zprávy
zdroje zpráv:High Resolution Layers - Louky (ATOM)
27.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Předpřipravená datová sada, která obsahuje data HRL - Louky ve formátu GeoTIFF v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK archivované do formátu ZIP. Data jsou zpřístupněna prostřednictvím služby ATOM.High Resolution Layers (HRL) jsou rastrová data s prostorovým rozlišením 20 a 100 m, který jsou součástí programu Copernicus pro monitorování území. Produkt Louky (Grassland) obsahuje vyklasifikovanou vrstvu luk (Grassland Layer – GRA). Data jsou vytvářena poloautomatickými postupy nad družicovými snímky každé 3 roky. Technické specifikace dat naleznete zde: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/hrl-grassland-technical-document-prod-2015, informace o programu na http://land.copernicus.eu.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
27.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
27.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.High Resolution Layers - Lesy (ATOM)
27.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Předpřipravená datová sada, která obsahuje data HRL - Forest ve formátu GeoTIFF v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK archivované do formátu ZIP. Data jsou zpřístupněna prostřednictvím služby ATOM.High Resolution Layers (HRL) jsou rastrová data s prostorovým rozlišením 20 m, který jsou součástí programu Copernicus pro monitorování území. Produkt Lesy (Forest) obsahuje 2 datové sady: Hustota lesních porostů (Tree Cover Density - TCD) a Druh lesa (Dominant Leaf Type - DLT). Data jsou vytvářena poloautomatickými postupy nad družicovými snímky každé 3 roky. Technické specifikace dat naleznete zde: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/hrl-forest, informace o programu na http://land.copernicus.eu.High Resolution Layers - Nepropustnost povrchu (ATOM)
27.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Předpřipravená datová sada, která obsahuje data HRL - Nepropustnost povrchu ve formátu GeoTIFF v souřadnicovém systému S-JTSK archivované do formátu ZIP. Data jsou zpřístupněna prostřednictvím služby ATOM.High Resolution Layers (HRL) jsou rastrová data s prostorovým rozlišením 20 a 100 m, který jsou součástí programu Copernicus pro monitorování území. Produkt Nepropustnost povrchu (Imperviousness) obsahuje 3 datové sady: Procento nepropustnosti povrchu (Degree of Imperviousness - IMD), Změnu procenta nepropustnosti povrchu (Degree of Imperviousness change - IMC) a Klasifikovanou změnu procenta nepropustnosti povrchu (Degree of Imperviousness change classified - IMCC). Data jsou vytvářena poloautomatickými postupy nad družicovými snímky každé 3 roky. Technické specifikace dat naleznete zde: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/hrl-imperviousness-technical-document-prod-2015, informace o programu na http://land.copernicus.eu.November 2018 News
26.11.2018 17:55 Carlson Software Click here to view the November 2018 Carlson NewsZaměřeno na vývoj nosiče Vega
26.11.2018 17:11 Český Kosmický PortálKosmická raketa Vega prokazuje svoji kvalitu. A díky zkušenostem ESA a evropského průmyslu se chystá zásluhou nových elementů od poloviny roku 2019 dále růst z hlediska výkonu, kapacity a flexibility.
Bentley Announcements from Year in Infrastructure 2018
26.11.2018 16:26 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
MicroStation Connections, USA
Read the articleHow to use the messaging features in Google Maps - Android Central (Google Maps)
26.11.2018 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsAltitude Angel's World-leading GuardianUTM Airspace Management Operating System Successfully Powered Operation Zenith: The UK's Most Comprehensive Drone Trial
26.11.2018 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars On Wednesday 21st November 2018, to an exclusive delegation of over 120 influential people involved in the drone industry, Altitude Angel, NATS, …Terra Drone acquires Skeye to accelerate global expansion
26.11.2018 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars TOKYO, Nov. 26, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Terra Drone Ltd, a global company with its headquarters in Japan, has acquired a majority stake in …Indian Social Entrepreneur Wins the First UN Geospatial Ambassador Award
26.11.2018 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW DELHI, November 26, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Sanjay Kumar, Founder and CEO of Geospatial Media & Communications, was conferred …Engility secures $71 million remote sensing systems engineering & integration contract
26.11.2018 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars CHANTILLY, Va., Nov. 26, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Engility Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: EGL), has won a $71 million award to provide systems …GetSAT Antennas Selected by Hughes and NAVAIR as SatCom Component for U.S. Coast Guard Airborne Missions
26.11.2018 16:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Hughes Networks System Leading Mission-Driven Beyond-Line-of-Sight (BLOS) Solution Utilizing GetSAT's MilliSAT TerminalsREHOVOT, Israel, Nov. 26, …
Synchro buys a key step in building Bentley’s construction capabilities
26.11.2018 16:21 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Extranet Evolution, UK
Read the articleBentley ProjectWise365 extends Microsoft integration
26.11.2018 16:11 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Extranet Evolution, UK
Read the articleBentley Systems Acquires LEGION Leading Pedestrian Simulation Software
26.11.2018 16:08 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
GeoConnexion, UK
Read the articleHack Partners Creates InfraHack with Bentley
26.11.2018 15:55 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Lidar News, USA
Read the articleBentley Systems pushes for better road safety technologies in GCC
26.11.2018 15:44 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Technical Review Middle East, Middle East
Read the articleChytrá obec Hodonice: Pasportizace nám pomáhá s plánováním
26.11.2018 13:57 TopGis Parkoviště, zeleň, veřejné osvětlení i kanalizace. Přesné zmapování majetku je pro všechny obce důležité. Hodonice na jihu Moravy se tohoto úkolu zhostily tak dobře, že si za něj vysloužily titul Chytrá obec 2017. Hlavně jim ale pomáhá s plánováním údržby i jejich dalšího rozvoje. Šetří čas i peníze. Řeč je o pasportizaci neboli o zaevidováníodborný referent v oddělení právních vtahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Pardubice
26.11.2018 13:25 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Pardubice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent v oddělení právních vtahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Pardubiceodborný referent v oddělení právních vtahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Pardubice
26.11.2018 13:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Pardubicky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vtahu-k-nemovodborný referent v oddělení právních vtahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Pardubice
26.11.2018 13:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Pardubicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent v oddělení právních vtahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Pardubice
Začátky s BIM 360 v HUTNÍM PROJEKTU Frýdek-Místek
26.11.2018 12:44 Konference BIM OpenVideo záznam prezentace z konference BIM Open ve které se dozvíte jak ve společnosti HUTNÍ PROJEKT Frýdek-Místek využívají cloudový nástroj BIM 360 Docs ke správě a komunikaci všech zúčastněných na konkrétním projektu pro jejich zákazníka v Indii.
The post Začátky s BIM 360 v HUTNÍM PROJEKTU Frýdek-Místek appeared first on BIM Open.
GSA Road report highlights user PNT requirements
26.11.2018 12:34 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) recently published a Report on Road User Needs and Requirements, as part of a series that examines user needs and requirements for position, navigation and timing (PNT) solutions in various sectors. These reports, which are an outcome of the first European GNSS User Consultation Platform (UCP), will help shape the discussion at the next UCP, to be held as part of European Space Week in Marseille on 3-4 December 2018.
Road applications have a dominant position in the GNSS market, and this will be further strengthened by policy decisions from public authorities and the advent of connected cars. The report notes that eCall and the Smart Tachograph are already good examples of European policy promoting GNSS, and the directive on interoperability of road toll systems in the European Union is another.
Stringent performance requirements
However, according to the report, we are moving from specific devices supporting specific applications, to a situation where the vehicle is a platform of connected services requiring more stringent performances for positioning, timing and navigation.
Autonomous vehicles will bring a new set of requirements, but it is not yet clear what the final role of GNSS will be in the complex guiding system installed in these cars. Nevertheless, there is a significant potential for GNSS use in road transport as the global car industry moves towards connected cars and automated driving.
Watch this: eCall - Emergency Positioning
However, the report notes that there is a low awareness among stakeholders of the new possibilities offered by EGNSS and that research and pilot projects are needed all along the road value chain to convince decisions-makers to incorporate the latest GNSS signals into their system architectures. Consultation with stakeholders and users will help increase awareness of, and confidence in, GNSS solutions. The EGNSS User Consultation Platform (UCP) plays a key role in this process.
The EGNSS User Consultation Platform
The UCP is a periodic forum organised by the European Commission and the GSA involving end users, user associations and representatives of the value chain, such as receiver and chipset manufacturers, application developers and the organisations and institutions dealing, directly and indirectly, with Galileo and EGNOS. The Platform is a part of the process developed at the GSA to collect user needs and requirements and take them as inputs for the provision of user-driven Galileo and EGNOS services.
And this: Register now to the EU Space Week in Marseille
The next User Consultation Platform will be held on 3-4 December, during European Space Week in Marseille. The main work of the UCP will be carried out in eight parallel panel sessions grouping users by market segment, with a dedicated session on the road sector.
This year, European Space Week also has a special session on Smart Cities, which will highlight how space applications are driving innovation in today’s smart cities, supporting applications in various areas – from intelligent mobility and the Internet of Things (IoT) to location-based services for health, transportation and everything in-between, including in the road transport sector.
To join the ongoing discussion and to ensure that future European space programme evolutions meet your needs and requirements, you can take part by registering to attend European Space Week here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovišt
26.11.2018 10:38 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovištOdborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovišt
26.11.2018 10:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-do-(1)Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovišt
26.11.2018 10:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovišt
26.11.2018 10:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovišt
26.11.2018 10:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-dokumeOdborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovišt
26.11.2018 10:32 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovištSdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Trutnov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sdeleni-k-urednim-hodinam-dne-31-12-2018Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 10:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Rychnov-nad-Kneznou/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sdeleni-k-urednim-hodinam-dne-31-12-2018Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Náchod zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Nachod/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sdeleni-k-urednim-hodinam-dne-31-12-2018Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Náchod zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Jičín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Jicin/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sdeleni-k-urednim-hodinam-dne-31-12-2018Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Králové zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Králové zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Hradec-Kralove/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sdeleni-k-urednim-hodinam-dne-31-12-2018Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Pro den 31. 12. 2018 jsou úřední hodiny stanoveny od 8:00 do 12:00.Sdělení k úředním hodinám dne 31.12.2018
26.11.2018 9:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sdeleni-k-urednim-hodinam-dne-31-12-2018Federal Geographic Data as a Strategic Resource (ArcNews Online)
26.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsModernizace státního mapového díla (pozvánka)
26.11.2018 8:41 GISportal.cz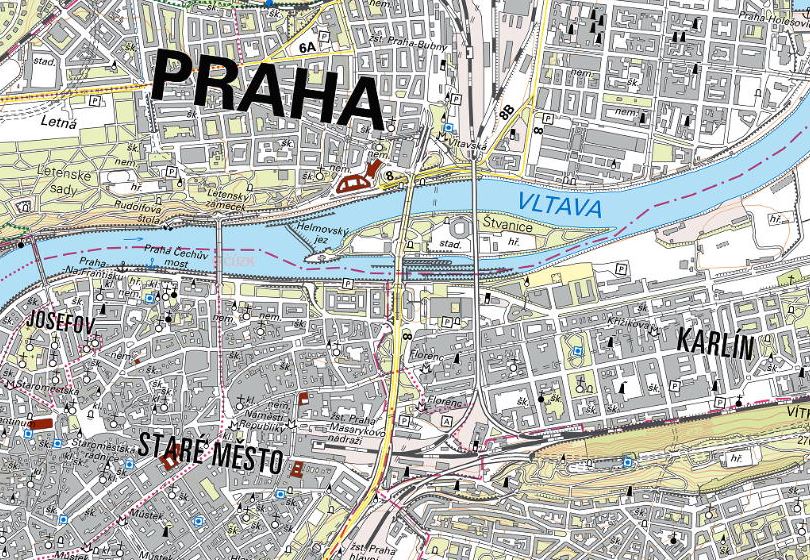
Sdružení Nemoforum srdečně zve na seminář Modernizace státního mapového díla, který se uskuteční ve čtvrtek 13. prosince 2018 v budově Zeměměřických a katastrálních úřadů. PROGRAM 10:00 – 10:10 ZAHÁJENÍ – Ing. Karel Štencel, místopředseda ČÚZK 10:10 – 12:10 PREZENTACE 10:10 – 10:40 Koncepce rozvoje zeměměřictví v letech 2015 až 2020 s výhledem do roku 2022 – Ing. Karel […]
The post Modernizace státního mapového díla (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
"Acquisitions, Open Source and Digital Twins" by Susan Smith
25.11.2018 10:20 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsByli jsme v Eurocontrolu v Bruselu na prvním setkání členů European Network of U-space Demonstrators
24.11.2018 9:23 UpVision Minulý týden jsme byli v Eurocontrolu v Bruselu na prvním jednání European Network of U-Space Demonstrators, kde členy za Českou republiku jsou UpVision, Řízení letového provozu a Ministerstvo dopravy.Podepsali jsme symbolicky Manifesto a diskutovali s Koenem De Vosem z Evropské komise, který má drony dlouhodobě na starost.
Fotky zde:
https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/115833877689730865211/+UpvisionCz1/posts/XLMYrZL7Md8
Government analysts use Google Street View to map urban greenery - PublicTechnology (Google Maps)
24.11.2018 4:05 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsINSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
24.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Copernicus improving daily lives in 99 stories
23.11.2018 18:00 ESA Observing the Earth
With seven Copernicus Sentinel missions in orbit delivering an almost unimaginable amount of freely-available data about our planet, the potential of tapping into this incredible resource to better the lives of citizens is almost limitless. A new publication that collects 99 stories from European public authorities highlights how we are all benefiting from Copernicus.
Picam360-SurfaceWalker: The Open Source Aquatic Drone
23.11.2018 17:49 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The world's first aquatic drone to let users experience "remote snorkeling". The funding amount has reached 100% on Kickstarter.TOKYO, Nov. 22, 2018 …
ESA podává pomocnou ruku u Marsu
23.11.2018 17:09 Český Kosmický PortálMars již brzy přivítá po šesti letech prvního nového obyvatele. Stane se tak zásluhou sondy NASA InSight, která má za úkol zkoumat nitro planety. Pozemní stanice ESA a sondy na oběžné dráze Marsu přitom budou hrát kritickou roli při směrování výsadkového modulu do cílové oblasti a při přenosu dat zpět na Zemi.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 23.11.2018 od 21:00 do cca 21:30
23.11.2018 13:05 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/240014Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 23.11.2018 od 21:00 do cca 21:30
23.11.2018 13:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 23.11.2018 v době od 21:00 do cca 21:30 bude z provozních důvodů přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu a Webových služeb DP.
Omlouváme se za komplikace a děkujeme za pochopení.
Přerušení provozu DP a WSDP v pátek 23.11.2018 od 21:00 do cca 21:30
23.11.2018 13:05 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,oznamujeme, že v pátek 23.11.2018 v době od 21:00 do cca 21:30 bude z provozních důvodů přerušen provoz Dálkového přístupu a Webových služeb DP.
Omlouváme se za komplikace a děkujeme za pochopení.
odborný referent / vrchní referent podatelny Katastrálního pracoviště Svitavy
23.11.2018 11:25 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Svitavy vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent / vrchní referent podatelny Katastrálního pracoviště Svitavyodborný referent / vrchní referent podatelny Katastrálního pracoviště Svitavy
23.11.2018 11:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Pardubicky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-podatelny-Katasodborný referent / vrchní referent podatelny Katastrálního pracoviště Svitavy
23.11.2018 11:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Svitavyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent / vrchní referent podatelny Katastrálního pracoviště Svitavy
Anticipating eCall for motorcycles, the Crash Care helmet is saving lives
23.11.2018 11:23 European GNSS Agency
The innovative Crash Care helmet utilises 3D sensors, Galileo-based positioning and mobile phone networks to detect, and respond to, motorcycle and bicycle accidents, like the eCall system for cars.
Imagine you are out riding you bicycle or cruising on your motorcycle along a picturesque country road. Far from anything, you simply take in the open road and enjoy the rural scenery. Then suddenly, out of nowhere, a deer darts out in front of you. You swerve to avoid hitting it and, in doing so, slide on some loose gravel. Falling off your bike, your head bounces against the pavement, leaving you unconscious in the middle of the road.
Normally, your well-being would depend on a vehicle coming by, seeing you and calling for help. But, luckily for you, your Crash Care smart helmet has already detected the accident and automatically alerted the emergency helpdesk about your location.
Help is on the way.
Automatic for the biker
The innovative, German made Crash Care device is a compact sensor that can be attached to nearly all types of motorcycle and bicycle helmets. Using a 3D sensor and gyroscope, the system not only detects when an accident happens, but also how strong the impact was. Thanks to its built-in Galileo-enabled receiver, Crash Care uses GNSS-based positioning information to determine the exact location of the accident.
“All of this information, along with previously added medical background information, is automatically transmitted via SMS to local emergency services and other third parties,” says Crash Care inventor Dr. Winrich Hoseit. “It even provides vital data, so doctors have a clear picture of the situation before the patient arrives in the emergency room.”
Crash Care is compatible with all European mobile networks. To provide users with more peace of mind, the system’s lithium battery guarantees a usage period of 10 years – with no need for recharging. Crash Care even automatically self-checks and notifies the user of any potential glitches.
Looking ahead
Although originally designed for motorcycles and bicycles, Dr. Hoseit notes that the system can also be used by equestrians, skiers, fire fighters, police officers, and the military. In fact, the company is currently in talks with the German military about developing a satellite-based system, as opposed to using mobile phone networks as the standard system does. There are also plans to implement the Crash Care system into hard hats, so those working in construction sites, remote oil rigs and other accident-prone sites can benefit from the extra layer of security the system provides.
Having been certified, Crash Care is set to hit the market by mid-2019. In total, 17,000 orders have already been placed across Germany, Austria, the UK and the Netherlands.
Aftermarket eCall
The Crash Care team is exploring the possibility of creating a version that can be inserted into vehicles, providing a service similar to Europe’s eCall system. eCall devices automatically dial the European emergency number 112 to alert rescue services in the event of an accident. The system sends the exact location to responders, along with the time of the incident and the direction of travel, even if the driver is unconscious or unable to make a phone call, thereby reducing the response time for road accidents and saving more lives.
“According to EU law, all new vehicles sold in Europe must be eCall enabled,” explains Dr. Hoseit. “What we aim to do is to make the Crash Care architecture available to provide the same service in legacy vehicles, or those that were manufactured before eCall went into effect.”
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Or
23.11.2018 11:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Pardubicky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-katastrrada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Or
23.11.2018 11:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Orlicívypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Orlicí
rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Or
23.11.2018 11:20 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Orlicí vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada / odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Orodborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
23.11.2018 11:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Pardubicky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-aktuodborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
23.11.2018 11:16 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Chrudim vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviodborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
23.11.2018 11:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Pardubický kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Chrudimvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Chrudim
Earth from space
23.11.2018 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
In this edition, explore the area around the Gulf with Copernicus Sentinel-3
The Gulf
23.11.2018 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
Earth observation image of the week: Copernicus Sentinel-3 takes us over the Gulf
Sestavte si vlastní mapu kvality života
23.11.2018 10:04 GISportal.cz
Zajímá vás, kde je v Česku nejlépe dostupný internet, velké procento věřících, čistý vzduch nebo nízká nezaměstnanost? Který z ukazatelů kvality života je důležitý právě pro vás? Pojďme si vytvořit na pár kliknutí personalizovanou mapu ideální lokality pro život. Vytvořit takovou mapu si můžete v nové mapové aplikaci na portálu irozhlas.cz. Mapa využívá platformy Mapbox […]
The post Sestavte si vlastní mapu kvality života appeared first on GISportal.cz.
NAPSALI O NÁS: Poskytovatel mapových služeb TopGis a vývojářská společnost Bio-Nexus se dohodli na převodu kmene zákazníků aplikace CLEERIO pro města a obce
23.11.2018 9:34 TopGis Brno, 22. listopadu 2018 – Společnost TopGis specializující se na mobilní a letecké mapování a webové mapové služby se dohodla se společností Bio-Nexus na převodu zákaznického kmene aplikace CLEERIO, jejímž vývojářem je právě Bio-Nexus. Akvizicí TopGis získává rozsáhlé portfolio klientů z řad obcí a měst a zároveň se firmě díky této dohodě otevírá cesta k20181123 - Změna v komprimaci souborů VFR
23.11.2018 9:11 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/2-Poskytovani-udaju-RUIAN-ISUI-VDP/Vymenny-format-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-VFR/20181123-Zmena-v-komprimaci-souboru-VFR20181123 - Změna v komprimaci souborů VFR
23.11.2018 9:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Změna komprimace VFR:O víkendu 7. - 9. 12. 2018 dojde ke změně v komprimaci souborů VFR z dosavadního formátu .gz na nový formát .zip. Ukázkové soubory některých typů VFR ke stažení.
Zveřejněno 23. 11. 2018
Leica Geosystems offers new Utility Surveyor Course
23.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Training class seeks to fill skills gap in the industry(Heerbrugg, Switzerland – 20 November 2018) – Leica Geosystems, part …
LiDARUSA Announces Z+F Mobile Systems
23.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars November 20, 2018 -- LiDARUSA is pleased to announce the integration of the Z+F scanners for mobile mapping.The Z+F Profiler is a high-speed, very …
Bluesky uses Leica CityMapper to capture major UK cities in 3D
23.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars First commercial use of Leica CityMapper in the region (Heerbrugg, Switzerland – 21 November 2018) – Leica …
INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
23.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
23.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Problémy s přihlašováním do aplikace DP/WSDP - odstraněny
22.11.2018 19:24 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé,problémy s přihlašováním do aplikace DP/WSDP byly odstraněny.
V případě, že problémy přetrvávají, kontaktujte naši podporu. Kontakty najdete zde: https://www.cuzk.cz/Katastr-nemovitosti/Poskytovani-udaju-z-KN/Dalkovy-pristup/Komunikace-se-sluzbou-uzivatelske-podpory-DP.aspx
Problémy s přihlašováním do aplikace DP/WSDP - odstraněny
22.11.2018 19:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé,problémy s přihlašováním do aplikace DP/WSDP byly odstraněny.
V případě, že problémy přetrvávají, kontaktujte naši podporu. Kontakty najdete zde: https://www.cuzk.cz/Katastr-nemovitosti/Poskytovani-udaju-z-KN/Dalkovy-pristup/Komunikace-se-sluzbou-uzivatelske-podpory-DP.aspx
Problémy s přihlašováním do aplikace DP/WSDP - odstraněny
22.11.2018 19:24 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/239946Oznámeno datum vypuštění mise zkoumající exoplanety
22.11.2018 17:00 Český Kosmický PortálMise CHEOPS (Characterising Exoplanet Satellite) se do vesmíru vydá mezi 15. říjnem a 14. listopadem 2019.
TopGis kupuje vybrané zákazníky Bio-Nexusu (Cleerio)
22.11.2018 16:33 GeoBusiness Společnost TopGis, která se specializuje na mobilní a letecké mapování a webové mapové služby, se dohodla se společností Bio-Nexus na převodu zákaznického kmene aplikace ... PřečístTopGis kupuje obecní a městské zákazníky Bio-Nexusu (Cleerio)
22.11.2018 16:33 GeoBusiness Společnost TopGis, která se specializuje na mobilní a letecké mapování a webové mapové služby, se dohodla se společností Bio-Nexus na převodu zákaznického kmene aplikace ... Přečíst20181122-Nová funkčnost pro ZPMZ
22.11.2018 16:32 ČÚZK /Zememerictvi/Zememericke-cinnosti/Aktuality-pro-zememerice/Nova-funkcnost-pro-ZPMZ20181122-Nová funkčnost pro ZPMZ
22.11.2018 16:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnízveřejnil novou aktualitu: Došlo k vystavení nové verze grafického klienta v Nahlížení do KN pro geodety (po přihlášení účtem do DP), který obsahuje nové tlačítko „ZPMZ“. Tato nová funkcionalita uživateli vrátí seznam veškerých ZPMZ, která jsou dostupná v daném výřezu obrazovky.
20181122-Nová funkčnost pro ZPMZ
22.11.2018 16:32 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Došlo k vystavení nové verze grafického klienta v Nahlížení do KN pro geodety (po přihlášení účtem do DP), který obsahuje nové tlačítko „ZPMZ“. Tato nová funkcionalita uživateli vrátí seznam veškerých ZPMZ, která jsou dostupná v daném výřezu obrazovky.20181122-Nová funkčnost pro ZPMZ
22.11.2018 16:32 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Došlo k vystavení nové verze grafického klienta v Nahlížení do KN pro geodety (po přihlášení účtem do DP), který obsahuje nové tlačítko „ZPMZ“. Tato nová funkcionalita uživateli vrátí seznam veškerých ZPMZ, která jsou dostupná v daném výřezu obrazovky.GIS Day 2018 ČR
22.11.2018 15:54 Ministerstvo vnitra Osvětově informační akce Prostorová data pro Digitální Česko aneb Jak mohou prostorová data přispět k naplňování programu vládyAktualizace dat ÚAP od poskytovatelů MERO ČR, a.s. a Řízení letového provozu ČR, s.p.
22.11.2018 14:45 Plzeňský kraj V datech územně analytických podkladů Plzeňského kraje byla provedena kompletní aktualizace dat ve správě poskytovatele MERO ČR, a.s. a aktualizace dat od poskytovatele Řízení letového provozu ČR, s.p..Climate analysis toolbox updated
22.11.2018 13:36 ESA Observing the Earth
An update to ESA’s climate analysis toolbox that combines information collected from numerous satellite missions is now available, and can supercharge climate-change research studies for scientists and degree-level students.
111th Group aerial photo using new DesignJet Z Printer to propel business
22.11.2018 13:04 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars November 22, 2018 - The 111th Group, an aerial photography specialist, has deployed a new HP DesignJet Z6 PostScript® Printer to …GSA Maritime and Inland Waterways report examines user PNT requirements
22.11.2018 12:30 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) recently published a Report on Maritime and Inland Waterways User Needs and Requirements as part of a series of eight similar reports examining user needs and requirements for position, navigation and timing (PNT) solutions. These reports will help shape the discussion at the next EGNSS User Consultation Platform (UCP), to be held as part of European Space Week in Marseille on 3-4 December 2018.
In the maritime and inland waterways (IWW) domains, GNSS is used for both navigation and positioning and it has become the primary means of navigation in many maritime and IWW applications. The GSA report provides an overview of GNSS-enabled maritime and IWW applications, sheds light on the current market and technology trends and outlines the key user requirements for GNSS, covering the most important market and technology trends of the sector, the main market players and the main user groups.
Watch this: EGNOS and Galileo for Waterborne Transport
Regulation and standards
Even though GNSS has gained widespread acceptance as the preferred positioning system for a majority of maritime applications, no existing GNSS is capable of meeting all operational requirements, especially integrity, without the use of augmentation systems including SBAS. However, the report notes that to consolidate the permanent and widespread use of SBAS, it will be necessary to have specific regulation concerning maritime users’ needs.
Indeed, with the notable exception of recreational navigation, regulation has a strong role in defining user requirements and represents a key driver for the adoption of new solutions for navigation and positioning, including satellite-based systems and services. Given the international scope of the maritime sector, the report notes that agreement and mutual understanding is needed in terms of regulation and standards if the sector is to fully benefit from GNSS potential.
In this context, improving maritime EGNSS based positioning and navigation will require the appropriate system evolution. This will be achieved by identifying clear user requirements, which is the goal of the EGNSS User Consultation Platform and of the critical analysis carried out in the report.
The EGNSS User Consultation Platform
The report’s findings will feed into discussions at the next EGNSS User Consultation Platform (UCP) in Marseille in December. The UCP is a periodic forum organised by the European Commission and the GSA, involving end users, user associations and representatives of the value chain, such as receiver and chipset manufacturers, application developers and the organisations and institutions dealing, directly and indirectly, with Galileo and EGNOS. The event is a part of the process developed at the GSA to collect user needs and requirements and take them as inputs for the provision of user-driven Galileo and EGNOS services.
Read this: H2H – leveraging EGNSS for safer maritime navigation
The next User Consultation Platform will be held on 3-4 December, during European Space Week. The main work of the UCP will be carried out in eight parallel panel sessions grouping users by market segment, with a dedicated session on Maritime.
This year, European Space Week also has a special session on Marine and Maritime, which will highlight how the Galileo and Copernicus programmes contribute to the sustainable management of our oceans and provide support for maritime operations. Specifically, the session will address aspects such as safety at sea, search and rescue, optimised maritime transport, sustainable fisheries, renewable energies, security and the fight against pollution.
The event will also feature a dramatic sea rescue simulation as part of which a Galileo search and rescue (SAR) beacon will be activated, triggering the deployment of a French rescue boat and helicopter to carry out a rescue operation. The demonstration will be followed by a debrief session on the technologies used, explaining how space is making maritime rescue faster, safer and more effective.
To join the ongoing discussion and to ensure that future European space programme evolutions meet your needs and requirements, you can take part by registering to attend European Space Week here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Open Geospatial Consortium announces HERE Technologies has joined OGC as a Principal Member
22.11.2018 12:15 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars As Principal Member, HERE will help to explore market and technology trends to drive standards for the development of interoperable location …Aktualizace údajů
22.11.2018 9:48 Ústecký kraj V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kraje byla provedena aktualizace údajů pro poskytovatele MERO ČR, a.s. – Jev 72, 73, 76, 77, 93Deoxygenation of the Ocean Affects Everyone, So Act Now (ArcNews Online)
22.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsXpressSAR Selects IAI's TECSAR Technology for Its High-Resolution X-Band Satellite Constellation
22.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars November 19, 2018, Arlington, VA- XpressSAR Inc. of Arlington, Virginia and Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) have signed a Memorandum of …United Nations/Germany High Level Forum concludes with recommendations to leverage the potential of space innovations to overcome sustainable development challenges
22.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VIENNA, 20 November 2018 (UN Information Service) – A record-breaking number of more than 300 participants from over 55 countries gathered at …Maxar Technologies to Present at Upcoming Investor Conferences
22.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, CO, Nov. 21, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Maxar Technologies (the "Company" or "Maxar") (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR), a global …odborný rada – metodik KN
22.11.2018 7:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - kancelář úřaduvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada – metodik KN
odborný rada – metodik KN
22.11.2018 7:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-rada-–-metodik-KNodborný rada – metodik KN
22.11.2018 7:30 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - kancelář úřadu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada – metodik KNRada/Odborný rada – Oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
22.11.2018 6:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Sokolovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/Odborný rada – Oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Rada/Odborný rada – Oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
22.11.2018 6:37 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-Odborny-rada-–-Oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-nemRada/Odborný rada – Oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
22.11.2018 6:37 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Sokolov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/Odborný rada – Oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostemGIS Esri v Česku 2018 – očima GISportalu (Den 2)
22.11.2018 6:00 GISportal.cz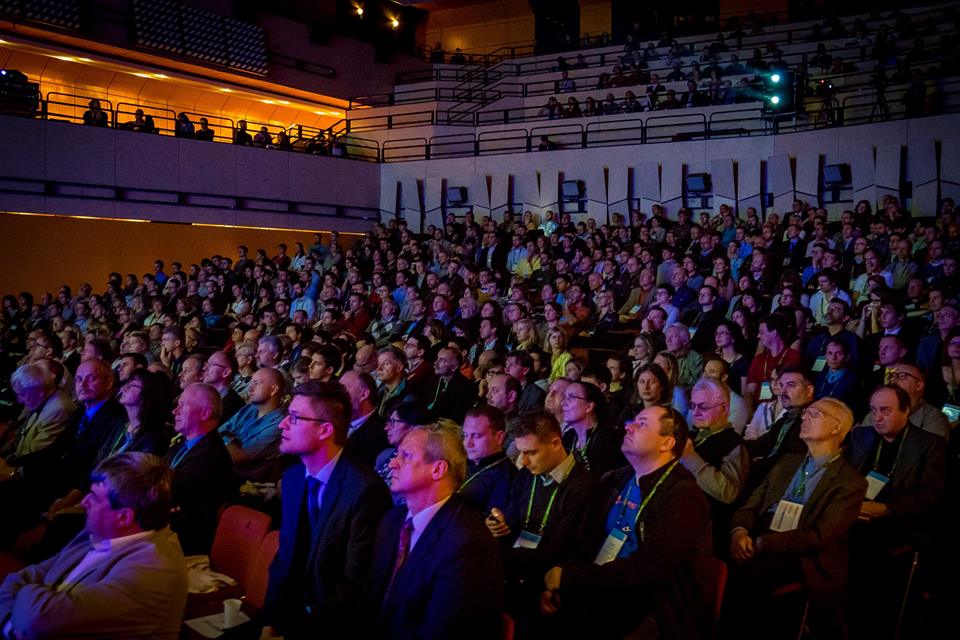
Ve čtvrtek se přednášky rozběhly o půl desáté hned ve třech sálech. V úvodu představili zástupci Vysoké školy báňské svou aplikaci na hodnocení kvality ovzduší Air Tritia se zajímavým mezistátním výzkumem. Účastníci se mohli na mapách i grafech přesvědčit, že znečištěný vzduch do Česka přichází z Polska i Slovenska a že mezioborová spolupráce je tak […]
The post GIS Esri v Česku 2018 – očima GISportalu (Den 2) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
22.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
22.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
22.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Oznámení o částečném omezení provozu Pobočky Plzeň
22.11.2018 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Z důvodu plánovaného přerušení dodávky elektrické energie bude v pátek 30. 11. 2018 částečně omezen provoz na Pobočce Plzeň (KPÚ pro Plzeňský kraj) v době od 13 do 14 h. Chod pobočky bude zajištěn.XY – The Findables Company Announces 2018 Semi-Annual Financial Report and Results
21.11.2018 19:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars First Half of 2018 Marked by High Sales Growth, Team Buildout, StrongCommunity Support for XYO Network Blockchain Platform
SAN DIEGO …















