zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Pokyny pro zpracování závěrečných prací
24.2.2022 0:00 Geografický ústav MUPokyny pro zpracování závěrečných prací jsou k dispozici ZDE.
L3Harris High-Resolution Weather Instrument Set to Launch March 1 on NOAA’s GOES-T Satellite
23.2.2022 19:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Highlights:
Provides 3X spectral coverage; 4X resolution; 5X faster than previous generation of satellites
Strengthens NOAA’s …
FM Handover – Equipment Maintenance: project update
23.2.2022 18:17 buildingSMART.orgThe Facility Management Handover – Equipment Maintenance (FMH-EM) project has been progressing with an initial phase where the Technical Team is developing a draft specification of technical requirements for a data exchange based on IFC4.3. These requirements consist of general framework requirements for this and any other FM Handover data exchanges and are currently being…
The post FM Handover – Equipment Maintenance: project update appeared first on buildingSMART International.
GeoPoint Surveying Acquires Subsurface Utility Company, Find It First
23.2.2022 17:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars TAMPA, Fla. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — February 23, 2022 —GeoPoint Surveying is proud to announce the acquisition of Find It First …
Airbus to Provide Imagery Services That Enable Intelinair’s Crop Analytics Platform
23.2.2022 17:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HERNDON, Va. & INDIANAPOLIS — (BUSINESS WIRE) — February 23, 2022 —Intelinair and Airbus announced today a multi-year …
National Average Property Tax Delinquency Rate Declines in 2021, CoreLogic Reports
23.2.2022 17:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Average national property tax delinquency rates declined from 6.3% in 2020 to 5.9% in 2021For the 2011 -2021 period, the average national property …
EUSPA welcomes ITRE committee members to its Prague headquarters
23.2.2022 17:21 European GNSS Agency
The visit was an opportunity for EUSPA to highlight the many synergies between EGNSS and Copernicus, and how these synergies benefit EU businesses and citizens.
On 23 February, the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) welcomed representatives from the European Parliament’s Committee on Industry, Research and Energy (ITRE) to its Prague headquarters. The committee representatives were also joined by European Commission representatives for a full schedule of presentations, demonstrations and discussions.
The visit, the first since the new regulation on the EU Space Programme came into effect, was an opportunity for committee members and representatives to get a close-up look at how Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus support many of the activities and services that fall within the committee’s portfolio of responsibilities.
“As custodians of the EU space policy, it’s crucial that the ITRE Committee continues to foster a strong partnership and collaboration with EUSPA’s team, who enable the policy to excel both here on earth and in space. We’re looking forward to hearing more about EUSPA’s management and protection of EU space infrastructure and how space-based innovation is increasingly brought in the daily lives of the EU citizens” declared ITRE Chair, Cristian Bușoi.
A key topic of discussion was how best to leverage the EU Space Programme’s many synergies.
“The EU Space Programme benefits our society at many levels. For example, with EGNOS we improve the accessibility of our EU airports, whereas with certain Galileo features such as the OSNMA we can better protect critical infrastructures. Generating daily over 16TB of data, Copernicus is a helping hand in understanding climate change. With GOVSATCOM, Europe will be benefitting from a first of its kind secure and resilient satcom infrastructure for governmental users.” said EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
Security was also a key theme of the visit. EUSPA’s position as the gatekeeper of security for the EU Space Programme was emphasised, especially as it relates to the safeguarding of space-related assets, both in space and on the ground. The contribution of the EU Space Programme to the safety of European citizens was showcased through concrete applications, such as Galileo’s support to international Search and Rescue (SAR) satellite services, eCall technology and the Public Regulated Service (PRS).
EUSPA’s GOVSATCOM responsibilities were also highlighted. As the entity entrusted with the procurement of the secure operational ground segment (GOVSATCOM Hubs), its operations and the coordination of the user-related aspects of GOVSATCOM, EUSPA is focused on expanding infrastructure development and fostering technological innovation within the service.
In line with the recent report commissioned by the ITRE committee, which examined how to facilitate access and create an open and competitive space market, a presentation on the downstream market and its innovation was given. The presentation focused on the benefits of space products made within the EU, and included a hands-on demonstration of various space technologies and applications. Attendees were able to test out smartphone applications, drones and even a motorbike, all enabled by the EU Space Programme’s technology.
Concluding the visit, the ITRE Committee and EUSPA agreed that maintaining alignment on the activities within the remit of the committee which are supported by EU space infrastructure will be key to further establishing a strong and competitive EU space sector.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
EUSPA welcomes ITRE committee members to its Prague headquarters
23.2.2022 17:21 European GNSS Agency
The visit was an opportunity for EUSPA to highlight the many synergies between EGNSS and Copernicus, and how these synergies benefit EU businesses and citizens.
On 23 February, the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) welcomed representatives from the European Parliament’s Committee on Industry, Research and Energy (ITRE) to its Prague headquarters. The committee representatives were also joined by European Commission representatives for a full schedule of presentations, demonstrations and discussions.
The visit, the first since the new regulation on the EU Space Programme came into effect, was an opportunity for committee members and representatives to get a close-up look at how Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus support many of the activities and services that fall within the committee’s portfolio of responsibilities.
“As custodians of the EU space policy, it’s crucial that the ITRE Committee continues to foster a strong partnership and collaboration with EUSPA’s team, who enable the policy to excel both here on earth and in space. We’re looking forward to hearing more about EUSPA’s management and protection of EU space infrastructure and how space-based innovation is increasingly brought in the daily lives of the EU citizens” declared ITRE Chair, Cristian Bușoi.
A key topic of discussion was how best to leverage the EU Space Programme’s many synergies.
“The EU Space Programme benefits our society at many levels. For example, with EGNOS we improve the accessibility of our EU airports, whereas with certain Galileo features such as the OSNMA we can better protect critical infrastructures. Generating daily over 16TB of data, Copernicus is a helping hand in understanding climate change. With GOVSATCOM, Europe will be benefitting from a first of its kind secure and resilient satcom infrastructure for governmental users.” said EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa.
Security was also a key theme of the visit. EUSPA’s position as the gatekeeper of security for the EU Space Programme was emphasised, especially as it relates to the safeguarding of space-related assets, both in space and on the ground. The contribution of the EU Space Programme to the safety of European citizens was showcased through concrete applications, such as Galileo’s support to international Search and Rescue (SAR) satellite services, eCall technology and the Public Regulated Service (PRS).
EUSPA’s GOVSATCOM responsibilities were also highlighted. As the entity entrusted with the procurement of the secure operational ground segment (GOVSATCOM Hubs), its operations and the coordination of the user-related aspects of GOVSATCOM, EUSPA is focused on expanding infrastructure development and fostering technological innovation within the service.
In line with the recent report commissioned by the ITRE committee, which examined how to facilitate access and create an open and competitive space market, a presentation on the downstream market and its innovation was given. The presentation focused on the benefits of space products made within the EU, and included a hands-on demonstration of various space technologies and applications. Attendees were able to test out smartphone applications, drones and even a motorbike, all enabled by the EU Space Programme’s technology.
Concluding the visit, the ITRE Committee and EUSPA agreed that maintaining alignment on the activities within the remit of the committee which are supported by EU space infrastructure will be key to further establishing a strong and competitive EU space sector.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Intermap Continues to Grow Data as a Service with New Multiyear Subscriptions
23.2.2022 15:25 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DENVER, Feb. 23, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — Intermap Technologies (TSX: IMP) (OTCQX: ITMSF) ("Intermap" or the "Company"), a global …GeoStabilization International® Expands Geohazard Monitoring and Mitigation with All-new Geohazard Asset Management Group
23.2.2022 15:25 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New offering uses geospatial data and proprietary analytics to increase proficiently in risk managementCOMMERCE CITY, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) …
Luokung Affiliate eMapgo Provides Mapping Services for Ford Smart Vehicles
23.2.2022 15:25 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars BEIJING, Feb. 23, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — Luokung Technology Corp. (NASDAQ: LKCO) ("Luokung" or the "Company"), a leading spatial-temporal …AURORA INSIGHT ANNOUNCES STRATEGIC INVESTMENT FROM MAXAR
23.2.2022 15:25 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Strategic investment will help accelerate Aurora Insight's technology offering and streamline the advancement of radio frequency-enhanced GEOINT …XAG Delivered the Largest Drone Fleet for Agriculture in Ukraine
23.2.2022 14:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars TERNOPIL, Ukraine, Feb. 22, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — A total fleet of 100 units of drone sprayers has been recently fulfilled by XAG, …Maptelligent is Pleased to Announce Its New Strategic Focus, Implementing the Latest in Location Intelligence Making Indoor Maps More Intelligent
23.2.2022 14:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars LAS VEGAS, NV, Feb. 23, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- via NewMediaWire – Maptelligent, Inc., (OTC PK: MAPT) www.maptelligent.com, its where indoor …SkyGrid Launches All-in-One Drone App for iOS Globally
23.2.2022 14:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SkyGrid Flight Control app now available worldwide for all iPhone and iPad users.AUSTIN, Texas, Feb. 23, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — …
SkyGrid Launches All-in-One Drone App for iOS Globally
23.2.2022 14:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SkyGrid Flight Control app now available worldwide for all iPhone and iPad users.AUSTIN, Texas, Feb. 23, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — SkyGrid, …
ArcGIS Dashboards
23.2.2022 14:19 blog ARCDATA Pokud jste se s aplikací ArcGIS Dashboards ještě neseznámili, rádi bychom to teď napravili. Jedná se o aplikaci zpracovávající data do přehledných grafických výstupů, jako jsou různé ukazatele a grafy. Ovládání aplikace je jednoduché, takže ani není třeba mít předchozí zkušenost s prací s GIS.Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
23.2.2022 13:29 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Teplice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviOdborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
23.2.2022 13:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-dokuOdborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracovi
23.2.2022 13:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Teplicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent / vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Teplice
Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2022
23.2.2022 12:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Casto-hledane-informace/Poskytovani-informaci-106-1999-Sb/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(1)/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(4)Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2022
23.2.2022 12:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský krajzveřejňuje obsah informace poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok
2022
Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2021
23.2.2022 11:19 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký krajvydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok 2021
2021
Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2021
23.2.2022 11:19 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Vyrocni-zpravy/Vyrocni-zprava-dle-zakona-c-106-1999-Sb-za-rok-(4)odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
23.2.2022 11:01 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Tábor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního praodborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pra
23.2.2022 11:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Táborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent - zápisy v řízení V a Z v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Tábor (ID SM 30000324/30003948)
20220223_Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
23.2.2022 10:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210113_odborny-rada,-reditel-Katastralniho-(4)20220223_Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
23.2.2022 10:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Vyhlášení výběrového řízení:Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení systemizovaného místa Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce"Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
23.2.2022 10:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - technická sekce vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekceRada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
23.2.2022 10:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - technická sekcevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
Rada / odborný rada oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu č. 03110 Technické sekce
23.2.2022 10:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralnihoRada/odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
23.2.2022 10:02 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-městovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
Rada/odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
23.2.2022 10:02 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-město vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - městoRada/odborný rada v oddělení právním č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
23.2.2022 10:02 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnim-c-1-na-KatastPojďte se dozvědět víc o Vltavě
23.2.2022 9:30 ARCDATAČeská televize vysílá dokumentární cyklus Václava Cílka, Jindřicha Soukala a Miroslava Hrdého Vltava, naše řeka. V deseti epizodách se v něm můžete seznámit se zajímavostmi krajiny v okolí Vltavy – cesta vás zavede od Českých Budějovic přes jihočeská blata po místa v sousedství našich největších přehrad. Nám bylo potěšením pro pořad připravit několik animovaných map s využitím podkladů od Zeměměřického úřadu.
Nejnovější díl Ve znamení delfína si můžete pustit dnes na ČT 2 ve 14.30 či se na něj po odvysílání společně s ostatními epizodami podívat v archivu pořadu Vltava, naše řeka.
buildingSMART International welcomes Mass Transit Railway (MTR) as a Standard member.
23.2.2022 8:47 buildingSMART.orgLondon, U.K. - February 23, 2022 - buildingSMART International is delighted to welcome Mass Transit Railway (MTR) as a Standard member. MTR is a major public transport network serving Hong Kong. Operated by the MTR Corporation Limited, it consists of heavy rail, light rail, and feeder bus service centred on a 10-line rapid transit network…
The post buildingSMART International welcomes Mass Transit Railway (MTR) as a Standard member. appeared first on buildingSMART International.
Kratos Reports Fourth Quarter and Fiscal 2021 Financial Results
23.2.2022 1:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Fiscal 2021 Revenues of $811.5 Million and Fourth Quarter 2021 Revenues of $211.6 Million Increased 8.5 percent and 2.5 Percent over Fiscal Year and …Maxar Technologies Reports Fourth Quarter and Full-Year 2021 Results
23.2.2022 1:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — February 22, 2022 —Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR) (“Maxar” or the …
HawkEye 360 CEO John Serafini Nominated for Via Satellite's 2021 Satellite Executive of the Year Award
22.2.2022 19:16 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Voting now open to help John Serafini win this prestigious annual awardHERNDON, Va., Feb. 22, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — HawkEye 360 Inc. …
DATAMARK Announces Third Annual Virtual Conference: DATAMARK Orbit
22.2.2022 17:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Complimentary educational event for the public safety and GIS communities taking place March 22-24, 2022SANTA ANA, Calif., Feb. 22, 2022 — …
S&P CORELOGIC CASE-SHILLER INDEX REPORTS 18.8% ANNUAL HOME PRICE GAIN FOR CALENDAR 2021
22.2.2022 17:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, Feb. 22, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — S&P Dow Jones Indices (S&P DJI) today released the latest results for the S&P …EDGE Unveils Swarming Drones Application for Unmanned Aerial Systems at UMEX 2022
22.2.2022 16:30 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Innovative application of AI technology allows drones to ‘swarm’ together in coordinated missionSwarming drones offer increased defensive and …
Juniper Systems Limited Launches Uinta Software for Android OS Devices
22.2.2022 16:30 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Uinta Data Collection and Mapping Software from Juniper Systems Limited now runs on Android devices; it continues to be available for devices running …BlackSky Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2021 Results
22.2.2022 16:30 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Achieves Record Q4 and Full Year Revenue, up 79% and 61% RespectivelySuccessfully Launches Six Satellites Within 20-Day Period
Company Provides …
DEWA’s Nanosatellite DEWA-SAT1 is Stable in its Low Earth Orbit
22.2.2022 16:30 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DUBAI, United Arab Emirates — (BUSINESS WIRE) — February 22, 2022 —Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) announced that …
DOTAZNÍK – TESTOVACÍ PROSTOR PRO DRONY V ČR
22.2.2022 14:47 UAVARádi bychom poprosili o vyplnění a sdílení dotazníku Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl k tématu Testovacího prostoru pro drony v ČR. Vyplnění nezabere více jak 3 minuty a jeho výsledky nám pomůžou při dalších jednáních s Ministerstvem dopravy a dalšími autoritami. Potřeba testovacího prostoru v ČR je stále více kritická pro budoucí testování a implementaci […]
The post DOTAZNÍK – TESTOVACÍ PROSTOR PRO DRONY V ČR appeared first on UAV Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl.
Mapa kriminality - Analytický nástroj pro prevenci kriminality ve městech
22.2.2022 11:31 T-MAPYThe post Mapa kriminality - Analytický nástroj pro prevenci kriminality ve městech appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
Bezpečnější města s analytikou od T-MAPY
22.2.2022 11:31 T-MAPYThe post Bezpečnější města s analytikou od T-MAPY appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
Mapa kriminality pro bezpečnější města
22.2.2022 11:31 T-MAPYThe post Mapa kriminality pro bezpečnější města appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
Analytická mapa kriminality - Nástroj pro prevenci kriminality ve městech
22.2.2022 11:31 T-MAPYThe post Analytická mapa kriminality - Nástroj pro prevenci kriminality ve městech appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
Bezpečnější města s mapou kriminality od T-MAPY
22.2.2022 11:31 T-MAPYThe post Bezpečnější města s mapou kriminality od T-MAPY appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
Pracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnosti
22.2.2022 11:18 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Pracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnostiPracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnosti
22.2.2022 11:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Volna-mista/Pracovnik-ce-vztahu-k-verejnostiPracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnosti
22.2.2022 11:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Pracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnosti
Pracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnosti
22.2.2022 11:18 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Pracovník/ce vztahů k veřejnosti
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace GI KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - venk
22.2.2022 11:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-v-oddeleni-aktualOdborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace GI KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - venk
22.2.2022 11:10 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-venkov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace GI KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - venkOdborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace GI KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - venk
22.2.2022 11:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-venkovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent/vrchní referent v oddělení aktualizace GI KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - venkov
Výroční zpráva Českého úřadu zeměměřického a katastrálního za rok 2021.
22.2.2022 10:53 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zveřejněna Výroční zpráva Českého úřadu zeměměřického a katastrálního za rok 2021.Výroční zpráva Českého úřadu zeměměřického a katastrálního za rok 2021.
22.2.2022 10:53 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2022/Vyrocni-zprava-Ceskeho-uradu-zememerickeho-a-katasVýroční zpráva Českého úřadu zeměměřického a katastrálního za rok 2021.
22.2.2022 10:53 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Zveřejněna Výroční zpráva Českého úřadu zeměměřického a katastrálního za rok 2021.Výroční souhrnná resortní zpráva za rok 2021
22.2.2022 10:46 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnívydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok
2021
Souhrnné přehledy o půdním fondu z údajů katastru nemovitostí České republiky 2022
22.2.2022 10:05 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2022/Souhrnne-prehledy-o-pudnim-fondu-z-udaju-katastruSouhrnné přehledy o půdním fondu z údajů katastru nemovitostí České republiky 2022
22.2.2022 10:05 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Zveřejněna publikace "Souhrnné přehledy o půdním fondu z údajů katastru nemovitostí České republiky 2022".Souhrnné přehledy o půdním fondu z údajů katastru nemovitostí České republiky 2022
22.2.2022 10:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Zveřejněna publikace "Souhrnné přehledy o půdním fondu z údajů katastru nemovitostí České republiky 2022".Zlatý erb 2022 bude „ročníkem služeb“ (TZ)
22.2.2022 8:43 GISportal.cz
Tradiční a oblíbená soutěž Zlatý erb, jejímž spolupořadatelem je společnost Triada, pro rok 2022 výrazně inovovala hodnotící kritéria s důrazem na uživatelskou přívětivost a informační hodnotu pro občany a návštěvníky obce. Letos probíhá už 24. ročník, na který se účastníci mohou přihlašovat od 18. ledna do 7. března do 14 hodin. Minulý ročník se konal […]
The post Zlatý erb 2022 bude „ročníkem služeb“ (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Končí starý vzhled domovské stránky ArcGIS Online
22.2.2022 8:40 ARCDATAOd léta 2020 je na ArcGIS Online k dispozici nový editor domovské stránky, který ji umožňuje sestavit z různých funkčních bloků a přizpůsobit její vzhled lépe, než bylo možné ve starší verzi. Nová verze také podporuje responzivní design, takže se přizpůsobuje podle toho, zda je prohlížena na počítači nebo na mobilním telefonu, je přístupnější ke čtečkám obsahu, a navíc do ní není možné vkládat vlastní HTML a CSS kód, což mohlo představovat určité bezpečnostní riziko.
Stará verze domovské stránky tak používá již zastaralé technologie, a proto dne 22. března 2022 budou všechny úvodní stránky, používající starý vzhled, převedeny na nový typ.
Pokud vaše organizace stále používá starší vzhled, uživatelům s právem editace domovské stránky se objevují upozornění o její zastaralosti a s návrhem na přechod na nový typ. Doporučujeme přechod provést nejpozději do 22. března – konfigurace nové domovské stránky zabere v novém editoru pouze několik minut.
Prostředí pro nastavení nové domovské stránky naleznete v nabídce Organizace – Nastavení – Domovská stránka.
L3Harris Completes Imager Integration for NOAA’s Advanced Environmental Satellite
21.2.2022 18:10 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Highlights:ABIs radically improve weather observation through advanced technology
Achieves resolution 4 times greater, 5 times faster than …
EUSPA helps European companies embrace Earth Observation
21.2.2022 13:00 European GNSS Agency
Speaking at last week’s Copernicus Horizon 2035 conference, EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa outlined how European businesses can benefit from Copernicus’ Earth observation services, data, and information.
If you’ve ever watched a news story about a natural disaster, chances are, the satellite images shown in the story came from Copernicus, Europe’s Earth Observation programme.
Why?
“Because Copernicus is the best Earth Observation system in the world,” said Thierry Breton, European Commissioner for the Internal Market, who made his remarks at Copernicus Horizon 2035.
Organised by the French Presidency of the Council of the European Union and the European Commission, the conference, which was held 16 – 17 February, put the spotlight on Copernicus, its achievements, goals and opportunities.
“By providing unique insights into the Earth and its environment, Copernicus helps governments, national agencies, institutions and researchers and of protect our planet for future generations,” said Rodrigo da Costa, Executive Director, European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA). ‘’But Copernicus is also of strategic importance to European SMEs, and we must ensure they make the most of the available date,’’ he concluded. Under the auspices of the European Commission, EUSPA is charged with promoting Copernicus’ services, data and market uptake.
The commercial potential of Copernicus
Beyond its use by governments and in emergency situations, Earth Observation also has significant commercial potential. For example, according to the latest edition of the EUSPA EO and GNSS Market Report, SMEs and start-ups account for more than 93% of European Earth Observation companies.
“Europe is seeing a vibrant Copernicus start-up scene unfolding, with hundreds of new ventures being created using Copernicus data and information,” noted Fiammetta Diani, EUSPA Head of Market, Downstream and Innovation, who also spoke at the conference.
With revenues set to double from approximately EUR 2.8 billion to over EUR 5.5 billion within the next decade, the market for Earth observation applications is boosted by a large pool of value-added services. This is especially the case within the climate services, urban development, energy, insurance, finance and agriculture segments.
“Farmers can use Copernicus-derived information to monitor the health of their crops and study the quality of their soil,” explained da Costa. “And urban planners can use Earth Observation data to design sustainable smart cities and build infrastructure that is more resilient against the impact of climate change.”
Copernicus also complements the other components of the EU Space Programmes, including Galileo and EGNOS. For example, construction companies can use European GNSS (EGNSS), together with Earth Observation, to first select locations with the best conditions and then monitor the building or infrastructure asset over its entire lifespan.
Maximising Copernicus’ benefits
However, to truly maximise Copernicus’ economic and societal benefits, European companies must fully embrace the power of Earth Observation.
To help, EUSPA is in constant communication with European companies, helping them on how they can best leverage Copernicus data, information and services.
“SMEs and start-ups are in the spotlight since they are key to enlarging the use of Copernicus. They are more agile, able to adjust new business models and technologies more swiftly. Besides, they can be closer to end-users and local authorities permitting them to innovate affordably,” said Diani.
EUSPA has also launched several Earth Observation focused funding opportunities for companies, including Horizon Calls and innovation competitions as part of the CASSINI programme focussing on entrepreneurs.
“Our intent is to position EUSPA as the go-to-source for all things related to Earth Observation and EGNSS,” concluded da Costa. “That means to be the single point of information, expertise and market intelligence that companies from across Europe can depend on when integrating European space solutions into their start-ups, enterprises, innovations and research.”
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
EUSPA helps European companies embrace Earth Observation
21.2.2022 13:00 European GNSS Agency
Speaking at last week’s Copernicus Horizon 2035 conference, EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa outlined how European businesses can benefit from Copernicus’ Earth observation services, data, and information.
If you’ve ever watched a news story about a natural disaster, chances are, the satellite images shown in the story came from Copernicus, Europe’s Earth Observation programme.
Why?
“Because Copernicus is the best Earth Observation system in the world,” said Thierry Breton, European Commissioner for the Internal Market, who made his remarks at Copernicus Horizon 2035.
Organised by the French Presidency of the Council of the European Union and the European Commission, the conference, which was held 16 – 17 February, put the spotlight on Copernicus, its achievements, goals and opportunities.
“By providing unique insights into the Earth and its environment, Copernicus helps governments, national agencies, institutions and researchers and of protect our planet for future generations,” said Rodrigo da Costa, Executive Director, European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA). ‘’But Copernicus is also of strategic importance to European SMEs, and we must ensure they make the most of the available date,’’ he concluded. Under the auspices of the European Commission, EUSPA is charged with promoting Copernicus’ services, data and market uptake.
The commercial potential of Copernicus
Beyond its use by governments and in emergency situations, Earth Observation also has significant commercial potential. For example, according to the latest edition of the EUSPA EO and GNSS Market Report, SMEs and start-ups account for more than 93% of European Earth Observation companies.
“Europe is seeing a vibrant Copernicus start-up scene unfolding, with hundreds of new ventures being created using Copernicus data and information,” noted Fiammetta Diani, EUSPA Head of Market, Downstream and Innovation, who also spoke at the conference.
With revenues set to double from approximately EUR 2.8 billion to over EUR 5.5 billion within the next decade, the market for Earth observation applications is boosted by a large pool of value-added services. This is especially the case within the climate services, urban development, energy, insurance, finance and agriculture segments.
“Farmers can use Copernicus-derived information to monitor the health of their crops and study the quality of their soil,” explained da Costa. “And urban planners can use Earth Observation data to design sustainable smart cities and build infrastructure that is more resilient against the impact of climate change.”
Copernicus also complements the other components of the EU Space Programmes, including Galileo and EGNOS. For example, construction companies can use European GNSS (EGNSS), together with Earth Observation, to first select locations with the best conditions and then monitor the building or infrastructure asset over its entire lifespan.
Maximising Copernicus’ benefits
However, to truly maximise Copernicus’ economic and societal benefits, European companies must fully embrace the power of Earth Observation.
To help, EUSPA is in constant communication with European companies, helping them on how they can best leverage Copernicus data, information and services.
“SMEs and start-ups are in the spotlight since they are key to enlarging the use of Copernicus. They are more agile, able to adjust new business models and technologies more swiftly. Besides, they can be closer to end-users and local authorities permitting them to innovate affordably,” said Diani.
EUSPA has also launched several Earth Observation focused funding opportunities for companies, including Horizon Calls and innovation competitions as part of the CASSINI programme focussing on entrepreneurs.
“Our intent is to position EUSPA as the go-to-source for all things related to Earth Observation and EGNSS,” concluded da Costa. “That means to be the single point of information, expertise and market intelligence that companies from across Europe can depend on when integrating European space solutions into their start-ups, enterprises, innovations and research.”
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
EUSPA helps European companies embrace Earth Observation
21.2.2022 13:00 European GNSS Agency
Speaking at last week’s Copernicus Horizon 2035 conference, EUSPA Executive Director Rodrigo da Costa outlined how European businesses can benefit from Copernicus’ Earth observation services, data, and information.
If you’ve ever watched a news story about a natural disaster, chances are, the satellite images shown in the story came from Copernicus, Europe’s Earth Observation programme.
Why?
“Because Copernicus is the best Earth Observation system in the world,” said Thierry Breton, European Commissioner for the Internal Market, who made his remarks at Copernicus Horizon 2035.
Organised by the French Presidency of the Council of the European Union and the European Commission, the conference, which was held 16 – 17 February, put the spotlight on Copernicus, its achievements, goals and opportunities.
“By providing unique insights into the Earth and its environment, Copernicus helps governments, national agencies, institutions and researchers and of protect our planet for future generations,” said Rodrigo da Costa, Executive Director, European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA). ‘’But Copernicus is also of strategic importance to European SMEs, and we must ensure they make the most of the available date,’’ he concluded. Under the auspices of the European Commission, EUSPA is charged with promoting Copernicus’ services, data and market uptake.
The commercial potential of Copernicus
Beyond its use by governments and in emergency situations, Earth Observation also has significant commercial potential. For example, according to the latest edition of the EUSPA EO and GNSS Market Report, SMEs and start-ups account for more than 93% of European Earth Observation companies.
“Europe is seeing a vibrant Copernicus start-up scene unfolding, with hundreds of new ventures being created using Copernicus data and information,” noted Fiammetta Diani, EUSPA Head of Market, Downstream and Innovation, who also spoke at the conference.
With revenues set to double from approximately EUR 2.8 billion to over EUR 5.5 billion within the next decade, the market for Earth observation applications is boosted by a large pool of value-added services. This is especially the case within the climate services, urban development, energy, insurance, finance and agriculture segments.
“Farmers can use Copernicus-derived information to monitor the health of their crops and study the quality of their soil,” explained da Costa. “And urban planners can use Earth Observation data to design sustainable smart cities and build infrastructure that is more resilient against the impact of climate change.”
Copernicus also complements the other components of the EU Space Programmes, including Galileo and EGNOS. For example, construction companies can use European GNSS (EGNSS), together with Earth Observation, to first select locations with the best conditions and then monitor the building or infrastructure asset over its entire lifespan.
Maximising Copernicus’ benefits
However, to truly maximise Copernicus’ economic and societal benefits, European companies must fully embrace the power of Earth Observation.
To help, EUSPA is in constant communication with European companies, helping them on how they can best leverage Copernicus data, information and services.
“SMEs and start-ups are in the spotlight since they are key to enlarging the use of Copernicus. They are more agile, able to adjust new business models and technologies more swiftly. Besides, they can be closer to end-users and local authorities permitting them to innovate affordably,” said Diani.
EUSPA has also launched several Earth Observation focused funding opportunities for companies, including Horizon Calls and innovation competitions as part of the CASSINI programme focussing on entrepreneurs.
“Our intent is to position EUSPA as the go-to-source for all things related to Earth Observation and EGNSS,” concluded da Costa. “That means to be the single point of information, expertise and market intelligence that companies from across Europe can depend on when integrating European space solutions into their start-ups, enterprises, innovations and research.”
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Výběrové řízení pro studijní pobyty Erasmus+ [Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie, byTopic]
21.2.2022 11:15 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Výběrové řízení pro studijní pobyty Erasmus+ v akademickém roce 2022/23 proběhne na katedře aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie 15.3.2022. Termín pro odevzdání podkladů je 1.3.2022.Výběrové řízení pro studijní pobyty Erasmus+ [Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie, byTopic]
21.2.2022 11:15 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Výběrové řízení pro studijní pobyty Erasmus+ v akademickém roce 2022/23 proběhne na katedře aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie 15.3.2022. Termín pro odevzdání podkladů je 11.3.2022.Rada / odborný rada - organizační pracovník kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský kraj
21.2.2022 10:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-organizacni-pracovnik-kancel-(1)Rada / odborný rada - organizační pracovník kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský kraj
21.2.2022 10:25 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada - organizační pracovník kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský krajRada / odborný rada - organizační pracovník kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský kraj
21.2.2022 10:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj kancelář ředitelevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada - organizační pracovník kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský kraj
QGIS 3.24 Tisler
21.2.2022 8:02 GISportal.cz
A je to opět zde – nová verze populárního open-source QGIS, tentokrát QGIS 3.24 Tisler je ke stažení a níže najdete visual changelog – tedy ukázku nových funkcí.
The post QGIS 3.24 Tisler appeared first on GISportal.cz.
TurboCAD Pro 2D / 3D 27 CZ v akční ceně s bonusy do 26. 02. 2022
19.2.2022 17:57 ŠPINAR - software Vážení zákazníci,dovolujeme si Vám nabídnout program TurboCAD Pro 2D / 3D 27 CZ pro kreslení ve 2D / 3D včetně vizualizací s akční slevou a bonusy do 19 2. 2022.
TurboCAD Pro 2D / 3D 27 CZ v akční ceně s bonusy do 26. 02. 2022
19.2.2022 17:57 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
dovolujeme si Vám nabídnout program TurboCAD Pro 2D / 3D 27 CZ pro kreslení ve 2D / 3D včetně vizualizací s akční slevou a bonusy do 19 2. 2022.
The post TurboCAD Pro 2D / 3D 27 CZ v akční ceně s bonusy do 26. 02. 2022 appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
"GISCafe Voice Industry Predictions 2022 – Part 4" by Susan Smith
19.2.2022 15:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsZajímavý článek o studentovi Geografického ústavu
19.2.2022 14:14 Geografický ústav MUNa internetových stránkách Přírodovědecké fakulty a také v celostátním deníku se objevil zajímavý článek o jednom ze studentů Geografického ústavu.
The Galileo Reference Centre evolves to support the constellation’s growing needs
18.2.2022 16:57 European GNSS Agency
The EU Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) publishes procurement on “GRC Infrastructure evolution, nominal operations support, and maintenance”. To encourage the widest participation possible, the Agency is organizing an industry day to present the details of the call on 10 March 2022 at 10.00 CET
The EU Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) published a procurement on the “GRC Nominal Operations Support, Infrastructure Development, Evolution, and Maintenance”. To encourage large participation, EUSPA is organising an industry day to present the details of the call on 10 March 2022 at 10.00 CET.
A service facility, located in Noordwijk, the Netherlands, the GRC performs independent service performance monitoring and reporting, service performance investigation and support, and campaign-based monitoring and experimentation, by itself and through cooperation with the EU Member States, Norway, and Switzerland. The GRC monitors not only Galileo but also other GNSSs and reports to various stakeholders.
The scope of the GRC Infrastructure Evolution, Nominal Operations Support, and Maintenance Framework Contract is to provide a turn-key service for GRC infrastructure releases (including operational validation activities), support the nominal operations, and follow up with the maintenance of the release in operation. It will include the design and implement an innovative solution for the next generation of the GRC. This will also include implementing a real-time solution into the GRC that will be capable of providing real-time monitoring of all Galileo services, precise reference time, and PRS navigation monitoring functionalities.
The GRC has a variety of tools developed for use within the facility as well as a strong operational team with a broad professional knowledge of GNSS systems and for these reasons greater functionalities are currently identified to be developed within the next generation of the GRC.
With this important procurement, EUSPA is looking for one or more partners to provide services and supplies to support the agency in shaping the future versions of the GRC infrastructure to support the evolutions of several GNSS services.
EUSPA is committed to promoting the widest participation possible by economic operators, including new entrants, in particular start-ups and SMEs. The agency is thus organising an industry day on 10 March 2022 at 10.00 to detail the procurement on “GRC Nominal Operations Support, Infrastructure Development, Evolution, and Maintenance”.
Participants will also have the opportunity to learn more about the mission of the GRC, the procurement documentation, and the submission process.
To attend the event, please register here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
The Galileo Reference Centre evolves to support the constellation’s growing needs
18.2.2022 16:57 European GNSS Agency
The EU Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) publishes procurement on “GRC Infrastructure evolution, nominal operations support, and maintenance”. To encourage the widest participation possible, the Agency is organizing an industry day to present the details of the call on 10 March 2022 at 10.00 CET
The EU Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) published a procurement on the “GRC Nominal Operations Support, Infrastructure Development, Evolution, and Maintenance”. To encourage large participation, EUSPA is organising an industry day to present the details of the call on 10 March 2022 at 10.00 CET.
A service facility, located in Noordwijk, the Netherlands, the GRC performs independent service performance monitoring and reporting, service performance investigation and support, and campaign-based monitoring and experimentation, by itself and through cooperation with the EU Member States, Norway, and Switzerland. The GRC monitors not only Galileo but also other GNSSs and reports to various stakeholders.
The scope of the GRC Infrastructure Evolution, Nominal Operations Support, and Maintenance Framework Contract is to provide a turn-key service for GRC infrastructure releases (including operational validation activities), support the nominal operations, and follow up with the maintenance of the release in operation. It will include the design and implement an innovative solution for the next generation of the GRC. This will also include implementing a real-time solution into the GRC that will be capable of providing real-time monitoring of all Galileo services, precise reference time, and PRS navigation monitoring functionalities.
The GRC has a variety of tools developed for use within the facility as well as a strong operational team with a broad professional knowledge of GNSS systems and for these reasons greater functionalities are currently identified to be developed within the next generation of the GRC.
With this important procurement, EUSPA is looking for one or more partners to provide services and supplies to support the agency in shaping the future versions of the GRC infrastructure to support the evolutions of several GNSS services.
EUSPA is committed to promoting the widest participation possible by economic operators, including new entrants, in particular start-ups and SMEs. The agency is thus organising an industry day on 10 March 2022 at 10.00 to detail the procurement on “GRC Nominal Operations Support, Infrastructure Development, Evolution, and Maintenance”.
Participants will also have the opportunity to learn more about the mission of the GRC, the procurement documentation, and the submission process.
To attend the event, please register here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2021
18.2.2022 13:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnívydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok
2021
Earth from Space: Tenerife, Canary Islands
18.2.2022 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth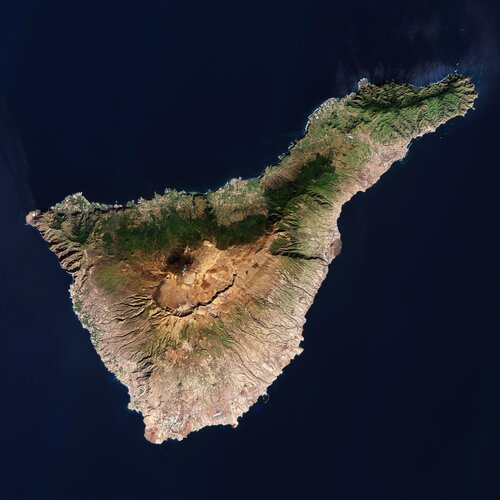
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Tenerife – the largest of Spain’s Canary Islands.
Earth from Space: Tenerife, Canary Islands
18.2.2022 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Tenerife – the largest of Spain’s Canary Islands.
odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z na Katastrálním pracovišti Krnov
18.2.2022 8:11 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Krnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z na Katastrálním pracovišti Krnovodborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z na Katastrálním pracovišti Krnov
18.2.2022 8:11 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-zapisy-v-rizeniodborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z na Katastrálním pracovišti Krnov
18.2.2022 8:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Krnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent/vrchní referent – zápisy v řízení V a Z na Katastrálním pracovišti Krnov
Airbus reports strong Full-Year (FY) 2021 results
18.2.2022 1:08 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 611 commercial aircraft delivered in 2021Financials reflect strong operational performance group-wide
Revenues € 52.1 billion; EBIT Adjusted …
Winners of 6th round of KiboCUBE selected to deploy CubeSats from the International Space Station
18.2.2022 0:38 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VIENNA, 16 February (UN Information Service) – The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration …GISCI Announces June 2022 GISCI Geospatial Core Technical Knowledge Exam
18.2.2022 0:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Des Plaines, IL (February 15, 2022) The next testing window for the GISCI Geospatial Core Technical Knowledge Exam® as a part of the …INTERGEO 2022: The power of the ´Digital Twins`
18.2.2022 0:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 3D MODELS MAKE THE WORLD SMARTER INTERGEO 2022 will take place from October 18 - 20 in Essen | Focus on Digital Twins: 3D city models, BIM in …UVL Robotics launched the first in the Middle East service of daily drone-based parcels delivery
17.2.2022 21:26 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars MOSCOW, Feb. 17, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — US-based company with the presence in Oman, UVL Robotics, launched the first in the Middle East …AI-powered mapping technology MapScale™ digitizes 10,000 floor plans daily; 5 billion sqft in 2022
17.2.2022 17:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars - As workplaces go hybrid, Fortune 500 companies need to become more digitalBOSTON, Feb. 17, 2022 — (PRNewswire) — As building …
GeoComm Announces Issuance of Indoor Mapping and Location Technology Patents
17.2.2022 17:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GeoComm is pleased to announce the issuance by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) of two new patents related to GeoComm's indoor …LAND INFO Announces Updated 10m USA Countrywide Land Use Land Cover Mapping Dataset
17.2.2022 16:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DENVER, Colorado, USA, 16 February 2022 – LAND INFO Worldwide Mapping LLC, the premier provider of mapping solutions for 5G wireless in North …CoreLogic Climate Change Catastrophe Report Estimates 1 in 10 U.S. Residential Properties Impacted by Natural Disasters in 2021
17.2.2022 16:41 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The annual report shows over 14.5 million homes impacted by hurricane, wildfire, winter storm or severe weatherIRVINE, Calif. — (BUSINESS …
Maris-Tech to Co-Develop Video-Based Advanced AI Systems For Drones and Autonomous Vehicles
17.2.2022 16:41 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars REHOVOT, Israel, Feb. 17, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Maris-Tech Ltd. (Nasdaq: MTEK, MTEKW) (“Maris-Tech”), a B2B provider of intelligent video …Skyfish Leverages Sony’s Alpha Cameras to Perfect Drone Photogrammetry and Create Engineering-Grade Digital Twins of Large Infrastructure
17.2.2022 16:41 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars MISSOULA, Mont., Feb. 17, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- American autonomous drone maker Skyfish today announced technical integration with Sony …Wanted: your new ideas for navigation
17.2.2022 15:52 ESA Navigation
It is hard to overstate the importance of knowing precisely where (and when) you are and where you are going within today’s economy and society. Do you have a promising idea to improve the current positioning state-of-the-art? Then ESA’s navigation-focused NAVISP research programme wants to hear from you, before the end of March.
Streamline your offshore wind farm design planning and certification
17.2.2022 15:23 Bentley SystemsPressCoverage
Energy Global, UK&I
Read the articleAll Systems Go
17.2.2022 14:38 Bentley SystemsPressCoverage
Irish Building Magazine, UK&I
Read the articleHow Digital Twins Are Adding Value to Construction Projects
17.2.2022 14:22 Bentley SystemsPressCoverage
Sourceable, Australia/New Zealand
Read the articleGalileo Service Operator: a vital link between space and user needs
17.2.2022 13:33 European GNSS Agency
With a robust and secure ground and space segment, EUSPA ensures that Galileo’s 2.5 billion users benefit from the world’s most precise positioning system
Not only is the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) charged with the development and provision of Galileo’s range of services, it also serves as the gatekeeper for the programme’s security.
This means protecting Galileo’s space and ground operations against threats such as cyber-attacks, interference and damage by space debris – a job EUSPA does in collaboration with its industry partners.
One of those partners is Spaceopal, a joint venture between Telespazio in Italy and DLR-GfR mbH in Germany.
Under EUSPA’s leadership, Spaceopal serves as the Galileo Service Operator, a role that involves operating and maintaining Galileo’s ground and space segments, along with ensuring that all of Galileo’s 2.5 billion users continue to benefit from the world’s most precise positioning system. The company’s role as Galileo Service Operator has just been confirmed for the next 5 years.
High performance services worldwide
Launched in 2016, Galileo is Europe’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). In addition to providing positioning information with greater precision than other GNSS systems, Galileo also offers a Search and Rescue (SAR) service. This important service allows emergency first responders to quickly locate and help people in distress while giving them feedback that the call has been received by its unique … etc.
EUSPA is also developing new Galileo services, including a High Accuracy Service (HAS) for high accuracy corrections, and the a authentication service Open Service Navigation Message Authentication service (OSNMA), which will provide receivers with a first level of protection against manipulation and spoofing.
A robust and secure ground and space segment
All these services depend on having a robust and secure ground and space segment, which is exactly what EUSPA’s contract with Spaceopal guarantees. For example, as the Galileo Service Operator, Spaceopal will run EUSPA’s Galileo Control Centres (GCC) in Fucino, Italy and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany.
Backed by a network of ground stations and facilities spread around the globe, the GCCs allow EUSPA to monitor and control Galileo’s current constellation of satellites, along with the addition of new ones (such as Galileo Launch 12 expected later this year, which – like every additional satellite added to the constellation - will bring an additional layer of accuracy to Galileo services).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Galileo Service Operator: a vital link between space and user needs
17.2.2022 13:33 European GNSS Agency
With a robust and secure ground and space segment, EUSPA ensures that Galileo’s 2.5 billion users benefit from the world’s most precise positioning system
Not only is the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) charged with the development and provision of Galileo’s range of services, it also serves as the gatekeeper for the programme’s security.
This means protecting Galileo’s space and ground operations against threats such as cyber-attacks, interference and damage by space debris – a job EUSPA does in collaboration with its industry partners.
One of those partners is Spaceopal, a joint venture between Telespazio in Italy and DLR-GfR mbH in Germany.
Under EUSPA’s leadership, Spaceopal serves as the Galileo Service Operator, a role that involves operating and maintaining Galileo’s ground and space segments, along with ensuring that all of Galileo’s 2.5 billion users continue to benefit from the world’s most precise positioning system. The company’s role as Galileo Service Operator has just been confirmed for the next 5 years.
High performance services worldwide
Launched in 2016, Galileo is Europe’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). In addition to providing positioning information with greater precision than other GNSS systems, Galileo also offers a Search and Rescue (SAR) service. This important service allows emergency first responders to quickly locate and help people in distress while giving them feedback that the call has been received by its unique Return Link Service.
EUSPA is also developing new Galileo services, including a High Accuracy Service (HAS) for high accuracy corrections, and the authentication service Open Service Navigation Message Authentication service (OSNMA), which will provide receivers with a first level of protection against manipulation and spoofing.
A robust and secure ground and space segment
All these services depend on having a robust and secure ground and space segment, which is exactly what EUSPA’s contract with Spaceopal guarantees. For example, as the Galileo Service Operator, Spaceopal will run EUSPA’s Galileo Control Centres (GCC) in Fucino, Italy and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany.
Backed by a network of ground stations and facilities spread around the globe, the GCCs allow EUSPA to monitor and control Galileo’s current constellation of satellites, along with the addition of new ones (such as Galileo Launch 12 expected later this year, which – like every additional satellite added to the constellation - will bring an additional layer of accuracy to Galileo services).
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.
Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®
17.2.2022 11:00 ČÚZK - Geoportál Aktualizace prohlížecí služby WMTS ZABAGED®Prohlížecí služba WMTS ZABAGED®, vytvořená za účelem poskytování podkladové mapy s rychlým překreslováním z předpřipravených mapových dlaždic, již poskytuje veškeré změny po lednové aktualizaci datové sady ZABAGED®.
Již dříve (souběžně s aktualizací) byly aktualizovány dynamické prohlížecí služby ZABAGED®, ZABAGED® (vizualizace nad ortofoto) ZABAGED® (vizualizace ZM10) poskytující obraz dat ZABAGED® přímo z publikační databáze.



















