zprávy
zdroje zpráv:20231102 - VŘ Veřejné zakázky
2.11.2023 15:47 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2023/20231102-VR-Verejne-zakazky20231102 - VŘ Veřejné zakázky
2.11.2023 15:47 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa odborný rada - Veřejné zakázky a centralizované zadávání.The new Horizon Europe Call is now open
2.11.2023 14:40 European GNSS Agency
With a commitment to advancing innovation in the European space sector, EUSPA continues to pave the way for the development of space downstream applications. By launching the third EUSPA call under Horizon Europe, EUSPA champions market development within the EU space downstream sector and fosters the adoption of space-based solutions. This initiative falls under Cluster 4 of the Horizon Europe Work Programme, dedicated to Digital, Industry, and Space, and promises fresh opportunities for innovation and growth.
The deadline for applications to the call is 14 February 2024.
This call features five compelling topics collectively aiming to advance space-based technologies and applications that address a range of critical challenges, from post-pandemic recovery to closing market gaps and enhancing security.
- EGNSS - Transition towards a green, smart, and more secure post-pandemic society (Innovation Action) - 3.5 million EUR
- EGNSS - Closing the gaps in mature, regulated, and long-lead markets (Innovation Action) - 8 million EUR
- Copernicus-based applications for businesses and policy-making (Research and Innovation Action) - 7 million EUR
- Designing space-based downstream applications with international partners (Research and Innovation Action) - 6 million EUR
- EU GOVSATCOM for a safer and more secure EU (Innovation Action) - 10 million EUR
"The new Horizon Europe call represents a remarkable opportunity for collaboration between the European space downstream industry and users. It offers SMEs, large players, academia, and public actors the chance to pioneer space-based applications that will yield tangible benefits for EU citizens, industries, and society as a whole, addressing pressing challenges ahead" affirms EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa. Details for the Call can be found here.
We are looking forward to consortia which will drive cutting-edge solutions based on EU Space Programme components.
Learn more during the Space Downstream Innovation Day on 21 November 2023
EUSPA's experts will provide in-depth insights into the current Horizon Europe call, highlighting the most relevant aspects and showcasing the results achieved.
Other funding opportunities related to the Fundamental Elements Programme, and the CASSINI initiative will also be tackled.
Register here. Deadline for the mandatory registration is 19 November.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
The new Horizon Europe Call is now open
2.11.2023 14:40 European GNSS Agency
With a commitment to advancing innovation in the European space sector, EUSPA continues to pave the way for the development of space downstream applications. By launching the third EUSPA call under Horizon Europe, EUSPA champions market development within the EU space downstream sector and fosters the adoption of space-based solutions. This initiative falls under Cluster 4 of the Horizon Europe Work Programme, dedicated to Digital, Industry, and Space, and promises fresh opportunities for innovation and growth.
The deadline for applications to the call is 14 February 2024.
This call features five compelling topics collectively aiming to advance space-based technologies and applications that address a range of critical challenges, from post-pandemic recovery to closing market gaps and enhancing security.
- EGNSS - Transition towards a green, smart, and more secure post-pandemic society (Innovation Action) - 3.5 million EUR
- EGNSS - Closing the gaps in mature, regulated, and long-lead markets (Innovation Action) - 8 million EUR
- Copernicus-based applications for businesses and policy-making (Research and Innovation Action) - 7 million EUR
- Designing space-based downstream applications with international partners (Research and Innovation Action) - 6 million EUR
- EU GOVSATCOM for a safer and more secure EU (Innovation Action) - 10 million EUR
"The new Horizon Europe call represents a remarkable opportunity for collaboration between the European space downstream industry and users. It offers SMEs, large players, academia, and public actors the chance to pioneer space-based applications that will yield tangible benefits for EU citizens, industries, and society as a whole, addressing pressing challenges ahead" affirms EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa. Details for the Call can be found here.
We are looking forward to consortia which will drive cutting-edge solutions based on EU Space Programme components.
Learn more during the Space Downstream Innovation Day on 21 November 2023
EUSPA's experts will provide in-depth insights into the current Horizon Europe call, highlighting the most relevant aspects and showcasing the results achieved.
Other funding opportunities related to the Fundamental Elements Programme, and the CASSINI initiative will also be tackled.
Register here. Deadline for the mandatory registration is 16 November.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
2.11.2023 14:15 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký krajodborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
2.11.2023 14:15 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-rada-reditel-kancelare-reditele-Katastralnodborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
2.11.2023 14:15 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj kancelář ředitelevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
2.11.2023 14:15 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
2.11.2023 14:15 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada - ředitel kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký krajRelive the Earth Observation Commercialisation Forum
2.11.2023 13:30 ESA Observing the Earth
ESA’s first Earth Observation Commercialisation Forum took place at ESA Headquarters in Paris on 30–31 October 2023. The event saw investors, institutions, entrepreneurs and different-sized companies from the Earth observation sector come together to discuss the commercial potential and challenges of Earth observation. Revisit the event by watching the streaming replay.
Program konference GIS Esri v ČR 2023
2.11.2023 12:35 GeoBusinessVe dnech 8. a 9. listopadu se v Praze uskuteční další ročník firemní konference GIS Esri v ČR, kterou pořádá společnost Arcdata Praha. Letos se konference vrací zpět do pražského Kongresového centra na Pankráci. Na programu je řada přednášek, ať již technologických, tak projektových. Zahájení konference a hlavní řečníci – 10.00–12.30 | Společenský sál, středa […]
The post Program konference GIS Esri v ČR 2023 appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Program konference GIS Esri v ČR 2023
2.11.2023 12:35 GeoBusiness Ve dnech 8. a 9. listopadu se v Praze uskuteční další ročník firemní konference GIS Esri v ČR, kterou pořádá společnost Arcdata Praha. Letos se konference vrací zpět do pražského Kongresového centra na Pankráci. Na programu je řada přednášek, ať již technologických, tak projektových. Zahájení konference a hlavní řečníci – 10.00–12.30 | Společenský sál, středa […]Program – 43. sympozium z dějin geodézie a kartografie
2.11.2023 12:15 ZeměměřičKoncem listopadu se v Praze v Národním technickém muzeu uskuteční sympozium z dějin geodézie a kartografie. Letošní v pořadí již čtyřicáté třetí setkání se koná 29. listopadu 2023 od 9 hodin. Program sympozia 9:00 Zahájení sympozia Předsedá Mgr. Jitka Močičková, Ph.D. (Historický ústav AV ČR) 9:10 Eva Novotná – Nejstarší glóbus v Čechách 9:25 Michal Jakl – Proroctví Havlase Pavlaty, sonda k Aretinově […]
The post Program – 43. sympozium z dějin geodézie a kartografie appeared first on Zeměměřič.
20231102_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
2.11.2023 10:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I. V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I."20231102_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace PI KN I.
2.11.2023 10:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-vychod/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(2)32. jednání KRS
2.11.2023 9:17 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 6. prosince 2023 proběhne distančně 32. jednání Koordinační rady správců DMVS a DTM.13. jednání TPS
2.11.2023 9:15 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 29. listopadu 2023 proběhne distančně 13. jednání Technické pracovní skupiny Koordinační rady správců DMVS a DTM.Dokument Dlaždicové služby ČR
2.11.2023 9:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do záložky Podklady IS DTM byl přidán dokument Dlaždicové služby České republikyProsincový den s CAD technikem – bezplatná online konzultace pro vaši firmu
2.11.2023 8:30 Arkance Systems1. prosince 2023 - přihlaste se na nový termín akce společnosti Arkance Systems. Těšíme se na vás.
Zpráva Prosincový den s CAD technikem – bezplatná online konzultace pro vaši firmu pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Nové verze 16.52
1.11.2023 14:52 GEPROPřipravili jsme pro vás nové verze 16.52 našich produktů. Stahovat je můžete z obvyklého umístění na našem download serveru. Novinky, které jsme pro vás nachystali: KOKEŠ MISYS Geoportál GEPRO PROLAND KOKEŠ Práce s daty Tisk mapy: doplněna možnost exportovat výkresy do PDF/A. Nová funkce Práce s výškami 3D rastru, umožňuje přenést výšky na body výkresů. …
Nové verze 16.52 Pokračovat ve čtení »
Článek Nové verze 16.52 se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
Nové verze 16.52
1.11.2023 14:52 GEPROPřipravili jsme pro vás nové verze 16.52 našich produktů. Stahovat je můžete z obvyklého umístění na našem download serveru. Novinky, které jsme pro vás nachystali: KOKEŠ MISYS Geoportál GEPRO PROLAND KOKEŠ Práce s daty Tisk mapy: doplněna možnost exportovat výkresy do PDF/A. Nová funkce Práce s výškami 3D rastru, umožňuje přenést výšky na body výkresů. […]
Článek Nové verze 16.52 se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
Nové verze 16.52
1.11.2023 14:52 GEPROPřipravili jsme pro vás nové verze 16.52 našich produktů. Stahovat je můžete z obvyklého umístění na našem download serveru. Novinky, které jsme pro vás nachystali: KOKEŠ MISYS Geoportál GEPRO PROLAND KOKEŠ Práce s daty Tisk mapy: doplněna možnost exportovat výkresy do PDF/A. Nová funkce Práce s výškami 3D rastru, umožňuje přenést výšky na body výkresů. …
Nové verze 16.52 Pokračovat ve čtení »
Článek Nové verze 16.52 se nejdříve objevil na GEPRO.
Objednávky knih a časopisů pro rok 2023 [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
1.11.2023 10:40 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK 15. 11. končí objednávky knih a časopisů pro rok 2023 prostřednictvím Knihovny geografie.Nový vzorkovník barev ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD
1.11.2023 9:33 ŠPINAR - softwareNový vzorkovník materiálů ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).
The post Nový vzorkovník barev ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Nový vzorkovník barev ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD
1.11.2023 9:33 ŠPINAR - software Nový vzorkovník materiálů ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).JVF DTM 1.4.3
31.10.2023 17:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Do záložky JVF DTM byl v souladu s harmonogramem vystaven návrh dokumentace k nové verzi JVF DTM 1.4.3. Po jejím posouzení bude následně schvalována Koordinační radou správců DMVS a DTM. S nasazením nové verze na produkční prostředí se počítá v průběhu prvního čtvrtletí roku 2024, termín bude upřesněn.SPOLEČNĚ PRO PODPORU BIM V ČESKU. OHLÉDNUTÍ ZA BIM DAY 2023
31.10.2023 15:46 czBIMJiž po dvanácté se uskutečnila konference BIM Day 2023. Přesto byla ale v něčem první. Ke sdružení czBIM se letos jako spolupořadatelé přidali Česká agentura pro...
Článek SPOLEČNĚ PRO PODPORU BIM V ČESKU. OHLÉDNUTÍ ZA BIM DAY 2023 se nejdříve objevil na czBIM.
SPOLEČNĚ PRO PODPORU BIM V ČESKU. OHLÉDNUTÍ ZA BIM DAY 2023
31.10.2023 15:46 czBIMJiž po dvanácté se uskutečnila konference BIM Day 2023. Přesto byla ale v něčem první. Ke sdružení czBIM se letos jako spolupořadatelé přidali Česká agentura pro...
Článek SPOLEČNĚ PRO PODPORU BIM V ČESKU. OHLÉDNUTÍ ZA BIM DAY 2023 se nejdříve objevil na czBIM.
SPOLEČNĚ PRO PODPORU BIM V ČESKU. OHLÉDNUTÍ ZA BIM DAY 2023
31.10.2023 15:46 czBIMJiž po dvanácté se uskutečnila konference BIM Day 2023. Přesto byla ale v něčem první. Ke sdružení czBIM se letos jako spolupořadatelé přidali Česká agentura pro...
Článek SPOLEČNĚ PRO PODPORU BIM V ČESKU. OHLÉDNUTÍ ZA BIM DAY 2023 se nejdříve objevil na czBIM.
Škoda Yeti 5C0 6326
31.10.2023 14:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Škoda Yeti 5C0 6326
Škoda Yeti 5C0 6326
31.10.2023 14:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Skoda-Yeti-5C0-6326role papíru, fólie do tiskárny, pap. do faxu atp.
31.10.2023 13:53 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
role papíru, fólie do tiskárny, pap. do faxu atp.
role papíru, fólie do tiskárny, pap. do faxu atp.
31.10.2023 13:53 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/role-papiru,-folie-do-tiskarny,-pap-do-faxu-atpodborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
31.10.2023 13:38 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Královéodborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
31.10.2023 13:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-rada-reditel-Katastralniho-pracoviste-Hradodborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
31.10.2023 13:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Královévypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
odborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
31.10.2023 13:38 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Králové vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Královéodborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
31.10.2023 13:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada - ředitel Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
XLIII. Sympozium z dějin geodézie a kartografie [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
31.10.2023 12:20 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK 29. listopadu 2023 od 9 hodin v Národním technickém muzeuE-ilustrace: Online databáze knižní ilustrace [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
31.10.2023 11:40 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK nový projekt Knihovědného oddělení knihovny Akademie věd ČRSpooky sights from space: world’s largest acidic lake
31.10.2023 9:15 ESA Observing the Earth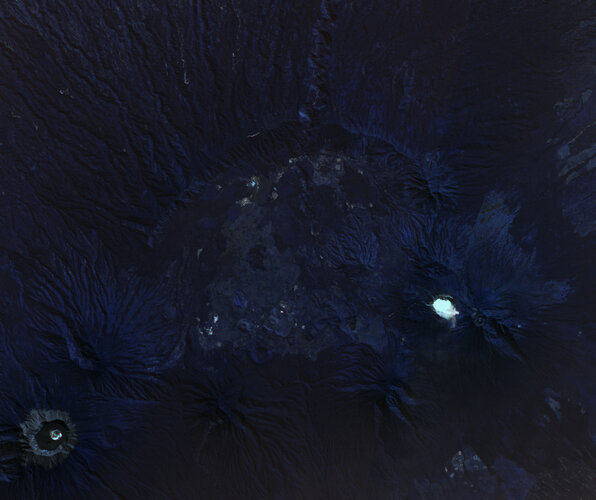 Image:
What’s spookier than the ‘largest acid cauldron on Earth?’ In East Java, Indonesia, lies the Kawah Ijen Crater Lake – the world’s largest acidic lake, a chilling spectacle perfect for Halloween.
Image:
What’s spookier than the ‘largest acid cauldron on Earth?’ In East Java, Indonesia, lies the Kawah Ijen Crater Lake – the world’s largest acidic lake, a chilling spectacle perfect for Halloween.
20231031_Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
31.10.2023 8:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Melnik/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(8)20231031_Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
31.10.2023 8:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Mělník Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada / odborný rada – informatik"Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
31.10.2023 8:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Mělníkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KN
31.10.2023 8:37 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Mělník vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení aktualizace KNHra života ve studiu šíření ohně
31.10.2023 8:34 GISportal.cz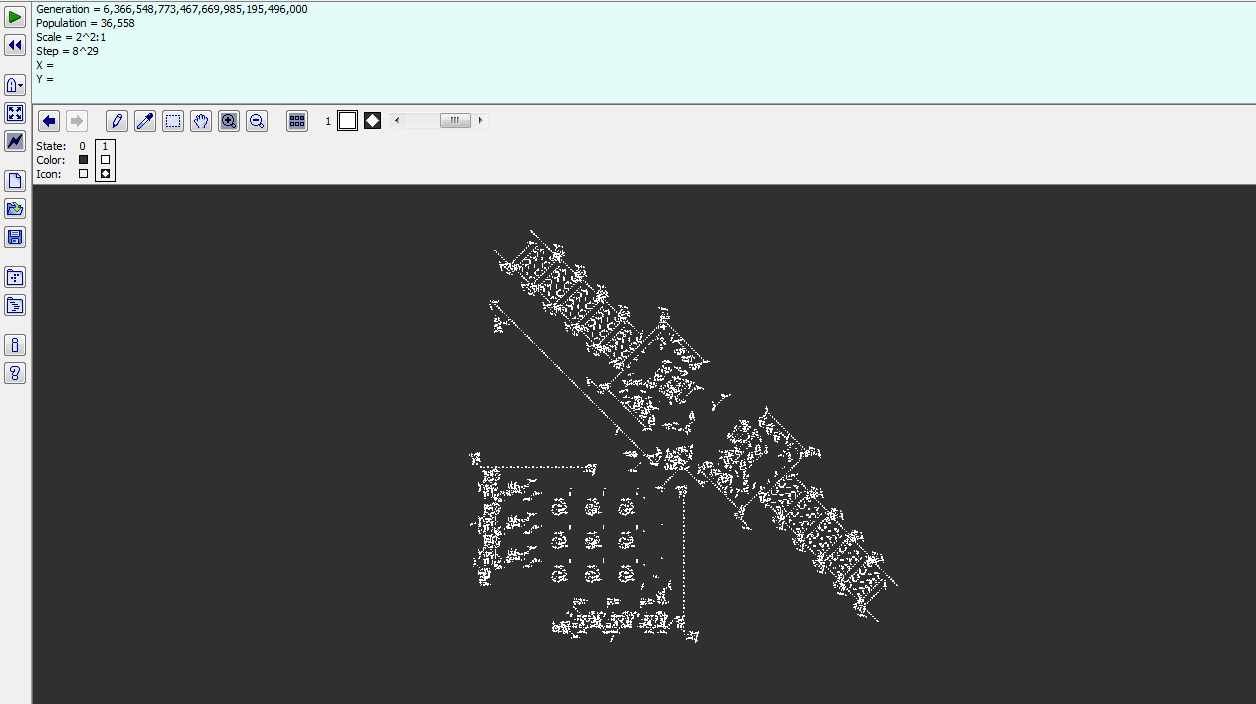
Hra života je matematický koncept vytvořený Johnem Conwayem v roce 1970. Tato hra je založena na celulárním automatu a zkoumá abstraktní modelování evoluce na dvourozměrné mřížce buněk. Jednoduchými pravidly „narození“ a „přežití“ se buňky na mřížce vyvíjejí, a tím vytvářejí zajímavé a komplexní vzory. Základní verze hry má tato 4 pravidla: Každá živá buňka s […]
The post Hra života ve studiu šíření ohně appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Výběrové řízení
31.10.2023 7:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rokycany zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě, ve znění pozdějších předpisů, vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu OKO1304, oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN, na Katastrálním úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj, na Katastrálním pracovišti Rokycany, se služebním působištěm v Rokycanech.Na služebním místě je státní služba (dále jen „služba“) vykonávána v oboru služby 55. Zeměměřictví a katastr nemovitostí.
Služební místo je zařazeno podle přílohy č. 1 k zákonu o státní službě do 9. platové třídy.
Služba na služebním místě bude vykonávána ve služebním poměru na dobu neurčitou.
Předpokládaným dnem nástupu do služby na služebním místě je 1. leden 2024.
Délka stanovené týdenní služební doby je 40 hodin.
Na služebním místě se umožňuje služba se zkrácenou služební dobou („kratší úvazek“).
Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
31.10.2023 7:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rokycanyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
31.10.2023 7:40 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Rokycany vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátuVvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
31.10.2023 7:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vvyberove-rizeni-na-sluzebni-misto-rada-odborn-(1)
Smernica na tvorbu geometrických plánov
30.10.2023 10:05
ÚGKK SR
V sekcii Kataster nehnuteľností - Aktuality je zverejnená prezentácia podpredsedu ÚGKK SR Ing. Vladimíra Raškoviča na 30.SGD v Žiline „Smernica na tvorbu geometrických plánov - dlhoočakávaný výsledok kompromisov a základ budúceho rozvoja"
Rada/odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI
30.10.2023 10:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-rizeni-o-oprave-chyby-v-SPI-(1Rada/odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI
30.10.2023 10:02 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Třinec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPIRada/odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI
30.10.2023 10:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Třinecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby v SPI
Výběrové řízení
30.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě, ve znění pozdějších předpisů, vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu, RPV0603, oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem, na Katastrálním úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj, na Katastrálním pracovišti Klatovy, se služebním působištěm v Klatovech.Na služebním místě je státní služba (dále jen „služba“) vykonávána v oboru služby 55. Zeměměřičství a katastr nemovitostí.
Služební místo je zařazeno podle přílohy č. 1 k zákonu o státní službě do 12. platové třídy.
Služba na služebním místě bude vykonávána ve služebním poměru na dobu neurčitou.
Předpokládaným dnem nástupu do služby na služebním místě je 1. březen 2024 nebo dohodou.
Délka stanovené týdenní služební doby je 40 hodin.
Na služebním místě se umožňuje služba se zkrácenou služební dobou („kratší úvazek“).
Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
30.10.2023 9:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vvyberove-rizeni-na-sluzebni-misto-rada-odborny-raVvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
30.10.2023 9:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Klatovyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladu
30.10.2023 9:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vvýběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – rozhodování o povolení vkladuVrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:54 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Ostrava vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátuVrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:54 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vrchni-referent-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-op-(6)Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:54 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Ostravavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Nový Jičínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:45 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Nový Jičín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátuVrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Bruntálvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 9:14 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Bruntál vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátuVŘ 584 Odborný/vrchní referent – obnova KO v TO (OOKO 1), 9.PT
30.10.2023 8:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
VŘ 584 Odborný/vrchní referent – obnova KO v TO (OOKO 1), 9.PT
VŘ 584 Odborný/vrchní referent – obnova KO v TO (OOKO 1), 9.PT
30.10.2023 8:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/VR-584-Odborny-vrchni-referent-–-obnova-KO-v-TO-(OVrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 8:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátu
30.10.2023 8:31 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj technický odbor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada – obnova katastrálního operátuNový vzorkovník barev ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28
29.10.2023 12:18 ŠPINAR - softwareNový vzorkovník materiálů RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).
The post Nový vzorkovník barev ICA a NCS pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28
27.10.2023 20:13 ŠPINAR - softwareNový vzorkovník materiálů RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).
The post Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28
27.10.2023 20:13 ŠPINAR - software Nový vzorkovník materiálů RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28
27.10.2023 20:13 ŠPINAR - softwareNový vzorkovník materiálů RA pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).
The post Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28
27.10.2023 20:13 ŠPINAR - softwareNová knihovna dvířek, lišt, lamel a palisandrů firmy AREDO pro DAEX DESIGN 24.
The post Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28
27.10.2023 20:13 ŠPINAR - softwareNový vzorkovník materiálů RA pro DAEX DESIGN 24 (TurboCAD Platinum s LightWorks a RedSDK).
The post Nový vzorkovník barev RAL pro DAEX DESIGN 24 a TurboCAD 28 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Krátka správa č. 47/2023
27.10.2023 15:27 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 47/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 47/2023
27.10.2023 15:27 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 47/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 46/2023
27.10.2023 15:22 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 46/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 46/2023
27.10.2023 15:22 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 46/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 45/2023
27.10.2023 15:20 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 45/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 45/2023
27.10.2023 15:20 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 45/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Watch live: ESA’s Earth Observation Commercialisation Forum
27.10.2023 13:45 ESA Observing the Earth
ESA’s first-ever Earth Observation Commercialisation Forum will take place next week at ESA Headquarters in Paris from 30 to 31 October 2023. The event will see investors, institutions, entrepreneurs and companies of any size from the Earth observation sector coming together to discuss the commercial potential and challenges of Earth observation. Follow our live steaming on ESA WebTV Two.
Dronedge 2024 – 9. ročník konference Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl
27.10.2023 10:09 UAVA Přijměte pozvání na letošní již 9. ročník konference Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl – Dronedge 2024. Datum: 11.9.2024 Místo: kino Dlabačov, Praha 6 Registrace bude spuštěnana přelomu červen/červenec 2024.Spolupořádali jsme Czechia-Korea Drone Roadshow a podepsali Memorandum s korejským KIAST
27.10.2023 10:09 UAVA Aliance byla spolupořadatelem a partnerem Czech Korea Drone Roadshow společně s Korejskou Trade Agency KOTRA, kde za velké účasti korejských i českých firem se konala v Praze B2B jednání a další konferenční program i za účasti českých autorit – ÚCL, ŘLP a Ministerstva dopravy. Současně podepsal prezident Aliance Memorandum o spolupráci s Korea Institute of […]Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 10:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Earth from Space: Elephant Island
27.10.2023 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Image:
This rare, almost cloud-free view of the remote Elephant Island in Antarctica was captured in February 2023 by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Image:
This rare, almost cloud-free view of the remote Elephant Island in Antarctica was captured in February 2023 by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis
27.10.2023 9:01 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace služby WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopisProhlížecí služba z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic WMTS ZABAGED® - polohopis, vytvořená za účelem využití datové sady ZABAGED® - polohopis jako podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním, již poskytuje veškeré změny po poslední pravidelné čtvrtletní aktualizaci dat.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací dat) byla aktualizována dynamická prohlížecí služba ZABAGED® - polohopis poskytující obraz dat přímo z publikační databáze, včetně možnosti vypínání vrstev, dotazů na atributy a stahování jednotlivých objektů ve formátu GeoJSON.
Pokud službu prohlížíte v našem Geoprohlížeči, je možné v seznamu vrstev přes menu "Možnosti" přejít na funkce stažení dat ZABAGED® - polohopis z celé ČR ve dvou souborových formátech a dvou souřadnicových systémech. Případně lze zvolit přípravu výřezu dat, který bude po krátkém zpracování nabídnut ke stažení v některém ze tří formátů a v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK.
Gearing up for EarthCARE
27.10.2023 9:00 ESA Observing the Earth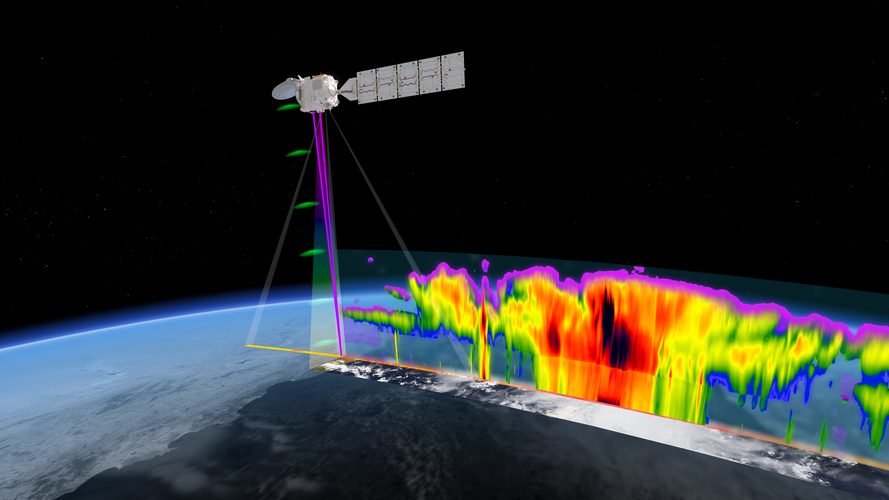
ESA and the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency are gearing up for a momentous milestone in Earth observation as launch of the EarthCARE satellite approaches.
Following years of rigorous development and extensive testing, the satellite is now undergoing its final round of tests in Europe before being shipped to the launch site early next year – bringing us one step closer to gaining unprecedented insights into the role that clouds and aerosols play in the climate system.
Spolupořádali jsme Czechia-Korea Drone Roadshow a podepsali Memorandum s korejským KIAST
27.10.2023 8:47 UAVAAliance byla spolupořadatelem a partnerem Czech Korea Drone Roadshow společně s Korejskou Trade Agency KOTRA, kde za velké účasti korejských i českých firem se konala v Praze B2B jednání a další konferenční program i za účasti českých autorit – ÚCL, ŘLP a Ministerstva dopravy. Současně podepsal prezident Aliance Memorandum o spolupráci s Korea Institute of […]
The post Spolupořádali jsme Czechia-Korea Drone Roadshow a podepsali Memorandum s korejským KIAST appeared first on UAV Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl.
Spolupořádali jsme Czechia-Korea Drone Roadshow a podepsali Memorandum s korejským KIAST
27.10.2023 8:47 UAVAAliance byla spolupořadatelem a partnerem Czech Korea Drone Roadshow společně s Korejskou Trade Agency KOTRA, kde za velké účasti korejských i českých firem se konala v Praze B2B jednání a další konferenční program i za účasti českých autorit – ÚCL, ŘLP a Ministerstva dopravy. Současně podepsal prezident Aliance Memorandum o spolupráci s Korea Institute of […]
The post Spolupořádali jsme Czechia-Korea Drone Roadshow a podepsali Memorandum s korejským KIAST appeared first on UAV Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl.
Zajímavá konference s názvem „Mapy jsou pro každého 2023“ proběhla na Vysočině
27.10.2023 7:17 TopGisTradičně jsme zúčastnili jako hlavní partner již devátého ročníku konference s názvem "Mapy jsou pro každého 2023", která se uskutečnila od 12. do 13. září 2023 na Vysočině. Program konference se letos logicky hodně zaměřoval na právě dokončované projekty Digitální technické mapy krajů a na praktické zkušenosti realizátorů. Shlédli jsme ale i zajímavé příspěvky ...
Článek Zajímavá konference s názvem „Mapy jsou pro každého 2023“ proběhla na Vysočině se nejdříve objevil na TopGis, s.r.o..
Mapy jsou pro každého 2023
27.10.2023 7:17 TopGisTradičně jsme zúčastnili jako hlavní partner již devátého ročníku konference s názvem "Mapy jsou pro každého 2023", která se uskutečnila od 12. do 13. září 2023 na Vysočině. Program konference se letos logicky hodně zaměřoval na právě dokončované projekty Digitální technické mapy krajů a na praktické zkušenosti realizátorů. Shlédli jsme ale i zajímavé příspěvky ...
Článek Mapy jsou pro každého 2023 se nejdříve objevil na TopGis, s.r.o..
odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
26.10.2023 11:41 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního praodborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
26.10.2023 11:41 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jindřichův Hradecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec (ID SM 30000192/30003816)
Six trends to watch in commercial Earth observation
26.10.2023 11:20 ESA Observing the Earth
With a multitude of opportunities for start-ups, established companies and investors, commercial Earth observation is a vibrant sector with fast-moving innovations in technology, datasets and downstream applications. ESA is a key driving force for the development of European Earth observation and provides impetus through its many programmes and initiatives.
To set the scene ahead of ESA’s Earth Observation Commercialisation Forum next week, here is some need-to-know background information on the evolution and state of play of the Earth observation industry.
Rada /odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
26.10.2023 10:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnim-c-1-na-KatastRada /odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
26.10.2023 10:42 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-město vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada /odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - městoRada /odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
26.10.2023 10:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-městovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada /odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město















