkušenost s databázovými systémy
• schopnost prezentovat a publikovat výsledky
Nabízíme:
• účast na zajímavé a různorodé práci spojené s vědeckými službami
• aktivity v mezinárodní spolupráci
• vysokou pracovní flexibilitu (vč. práce z domova)
• účast na definování úkolů a organizaci práce
• podporu v osobním růstu
• podmínky vhodné při VŠ studiu (při částečném úvazku)
Požadované dokumenty:
• motivační dopis
• strukturovaný životopis
• ukázky vlastního zdrojového kódu (má-li uchazeč k dispozici)
Pozice pro správce zajišťování vědeckých služeb a vývoj nových aplikací pro Globální Navigační Družicové Systémy (GNSS):
Požadujeme:
• znalost práce v prostředí Linux
• základní znalost programování
• vysoká osobní motivace
• zájem o rozšiřování znalostí a dovedností
• samostatnost a spolehlivost
• schopnost týmové práce
Výhodou žadatele může být:
• vysokoškolské vzdělání v oblasti přírodních či technických věd
• orientace v problematice GNSS
• zkušenost práce s databázovými systémy
• znalost objektového programování
• schopnost komunikace v anglickém jazyce
Nabízíme:
• účast na zajímavé a různorodé práci spojené s vědeckými službami
• aktivity v mezinárodní spolupráci
• vysokou pracovní flexibilitu (vč. práce z domova)
• účast na definování úkolů a organizaci práce
• podporu v osobním růstu
• podmínky vhodné při VŠ studiu (při částečném úvazku)
Požadované dokumenty:
• motivační dopis
• strukturovaný životopis
• dvě ukázky vlastního zdrojového kódu (má-li uchazeč k dispozici)
Pozice jsou nabízeny pro částečný či plný úvazek
Písemné přihlášky včetně požadovaných dokumentů zasílejte v elektronické podobě na adresu jan.dousa[at]pecny.cz do 31. března, 2019.
Podrobnější informace:
Ing. Jan Douša, Ph.D. (jan.dousa[at]pecny.cz), http://www.pecny.cz
Bentley Institute's Digital Advancement Academies Receive BIM Award for BIM Enabler/Consultant of the Year
8.3.2019 14:46 Bentley SystemsBentley Institute’s Digital Advancement Academies have been named as the winner of the BIM Enabler/Consultant of the Year Award at BIM Show Live 2019 in Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. The annual BIM Awards, part of the national conference, honor and recognize the world’s best BIM work by celebrating exceptional and innovative use of BIM in the built environment.
Iain Miskimmin, senior academies manager for Bentley Institute’s Digital Advancement Academies, said, “It’s an honor for Bentley Institute to be recognized for the work we have been doing in this important area since 2012. Having helped to deliver some of the first projects in the UK to embrace a BIM strategy, it’s inspiring to see how far we have come, and how our Digital Advancement Academies continue to support leaders and innovators in the digital built environment to advance digital (BIM) strategies.”
The BIM Awards were judged by experts in BIM strategy and implementation for today’s modern digital built environment. Awards were given in ten categories.
Learn more about the awards categories, winners, and judges.
The awards were announced the evening before the main program kicked off for BIM Show Live 2019, which also featured presentations by experts in the construction industry, including David Philp, Global BIM/MIC Consultancy Director, AECOM and co-author of Building Information Modeling for Dummies. Learn more about the conference speakers.
##
Caption and hi-res image: Adam Young (left), associate academies manager, and Iain Miskimmin (center), senior academies manager for Bentley Institute’s Digital Advancement Academies, accepted the BIM Enabler/Consultant of the Year Award at BIM Show Live 2019.
About Bentley Institute’s Digital Advancement Academies
An initiative of Bentley Systems, Bentley Institute’s Digital Advancement Academies offer a unique, neutral environment for industry innovators to openly discuss challenges and successes in the built environment, to accelerate and optimize digital (BIM) strategy. Bentley Institute partners with industry to act as a catalyst for knowledge exchange, using a process-focused approach to support execution of outcome-based objectives in the creation and operation of digital and physical assets.
International Women’s Day: learning from successful women in tech
8.3.2019 10:50 European GNSS Agency
International Women’s Day is an opportunity to share success stories from successful women and become inspired by what they have achieved in their respective workplaces. As such, GSA has gathered testimonials from successful professionals working with European Satellite Navigation technologies to inspire others both in the field and beyond.
Each of these inspiring women was first asked, what has been essential in their careers. Their answers covered the need for perseverance, hard work and not being afraid to take chances and risks.
“I've never refused an opportunity if it appeared or doubted a new career decision…it's important to understand that being a little scared is a part of the game, and hence if you're never scared, you just might not be challenging yourself enough,” said, Ewa Kadziolka, CEO & Founder, Centrip.
Unique set of challenges
A career is not without its own unique set of challenges, and each of these women has experienced their own throughout their professional lives. From learning to just keep going, to being in the minority, from balancing motherhood with full time work, to learning to be adaptable and think on your feet, each challenge is unique and has provided many a lesson that these women have drawn upon.
Read this: Help shape the future of Galileo and EGNOS
“Being female engineers is a challenge and a great opportunity at the same time. When we started at university we as women were always a minority, and today we represent 40% of the people in our research group and two of us are responsible for a research unit. However, this situation is far from standard; to say it in engineering language: we are on the queue of the Gaussian distribution! To add a challenge to a challenge, most of us are also mothers,” said Gabriella Povero, Emanuela Falletti, Beatrice Motella, Micaela Troglia Gamba, Navigation Technologies at Fondazione LINKS.
Having gone through these unique challenges, it is also important for these established female professionals to pass on their wisdom to other young women in their respective professional domains. All of these inspiring women agreed that it is important for fellow females to recognise their capacities, fight for what they want and surround themselves with the right people.
“Nowadays, to think that we cannot become what we want to be simply because we are women is not correct. Both legally and culturally there are no obstacles to achieve our goals”, said Isabel GONZALEZ, End User Support Manager from CNH Industrial.
Determination and passion
“Never stop fighting and never let anyone tell you who you should be or what you can or can’t do,” said Oihana Otaegui, Head of ITS and Engineering at Vicomtech.
Finally, these women acknowledged that they would not be where they are today without inspiration from their families, the people around them and others that they look up to in their fields.
“Out of all the determined and passionate people I have met so far, my mother is definitely my symbol of emancipation, tenacity and courage,” said Micaela Troglia Gamba from Navigation Technologies at Fondazione LINKS.
Thank you to these inspiring women for sharing their experiences and insights and Happy International Women’s Day!
If you want to be a part of the EU GNSS community, have a look at our open vacancies and apply.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
International Women’s Day: learning from successful women in tech
8.3.2019 10:50 European GNSS Agency
International Women’s Day is an opportunity to share success stories from successful women and become inspired by what they have achieved in their respective workplaces. As such, GSA has gathered testimonials from successful professionals working with European Satellite Navigation technologies to inspire others both in the field and beyond.
Each of these inspiring women was first asked, what has been essential in their careers. Their answers covered the need for perseverance, hard work and not being afraid to take chances and risks.
“I've never refused an opportunity if it appeared or doubted a new career decision…it's important to understand that being a little scared is a part of the game, and hence if you're never scared, you just might not be challenging yourself enough,” said, Ewa Kadziolka, CEO & Founder, Centrip.
Unique set of challenges
A career is not without its own unique set of challenges, and each of these women has experienced their own throughout their professional lives. From learning to just keep going, to being in the minority, from balancing motherhood with full time work, to learning to be adaptable and think on your feet, each challenge is unique and has provided many a lesson that these women have drawn upon.
Read this: Help shape the future of Galileo and EGNOS
“Being female engineers is a challenge and a great opportunity at the same time. When we started at university we as women were always a minority, and today we represent 40% of the people in our research group and two of us are responsible for a research unit. However, this situation is far from standard; to say it in engineering language: we are on the queue of the Gaussian distribution! To add a challenge to a challenge, most of us are also mothers,” said Gabriella Povero, Emanuela Falletti, Beatrice Motella, Micaela Troglia Gamba, Navigation Technologies at Fondazione LINKS.
Having gone through these unique challenges, it is also important for these established female professionals to pass on their wisdom to other young women in their respective professional domains. All of these inspiring women agreed that it is important for fellow females to recognise their capacities, fight for what they want and surround themselves with the right people.
“Nowadays, to think that we cannot become what we want to be simply because we are women is not correct. Both legally and culturally there are no obstacles to achieve our goals”, said Isabel GONZALEZ, End User Support Manager from CNH Industrial.
Determination and passion
“Never stop fighting and never let anyone tell you who you should be or what you can or can’t do,” said Oihana Otaegui, Head of ITS and Engineering at Vicomtech.
Finally, these women acknowledged that they would not be where they are today without inspiration from their families, the people around them and others that they look up to in their fields.
“Out of all the determined and passionate people I have met so far, my mother is definitely my symbol of emancipation, tenacity and courage,” said Micaela Troglia Gamba from Navigation Technologies at Fondazione LINKS.
Thank you to these inspiring women for sharing their experiences and insights and Happy International Women’s Day!
If you want to be a part of the EU GNSS community, have a look at our open vacancies and apply.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
International Women’s Day: learning from successful women in tech
8.3.2019 10:50 European GNSS Agency
International Women’s Day is an opportunity to share success stories from successful women and become inspired by what they have achieved in their respective workplaces. As such, GSA has gathered testimonials from successful professionals working with European Satellite Navigation technologies to inspire others both in the field and beyond.
Each of these inspiring women was first asked, what has been essential in their careers. Their answers covered the need for perseverance, hard work and not being afraid to take chances and risks.
“I've never refused an opportunity if it appeared or doubted a new career decision…it's important to understand that being a little scared is a part of the game, and hence if you're never scared, you just might not be challenging yourself enough,” said, Ewa Kadziolka, CEO & Founder, Centrip.
Unique set of challenges
A career is not without its own unique set of challenges, and each of these women has experienced their own throughout their professional lives. From learning to just keep going, to being in the minority, from balancing motherhood with full time work, to learning to be adaptable and think on your feet, each challenge is unique and has provided many a lesson that these women have drawn upon.
Read this: Help shape the future of Galileo and EGNOS
“Being female engineers is a challenge and a great opportunity at the same time. When we started at university we as women were always a minority, and today we represent 40% of the people in our research group and two of us are responsible for a research unit. However, this situation is far from standard; to say it in engineering language: we are on the queue of the Gaussian distribution! To add a challenge to a challenge, most of us are also mothers,” said Gabriella Povero, Emanuela Falletti, Beatrice Motella, Micaela Troglia Gamba, Navigation Technologies at Fondazione LINKS.
Having gone through these unique challenges, it is also important for these established female professionals to pass on their wisdom to other young women in their respective professional domains. All of these inspiring women agreed that it is important for fellow females to recognise their capacities, fight for what they want and surround themselves with the right people.
“Nowadays, to think that we cannot become what we want to be simply because we are women is not correct. Both legally and culturally there are no obstacles to achieve our goals”, said Isabel GONZALEZ, End User Support Manager from CNH Industrial.
Determination and passion
“Never stop fighting and never let anyone tell you who you should be or what you can or can’t do,” said Oihana Otaegui, Head of ITS and Engineering at Vicomtech.
Finally, these women acknowledged that they would not be where they are today without inspiration from their families, the people around them and others that they look up to in their fields.
“Out of all the determined and passionate people I have met so far, my mother is definitely my symbol of emancipation, tenacity and courage,” said Micaela Troglia Gamba from Navigation Technologies at Fondazione LINKS.
Thank you to these inspiring women for sharing their experiences and insights and Happy International Women’s Day!
If you want to be a part of the EU GNSS community, have a look at our open vacancies and apply.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Earth from Space
8.3.2019 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
This week's edition features a Copernicus Sentinel-3 view over New Zealand
Earth from Space
8.3.2019 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
This week's edition features a Copernicus Sentinel-3 view over New Zealand
New Zealand
8.3.2019 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
Earth observation image of the week: Copernicus Sentinel-3 takes us over New Zealand
New Zealand
8.3.2019 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
Earth observation image of the week: Copernicus Sentinel-3 takes us over New Zealand
GIS Software Engineer/Developer
8.3.2019 8:56 CybELE is a start-up company that integrates remote sensing technology and earth observation data with the legal environment to address a problem of environmental criminality. We combine all available geospatial information together with legal context to generate detailed environmental criminal activity report that can be used at court. We are the winner of the Copernicus […]Přihlaste svůj BIM projekt do soutěže Year in Infrastructure
8.3.2019 7:37 GeoBusiness Společnost Bentley Systems ohlásila příjem nominací na ocenění Year in Infrastructure 2019. Přihlášené projekty hodnotí nezávislí porotci z řad průmyslových expertů. Poslední den, kdy svůj ... PřečístSmíšená realita pro projekty výstavby infrastruktury s použitím technologie Microsoft HoloLens 2
8.3.2019 7:15 GeoBusiness Společnost Bentley Systems představila svoji aplikaci SYNCHRO XR pro imerzivní vizualizaci 4D digitálních dvojčat staveb spolu s novou technologií Microsoft HoloLens 2, kterou představila společnost Microsoft během ... PřečístBezplatné workshopy na GIS Ostrava 2019
8.3.2019 6:45 GeoBusiness V rámci sympozia GIS Ostrava 2019 se uskuteční tři workshopy. Jsou podpořeny v rámci projektu OPVVV Technika pro budoucnost 2.0, proto jsou bezplatné, Kapacita ... PřečístNepřírodní biotopy – mapování 2001-2005
8.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Hranice segmentů biotopů silně ovlivněných nebo vytvořených člověkem, pokud byly zaznamenány při mapování biotopů přírodních a přírodně blízkých. Znalost rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů tedy není plošná, vrstva poskytuje informace o rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů pouze na malé části území ČR.Data z mapování biotopů neposkytují vyčerpávající informaci o vegetaci, resp. biotopech daného území. Mapování bylo metodicky nastaveno na celostátní úrovni, a především efemérní biotopy tak mohlo pominout. V lokálním měřítku je proto pouze zjednodušeným podkladem. Pro detailnější informaci je třeba vyhledat jiné datové zdroje. Klasifikace biotopů viz CHYTRÝ, M.; KUČERA, T.; KOČÍ, M. (eds.) et al. (2001). Katalog biotopů České republiky: Interpretační příručka k evropským programům Natura 2000 a Smaragd. Vyd. 1. Praha: Agentura ochrany přírody a krajiny ČR. 307 s. ISBN 80-86064-55-7.Popis charakteristik biotopů a segmentů viz Guth, J. (ed.), 2002: Metodiky mapování biotopů soustavy Natura 2000 a Smaragd. 3. přepracované vydání. Ms., AOPK ČR, Praha, 48 pp.Vrstva obsahuje jednoduché prvky (Singlepart Features), kardinalita vztahu mezi záznamy v tabulkách 1 : N.© AOPK ČR, 2006Nepřírodní biotopy – mapování 2007-2018
8.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Hranice segmentů biotopů silně ovlivněných nebo vytvořených člověkem, pokud byly zaznamenány při aktualizaci mapování biotopů přírodních a přírodně blízkých. Znalost rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů tedy není plošná, vrstva poskytuje informace o rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů pouze na malé části území ČR.Data z mapování biotopů neposkytují vyčerpávající informaci o vegetaci, resp. biotopech daného území. Mapování je metodicky nastaveno na celostátní úrovni, a především efemérní biotopy tak může pominout. V lokálním měřítku proto představuje pouze zjednodušený podklad. Pro detailnější informaci je třeba vyhledat jiné datové zdroje. Mapování biotopů je opakováno ve dvanáctileté periodě. Základní mapování bylo provedeno v letech 2001–2005.Klasifikace biotopů viz CHYTRÝ, M.; KUČERA, T.; KOČÍ, M. (eds.) et al. (2010). Katalog biotopů České republiky. 2.upr. a rozš.vyd. Praha: Agentura ochrany přírody a krajiny ČR. 445 s. ISBN 978-80-87457-03-0.Popis charakteristik biotopů a segmentů viz platná metodika mapování biotopů (Portál ISOP/Mapování biotopů). Vrstva obsahuje jednoduché prvky (Singlepart Features), kardinalita vztahu mezi záznamy v tabulkách 1 : N. © AOPK ČR, 2017Vyhledávací (geokódovací) služba nad daty RÚIAN
8.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Vyhledávací (geokódovací) služba nad daty RÚIAN (GeocodeSOE) umožňuje dosažení jednotných výsledků vyhledávání a lokalizace v různých mapových aplikacích podle aktuálních údajů Registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí (RÚIAN). Zdrojová data služby jsou denně aktualizována pomocí aplikace Veřejný dálkový přístup k RÚIAN.Funkce GeocodeSOE jsou dostupné prostřednictvím jejího REST rozhraní na úrovni protokolu http(s). Prvky RÚIAN lze vyhledávat a lokalizovat nad mapou (např. Prohlížecí služba nad daty RÚIAN http://ags.cuzk.cz/arcgis/rest/services/RUIAN/Prohlizeci_sluzba_nad_daty_RUIAN/MapServer) podle následujících kategorií: vyšší územně samosprávný celek, okres, obec s rozšířenou působností, obec s pověřeným obecním úřadem, obec, část obce, správní obvod v Praze, městské obvody a městské části, katastrální území, základní sídelní jednotka, ulice, adresa, parcela.Prohlížecí služba nad daty RÚIAN
8.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Prohlížecí služba nad daty Registru územní identifikace adres a nemovitostí (RÚIAN) je poskytována prostřednictvím rozhraní REST a WMS. Rozhraní služby poskytuje i dotazování na atributové záznamy objektů RÚIAN (v případě WMS pomocí operace GetFeatureInfo). Zdrojová data služby jsou denně aktualizována pomocí aplikace Veřejný dálkový přístup k RÚIAN.Orbit GT and Comsof to present at FTTH Conference 2019, Amsterdam.
7.3.2019 20:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Lokeren, Belgium, March 7st, 2019Orbit GT is joining Comsof to present at the FTTH Conference in Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Wed Mar 13th …
TomTom and Elektrobit Reveal First HD Map Horizon for Automated Driving
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GENEVA — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 6, 2019 —TomTom (TOM2),
the leading independent location technology specialist, and …
CycloMedia Acquires Floating Point FX to Fuel US and International Growth
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Acquisition Strengthens CycloMedia’s US Presence, Enhances DataAnalytics Capabilities
MILL VALLEY, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) …
Esri Developer Tools Empower Public Sector at Civic Innovation Eco Challenge
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Esri Sponsors Competition to Showcase App Development for City'sSustainability
REDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March …
CoreLogic Reports Homeowners with Negative Equity Increased by 35,000 in the Fourth Quarter of 2018
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The quarterly increase in negative equity was the first increase in12 quarters
The number of owners with negative …
Field Squared Announces General Availability of Zero-Effort Integration to Esri ArcGIS
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Esri Customers Can Now Sync Esri ArcGIS Map Data and Automate Workflows in Field SquaredHIGHLANDS RANCH, Colo., March 7, 2019 — (PRNewswire) …
Kratos XQ-58A Valkyrie Completed its Maiden Flight on March 5, 2019
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, March 07, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc. (NASDAQ:KTOS), a leading National Security Solutions …Security First Insurance Takes Flight to Improve Customer Claims Experience
7.3.2019 19:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars ORMOND BEACH, Fla., March 7, 2019 — (PRNewswire) — Security First Insurance has partnered with Loveland Innovations® to …Březnový Missing maps mapathon pro organizaci Lékaři bez hranic ve společnosti CleverMaps
7.3.2019 18:00 Geografický ústav MUÚnorový brněnský mapathon úspěšně skončil. Ať žije březnový brněnský mapathon!
- V únoru jsme během tří hodin mapathonu splnili úkol, který byl Lékaři bez hranic vyhlášen jako urgentní výzva jen pár minut před tím. Zmapovali jsme přes 2700 budov a 60 km cest v oblasti uprchlického tábora v Súdánu.
- Přijďte podpořit práci Lékařů bez hranic tím, že pomůžete do otevřené mapy světa OpenStreetMap zmapovat místa, která jsou ohrožena humanitárními krizemi.
- Tentokrát to ale bude jiné než obvykle. Mapathon se tentokrát koná v krásných prostorách jedné z nejvýznamnějších brněnských firem v našem geoinformačním oboru - CleverMaps. Přijďte si zamapovat po boku profesionálů.
Kdy a kde to bude?
ve čtvrtek 7. 3. 2019 od 18:00 do 21:00
budova Vienna Point 2, 13. patro
Vídeňská 101/119d
619 00 Brno-jih
Přesné místo mapathonu: https://www.openstreetmap.org/way/157878480.
Registrace: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/brnensky-mapathon-s-clevermaps-registration-55958083133.
Na místo se dostanete pohodlně tramvají na zastávku Moravanské lány nebo autem, zaparkovat se dá večer snadno.
Začátek je plánovaný na 18:00, ale přijďte raději o chvíli dříve, ať můžeme začít včas.
Co se na setkání bude dít?
Na mapathonu budeme společně podle satelitních snímků vytvářet v OpenStreetMap mapu jednoho z míst, na kterém působí Lékaři bez hranic.
Pokud nemáte zkušenosti, nevadí. Všechno se na místě naučíte a po krátkém školení už budete moci sami mapovat. Pokud máte zkušenosti, tím lépe. Budeme pracovat ve dvou skupinách:
-
Skupina začátečníků bude při školení získávat první zkušenosti s editací OpenStreetMap
-
Zkušenější mapéři se budou mít možnost naučit program JOSM – volně dostupný pokročilý editor pro OpenStreetMap.
Samozřejmě, zváni jsou i zkušení uživatelé, kteří už žádné školení nepotřebují a chtějí jen nerušeně mapovat či validovat.
Mám si něco připravit?
Pokud ještě nemáte účet na OpenStreetMap, vytvořte si ho zde: https://www.openstreetmap.org/user/new.
Pokud chcete být ve skupině pokročilých mapérů učících se JOSM, je nutné si přinést vlastní notebook a k němu určitě i myš. Je také vhodné mít na počítači předem nainstalován program JOSM. Je volně ke stažení na adrese https://josm.openstreetmap.de. Program vyžaduje nainstalovaný programovací jazyk Java.
Těší se na Vás organizační tým brněnských mapathonů a společnost CleverMaps.
Bližší informace: Radim Štampach (stampach@mail.muni.cz)
Březnový Missing maps mapathon pro organizaci Lékaři bez hranic ve společnosti CleverMaps
7.3.2019 18:00 Geografický ústav MUÚnorový brněnský mapathon úspěšně skončil. Ať žije březnový brněnský mapathon!
- V únoru jsme během tří hodin mapathonu splnili úkol, který byl Lékaři bez hranic vyhlášen jako urgentní výzva jen pár minut před tím. Zmapovali jsme přes 2700 budov a 60 km cest v oblasti uprchlického tábora v Súdánu.
- Přijďte podpořit práci Lékařů bez hranic tím, že pomůžete do otevřené mapy světa OpenStreetMap zmapovat místa, která jsou ohrožena humanitárními krizemi.
- Tentokrát to ale bude jiné než obvykle. Mapathon se tentokrát koná v krásných prostorách jedné z nejvýznamnějších brněnských firem v našem geoinformačním oboru - CleverMaps. Přijďte si zamapovat po boku profesionálů.

Kdy a kde to bude?
ve čtvrtek 7. 3. 2019 od 18:00 do 21:00
budova Vienna Point 2, 13. patro
Vídeňská 101/119d
619 00 Brno-jih
Přesné místo mapathonu: https://www.openstreetmap.org/way/157878480.
Registrace: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/brnensky-mapathon-s-clevermaps-registration-55958083133.
Na místo se dostanete pohodlně tramvají na zastávku Moravanské lány nebo autem, zaparkovat se dá večer snadno.
Začátek je plánovaný na 18:00, ale přijďte raději o chvíli dříve, ať můžeme začít včas.
Co se na setkání bude dít?
Na mapathonu budeme společně podle satelitních snímků vytvářet v OpenStreetMap mapu jednoho z míst, na kterém působí Lékaři bez hranic.
Pokud nemáte zkušenosti, nevadí. Všechno se na místě naučíte a po krátkém školení už budete moci sami mapovat. Pokud máte zkušenosti, tím lépe. Budeme pracovat ve dvou skupinách:
-
Skupina začátečníků bude při školení získávat první zkušenosti s editací OpenStreetMap
-
Zkušenější mapéři se budou mít možnost naučit program JOSM – volně dostupný pokročilý editor pro OpenStreetMap.
Samozřejmě, zváni jsou i zkušení uživatelé, kteří už žádné školení nepotřebují a chtějí jen nerušeně mapovat či validovat.
Mám si něco připravit?
Pokud ještě nemáte účet na OpenStreetMap, vytvořte si ho zde: https://www.openstreetmap.org/user/new.
Pokud chcete být ve skupině pokročilých mapérů učících se JOSM, je nutné si přinést vlastní notebook a k němu určitě i myš. Je také vhodné mít na počítači předem nainstalován program JOSM. Je volně ke stažení na adrese https://josm.openstreetmap.de. Program vyžaduje nainstalovaný programovací jazyk Java.
Těší se na Vás organizační tým brněnských mapathonů a společnost CleverMaps.
Bližší informace: Radim Štampach (stampach@mail.muni.cz)
Advancing to CONNECT Edition
7.3.2019 16:09 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Microstation Connections, USA
Read the articleBentley Goes Big with Microsoft Hololens 2—New Mixed Reality App for Infrastructure Projects
7.3.2019 16:01 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Architosh, USA
Read the articleImmersive Digital Twins Helps China Shanghai Railway Engineering Establish New Practices to Deliver Sewage Treatment Plant
7.3.2019 15:56 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
AECCafe, USA
Read the articleMicrosoft HoloLens 2 hands-on: A giant leap closer to mixed reality
7.3.2019 15:53 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Engadget, USA
Read the articleProvoz WSDP 2.7 bude ukončen
7.3.2019 15:50 GEPROČÚZK ukončí provoz webových služeb dálkového přístupu verze 2.7 (WSDP) ke dni 31.3.2019.… >>
Připraveni na změnu WSDP
7.3.2019 15:50 GEPROČÚZK ukončí provoz webových služeb dálkového přístupu verze 2.7 (WSDP) ke dni 31.3.2019.… >>
ASCE Members ‘Invent Amazing’ During #EWeek2019
7.3.2019 15:49 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
ASCE, USA
Read the articleodborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy katastrálního op
7.3.2019 15:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj - odbor obnovy katastrálního operátuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu (3040) na Katastrálním úřadu pro Jihočeský kraj
odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy katastrálního op
7.3.2019 15:12 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj - odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy katastrálního opodborný referent/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu - v oddělení obnovy katastrálního op
7.3.2019 15:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odb_ref_vrchni_referent_OKOZnámky minulé tekoucí vody na Marsu
7.3.2019 12:12 Český Kosmický PortálSnímky ze sondy ESA Mars Express ukazují rozvětvený vysušený systém koryt a údolí, které jsou neklamnými znaky přítomnosti dávné tekoucí vody. A ta je pak důkazem dřívějšího teplejšího a vlhčího podnebí na Marsu.
Známky minulé tekoucí vody na Marsu
7.3.2019 12:12 Český Kosmický PortálSnímky ze sondy ESA Mars Express ukazují rozvětvený vysušený systém koryt a údolí, které jsou neklamnými znaky přítomnosti dávné tekoucí vody. A ta je pak důkazem dřívějšího teplejšího a vlhčího podnebí na Marsu.
The GSA and Galileo at MWC Barcelona
7.3.2019 11:57 European GNSS Agency
Whether smartphones, drones, robots or autonomous vehicles, many of the innovations making headlines at this year's MWC in Barcelona absolutely depend on GNSS. Advanced positioning services like those being delivered by Galileo are helping to transform the latest technologies into functional mass market solutions.
Mobile World Congress (MWC) is the largest mobile connectivity event in the world. The 2019 edition in Barcelona brought together futuristic and pioneering technologies from more than 2400 companies. The European GNSS Agency (GSA) was there as well, promoting Galileo, Europe's flagship satellite navigation programme.
One catchphrase seemingly on everyone's lips in Barcelona was 'the future is now'. For the GSA, the future is 'here and now'. The 'here' of course refers to location, without which many of today's leading-edge mobile and connected systems simply wouldn't work.
A case in point is the new Ooredoo pilot-less flying taxi, the world’s first self-driving, 5G-connected, aerial passenger vehicle. Recently unveiled and test-flown in Qatar, it can transport two people for up to 20 minutes at 130 km per hour. Essentially a massive multi-rotor drone with a very comfortable passenger compartment, the vehicle made a big splash at MWC Barcelona, where Congress attendees were queuing up for a chance just to sit in it. Of course the flying taxi relies on state-of-the-art, satellite-based navigation technologies like Galileo to ensure precise and reliable positioning.
Ooredoo, a Doha-based company, highlighted 5G connectivity as a key enabling feature of the new flying taxi. Indeed, 5G was a sort of recurring theme throughout the Barcelona event. 5G represents the latest generation of cellular mobile communications, delivering ultra-wide bandwidth and massive input and output capabilities. This means increased speed and flexibility, enabling vastly improved performance and making possible a variety of new services.
GNSS and 5G come together
"What we are seeing right now is the convergence of 5G and GNSS," said GSA officer Alberto Fernández-Wyttenbach. "Together you get the combination of precision location from GNSS, and then with 5G you get the speed for real-time reactivity and control, so fast 5G connectivity is a perfect partner for GNSS. We know, for example, in the automotive industry, you have an important association that is working to bring 5G into automotive, an industry where GNSS is already a requisite feature."
The 5G Automotive Association (5GAA) is a global, cross-industry organisation that includes companies from the automotive, technology, and telecommunications industries, working to develop complete solutions for future road mobility and transport. 5GAA sees 5G as a vital platform for enabling Cooperative Intelligent Transportation Systems (C-ITS). With its exceptional bandwidth, 5G can easily handle safety-critical connectivity while supporting enhanced 'Vehicle-to-Everything' (V2X) communications and other connected mobility needs.
"We know that some 5GAA members are looking at 5G as the way to send real-time GNSS corrections to cars," said Fernández-Wyttenbach, "because it gives you this very quick reaction time."
Korea Telecom's new 5G-based road emergency response system, also on display at MWC, is a clear example of the synergy that is possible by combining 5G connectivity and GNSS-based navigation. Europe already has in place its eCall system, where a call centre automatically receives location information from vehicles in distress, thanks to on-board GNSS. The Korea Telecom´s 5G Remote Cockpit system goes a step further. In the event of an emergency where a driver is incapacitated, a human operator at a call centre actually takes over control of the car remotely, driving it to a location where emergency services are available.
"The technology is ready," said Fernández-Wyttenbach. "5G gives you very fast communication, which allows actual control of the car. Without that capability of near-instant transmission of the control signal, you cannot drive a car remotely; if you tried to turn the car around a curve in the road, you would be too late and you would crash. With 5G this is now possible." Complementarity is the key thing, he said, "because of course, without the GNSS positioning as a starting point, 5G cannot accomplish this kind of thing by itself."
There are limitations to 5G; the connection is faster and broader, but a certain density of transmitting stations is needed, even more so than with a 4G connection, so there will likely be some areas with imperfect coverage.
Nevertheless, said Fernández-Wyttenbach, "This year everybody is speaking about 5G. Before, 5G was mostly about consumer electronics, but now we have these transverse markets that are moving all the time." One of these is automotive, as mentioned above. Another is healthcare, where a number of companies are now demonstrating the delivery of medical services to remote locations supported by fast 5G connectivity.
Putting Galileo in your hands
The one thing you'd expect to see at an event with 'Mobile' in the name is smartphones, and there were indeed a number of remarkable new models to be admired at MWC. Of particular note were the new folding phones. The Samsung Galaxy Fold and the Huawei Mate X both feature displays that fold open into a small tablet-like format. The Mate X also features a 5G modem, and of course all are Galileo-ready.
Since 2016, when the first Galileo-enabled smartphone was launched, more and more manufacturers have been choosing to include Galileo-capable GNSS receivers in their premium handsets, in order to provide users with better accuracy and availability, especially in difficult environments.
The success of Galileo in terms of its uptake by smartphone manufacturers is something the GSA likes to talk about, and there could be no better place to do so than at MWC 2019. A range of Galileo-enabled mobile devices were on display in the GSA's exhibition space, highlighting European GNSS's increasing presence in smartphones. At last count, there were about 80 smartphone models equipped with Galileo, and all of that is thanks to the work of the GSA, which has made downstream market uptake a priority.
Also getting noticed at MWC 2019 were two recent dual-frequency GNSS models from Chinese manufacturer Xiaomi, the Mi8 and the top-of-the-line Mi9. Traditionally, mobile, location-based applications have been powered by single-frequency GNSS receivers operating under stringent battery-power and footprint constraints. With a dual-frequency chipset, these devices now benefit from better accuracy, ionosphere error cancellation, improved tracking and better multipath resistance.
Dual-frequency GNSS chipsets are of course also appearing in the automotive sector. With connected cars and autonomous vehicles soon to hit the roads, there is a clear need for accurate and reliable positioning information. And in case anyone missed it, Galileo is now the world's leading provider of dual-frequency GNSS, with more operational dual-frequency satellites in orbit than any other global system.
The GSA's Market Development Officer in charge of LBS Justyna Redelkievicz said, "We're seeing the new smartphones, the autonomous cars, drones and robotics – it's all here and it all needs location. At the GSA, we believe accuracy matters and we are here to say it, loud and clear. We are happy with how things are going with Galileo. It's going very well, it's growing, we have more users, and it's dual!"
Plainly, vehicle positioning and navigation remain key areas of innovation for GNSS technologies. In parallel, the GSA has been working hard to get these same technologies into people's hands. Based on what attendees could see at MWC 2019, this effort would seem to be paying off.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
WMS Ortofotomapa – nová data na celé Moravě
7.3.2019 10:39 TopGis Na našem WMS serveru jsme zaktualizovali naši datovou sadu ortofotomap a našim partnerům nyní poskytujeme nejaktuálnější a nejpodrobnější plošné podklady z leteckého snímkování. V loňském roce jsme dle plánu pokračovali v plošném snímkování naší vlasti, tentokrát se naše letadla proháněla po obloze v její východní části. Počasí nám přálo, území máme komplet zachycené, snímky zpracované a nyní iWMS Ortofotomapa – nová data na celé Moravě
7.3.2019 10:39 TopGis Na našem WMS serveru jsme zaktualizovali naši datovou sadu ortofotomap a našim partnerům nyní poskytujeme nejaktuálnější a nejpodrobnější plošné podklady z leteckého snímkování. V loňském roce jsme dle plánu pokračovali v plošném snímkování naší vlasti, tentokrát se naše letadla proháněla po obloze v její východní části. Počasí nám přálo, území máme komplet zachycené, snímky zpracované a nyní iBluesky and Getmapping Launch Online Aerial Mapping Service for UK Public Sector
7.3.2019 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars March 06, 2019 -- As part of the Aerial Photography for Great Britain (APGB) contract with the UK’s Geospatial Commission, Bluesky and …Yuneec International and Mobilicom form Strategic Partnership for the Commercial & Federal Drone Market
7.3.2019 7:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New drone solutions that are optimal for long-range, non-line-of-sight, beyond-line of sight and urban operations within applications including …odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
7.3.2019 7:04 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Olomoucvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
7.3.2019 7:04 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Olomouc vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent – návrh zápisu v katastruPrázdniny pod Sluncem 2019 na hvězdárně Ondřejov
7.3.2019 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Astronomický ústav AV ČR pořádá pro středoškolské studenty od 19. do 22. července 2019 na hvězdárně v Ondřejově akci Prázdniny pod Sluncem 2019. Zajímáš se o Vesmír a o Slunce a jeho aktivitu? Účastnit se přednášek, praktik i volnočasových aktivit a dozvědět se tak ještě více? Potom navštiv webovou stránku Prázdniny pod Sluncem23. kartografická konference - důležité termíny
7.3.2019 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformaceOd 18. do 20. září proběhne v Kutné Hoře 23. kartografická konference, kterou pořádá Česká kartografická společnost tentokrát ve spolupráci s katedrou aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie PřF UK a katedrou geomatiky ČVUT s podtitule Kartografie v proměnách času.
Důležité termíny:
12. duben 2019 - termín odeslání přihlášky ke konfernčnímu grantu
30.
Poslední místa na GIVS 2019
7.3.2019 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformacePoslední místa zbývají do naplnění kapacity sálu pro letošní ročník konference Geoinformace ve veřejné správě. Zároveň je možné ještě týden využít registrace za zvýhodněné vložné. A na jaká témata se v květnu na Novotného lávce můžete těšit?
DTM ČR
GeoInfoStrategie
BIM a GIS
Významné projekty veřejné správy, INSPIRE, DMVS
Smart City a
Workshop and Presentation Proposals Invited for URISA 2019 Caribbean GIS Conference
7.3.2019 1:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars
March 6, 2019 (Des Plaines, IL USA) URISA is pleased to announce the 2019 Caribbean …
Nepřírodní biotop – mapování 2007-2018
7.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Hranice segmentů biotopů silně ovlivněných nebo vytvořených člověkem, pokud byly zaznamenány při aktualizaci mapování biotopů přírodních a přírodně blízkých. Znalost rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů tedy není plošná, vrstva poskytuje informace o rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů pouze na malé části území ČR.Data z mapování biotopů neposkytují vyčerpávající informaci o vegetaci, resp. biotopech daného území. Mapování je metodicky nastaveno na celostátní úrovni, a především efemérní biotopy tak může pominout. V lokálním měřítku proto představuje pouze zjednodušený podklad. Pro detailnější informaci je třeba vyhledat jiné datové zdroje. Mapování biotopů je opakováno ve dvanáctileté periodě. Základní mapování bylo provedeno v letech 2001–2005.Klasifikace biotopů viz CHYTRÝ, M.; KUČERA, T.; KOČÍ, M. (eds.) et al. (2010). Katalog biotopů České republiky. 2.upr. a rozš.vyd. Praha: Agentura ochrany přírody a krajiny ČR. 445 s. ISBN 978-80-87457-03-0.Popis charakteristik biotopů a segmentů viz platná metodika mapování biotopů (Portál ISOP/Mapování biotopů). Vrstva obsahuje jednoduché prvky (Singlepart Features), kardinalita vztahu mezi záznamy v tabulkách 1 : N. © AOPK ČR, 2017Nepřírodní biotop – mapování 2001-2005
7.3.2019 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Hranice segmentů biotopů silně ovlivněných nebo vytvořených člověkem, pokud byly zaznamenány při mapování biotopů přírodních a přírodně blízkých. Znalost rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů tedy není plošná, vrstva poskytuje informace o rozšíření nepřírodních biotopů pouze na malé části území ČR.Data z mapování biotopů neposkytují vyčerpávající informaci o vegetaci, resp. biotopech daného území. Mapování bylo metodicky nastaveno na celostátní úrovni, a především efemérní biotopy tak mohlo pominout. V lokálním měřítku je proto pouze zjednodušeným podkladem. Pro detailnější informaci je třeba vyhledat jiné datové zdroje. Klasifikace biotopů viz CHYTRÝ, M.; KUČERA, T.; KOČÍ, M. (eds.) et al. (2001). Katalog biotopů České republiky: Interpretační příručka k evropským programům Natura 2000 a Smaragd. Vyd. 1. Praha: Agentura ochrany přírody a krajiny ČR. 307 s. ISBN 80-86064-55-7.Popis charakteristik biotopů a segmentů viz Guth, J. (ed.), 2002: Metodiky mapování biotopů soustavy Natura 2000 a Smaragd. 3. přepracované vydání. Ms., AOPK ČR, Praha, 48 pp.Vrstva obsahuje jednoduché prvky (Singlepart Features), kardinalita vztahu mezi záznamy v tabulkách 1 : N.© AOPK ČR, 2006Stříbrná medaile Masarykovy univerzity pro prof. Rudolfa Brázdila
7.3.2019 0:00 Geografický ústav MUDne 6. března předal rektor Mikuláš Bek Zlaté a stříbrné medaile lidem, kteří v posledních dekádách rozvíjeli Masarykovu univerzitu. Mezi oceněnými byl také profesor na Geografickém ústavu Rudolf Brázdil, který se významně zasadil především o rozvoj historické klimatologie.
Gratulujeme!
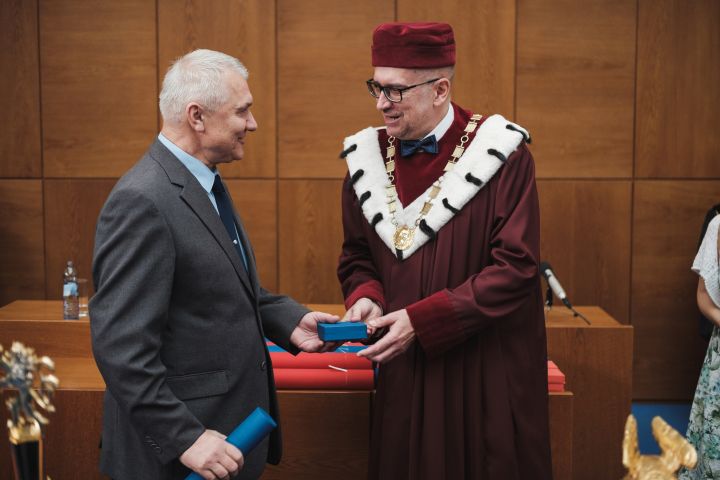

Bližší informace naleznete na webu https://www.em.muni.cz/udalosti/11466-nejlepsi-z-nejlepsich-cenu-prevzaly-osobnosti-ktere-formovaly-univerzitu.
PAKISTAN: Satellite Imagery confirms India missed target in Pakistan airstrike
6.3.2019 20:05 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Satellite image at 50 cm resolution showing madrasa buildings still standing at the site of Indian bombing. Satellite Imagery © 2019 …Microdrones and ESP Associates showcase mdLiDAR3000 workflow in 3 new videos
6.3.2019 16:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars ROME, N.Y., March 05, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Microdrones, in conjunction with ESP Associates, launched a new series of three videos, featuring …Kratos Receives $20.8 Million in Unmanned Aerial Drone System Contract Awards
6.3.2019 16:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, March 06, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc.(NASDAQ:KTOS), a leading National Security Solutions …Kratos Receives $20.8 Million in Unmanned Aerial Drone System Contract Awards
6.3.2019 16:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, March 06, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc.(NASDAQ:KTOS), a leading National Security Solutions …Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 20
6.3.2019 16:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok
2018
Výroční zpráva za rok 2018
6.3.2019 16:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahuvydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok
2018
Výroční zpráva za rok 2018
6.3.2019 16:22 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Vyrocni-zpravy/Vyrocni-zprava-dle-zakona-c-106-1999-Sb-za-rok-(1)Program Thunderbird při použit
6.3.2019 16:20 GEUSware Program Thunderbird při použití této funkce neumožní mail editovat, ale okamžitě ho odešle. Jde pouze o problém "mailového programu" Thunderbirdu ve verzi 60.5.2 (32 bit), ostatních e-mail programů a klientů se to netýká. Je to způsobené aktualizací Thunderbirdu, která byla vydaná 25.2.2019.Nový testovací stav pro horní stupeň rakety Ariane 6
6.3.2019 16:12 Český Kosmický PortálNa konci února slavnostně otevřelo německé letecko-kosmické středisko DLR v Lampoldshausenu nový testovací stav, který simuluje start kompletního horního stupně rakety Ariane 6.
Nový testovací stav pro horní stupeň rakety Ariane 6
6.3.2019 16:12 Český Kosmický PortálNa konci února slavnostně otevřelo německé letecko-kosmické středisko DLR v Lampoldshausenu nový testovací stav, který simuluje start kompletního horního stupně rakety Ariane 6.


















