zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Přidělení oprávnění pro sbírku listin všem uživatelům ztotožněných zákaznických účtů DP/WSDP.
16.11.2018 11:33 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážený uživateli dálkového přístupu.Oznamujeme, že v rámci přerušení provozu Dálkového přístupu a Webových služeb DP 16.11. – 18.11. bude přiděleno oprávnění pro přístup ke sbírce listin všem uživatelům zákaznických účtů DP/WSDP včetně jejich podúčtů, u kterých byla prokázána totožnost jeho uživatele.
Přidělení oprávnění pro sbírku listin všem uživatelům ztotožněných zákaznických účtů DP/WSDP.
16.11.2018 11:33 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážený uživateli dálkového přístupu.Oznamujeme, že v rámci přerušení provozu Dálkového přístupu a Webových služeb DP 16.11. – 18.11. bude přiděleno oprávnění pro přístup ke sbírce listin všem uživatelům zákaznických účtů DP/WSDP včetně jejich podúčtů, u kterých byla prokázána totožnost jeho uživatele.
ɸ and commercialisation
16.11.2018 11:10 ESA Observing the Earth
The main focus of day four at ESA’s ɸ-week was on the opportunities Earth observation can bring to business and the economy
Německé a české plány města Brna budou jedním z témat 39. sympozia
16.11.2018 10:56 GeoBusiness 39. sympozium z dějin geodézie a kartografie se uskuteční 28. listopadu 2018 od 9 hodin v prostorách Národního technického muzea v Praze (Kostelní 42, ... PřečístAnalytik IKT
16.11.2018 10:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Analytik IKT
Analytik IKT
16.11.2018 10:45 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Analytik IKT
Analytik IKT
16.11.2018 10:45 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Analytik IKTAnalytik IKT
16.11.2018 10:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Analytik-IKTEarth from Space
16.11.2018 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
In this edition, we explore Fogo, a small volcanic island in the Republic of Cabo Verde
Fogo
16.11.2018 10:05 ESA Observing the Earth
Earth observation image of the week: Copernicus Sentinel-2 takes us over the small volcanic island of Fogo in the Republic of Cabo Verde
Is it a bird? Is it a plane?
16.11.2018 9:45 ESA Observing the Earth
It may not be your actual Superman, but participants to ESA’s ɸ-week are certainly embracing some ‘superhero’ ideas for the future of Earth observation, including high-flying platforms – something between a satellite and an aircraft.
referent KN – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
16.11.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Praha vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo referent KN – obnova a revize katastrálního operáturada/vrchní referent – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
16.11.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Praha vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo rada/vrchní referent – obnova a revize katastrálního operátureferent KN – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
16.11.2018 9:31 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/referent-KN-–-obnova-a-revize-katastralniho-operatrada/vrchní referent – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
16.11.2018 9:31 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/referent-KN-–-obnova-a-revize-katastralniho-operatrada/vrchní referent – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
16.11.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Prahavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/vrchní referent – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
referent KN – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
16.11.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Prahavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
referent KN – obnova a revize katastrálního operátu
Microdrones launches new mdLiDAR3000, two new Mapper systems
16.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsPerforming Data Checks Keeps Water Running (ArcNews Online)
16.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsGISday 2018
16.11.2018 7:55 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucOpět jako každý rok se na Katedře geoinformatiky uskutečnil „Den otevřených dveří GIS-ů“ – GISday. Letos pro velký zájem se na nás první školy přijely podívat již v pátek 9. 11. 2018 a pak tradičně ve středu 15. 11. 2018. Velké množství potencionálních zájemců o studium se ze zajímavé přednášky dozvědělo něco nového o studiu […]
The post GISday 2018 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
GISday 2018
16.11.2018 7:55 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucOpět jako každý rok se na Katedře geoinformatiky uskutečnil “Den otevřených dveří GIS-ů” – GISday. Letos pro velký zájem se na nás první školy přijely podívat již v pátek 9. 11. 2018 a pak tradičně ve středu 15. 11. 2018. Velké množství potencionálních zájemců o studium se ze zajímavé přednášky dozvědělo něco nového o studiu […]
The post GISday 2018 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
CORINE Land Cover 2018 (E-shop - předpřipravená datová sada)
16.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Předpřipravená datová sada, která obsahuje soubory (CLC18_CZ, CLC12R_CZ a CHA18_CZ) ve formátu SHP archivované do formátu ZIP. Data jsou zpřístupněna v e-shopu Národního geoportálu INSPIRE. CLC 2018 - Databáze s klasifikací pokryvu zemského povrchu v rozsahu ČR v roce 2018. Databáze CLC 2018 byla interpretována z aktualizované databáze CLC 2012. Velikost nejmenší mapovací jednotky pro polygony CLC 2018 byla stanovena na 25 ha.CLC 2012 - Revidovaná databáze s klasifikací pokryvu zemského povrchu v rozsahu ČR v roce 2012. V rámci tvorby databáze CLC2018 byla revidována a aktualizována databáze CLC 2012. Velikost nejmenší mapovací jednotky pro polygony CLC 2012 je stanovena na 25 ha.CLC 2012-2018 - Změnová databáze CORINE Land Cover 2018 byla odvozena z databáze s klasifikací pokryvu zemského povrchu v roce 2012 vizuálním porovnáním rastrových podkladů z roku 2012 a 2018. Zaznamenány byly všechny změny splňující mapovací kritéria (rozloha > 5 ha, posun hranic > 100 m).Multi-objective optimisation reaching new heights with latest scheduling software release
16.11.2018 0:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The leaders in intelligent mine scheduling optimisation have pushed the benchmark even higher with the recent release of Maptek Evolution 5.1.Close …
Pro přistávací misi ExoMars byla navržena oblast Oxia Planum
15.11.2018 23:02 Český Kosmický PortálPracovní skupina ExoMars LSSWG (Landing Site Selection Working Group) doporučila oblast Oxia Planum jako místo přistání pro rover a povrchovou vědeckou platformu, které připravuje společně ESA a Roskosmos k vyslání na Mars v roce 2020.
Elsevier Integrates Geofacets into Esri ArcGIS to Help Geoscientists Find Information Faster and Further Reduce Research Time
15.11.2018 17:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, November 15, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Researchers can now seamlessly discover and analyze information from 100+ of the top …Intermap Technologies Reports 2018 Third Quarter Financial Results
15.11.2018 17:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DENVER, Nov. 14, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — (TSX: IMP) (ITMSF:BB) – Intermap Technologies Corporation ("Intermap" or the …MacB Partners on U.S. Army INSCOM Contract for the 116th Military Intelligence Brigade
15.11.2018 17:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars FORT GORDON, Ga., Nov. 15, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- MacAulay-Brown, Inc. (MacB), an Alion company, announced today that it has partnered with BAE …Hyundai Motor Partners with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Startup 'Top Flight' to Take Future Mobility to New Heights
15.11.2018 17:23 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars - Hyundai teams up with Boston-based startup to accelerate commercial application and deployment of UAVs across various sectors and marketsSEOUL, …
Observatoř Gaia našla hvězdy putující mezi galaxiemi
15.11.2018 17:07 Český Kosmický PortálTým astronomů zkoumající nejnovější datovou sadu z mise ESA Gaia, ktreý pátrá po rychle se pohybujících hvězdách vyvržených z Mléčné dráhy, byl překvapený, když namísto toho našel hvězdy mířící opačným směrem. Dost možná, že z jiné galaxie.
Zkušební zážeh prověřil 3D tiskem vyrobenou spalovací komoru pro nosič Vega
15.11.2018 16:58 Český Kosmický PortálPrvní části z připravovaných vylepšení pro budoucí verze nosné rakety Vega po roce 2025 byly úspěšně otestovány. Stalo se tak na půdě továrny Avio v italském Colleferro.
Oman Gas Company project named as finalist for Bentley Systems' Year in Infrastructure 2018 Awards
15.11.2018 16:15 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Oil & Gas Middle East, Middle East
Read the articleAudio interview with Kristen Dietrich and Water Talk at WEFTEC 2018
15.11.2018 16:11 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
WaterTalk, USA
Read the articleProcess Industries Academy: Siemens and Bentley are teaming up
15.11.2018 16:06 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
cpp.de, DACH
2018 InterGeo Conference, Jan Blaauboer, Strategic Partnerships, Director Business Development
15.11.2018 15:59 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
GISCafe, USA
Read the articleFive Minutes with Greg Bentley
15.11.2018 15:10 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
ENR, USA
Read the articlePartnership connects digital and real-world facilities
15.11.2018 15:07 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
EE Publishers, Sub Sahara Africa
Read the articleHAPS – missions to the edge of space to watch over Earth
15.11.2018 14:21 ESA Navigation
Is it a bird? Is it a plane? No, it’s a High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) — an uncrewed airship, plane or balloon watching over Earth from the stratosphere. Operating like satellites but from closer to Earth, HAPS are the ‘missing link’ between drones flying close to Earth’s surface and satellites orbiting in space.
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Břeclav
15.11.2018 14:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-do-(2)Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Břeclav
15.11.2018 14:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Břeclavvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Břeclav
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Břeclav
15.11.2018 14:01 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Břeclav vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti BřeclavVedoucí oddělení – odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace KN č. 1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Znojmo
15.11.2018 13:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vedouci-oddeleni-–-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualiVedoucí oddělení – odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace KN č. 1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Znojmo
15.11.2018 13:12 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Znojmo vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vedoucí oddělení – odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace KN č. 1 na Katastrálním pracovišti ZnojmoVedoucí oddělení – odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace KN č. 1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Znojmo
15.11.2018 13:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Znojmovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vedoucí oddělení – odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace KN č. 1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Znojmo
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
15.11.2018 13:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-na-(2)Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
15.11.2018 13:09 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hodonín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti HodonínOdborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
15.11.2018 13:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hodonínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Hodonín
vrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviš
15.11.2018 11:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Volna-mista/vrchni-ref-rada-obnova-KP-STvrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviš
15.11.2018 11:45 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Strakonice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo vrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracovišvrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviš
15.11.2018 11:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Strakonicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
vrchní referent/rada - obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Strakonice
GSA Rail report tracks user PNT requirements
15.11.2018 10:58 European GNSS Agency
A Report on Rail User Needs and Requirements, recently published by the European GNSS Agency (GSA), examines user needs and requirements for position, navigation and timing (PNT) solutions in the rail sector. These reports, which are an outcome of the first European GNSS User Consultation Platform (UCP), will help shape the discussion at the next UCP, to be held as part of European Space Week in Marseille on 3-4 December 2018.
GNSS is already widely used for non-safety and non-liability relevant rail applications, such as passenger information systems. However, as GNSS can support solutions for safety relevant applications that have emerged in recent years, rail stakeholders around the world are also investigating the possibilities for GNSS introduction to cover such advanced and technically complex use-cases.
Rail, however, is a highly regulated domain and the introduction of new technologies is a time-consuming process. Understanding rail user requirements as well as their specifications in terms of GNSS is crucial to foster GNSS penetration in this market. Rail and GNSS communities have been working together for many years to increase this understanding.
Watch this: EGNOS and Galileo for Rail
Limitations and development axes
The main limitations for GNSS penetration in rail PNT applications concern Signal-in-Space obscuration, for example at stations, deep cuttings or in tunnels; the very high availability and integrity requirements for train position determination; excessive positioning errors due to local effects such as multipath; and also high accuracy requirements for some specific functions, like train positioning on parallel tracks.
Given these limitations, the main axes of development for GNSS applications in rail are safety relevant and liability relevant applications where EGNSS differentiators can play a key role. Within the context of the European Railway Traffic Management System (ERTMS), GNSS could be used as way of reducing the need for physical balises in the European Train Control System (ETCS). Outside of the ERTMS, GNSS is already being deployed for train control, particularly in Positive Train Control applications in the USA.
Read this: European GNSS contributes to the evolution of ERTMS
In recent years, the rail and GNSS communities have conducted a lot of work to try and understand their respective safety philosophies. However, work is still needed to define user requirements applicable to GNSS and, in particular, to establish quantified requirements. The EGNSS User Consultation Platform is a key tool in this process.
The EGNSS User Consultation Platform
The UCP is a periodic forum organised by the European Commission and the GSA involving end users, user associations and representatives of the value chain, such as receiver and chipset manufacturers, application developers and the organisations and institutions dealing, directly and indirectly, with Galileo and EGNOS. The Platform is a part of the process developed at the GSA to collect user needs and requirements and take them as inputs for the provision of user-driven Galileo and EGNOS services.
The next User Consultation Platform will be held on 3-4 December, during European Space Week in Marseille. The main work of the UCP will be carried out in eight parallel panel sessions grouping users by market segment, with a dedicated session on the rail sector.
This year, European Space Week also has a special session on Infrastructure Management, which will highlight how the Galileo and Copernicus programmes contribute to the operation and monitoring of complex infrastructure networks, including rail networks. Infrastructures around the world also face challenges relating to climate change. Here too, European GNSS offers a solution. This session will showcase potential solutions and best-practices for using Copernicus and Galileo to manage infrastructures, both in Europe and worldwide.
To join the ongoing discussion and to ensure that future European space programme evolutions meet your needs and requirements, you can take part by registering to attend European Space Week here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
ɸ and future EO
15.11.2018 10:56 ESA Observing the Earth
The excitement and enthusiasm at ESA’s ɸ-week continues with participants exploring the wealth of new opportunities on the horizon
Studenti na exkurzi
15.11.2018 10:42 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucZačátkem týdne se naši studenti 3. ročníku zúčasnili odborné exkurze v geoinformaticky orientovaných firmách v Ostravě a Brně. Navštívili například ústředí ŘSD, horké linky 112, Moravskoslezského kraje, Kancelář Architekta a Magistrát města Brna nebo firmy TopGIS, T-MAPY, DIGIS, VARS, ASSECO CE a jiné. Vidět nejěn bývalé absolventy ale i aplikaci různých oblastí geoinformatiky v praxi […]
The post Studenti na exkurzi appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
KGIrun challenge
15.11.2018 10:38 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucMožná jste si všimli, že jsme tento týden opomněli uspořádat tradiční KGIrun. Usilovně jsme totiž připravovali něco většího – pravou GISáckou hecovačku, která motivuje trávit aktivně volné hodiny venku jak zkušené běžce, tak i úplné nováčky, kteří chtějí s běháním teprve začít. Vytipovali jsme pro vás unikátní a velmi pestrý výběr 17 běžeckých a cyklo […]
The post KGIrun challenge appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
15.11.2018 9:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Olomoucvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
15.11.2018 9:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-rada-–-rizeni-o-oprave-chyby-(1)odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
15.11.2018 9:20 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Olomouc vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada – řízení o opravě chybyodborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
15.11.2018 9:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-rada-–-rizeni-o-oprave-chybyodborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
15.11.2018 9:08 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Olomouc vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný rada – řízení o opravě chybyodborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
15.11.2018 9:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Olomoucvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný rada – řízení o opravě chyby
Postdoc in Question-based Analysis of Geographic Information with Semantic Queries
15.11.2018 9:02 Job description https://ssl1.peoplexs.com/Peoplexs22/CandidatesPortalNoLogin/Vacancy.cfm?PortalID=4124&VacatureID=1012431 In the age of big data, geographic information has become a central means for data scientists of various disciplines to embed their analysis into a spatio-temporal context, from human mobility patterns and social inequality to the investigation of personal health. However, as the variety of data sources and software available on the […]Postdoc in Question-based Analysis of Geographic Information with Semantic Queries
15.11.2018 9:02 Job description https://ssl1.peoplexs.com/Peoplexs22/CandidatesPortalNoLogin/Vacancy.cfm?PortalID=4124&VacatureID=1012431 In the age of big data, geographic information has become a central means for data scientists of various disciplines to embed their analysis into a spatio-temporal context, from human mobility patterns and social inequality to the investigation of personal health. However, as the variety of data sources and software available on the […]2 PhD positions in Question-based Analysis of Geographic Information with Semantic Queries
15.11.2018 9:00 Job description https://ssl1.peoplexs.com/Peoplexs22/CandidatesPortalNoLogin/Vacancy.cfm?PortalID=4124&VacatureID=1012444 In the age of big data, geographic information has become a central means for data scientists of various disciplines to embed their analysis into a spatio-temporal context, from human mobility patterns and social inequality to the investigation of personal health. However, as the variety of data sources and software available on the […]2 PhD positions in Question-based Analysis of Geographic Information with Semantic Queries
15.11.2018 9:00 Job description https://ssl1.peoplexs.com/Peoplexs22/CandidatesPortalNoLogin/Vacancy.cfm?PortalID=4124&VacatureID=1012444 In the age of big data, geographic information has become a central means for data scientists of various disciplines to embed their analysis into a spatio-temporal context, from human mobility patterns and social inequality to the investigation of personal health. However, as the variety of data sources and software available on the […]Esri Academy Is Your New Destination for Lifelong Learning (ArcUser Online)
15.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsInterview with Yuri Raizman, Chief Scientist of Phase One Industrial at Intergeo 2018
15.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsOGC seeks public comment on Hierarchical Data Format Version 5 (HDF5) Core Standard
15.11.2018 1:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HDF5 provides a flexible, extensible, and efficient data model, programming interface, and storage model for keeping and managing spatial data.14 …
Regionální 3D strukturně geologický model lokality Horka
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE 3D strukturně-geologický model lokality Horka byl vytvořen v SW MOVE verze 2015.2. Základ tvoří nově zkompilovaná povrchová geologická mapa odkrytá lokality Horka včetně průběhu hlavních zlomů, která byla vytvořena v rámci řešení zakázky pro SÚRAO. Vstupní data zahrnují: geologickou mapu 1 : 50 000, archivní účelové geologické mapy a řezy, hloubková data v digitální i tištěné podobě (vrtná data, geologické profily, geofyzikální interpretace, strukturní data z povrchových výchozů).INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Regionální 3D strukturně geologický model lokality Čihadlo
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE 3D strukturně-geologický model lokality Čihadlo byl vytvořen v SW MOVE verze 2015.2. Základ tvoří nově zkompilovaná povrchová geologická mapa odkrytá lokality Čihadlo včetně průběhu hlavních zlomů, která byla vytvořena v rámci řešení zakázky pro SÚRAO. Vstupní data zahrnují: geologickou mapu 1 : 50 000 a 1 : 25 000, archivní účelové geologické mapy, hloubková data v digitální i tištěné podobě (vrtná data, geologické profily, archivní geofyzikální interpretace, strukturní data z povrchových výchozů).Regionální 3D strukturně geologický model lokality Březový potok
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE 3D strukturně-geologický model lokality Březový potok byl vytvořen v SW MOVE verze 2016.1. Základ tvoří nově zkompilovaná povrchová geologická mapa odkrytá lokality Březový potok, včetně průběhu hlavních zlomů, která byla vytvořena v rámci řešení zakázky pro SÚRAO. Vstupní data zahrnují: geologickou mapu 1 : 50 000 a 1 : 25 000, archivní účelové geologické mapy a mapové podklady z uranového průzkumu, hloubková data v digitální i tištěné podobě (vrtná data, geologické profily, strukturní data z povrchových výchozů).Regionální 3D strukturně geologický model lokality Hrádek
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE 3D strukturně-geologický model lokality Hrádek byl vytvořen v SW MOVE verze 2016.1. Základ tvoří nově zkompilovaná povrchová geologická mapa odkrytá lokality Hrádek, včetně průběhu hlavních zlomů, která byla vytvořena v rámci řešení zakázky pro SÚRAO. Vstupní data zahrnují: geologickou mapu 1 : 50 000 a 1 : 25 000, archivní účelové geologické mapy a mapové podklady z uranového průzkumu, hloubková data v digitální i tištěné podobě (vrtná data, geologické profily, strukturní data z povrchových výchozů).INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Regionální 3D strukturně geologický model lokality Magdaléna
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE 3D strukturně-geologický model lokality Kraví hora byl vytvořen v SW MOVE verze 2016.1. Základ tvoří nově zkompilovaná povrchová geologická mapa odkrytá lokality Magdaléna včetně průběhu hlavních zlomů, která byla vytvořena v rámci řešení zakázky pro SÚRAO. Vstupní data zahrnují: geologickou mapu 1 : 50 000 a 1 : 25 000, archivní účelové geologické mapy, hloubková data v digitální i tištěné podobě (vrtná data, geologické profily, strukturní data z povrchových výchozů).Regionální 3D strukturně geologický model lokality Čertovka
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE 3D strukturně-geologický model lokality Čertovka byl vytvořen v SW MOVE 2015. Základ tvoří nově zkompilovaná povrchová geologická mapa odkrytá lokality Čertovka, včetně průběhu hlavních zlomů, která byla vytvořena v rámci řešení zakázky pro SÚRAO. Vstupní data zahrnují: geologickou mapu 1 : 50 000 a 1 : 25 000, archivní účelové geologické mapy, hloubková data v digitální i tištěné podobě (vrtná data, geologické profily, archivní geofyzikální interpretace, strukturní data z povrchových výchozů).INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
15.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 26. 11. 2018 je to 96,16% území České republiky, t.j. 75 840,00km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.ACE enterprise Slovakia do rukou Bentley Systems
14.11.2018 23:20 GeoBusiness Firma Bentley Systems oznámila akvizici bratislavské společnosti ACE enterprise Slovakia. ACE enterprise Slovakia poskytuje řešení pro rychlý vývoj aplikací a integraci informačních systémů pro ... PřečístCarlson Machine Control Releases Rugged All-In-One Vx7 Smart Antenna
14.11.2018 22:07 Carlson Software MAYSVILLE, Kentucky, U.S.A. (November 2018) — Carlson Machine Control has released the Vx7 GNSS antenna as a more rugged replacement to its predecessor the Vx6. The Vx7 is a multi-frequency, multi-GNSS smart antenna with RTK-level position and precise heading. Built as a solution for machine control and similar applications, the antenna easily mounts to dozers, […]Best Practice in Mine Rehabilitation Course Featured Carlson Natural Regrade
14.11.2018 21:57 Carlson Software The Universidad Complutense Madrid recently presented an International Complutense Course featuring world-renowned specialists in the design and modeling of fluvial geomorphic mine restorations. A total of 36 attendees came from nine countries representing five continents. The lecturers and trainers included Professor Greg Hancock from the University of Newcastle (Australia), an international authority on the use […]Harnessing artificial intelligence for sustainability goals
14.11.2018 18:19 ESA Observing the Earth
As ESA’s ɸ-week continues to provoke and inspire participants on new ways of using Earth observation for monitoring our world to benefit the citizens of today and of the future, it is clear that artificial intelligence is set to play an important role.
ɸ and citizen science
14.11.2018 17:55 ESA Observing the Earth
During ɸ-week, Margaret Gold from the European Citizen Science Association talks about the advantages of citizens getting involved to support Earth observation
Major telco company partners with Vricon to accelerate 5G rollouts across the USA
14.11.2018 17:44 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars McLean, VA, Nov. 14, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Vricon is pleased to announce that a major U.S. telecommunications company recently acquired …Huawei Launches Digital Platform for Smart Cities at Smart City Expo World Congress 2018
14.11.2018 17:44 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars BARCELONA, Spain, Nov. 13, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Today, at the Smart City Expo World Congress (SCEWC) 2018 Huawei showcased its Digital …Inaugural Spatial Summit by XYO Network a Blow-Out Success, Drawing More than 700 Global Attendees to San Diego
14.11.2018 17:44 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Ed Helms, Vinny Lingham, Larry Sanger, and Dennis Rodman Join Forces toSupport Location Validation Technology Company at First-Annual XYO …
Aurora Flight Sciences Reveals Solar-Powered Autonomous Aircraft Odysseus
14.11.2018 17:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Odysseus is a groundbreaking persistence aircraft inspired by the need for climate and atmospheric researchMANASSAS, Va., Nov. 14, 2018 — …
Announcing the Programmable Tello EDU Drone, Now Available at Apple and DJI
14.11.2018 17:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SHENZHEN, China, Nov.14, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Ryze Tech, creator of the Tello mini drone, is launching Tello EDU, a programmable unit …Managing change in infrastructure
14.11.2018 15:57 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Informed Infrastructure, USA
Read the articleCCNY & partners develop GPS-type app for the visually impaired
14.11.2018 15:53 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
City College of NY, USA
Read the articleBuilding Connected Networks
14.11.2018 15:47 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
ARC Web, USA
Read the articleAn Introduction to Generative Design
14.11.2018 15:43 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Cadalyst, USA
Read the articleReality Modeling Drives Efficient Design Management of Anderson Road Quarry
14.11.2018 15:38 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Infrabuddy, India
Read the articlePahang water utility develops asset improvement plan
14.11.2018 15:28 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
World Water, UK
Read the articleAktualizace údajů
14.11.2018 12:24 Ústecký kraj V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kraje byla provedena aktualizace údajů pro poskytovatele Úřad pro civilní letectví – Jev 103LetMeAut takes the prize at EU space hackathon
14.11.2018 12:01 European GNSS Agency
LetMeAut, an application that leverages Galileo high accuracy to make everyday tasks easier for people with autism, was declared the winner at the 2nd EU Space Programmes Hackathon, which brought experts and developers interested in shaping the future of location-based services (LBS), the Internet of Things (IoT) and Earth Observation together in Padua, Italy on 24-26 October 2018.
The overload of sensory stimuli in the modern urban environment can make everyday experiences like walking in the park or going to school an extremely daunting task for somebody suffering from autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
There are already apps available on the market that allow people affected by ASD to visualise the tasks that they should accomplish throughout the day and tick them off as they are completed, but they do not give them the possibility of moving autonomously outside, while allowing caregivers to monitor stress and risk levels and to intervene in the event of a crisis.
Timely solution
With over 500,000 people suffering from ASD in Italy alone - a number that is on the increase, putting strain on the Italian healthcare services - the +39 team from the University of Padua saw a clear need for an app that would help make ASD sufferers more autonomous.
At the Padua hackathon, the team started to develop an app that uses precise positioning and other inputs, such as Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) and heart rate sensors, to monitor people affected by ASD as they carry out their tasks or take a journey through town. The app removes the need for constant supervision by a caregiver. However, machine learning and deep learning will enable the solution to recognise falls, panic attacks or other anomalous behaviour and alert parents or supervisors immediately, so they can take action.
Galileo precision
“Galileo is a key component of the application,” team member Cristina Gava said. “First of all there is the speed of time to first fix, which is much faster than with GPS alone. This is important, as the app needs to respond quickly. Secondly, but no less important, is the high accuracy that Galileo offers – if the app is to provide meaningful information on what actions the user should take, then it needs to know exactly what side of the street they are on, for example. Galileo provides this accuracy, especially in urban environments,” she said.
“There are two main stages involved in our work – the first is to develop and build the app, and the second main stage is to teach the subjects and caregivers how to use it,” +39 team member Matteo Stringher said, adding that feedback from users would also be taken on board when fine-tuning the solution.
To receive additional feedback from users, the team hopes to have the opportunity to cooperate with ‘Vivi la città’, an independent project working with people affected by ASD in the Italian city of Pordenone. “This will give us the opportunity to test the app with autism sufferers going about their daily tasks in real-life situations – in schools, at the bakery or in the pizzeria,” Stringher said.
European Space Week
The LetMeAut app was judged to be the winner by a board composed of senior officials from the European GNSS Agency (GSA), European Space Agency (ESA), Unismart and the University of Padua, and the +39 team will now have the opportunity to present their app at the 2018 European Space Week in Marseille, on 3-6 December 2018.
Until then, the team is continuing to work on the app, collecting feedback from parents, doctors, psychologists and autism associations. They will use this information to fine-tune their solution and prepare a working mock-up to present in Marseille.
The Padua Hackathon winners will not be the only ones to receive prizes in Marseille, the event will also see the winners of the Act in Space Hackathon receive their award. All in all, European Space Week will be an excellent opportunity for young talents to showcase their developments, exposing them to potential investors and acting as a springboard to business development opportunities, bridging the gap between ideas and working solutions that people can use.
To register to attend European Space Week, click here.
Space for your App
At the 2nd EU Space Programmes Hackathon, engineers, geologists, economists and sociologists joined with app developers, coders, graphic and web designers, data scientists and marketers to develop ideas that tackle societal challenges, and to discover how space technologies can help transform these ideas into reality.
The assembled hackers focused in particular on applications dealing with smart mobility, augmented reality, geo-marketing, and mapping and GIS. Also targeted were fitness, sport and mHealth, business applications and social networking. The hackers had access to an API provided by the European Space Agency (ESA) that allowed easy access to Earth Observation data. They also had Galileo enabled hardware and GNSS raw measurements to play with.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
ɸ-week and AI
14.11.2018 11:45 ESA Observing the Earth
The focus of the second day of ESA’s ɸ-week was on applying artificial intelligence to Earth observation, and a boot camp
Odkazy na externí mapové aplikace
14.11.2018 11:00 Středočeský kraj Záložka Odkazy byla aktualizována. Byly do ní přidány nové odkazy na aplikace jiných poskytovalů. Jedná se o odkaz na nový Geoportál Státní plavební správy. Zároveň přibyl odkaz na projekt Intersucho, jehož provozovateli jsou CzechGlobe, Mendelova univerzita v Brně a Státní pozemkový úřad. Posledním přidaným odkazem je mapová aplikace zobrazující zpracování satelitních snímků družice Sentinel od společnosti Esri.Referent IS veřejné správy
14.11.2018 10:54 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Referent IS veřejné správyReferent IS veřejné správy
14.11.2018 10:54 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Referent IS veřejné správy
Referent IS veřejné správy
14.11.2018 10:54 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Referent-IS-verejne-spravyReferent IS veřejné správy
14.11.2018 10:54 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Referent IS veřejné správy
Projekce filmu The Mapmakers from Gotha [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
14.11.2018 10:00 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK V pondělí 19. 11. v Levé rýsovně (3. patro) od 13:10 h.Rada/odborný rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií SIKT0
14.11.2018 9:57 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - odbor informatiky vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií SIKT0Rada/odborný rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií SIKT0
14.11.2018 9:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - odbor informatikyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií SIKT0
Rada/odborný rada – správce informačních a komunikačních technologií SIKT0
14.11.2018 9:57 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/rada-odborny-rada-–-spravce-informacnich-a-kom-(1)UNICEF and ɸ: Earth observation and innovation for the most vulnerable
14.11.2018 9:38 ESA Observing the Earth
Every day, UNICEF works to help children that are victims of poverty, disease, conflict, migration and more. These problems are not only tragic, but also extremely complex. To further improve the way it works, UNICEF is taking a non-traditional approach by looking at breakthrough technology, Earth observation, big data and artificial intelligence.
Field Apps Help Utility Streamline Work (ArcNews Online)
14.11.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsZurich prezentoval 3D model budov ve městě
14.11.2018 8:55 GISportal.cz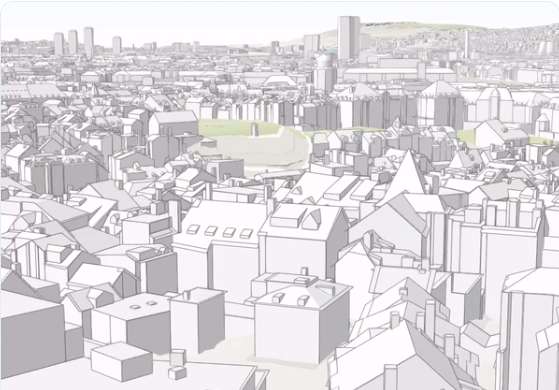
3D budovy se v nejrůznějších vizualizacích začínají objevovat čím dál častěji, a to i díky tomu, že některá města poskytují 3D modely budov jako otevřená data. Mnoho takových vizualizací pochází z New Yorku, ale 3D modely budov jako open data zveřejnila již před časem také Praha. V pondělí se k výše zmíněným městům připojil švýcarský […]
The post Zurich prezentoval 3D model budov ve městě appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Zürich prezentoval 3D model budov ve městě
14.11.2018 8:55 GISportal.cz
3D budovy se v nejrůznějších vizualizacích začínají objevovat čím dál častěji, a to i díky tomu, že některá města poskytují 3D modely budov jako otevřená data. Mnoho takových vizualizací pochází z New Yorku, ale 3D modely budov jako open data zveřejnila již před časem také Praha. V pondělí se k výše zmíněným městům připojil švýcarský […]
The post Zürich prezentoval 3D model budov ve městě appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Rada/Odborný rada – Interní auditor
14.11.2018 7:16 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/Odborný rada – Interní auditorRada/Odborný rada – Interní auditor
14.11.2018 7:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/Odborný rada – Interní auditor
Rada/odborný rada – Interní auditor
14.11.2018 7:16 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – Interní auditorRada/odborný rada – Interní auditor
14.11.2018 7:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Karlovarský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – Interní auditor
Rada/odborný rada – Interní auditor
14.11.2018 7:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-–-Interni-auditorRada/Odborný rada – Interní auditor
14.11.2018 7:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Karlovarsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-–-Interni-auditorINSPIRE datová sada pro téma Využití území - kraj Zlínský
14.11.2018 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE INSPIRE datová sada pro téma Využití území - kraj Zlínský, odvozená z ploch a koridorů zásad územního rozvoje Zlínského kraje, aktualizované 2018.CubeWerx signs multi-year contract to provide managed imagery services to SGIC
13.11.2018 21:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Gatineau, QC, Canada, November 13, 2018 – CubeWerx announced today it has signed a four-year contract to provide managed imagery services …Orbit GT upgrades 3D Mapping Cloud to support Meshes, DEMs
13.11.2018 19:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Barcelona, Spain, November 13th, 2018.Orbit GT upgrades 3D Mapping Cloud to support Textured Meshes and DEMs.
“I’m pleased to announce …
Siemens Says AI Can Boost Power Plant Profit by 20%: Q&A
13.11.2018 19:24 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Bloomberg NEF, UK
Read the articleSeequent Acquires Geosoft: Merger of Leapfrog and Geosoft Brands Creates Subsurface Geoscience and Modelling Powerhouse
13.11.2018 18:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Acquisition brings together leading developers of geological modelling and geoscience software solutions for mining, civil engineering, energy and …TomTom Telematics Named Europe's Largest Provider of Fleet Management Solutions for Fourth Year Running
13.11.2018 18:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars AMSTERDAM — (BUSINESS WIRE) — November 12, 2018 —Market analyst firm, Berg Insight, has recognized TomTom Telematics as …















