zprávy
zdroje zpráv:odborný referent/vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
22.4.2020 18:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Prahavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent/vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
odborný referent/vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
22.4.2020 18:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-hlavni-mesto-Prahu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-navrh-zapisu-vodborný referent/vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastru
22.4.2020 18:14 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro hlavní město Prahu - Katastrální pracoviště Praha vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent/vrchní referent – návrh zápisu v katastruLeddarTech Partners with Ningbo Sunny Automotive Optech Co. Ltd to Accelerate LiDAR Deployment for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems and Autonomous Driving Applications
22.4.2020 16:36 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars QUEBEC CITY, April 22, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- LeddarTech®, an industry leader in providing the most versatile and scalable auto and mobility …Accela Announces New COVID-19 Response Solution to Help Cities Manage the Process of Re-Opening Businesses
22.4.2020 16:36 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 30-minute webinar on Friday, April 24th will showcase new cloud solution to help state and local governments safely usher in the next phase of …Doosan Mobility Innovation Completed Contactless Drone Delivery to Remote Islands Without a Proper Mask Supplier
22.4.2020 16:36 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SEOUL, South Korea — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 22, 2020 —On April 16th, Doosan Mobility Innovation distributed protective masks to …
BlackSky Launches Spectra On-Demand Secure Bundle for Intelligence Analysts
22.4.2020 16:36 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars For the first time, BlackSky offers remote access for intelligence analysts due to COVID-19 pandemicHERNDON, Va. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — …
Quantimet Environmental Data Visualization Software is Now Available with Remote Sensor Controls, a World Map View, and Cloud-Based Data Logging to Select Customers
22.4.2020 16:36 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Torrance,CA, April 22, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- April 22, 2020 – Torrance, CA – Intellisense Systems, Inc., a leading provider of integrated …Jsme hrdým členem Fóra o autonomních vozidlech
22.4.2020 16:30 CEDA Maps a.s. Praha, 22. dubna 2020 - Máme velikou radost, že jsme se stali členem Open AutoDrive Forum. Cílem fóra je vývoj autonomního řízení. My se v rámci něj soustředíme na problematiku HD map. Dostali jsme se tak do prestižní společnosti firem jako BMW, Audi, Google nebo Panasonic a dalších významných technologických gigantů, kteří dlouhodobě pracují na vývoji v této oblasti.Jak vypadá štáb Chytré karantény?
22.4.2020 13:10 ARCDATAVčerejší reportáž Událostí ČT zavedla diváky do Centrálního řídícího týmu Covid-19, který má na starosti projekt Chytré karantény. První část reportáže zachycuje použití aplikací na mapovém portálu a sami tak můžete vidět, jak technologie ArcGIS pomáhají při sledování dostupných prostředků, koordinaci vytížení jednotlivých odběrných míst a laboratoří a celou řadou dalších úloh zajišťujících správný průběh tohoto důležitého projektu.
Konzultace a pomoc s tímto projektem jsou pro nás úžasnou výzvou a zkušeností.
Looking to space for solutions on Earth Day
22.4.2020 12:09 European GNSS Agency
Earth Day is celebrated around the world on April 22. Since its early days back in the seventies, Earth Day has striven to build the world’s largest environmental movement to drive transformative change for people and the planet. As an engine of this transformative change, space tech supports the goals of Earth Day by enabling innovative solutions that promote sustainable economic growth that is decoupled from resource use.
The world is faced with an existential threat brought about by growing demand for resources on one hand, and climate change and environmental degradation on the other. To effectively deal with this challenge, innovative solutions are needed to make the global economy more sustainable, boost the efficient use of resources, restore biodiversity and cut pollution.
Satellite technologies – both GNSS positioning and Earth observation – are already contributing to increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact in a number of core sectors of the economy. On Earth Day, we take a look at how these space solutions and applications are playing an increasingly important role in creating a more sustainable planet.
From Farm to Fork
The agriculture sector has been an enthusiastic early adopter of satellite technology and now over 90% of tractors in the EU are already EGNOS-enabled. The benefits in terms of greening EU agriculture are clear. Satellite-enabled precision farming allows farmers to save fuel by avoiding overlaps in field cultivation. They can also reduce pesticide and fertiliser use thanks to more targeted application. One example of a solution that leverages EGNSS (Galileo and EGNOS) to improve agricultural performance is Tractor Navigator, a prize-winner at last year’s MyGalileoApp competition.
Watch this: European Satellites for Agriculture
By providing data on soil condition, drought, crop development and other conditions on the farm, Earth observation satellites also enable farmers to make more informed decisions. Using this data, farmers can plan where and when to irrigate, or how much fertilizer to apply, for example. Satellite images can also be used as a tool to predict agricultural output, which can be critical in anticipating crop failures and mitigating the effects of food shortages. Satellites also provide data on air quality and atmospheric composition, making it possible to monitor emissions of CO2, NOx and other greenhouse gasses. As such, Earth observation is a key tool in global efforts to monitor and mitigate the effects of climate change.
GNSS and greener transport
But it is not just on the farm that space tech is driving green innovation. On our roads too, GNSS also plays a role in many of the disruptive and innovative trends and apps that are making passenger and freight transport more sustainable - from drone deliveries to Mobility as a Service (MaaS). Satellite-based navigation generally makes life on the road easier – it significantly reduces congestion and, as a result, the carbon footprint of the road sector is significantly diminished.
Ride-sharing and other sustainable mobility solutions all rely on precise positioning. In one example, the Galileo 4 Mobility project is leveraging Galileo for MaaS by identifying the geolocation needs of various stakeholders and is demonstrating the benefits of Galileo through pilot demonstrators of shared mobility services.
And this: EGNOS for Aviation - High Precision, Low investment
In the air too EGNSS, in particular EGNOS, is helping to make flying cleaner and more accessible. EGNOS-enabled procedures at airports result in fewer aborted landings. This in turn means significant fuel savings for airlines, which has a corresponding impact on carbon emissions in the sector.
Sustainable energy
Space technologies are also playing a major role in the area of sustainable energy, with both Earth observation and GNSS positioning supporting applications and services in the sector. In one such case, the Horizon 2020-funded EASY PV project uses GNSS to help photovoltaic (PV) field owners to boost energy production. Another project, LARA, is using state-of-the-art GNSS technologies and interactive computer graphics to allow utility workers to ‘see’ 3D models of underground water, gas and electric grids without digging, thereby significantly increasing the efficiency of network maintenance.
Earth observation also makes a major contribution to improved sustainability in the energy sector, by providing information related to weather (wind, solar and hydro) and energy (capacity factors, demand, volatility) forecasts at a regional and national level in Europe. This allows energy providers and policy-makers to make informed choices on the future energy mix.
Sustainability is one of the critical challenges of our times – sustainability of consumption, sustainability of transport and sustainability of the energy that we use to heat our homes and power our economies. Space tech – EGNSS and Earth observation – is making an increasingly important contribution to achieving sustainability targets in these areas and, as such, is a key asset in Europe’s environmental toolbox.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Bezpilotně 2020
22.4.2020 11:25 Geotronics DRONY - Nenechte si ujít letošní netradiční ročník Bezpilotně 2020.Steering drones for power generation
22.4.2020 11:02 ESA Navigation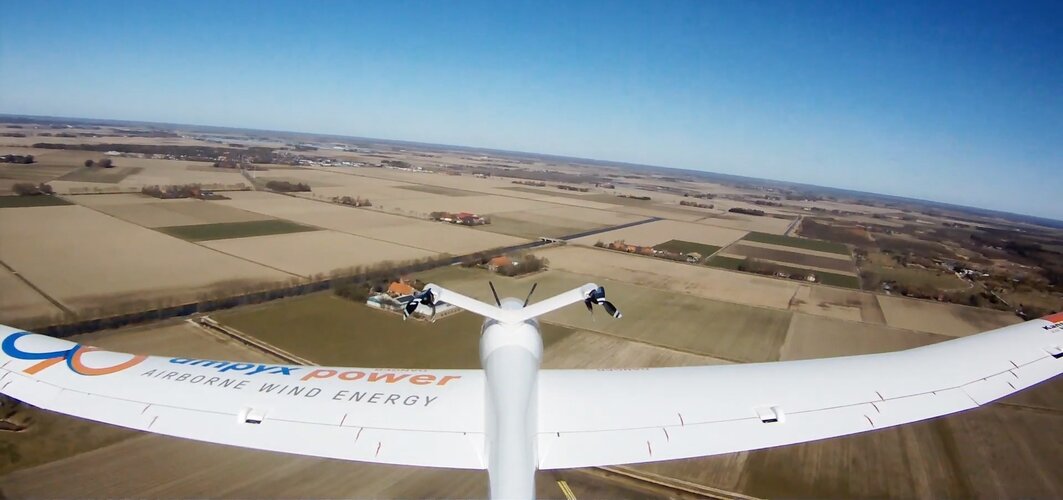 Image:
Steering drones for power generation
Image:
Steering drones for power generation
Steering drones for power generation
22.4.2020 11:02 ESA Navigation Image:
Steering drones for power generation
Image:
Steering drones for power generation
Uzavření pracoviště
22.4.2020 10:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Sumperk/O-uradu/Aktuality/Uzavreni-pracovisteUzavření pracoviště
22.4.2020 10:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Šumperk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: OZNÁMENÍVe středu 6. května 2020 bude katastrální pracoviště z důvodu přerušení dodávky elektřiny provozovatelem distribuční soustavy společností ČEZ Distribuce, a.s. UZAVŘENO.
Děkujeme za pochopení.
Earth Day: taking the pulse of our planet
22.4.2020 9:20 ESA Observing the Earth
Today marks the 50th anniversary of Earth Day. For Earth-observing satellites, every day is Earth Day. While news of COVID-19 dominates headlines and many of us practice social distancing, there still remains the need for action on climate change – and satellites are vital in providing the key facts on this global issue.
Klávesové zkratky v ArcGIS Pro v češtině
22.4.2020 9:08 ARCDATAPřeložili jsme do češtiny dokument Klávesové zkratky v ArcGIS Pro, který obsahuje zkratky týkající se například navigace v mapě, tabulek, panelu obsah, práce s rastrovými a časovými daty a samozřejmě také editace.
Dokument Klávesové zkratky v ArcGIS Pro ve formátu PDF.
Pokud byste si chtěli stáhnout spíš anglický originál, naleznete jej na adrese http://links.esri.com/arcgis-pro-shortcuts
Vyhlášení platnosti - pozemková úprava v k. ú. Tachov u Doks
22.4.2020 8:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Česká Lípazveřejnil novou aktualitu: Dne 21. 4. 2020 byla vyhlášena platnost obnoveného katastrálního operátu na podkladě výsledků komplexní pozemkové úpravy v katastrálním území Tachov u Doks. Podrobnosti viz úřední deska.
Vyhlášení platnosti - pozemková úprava v k. ú. Tachov u Doks
22.4.2020 8:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Ceska-Lipa/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vyhlaseni-platnosti-pozemkova-uprava-v-k-u-TacVyhlášení platnosti - pozemková úprava v k. ú. Žďár v Podbezdězí
22.4.2020 8:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Ceska-Lipa/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vyhlaseni-platnosti-pozemkova-uprava-v-k-u-ZdaVyhlášení platnosti - pozemková úprava v k. ú. Žďár v Podbezdězí
22.4.2020 8:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Česká Lípazveřejnil novou aktualitu: Dne 20. 4. 2020 byla vyhlášena platnost obnoveného katastrálního operátu na podkladě výsledků komplexní pozemkové úpravy v katastrálním území Žďár v Podbezdězí. Podrobnosti viz úřední deska.
Dobnový online mapathon (pozvánka) – 28. 4. 2020
22.4.2020 8:25 GISportal.cz
Podpořte práci humanitárních organizací tím, že pomůžete zmapovat místa, která jsou nejvíce ohrožena krizemi. Mapathon společně organizují Lékaři bez hranic a dobrovolníci z české komunity Missing Maps. Srdečně zveme úplné začátečníky i ty, kdo už mapovat umí. Co se na mapathonu bude dít? Budeme společně podle satelitních snímků vytvářet v Open Street Map mapu pro týmy Lékařů bez […]
The post Dobnový online mapathon (pozvánka) – 28. 4. 2020 appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Test VÚV dataset - harvest TPS
22.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Vrstva obsahuje vymezení chráněných území s vazbou na vodu a je formálně upravena pro potřeby reportingu podle směrnice 2000/60/ES (WFD). Obsažena jsou chráněná území, která nebyla reportována na základě jiné legislativy, tedy Ramsarské mokřady a maloplošná zvláště chráněná území. Prostorová i popisná složka dat byla upravena podle směrných dokumentů a požadavků Evropské komise na reporting Plánů oblastí povodí v roce 2016.Trade events for Lidar, Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing, 3D and Building Technology Professionals Rescheduled & Will Take Place Together July 27-29, 2020 in Chicago
22.4.2020 0:04 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars International Lidar Mapping Forum, ASPRS Annual Conference, SPAR 3D Expo & Conference, AEC Next Technology Expo & Conference, USIBD Symposium …Činnost SPÚ po ukončení nouzového režimu
21.4.2020 22:11 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Ing. Martin Vrba, ústřední ředitel SPÚ, informoval, že v pondělí 20. 4. 2020 je ukončen nouzový režim na SPÚ. V této souvislosti jsou platná následující opatření: Vedení SPÚ odvolalo pozastavení činností související s nutností osobních aktivit účastníků řízení. Projednávání s vlastníky je povoleno, ovšem za dodržení předepsaných hygienických podmínek (viz příloha). Upozorňuji, že povolení těchto činností neznamená pro pobočky povinnost je […]GEODEZIE PLCH: nový člen APG
21.4.2020 21:46 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Novým členem APG se 14. 4. 2020 stala společnost GEODEZIE PLCH s.r.o. zastoupena Ing. Přemyslem Plchem se sídlem v Blansku.USGIF Announces 2020 Achievement Award Winners
21.4.2020 21:10 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Outstanding organizations and individuals recognized for contributions to the geospatial intelligence communityHerndon, Virginia (April, …
OGC seeks public comment on Version 1.2 of CDB Standard for use in modeling & simulation
21.4.2020 21:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New version improves compatibility with other libraries and allows diverse file formats to be easily incorporated and used.21 April 2020: The …
Aktualizace změny harmonogramu letního semestru
21.4.2020 20:39 Aktualizace změny letního semestru AR 2019/2020 na Hornicko-geologické fakultě, VŠB-TUO s ohledem na situaci spojenou se šířením epidemie koronaviru COVID-19.Derry, New Hampshire PD Chooses CompassCom® GPS Tracking Integrated with Motorola® Astro P25 Network
21.4.2020 20:24 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Derry, New Hampshire - (April 22, 2020) - As part of a recent LMR system upgrade, the Derry New Hampshire Police Department recently installed …Derry, New Hampshire PD Chooses CompassCom® GPS Tracking Integrated with Motorola® ASTRO P25 Network
21.4.2020 20:24 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Derry, New Hampshire - (April 22, 2020) - As part of a recent LMR system upgrade, the Derry New Hampshire Police Department recently installed …Draganfly’s ‘Pandemic Drone’ technology Conducts Initial Flights Near New York City to Detect COVID-19 Symptoms and Identify Social Distancing
21.4.2020 17:24 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Connecticut hotspot becomes first U.S. municipality to test drone technology to assist first responders in reducing coronavirus spread and mitigate …DroneUp, UPS, Virginia Center for Innovative Technology (CIT), and Workhorse Group Test Unmanned Systems for Coronavirus Response
21.4.2020 17:24 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars - Collaborators seek ways to support US Coronavirus response amid social distancing protocolsLAWRENCEVILLE, Va., April 21, 2020 — (PRNewswire) …
COVID-19: Aeolus and weather forecasts
21.4.2020 16:38 ESA Observing the Earth
We are all too aware that COVID-19 is a serious threat to health, is putting huge pressure on healthcare systems and it could leave the global economy struggling for years to come. With lockdown measures in force across the globe, the pandemic is also affecting aspects of everyday life that may not be so obvious. The drop in commercial flights, for example, has led to fewer measurements for weather forecasts, but fortunately, ESA’s Aeolus satellite mission is helping to fill the gap.
COVID-19: Aeolus and weather forecasts
21.4.2020 16:38 ESA Observing the Earth
We are all too aware that COVID-19 is a serious threat to health, is putting huge pressure on healthcare systems and it could leave the global economy struggling for years to come. With lockdown measures in force across the globe, the pandemic is also affecting aspects of everyday life that may not be so obvious. The drop in commercial flights, for example, has led to fewer measurements for weather forecasts, but fortunately, ESA’s Aeolus satellite mission is helping to fill the gap.
Summit Koncepce BIM 2020 naplánován na listopad
21.4.2020 16:12 BIM NewsČeská agentura pro standardizaci oznámila, že na čtvrtek 19. listopadu 2020 je v Praze naplánován druhý ročník Summitu Koncepce BIM. Cílem je seznámit účastníky se zkušenostmi státu a veřejné správy při zavádění tzv. Koncepce BIM. Summit opět spolupořádá odbor Koncepce BIM České agentury pro standardizaci s Ministerstvem průmyslu a obchodu ČR a je součástí plánu […]
The post Summit Koncepce BIM 2020 naplánován na listopad appeared first on BIM News.
Závada na telefonickém spojení na KP Kyjov
21.4.2020 15:19 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kyjov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Zavada-na-telefonickem-spojeni-na-KP-KyjovZávada na telefonickém spojení na KP Kyjov
21.4.2020 15:19 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kyjov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Závada na telefonickém spojení na KP Kyjov20200422 – volné místo - Odborný rada v OMaK kanceláře ředitele KÚ na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
21.4.2020 12:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Nabídka volného pracovního místa - Odborný rada v oddělení metodiky a kontroly kanceláře ředitele katastrálního úřadu na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
20200422 – volné místo - Odborný rada v OMaK kanceláře ředitele KÚ na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
21.4.2020 12:13 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20200422-–-volne-misto-Odborny-rada-v-OMaK-kance20200422 – volné místo - Vedoucí oddělení MaK v kanceláři ředitele KÚ na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
21.4.2020 11:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20200422-–-volne-misto-Vedouci-oddeleni-MaK-v-ka20200422 – volné místo - Vedoucí oddělení MaK v kanceláři ředitele KÚ na Katastrálním úřadu pro ÚK
21.4.2020 11:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného pracovního místa - Vedoucí oddělení metodiky a kontroly v kanceláři ředitele katastrálního úřadu na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký krajV holandském časopisu GIM International Jakub už počtvrté na obálce
21.4.2020 9:32 UpVisionV novém čísle holandského časopisu GIM International je Jakub už po čtvrté na titulní stránce časopisu a odpovídá jako mezinárodní odborník v nové rubrice Ask the specialist na dotaz týkající se UAV, mapování a 3D vizualizací.
The post V holandském časopisu GIM International Jakub už počtvrté na obálce appeared first on Upvision.
V holandském časopisu GIM International Jakub už počtvrté na obálce
21.4.2020 9:32 UpVisionV novém čísle holandského časopisu GIM International je Jakub už po čtvrté na titulní stránce časopisu a odpovídá jako mezinárodní odborník v nové rubrice Ask the specialist na dotaz týkající se UAV, mapování a 3D vizualizací.
The post V holandském časopisu GIM International Jakub už počtvrté na obálce appeared first on Upvision.
úprava provozu od 20.4.2020
21.4.2020 9:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Klatovyzveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy od 20.4.2020 dočasně upravuje provoz
úprava provozu od 20.4.2020
21.4.2020 9:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální pracoviště Klatovy od 20.4.2020 dočasně upravuje provozúprava provozu od 20.4.2020
21.4.2020 9:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Klatovy/O-uradu/Aktuality/uprava-provozu-od-20-4-2020Mapa karanteny
21.4.2020 8:07 GISportal.cz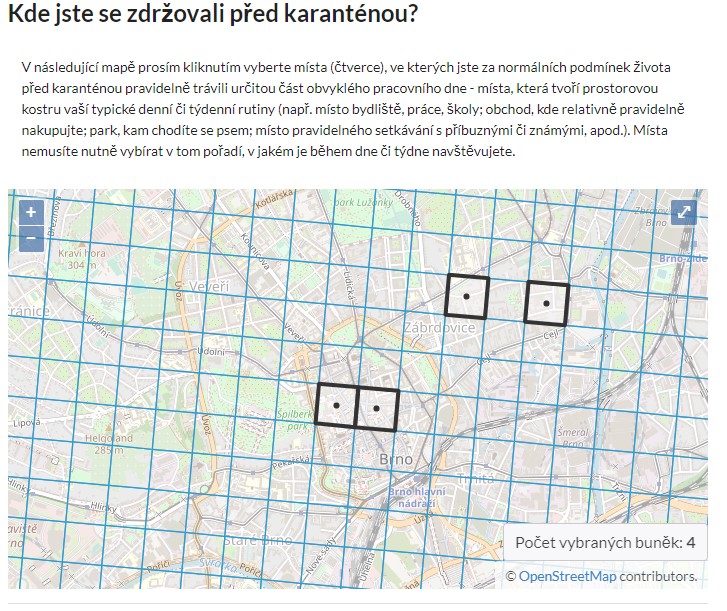
Společnost Altimapo, která je spin-offem Masarykovy univerzity, ve spolupráci s Geografickým ústavem MU Brno vytváří Mapu karantény. Sběr polohových dat funguje nad čtvercovou sítí používanou v projektu metropolitní gridové statistiky BrnoUrbanGrid, avšak data jsou sbírána pro celé Česko. Cílem projektu je získat znalosti o prostorovém chováním obyvatel v době karantény. Jde o sdílení zkušeností využitelných […]
The post Mapa karanteny appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Výběrové řízení
21.4.2020 7:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-jih zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj, vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD09, Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-jih.Výběrové řízení
21.4.2020 7:34 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vyberove-rizeni-(2)Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD09
21.4.2020 7:28 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-jih vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD09Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD09
21.4.2020 7:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-jihvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD09
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD09
21.4.2020 7:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-vedouci-oddeleni-aktualiza-(1)vyhlášení výběrového řízení - investiční referent
21.4.2020 6:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/O-uradu/Aktuality/vyhlaseni-vyberoveho-rizeni-investicni-referentvyhlášení výběrového řízení - investiční referent
21.4.2020 6:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo vrchní referent/rada – investiční referent v oddělení ekonomicko-správním Kanceláře ředitele katastrálního úřadu na Katastrálním úřadu pro Vysočinu.APGEO - ČINNOST SPÚ PO UKONČENÍ NOUZOVÉHO REŽIMU
21.4.2020 2:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice SPÚ: V pondělí 20. 4. 2020 je ukončen nouzový režim.APGEO - ČINNOST SPÚ PO UKONČENÍ NOUZOVÉHO REŽIMU
21.4.2020 2:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Ing. Martin Vrba, ústřední ředitel SPÚ, informoval, že v pondělí 20. 4. 2020 je ukončen nouzový režim na SPÚ...APGEO - GEODEZIE PLCH: NOVÝ ČLEN APG
21.4.2020 2:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Novým členem APG se 14. 4. 2020 stala společnost GEODEZIE PLCH s.r.o. zastoupena Ing. Přemyslem Plchem se sídlem ...Uzavření pracoviště KPÚ pro Plzeňský kraj
21.4.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Z důvodu havarijní opravy a výměny vodovodní přípojky bude v pátek 24. dubna 2020 po celý den zcela uzavřena budova na nám. Generála Píky 8, Plzeň, ve které sídlí i KPÚ pro Plzeňský kraj. V tento den proto nebude možné poskytovat ani elektronické poradenství. Děkujeme za pochopení.Interview with Mark Safran, Senior Program Manager at Dewberry
20.4.2020 23:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsAirbus will support France and India to monitor climate change with TRISHNA
20.4.2020 21:42 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Paris, 20 April 2020 – The French Space Agency (Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales, CNES) has recently signed a contract with Airbus …UNECA and Global Partnership for Sustainable Development Data collaborate to fight COVID-19 with better data for a resilient Africa
20.4.2020 18:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) and the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development Data (GPSDD) have unveiled an …Kongsberg Geospatial Selected for Ohio UTM Drone Project Team
20.4.2020 16:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Drone Companies & Ohio Universities Partner to Win Milestone ProjectOTTAWA, Ontario, April 19, 2020 — (PRNewswire) —
OTTAWA, Ontario, …
HERE Technologies Achieves Red Hat OpenShift Operator Certification for Cloud-Native Location Services on Red Hat OpenShift
20.4.2020 16:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HERE location data and services now available as a supported and certified Red Hat OpenShift Operator …Kratos Awarded $2.7 Million Sole-Source Award for Drone Mission Command and Control Kits
20.4.2020 16:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, April 20, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc. (NASDAQ:KTOS), a leading National Security Solutions …Data Analysis Recovers $2.27M in FSRM Funding at Air Force Base
20.4.2020 16:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Woolpert GIS Specialist Matthew Wellinski discovers data anomalies in FSRM funding at Hurlburt Field and develops a process that could translate to …Online výstava Počátky teroru [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
20.4.2020 16:40 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Výstava nabízí neotřelý pohled na dění v odstoupených pohraničních oblastech Československa po podepsání mnichovské dohody.Digital twins drive innovation in the energy sector
20.4.2020 15:29 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Plant Engineering, USA
Read the articlevrchní referent-rada-investiční referent v oddělení ekonomicko-správním Kanceláře ředitele Katastrál
20.4.2020 13:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/vrchni-referent-rada-investicni-referent-v-oddelenvrchní referent-rada-investiční referent v oddělení ekonomicko-správním Kanceláře ředitele Katastrál
20.4.2020 13:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu kancelář ředitelevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
vrchní referent-rada-investiční referent v oddělení ekonomicko-správním Kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu
vrchní referent-rada-investiční referent v oddělení ekonomicko-správním Kanceláře ředitele Katastrál
20.4.2020 13:25 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo vrchní referent-rada-investiční referent v oddělení ekonomicko-správním Kanceláře ředitele KatastrálEnding global plant tracking, Proba-V assigned new focus
20.4.2020 12:18 ESA Observing the Earth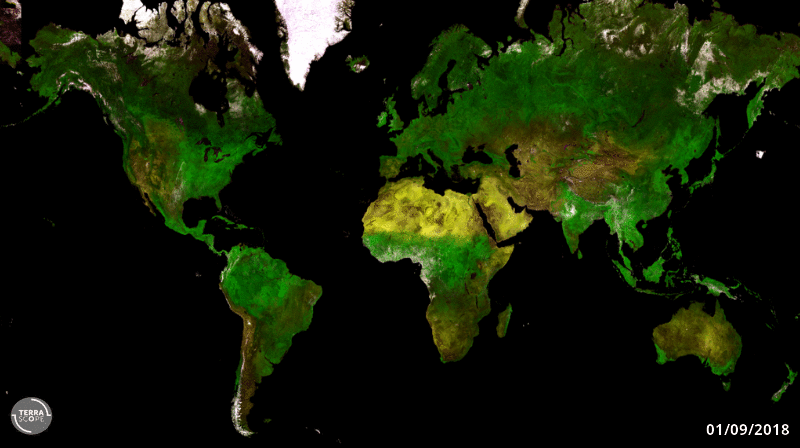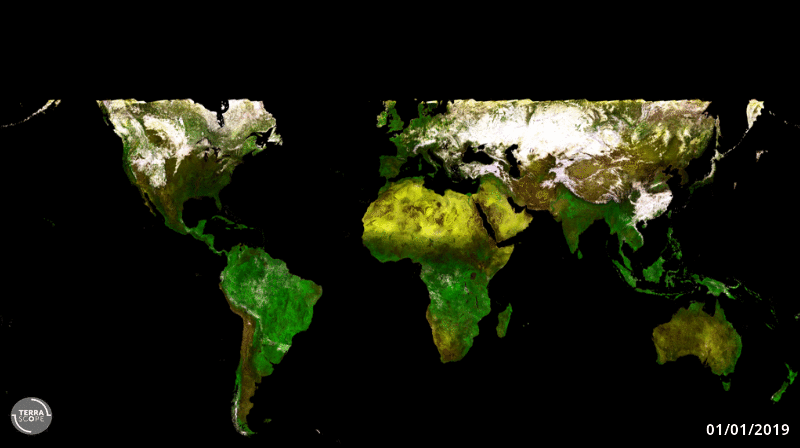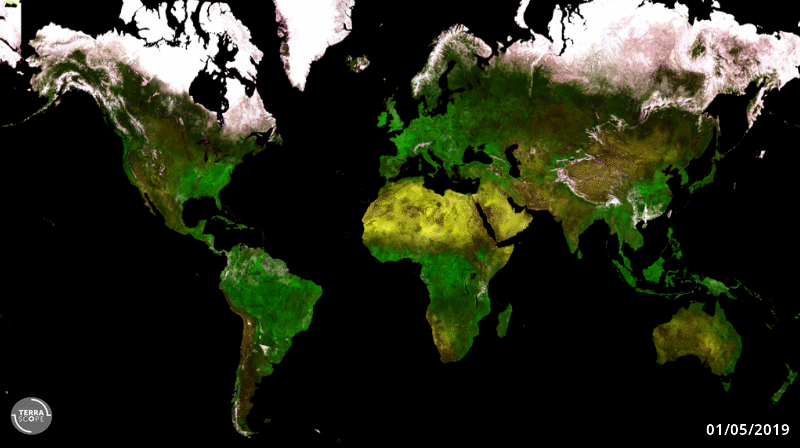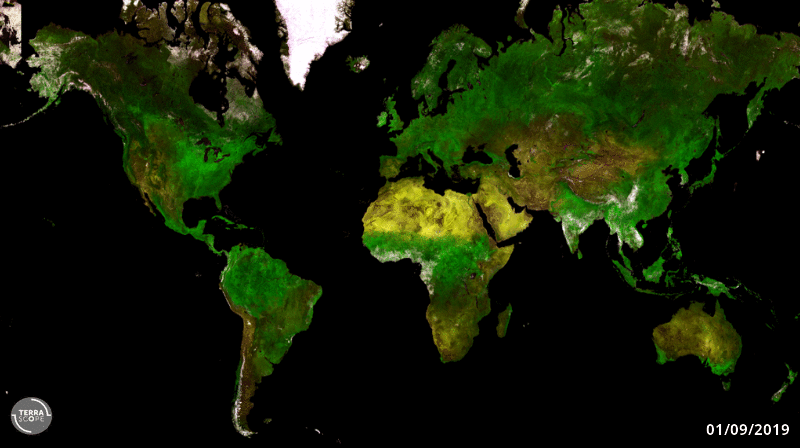
ESA’s cubic-metre-sized Proba-V minisatellite will soon end its nearly seven-year global mission to monitor the daily growth of all Earth’s vegetation. As Copernicus Sentinel-3 takes on this task instead, Proba-V will be free to perform experimental monitoring over Europe and Africa – including co-observations with new companion missions.
Osobní automobil Suzuki Ignis 1.5
20.4.2020 11:52 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Osobni-automobil-Suzuki-Ignis-1-5Osobní automobil Suzuki Ignis 1.5
20.4.2020 11:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Osobní automobil Suzuki Ignis 1.5
úprava úředních hodin pro veřejnost
20.4.2020 10:46 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Jihlava/O-uradu/Aktuality/uprava-urednich-hodin-pro-verejnostúprava úředních hodin pro veřejnost
20.4.2020 10:46 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Jihlava zveřejnil novou aktualitu:V souladu s usnesením vlády č. 396 o prodloužení nouzového stavu ze dne 9. dubna 2020 jsou úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 17,00 hod.
V tyto úřední hodiny lze rovněž vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna u vchodu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště.
Schránka je vybírána ve dnech PO-ČT v době od 8:00 – 14:00 hodin, v PÁ v době od 8:00-13:00.
Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu:S účinností ode dne 20. dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.
Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20.dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20.dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20. dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20.dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20.dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Pelhrimov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Schranka2Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu:S účinností ode dne 20. dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.
Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Pelhřimov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20.dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Schránka2
20.4.2020 10:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: S účinností ode dne 20. dubna 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Vysočinu i nadále omezení služeb vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, avšak rozšiřují se úřední hodiny pro veřejnost v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 17 hodin.Pro bezkontaktní podání je i nadále zpřístupněna schránka ve 2.patře vedle podatelny katastrálního pracoviště, a to ve dnech pondělí a středa v době od 8 do 17 hodin, a ve dnech úterý, čtvrtek a pátek v době od 8 do 14 hodin.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon: 565 301 771.
Upozornění
20.4.2020 9:34 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Upozorneni-(1)Upozornění
20.4.2020 9:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj od 20.4.2020 upravuje provoz katastrálních pracovišťOmezení provozu
20.4.2020 9:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Žďár nad Sázavou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V souladu s usnesením vlády č. 396 ze dne 9. dubna 2020 jsou úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8.00 do 17.00 hodin, je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna u vstupu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště. Schránka je zpřístupněna nepřetržitě. Schránka je zaměstnanci vybírána minimálně 1x za 2 hodiny v pondělí a ve středu době od 8:00 do 17:00 hodin a v úterý, čtvrtek a pátek od 8:00 do 14:00 hodin. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.“Omezení provozu
20.4.2020 9:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V souladu s usnesením vlády č. 396 ze dne 9. dubna 2020 jsou úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8.00 do 17.00 hodin, je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna u vstupu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště. Schránka je zpřístupněna nepřetržitě. Schránka je zaměstnanci vybírána minimálně 1x za 2 hodiny v pondělí a ve středu době od 8:00 do 17:00 hodin a v úterý, čtvrtek a pátek od 8:00 do 14:00 hodin. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.“Omezení provozu
20.4.2020 9:34 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V souladu s usnesením vlády č. 396 ze dne 9. dubna 2020 jsou úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8.00 do 17.00 hodin (více na úření desce), je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna u vstupu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště. Schránka je zpřístupněna nepřetržitě. Schránka je zaměstnanci vybírána minimálně 1x za 2 hodiny v pondělí a ve středu době od 8:00 do 17:00 hodin a v úterý, čtvrtek a pátek od 8:00 do 14:00 hodin. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.“Microsoft a Esri spolupracují na projektu AI for Earth
20.4.2020 9:30 ARCDATASpolečnost Microsoft se dlouhodobě zajímá o dopad svých aktivit na ekologii planety. V rámci snahy o minimalizaci uhlíkové stopy a dosažení uhlíkové neutrality se zaměřuje také na ochranu biodiverzity a světových ekosystémů.
Brad Smith, prezident Microsoftu, píše na svém blogu o projektech AI for Earth a Planetary Computer a také o důvodech, proč si jako partnera pro tyto projekty vybrali společnost Esri.
Výběrové řízení
20.4.2020 9:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada - ředitel katastrálního pracoviště – RKP10, Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město.Výběrové řízení
20.4.2020 9:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vyberove-rizeni-(1)Výběrové řízení
20.4.2020 9:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Tachov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Ředitelka Katastrálního úřadu pro Plzeňský kraj vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace – VOAD15, Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště TachovVýběrové řízení
20.4.2020 9:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vyberove-rizeni
Nové číslo GaKO
20.4.2020 9:20
ÚGKK SR
Nové číslo časopisu Geodetického a Kartografického Obzoru 04/2020
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace
20.4.2020 9:17 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-vedouci-oddeleni-aktualizace-aRada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace
20.4.2020 9:17 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Tachov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentaceRada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace
20.4.2020 9:17 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Tachovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace
Rada/odborný rada - ředitel katastrálního pracoviště
20.4.2020 9:04 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-reditel-katastralniho-pracovisRada/odborný rada - ředitel katastrálního pracoviště
20.4.2020 9:04 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-městovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada - ředitel katastrálního pracoviště
Rada/odborný rada - ředitel katastrálního pracoviště
20.4.2020 9:04 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Plzeň-město vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada - ředitel katastrálního pracovištěV době krize umožňují dodavatelé CAD softwaru provozovat firemní aplikace i na domácích počítačích
20.4.2020 8:52 Konstruktér Stejně jako pro mnohé další profese znamenala i pro řadu konstruktérů pandemie Covid-19 nutnost pracovat [...]TKP geo v aplikaci AMG vizualizuje Covid-19
20.4.2020 8:51 ZeměměřičSpolečnost TKP geo představila svoji vizualizační aplikaci AMG COVID-19. COVID-19 (z anglického spojení coronavirus disease 2019) je infekční onemocnění, které je způsobeno novým koronavirem SARS-CoV-2 (dříve označovaným jako 2019-nCoV), jenž se začal šířit v prosinci 2019 z Čínského města Wu-chan. Označení COVID-19 bylo Světovou zdravotnickou organizací prohlášeno za oficiální dne 11. února 2020. Aplikace AMG Covid-19 obsahuje přehled celosvětové […]
The post TKP geo v aplikaci AMG vizualizuje Covid-19 appeared first on Zeměměřič.
KGItalk na téma Nové technologie v lokační analýze
20.4.2020 8:33 GISportal.cz
V dalším díle pořadu KGItalk, který organizuje katedra geoinformatiky PřF UP Olomouc vystoupí Lukáš Puchrik, spoluzakladatel společnosti CleverMaps, jedné ze zakladajících firem iniciativy data proti covid (COVID19CZ). Pořad bude online ve středu 22. dubna od 14:00 na YouTube kanále KGI.
The post KGItalk na téma Nové technologie v lokační analýze appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Mapa Karantény
20.4.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformaceDalší geoinformatická výzva v rámci současné mimořádné situace, kterou právě prožíváme v souvislosti s pandemií COVID-19. Tým společnosti Altimapo, která je spin-offem Masarykovy univerzity, ve spolupráci s Magistrátem města Brna vytvořila dotazník pro sběr dat o změnách denních rytmů(zvyklostí) v době karantény.
Více naleznete na:
AMG aplikace k současnému COVID-19
19.4.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace AMG aplikace k současnému COVID-19…TPK geo s.r.o se připájí k producentům mapových aplikací sledujících vývoj Coronaviru ve světe.
Slovy ředitele společnosti, Roberta Šinknera,Když to nemůžeš zmapovat (tj. zobrazit v prostoru, čase a souvislostech), nemůžeš to řídit… Správné (geo)informace ve správných souvislostech pomáhají zmenšit obavy atd.
Aplikace
"Web App TopoGrafi Captures Buried Asset Data for Utility and Infrastructure Sectors" by Susan Smith
19.4.2020 5:51 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsKOKEŠ 14 TRIAL – studentům zdarma
18.4.2020 12:52 GEPROKOKEŠ 14 TRIAL je příspěvkem společnosti GEPRO v současné epidemii koronaviru, určený studentům středních a vysokých škol v České republice a Slovenské republice, kteří potřebují pracovat se systémem KOKEŠ a nemohou do školních učeben.… >>
Jednoduché pozemkové úpravy a ich vplyv na okolité územie
18.4.2020 11:34 Komora pozemkových úprav SRUsporiadanie pozemkového vlastníctva môže mať vplyv aj na spôsob užívania pozemkov mimo obvodu projektu pozemkových úprav
Fortem Technologies Announces Shipment of New DroneHunter F700 - World's Only Radar-Based Autonomous Interceptor Drone For Tracking and Stopping Dangerous Drones
18.4.2020 3:08 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars PLEASANT GROVE, Utah, April 16, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — Fortem Technologies, Inc., a market leader of counter-drone security and …USGIF Announces 2020 Stu Shea Endowed Scholarship Recipient
17.4.2020 22:52 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Pennsylvania State University’s Wendy L. Zeller Zigaitis becomes the third recipient of $15,000 scholarshipHerndon, Virgina (April, 17, …
NGA and Maxar Work Together to Expand Government Adoption of NOME – Online Access to Collaborative Mapping Tools and Current Satellite Imagery
17.4.2020 21:05 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars April 17, 2020 -- The COVID-19 pandemic has had a sudden and profound impact on the world. The U.S. Defense and Intelligence …Katastrální úřady rozšiřují úřední hodiny pro veřejnost
17.4.2020 19:35 ZeměměřičČeský úřad zeměměřický a katastrální oznámil, že s účinností od 20. dubna 2020 dochází na katastrálních pracovištích k rozšíření úředních hodin pro veřejnost. Bližší informace o úředních hodinách konkrétního katastrálního pracoviště získáte na webu – viz stránky katastrálních úřadů. ČÚZK žádá návštěvníky, aby využívali rozšířené úřední hodiny v plném rozsahu a pomohli tím minimalizovat počet současně čekajících klientů.
The post Katastrální úřady rozšiřují úřední hodiny pro veřejnost appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Oil & Gas Impact Assessment - A New Mapping Tool For Industry
17.4.2020 18:42 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars ReportViz Allows Users to Assess Impact of Oil and Gas ExplorationCartoVista partner, ICI Innovations, has developed an interactive mapping …


















