zprávy
zdroje zpráv:OA Škoda Octavia 1.6 (2004)
6.8.2018 10:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/OA-Skoda-Octavia-1-6-(2004)Interview with Bryan Martindale, DesignJet Business Manager, HP at ESRI UC 2018
6.8.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsNová verze eCognition v9.3
6.8.2018 9:00 Gisat Aktuální verze Trimble eCognition v9.3 nabízí řadu novinek pro objektovou klasifikaci: vylepšená analýza 3D mračen, DeepLearning, superpixelová segmentace ...Hledáme: Specialista mobilního mapování
6.8.2018 8:00 TopGis Společnost TopGis, s.r.o. vypisuje výběrové řízení na pozici „Specialista mobilního mapování“ na DPP nebo DPČ na dobu určitou od 20.8.2018 – 31.10.2018. Pracovní náplň: Požadavky: Pracoviště: Pracovní poměr formou DPP nebo DPČ na dobu určitou 06/2018 – 10/2018 V případě Vašeho zájmu nám pošlete Váš strukturovaný životopis na emailovou adresu kariera@topgis.cz. Odpovědí na inzerát či zasláním Vašeho životopisuPodzimní brigáda: Specialista mobilního mapování
6.8.2018 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformaceSpolečnost TopGis, s.r.o. vypisuje výběrové řízení na pozici „Specialista mobilního mapování“ na DPP nebo DPČ na dobu určitou od 20.8.2018 – 31.10.2018.
Pracovní náplň:
sběr dat pomocí systému mobilního mapování
aktivní řízení automobilu
obsluha zařízení pro sběr dat v systému mobilního mapování (jedná se o všechny činnosti spojené s obsluhou
Registrujte se na GIS v plánování měst a regionů 2018
6.8.2018 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Česká asociace pro geoinformace (CAGI) a Vysoká škola regionální rozvoje a Bankovní institut - AMBIS, a.s. Vás srdečně zvou k účasti na 4. ročníku konference GIS v plánování měst a regionů, která se uskuteční v Praze v termínu 13. 9. 2018. Tématem letošní konference je GIS při zajištění bezpečnosti v regionech.Více informací včertně registrace naleznete
Airbus Defence and Space selected by Telesat to further develop the design of its LEO satellite constellation.
3.8.2018 21:24 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Toulouse, 3 August 2018 – Airbus Defence and Space has been selected by Telesat as a major industrial partner to support their System …CompTIA ChannelCon 2018 Adjourns in Nation's Capital with Sessions on Cybersecurity, Drones and Other Emerging Trends and Technologies
3.8.2018 19:24 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WASHINGTON, Aug. 3, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — CompTIA ChannelCon 2018, the tech industry's premier education, networking and …The world's fastest solution for high quality 3D tomography
3.8.2018 16:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The ARTOS 3D ultramicrotome expands 3D image reconstruction applications for cell biology researchBALTIMORE and WETZLAR, Germany, Aug. 3, 2018 …
20180803 - Vzorová data VF ISKN ve verzi 5.3
3.8.2018 11:01 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKN Vzorová data VF ISKN ve verzi 5.3. WS služba ctiOS bude zpřístupněna v nejbližším možném termínu.20180803 - Vzorová data VF ISKN ve verzi 5.3
3.8.2018 11:01 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKNWS služba ctiOS bude zpřístupněna v nejbližším možném termínu.
20180803 - Vzorová data VF ISKN ve verzi 5.3
3.8.2018 11:01 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKN Vzorová data VF ISKN ve verzi 5.3. WS služba ctiOS bude zpřístupněna v nejbližším možném termínu.Starý Trimble za nový
3.8.2018 9:37 Geotronics GIS - Vyměňte starý Trimble Geo za nový na protiúčet."3D Laser Mapping Ltd and GeoSLAM Ltd Merge to Offer Next-Gen Mobile Mapping Products" by Susan Smith
3.8.2018 9:02 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsAutodesk Extends Invitation to Join Financial Results Conference Call
3.8.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Second Quarter Fiscal 2019 Financial Results Conference Call to be Held Thursday, August 23, 2:00 p.m. Pacific TimeSAN RAFAEL, Calif., Aug. 1, 2018 …
Interview with Sabrina Carter, Business Development Manager, HP at ESRI UC 2018
3.8.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsOcenění AOPK ČR v oblasti využívání informačních technologií (TZ)
3.8.2018 8:11 GISportal.cz
AOPK ČR byla dne 11. 7. 2018 oceněna na uživatelské konferenci produktů firmy Esri v San Diegu prestižní cenou „Special Achievement in GIS“ udělovanou prezidentem společnosti Esri Jackem Dangermondem, který se významným způsobem angažuje v oblasti ochrany přírody. Cena je udělována za významný počin v oblasti využívání geografických informačních technologií (GIS). V případě AOPK ČR jde především o […]
The post Ocenění AOPK ČR v oblasti využívání informačních technologií (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Maxar Technologies Commends United States Senate Commerce Committee’s Approval of S. 3277
3.8.2018 2:51 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — August 2, 2018 —Maxar Technologies (formerly MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates …
Adresní místa
3.8.2018 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Mapová služba zobrazující adresní místa v Karlovarském krajiMapfit Continues Its Efforts to Reshape the Mapping API Industry with Appointment of New CEO
2.8.2018 19:31 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, Aug. 2, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Mapfit today announced that it has appointed accomplished technology executive and investor, …Ballard Reports Q2 2018 Results
2.8.2018 16:29 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars VANCOUVER, Aug. 1, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Ballard Power Systems (NASDAQ: BLDP; TSX: BLDP) today announced consolidated financial results …AirMap UTM Deployed in Czech Republic to Manage the Country's Busiest Airspace
2.8.2018 16:29 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SANTA MONICA, Calif., Aug. 2, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Today, AirMap, the world's leading airspace management platform for drones, …AUVSI’s McMahon, ISR Idea’s Poss To Bring Keynotes at UAS Tech Forum
2.8.2018 16:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Annual Event to be Held in Broken Arrow Sept. 12-13BROKEN ARROW, Okla. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — August 2, 2018 —
…
Esri Announces Living Atlas Innovations to Revolutionize Digital Twin Technology
2.8.2018 16:27 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The Annual Esri User Conference Showcased New Features, Including theEarth Systems Monitor App
REDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS …
Komatsu partners with Propeller to bring enterprise-grade drone analytics solutions to the construction industry
2.8.2018 16:27 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Komatsu America Corp. and Propeller Aero Inc. are partnering to boost the efficiency of construction job sites using drone-powered mapping and …Wind satellite fuelled for flight
2.8.2018 15:43 ESA Observing the Earth
With liftoff less than three weeks away, ESA’s Aeolus satellite has been fuelled and is almost ready to be sealed within its Vega rocket fairing.
Vrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
2.8.2018 15:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vsetínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
Vrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
2.8.2018 15:42 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vsetín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KNVrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
2.8.2018 15:42 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vsetín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KNVrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
2.8.2018 15:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operVrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
2.8.2018 15:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operVrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
2.8.2018 15:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vsetínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení dokumentace KN
Vypuštění nových družic rozšířilo globální záběr systému Galileo
2.8.2018 15:21 Český Kosmický PortálNosná raketa Ariane 5 vynesla na oběžnou dráhu kvarteto družic Galileo. Díky tomu se konstelace systému Galileo rozrostla na 26 satelitů, čímž dosáhla globálního pokrytí.
Vypuštění nových družic rozšířilo globální záběr systému Galileo
2.8.2018 15:21 Český Kosmický PortálNosná raketa Ariane 5 vynesla na oběžnou dráhu kvarteto družic Galileo. Díky tomu se konstelace systému Galileo rozrostla na 26 satelitů, čímž dosáhla globálního pokrytí.
ERL Emergency 2019 – robots to the rescue!
2.8.2018 13:56 European GNSS Agency
In emergency situations, robotic systems play a key role in providing rescue teams with remote access to an emergency site. The ERL Emergency Local Tournament 2019 aims to foster advanced developments of autonomous capabilities and seamless navigation for emergency robotic systems.
The European Robotics League (ERL) is an innovative robot competition that stems from its predecessors - the euRathlon and RoCKIn competitions - and focuses on tasks that robots must execute in realistic emergency situations. The competition is composed of multiple local tournaments, held in different locations across Europe, in addition to a few major events.
The first of the challenges was announced in July 2018, and focused on land and sea robotic systems. The second, to be held in February 2019 at the premises of the Advanced Centre for Aerospace Technologies (CATEC) in Seville, Spain, will include air and land robots working in an outdoor/indoor environment. You can find more information about the challenges here.
Read this: Integrating GNSS in UAVs for faster SAR
Teams participate in a minimum of two tournaments (local and/or major) per year and get scores based on their performances. Each team’s top two tournament scores are then added together and the teams are ranked based on their cumulative score. Prizes for the top teams are awarded at the following year’s European Robotics Forum (ERF).
GSA Special Prize
The European Global Navigation Satellite Systems Agency (GSA) will award a special prize at ERL Emergency 2019 focusing on robots that make use of solutions based on Galileo and EGNOS.
For air robots, this challenge will involve two types of tasks: horizontal accuracy in landings at a specific geographic coordinate; and vertical accuracy while hovering at a specific geographic coordinate. For land robots, there will be only one type of task - horizontal accuracy during waypoint-based navigation.
Visual markers will be used to support the assessment of both types of task. To be eligible for the award, a team must have executed valid trials of the tasks. The team deemed to have achieved the best results will be declared the winner. For information on Galileo capable receivers and navigation kits for robotic systems visit https://www.usegalileo.eu/EN/.
Register now!
If you are interested in participating in this ERL Emergency Local Tournament, you should register your team by filling in this form by the deadline of August 15. For more information, click here.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Vyhráli jsme s americkým AirMap tendr ŘLP na poskytování UTM služby
2.8.2018 11:53 UpVision Vyhráli jsme s firmou AirMap tendr Řízení letového provozu na poskytování UTM služby - řízení bezpilotního letového provozu pro řízený vzdušný prostor v České republice.Více na stránkách ŘLP:
http://www.rlp.cz/spolecnost/tisk/tiskzpravy/Stranky/Sdru%C5%BEen%C3%AD-firem-AirMap--UpVision-zv%C3%ADt%C4%9Bzilo-v-tendru.aspx
Sdružení firem AirMap / UpVision zvítězilo v tendru na poskytování služby řízení bezpilotního letového provozu pro řízený vzdušný prostor v České republice (TZ)
2.8.2018 11:30 GISportal.cz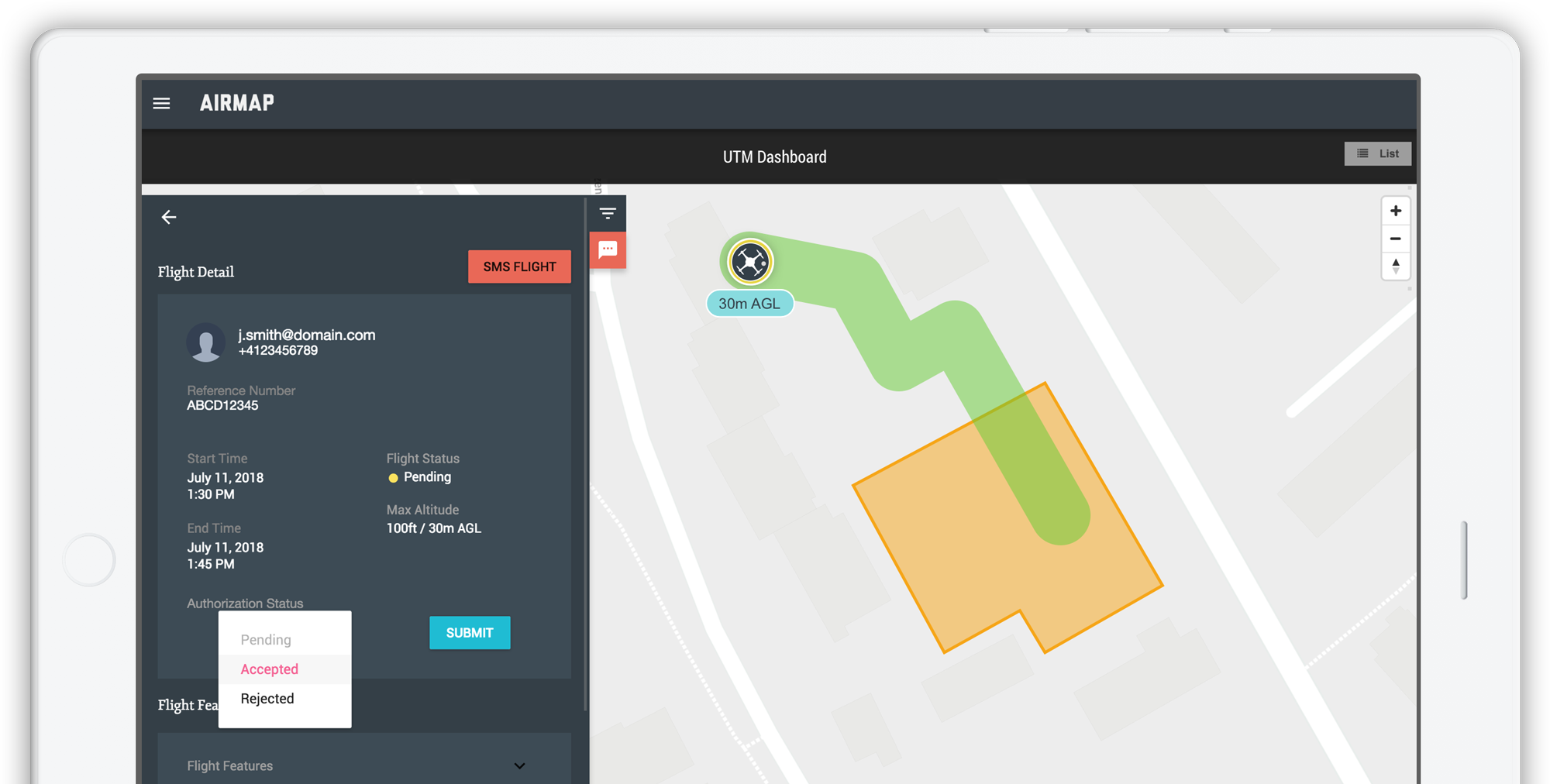
Firma AirMap, přední světový poskytovatel řešení pro řízení bezpilotního letového provozu, oznámila, že její UTM platforma bude nasazena v Řízení letového provozu České republiky (ŘLP ČR, s.p.), za účelem poskytování situačního povědomí a možnosti podávání žádostí o provedení letů rostoucí komunitě provozovatelů dronů. ŘLP ČR nasazuje platformu AirMap UTM ke správě žádostí pro lety […]
The post Sdružení firem AirMap / UpVision zvítězilo v tendru na poskytování služby řízení bezpilotního letového provozu pro řízený vzdušný prostor v České republice (TZ) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
20180802 -Technický problém
2.8.2018 9:31 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/2-Poskytovani-udaju-RUIAN-ISUI-VDP/Vymenny-format-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-VFR/20180802-Technicky-problem20180802 -Technický problém
2.8.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Při generování stavového VFR za měsíc červenec 2018 se objevily technické problémy, které byly 2. 8. 2018 kolem 22. hodiny vyřešeny.Zveřejněno 3. 8. 2018
20180802 -Technický problém
2.8.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Při generování stavového VFR za měsíc červenec 2018 se objevily technické problémy, které byly 2. 8. 2018 kolem 22. hodiny vyřešeny.Zveřejněno 3. 8. 2018
20180802 -Technický problém
2.8.2018 9:31 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/2-Poskytovani-udaju-RUIAN-ISUI-VDP/Vymenny-format-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-VFR/20180802-Technicky-problem20180802 -Technický problém
2.8.2018 9:31 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Při generování stavového VFR za měsíc červenec 2018 se objevily technické problémy, které operativně řešíme.Omlouváme se za způsobené komplikace.
Zveřejněno 2. 8. 2018
Nabídka nepotřebného majetku - 08/2018
2.8.2018 9:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Nabídka nepotřebného majetku - 08/2018
Nabídka nepotřebného majetku - 08/2018
2.8.2018 9:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Nabidka-nepotrebneho-majetku-08-2018Nabídka nepotřebného majetku - 08/2018
2.8.2018 9:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Nabidka-nepotrebneho-majetku-08-2018Nabídka nepotřebného majetku - 08/2018
2.8.2018 9:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Nabídka nepotřebného majetku - 08/2018
Interview with Rebecca Lasica, Director of Enterprise Platforms and Partners, Harris Corp at ESRI UC 2018
2.8.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsUniversity of North Alabama Offers Online GIS Analyst Certificate Program
1.8.2018 21:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars University of North Alabama Offers Online GIS Analyst Certificate Program - This certificate program consists of seven courses which can be completed …Bluesky Aerial Survey Helps Malta Develop GeoSpatial Infrastructure
1.8.2018 16:59 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars August 1, 2018 -- Aerial mapping company Bluesky has captured aerial photography and 3D map coverage of Malta. Working alongside tender lead IIC …Pitney Bowes Announces Second Quarter 2018 Financial Results
1.8.2018 16:53 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars STAMFORD, Conn. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — August 1, 2018 —Pitney Bowes Inc. (NYSE: PBI), a global technology company that …
Garmin reports second quarter revenue and earnings growth; Raises guidance for 2018
1.8.2018 16:53 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SCHAFFHAUSEN, Switzerland — (BUSINESS WIRE) — August 1, 2018 —Garmin Ltd. (Nasdaq: GRMN – News) today announced results …
Dnes vyšel Jakubův článek na Lupa.cz o evropské legislativě pro drony
1.8.2018 16:09 UpVision Dnes vyšel Jakubův článek na Lupa.cz o evropské legislativě pro drony s aktuálním přehledem a vývojem.Více zde:
https://www.lupa.cz/clanky/neni-treba-panikarit-aneb-co-prinese-celounijni-evropska-legislativa-pro-drony/
Nepotřebný majetek - výběrové řízení
1.8.2018 14:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Nepotřebný majetek - výběrové řízení
Nepotřebný majetek - výběrové řízení
1.8.2018 14:22 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Nepotrebny-majetek-vyberove-rizeni-(1)20180716 Rada/odborný rada – interní auditor Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20180709-Odborny-referent-oddeleni-dokumentace-(2)20180801 Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kra
1.8.2018 14:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj"20180801 Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kra
1.8.2018 14:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20180709-Odborny-referent-oddeleni-dokumentace-(2)20180801 Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kra
1.8.2018 14:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj"20180801 Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kra
1.8.2018 14:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20180709-Odborny-referent-oddeleni-dokumentace-(2)Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:00 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-oddeleni-podpory-ICT-–-informatiRada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:00 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - technická sekce vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský krajRada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:00 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - technická sekcevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:00 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - technická sekcevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:00 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - technická sekce vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský krajRada/odborný rada oddělení podpory ICT – informatik Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj
1.8.2018 14:00 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-oddeleni-podpory-ICT-–-informatiSoutěž Vesmír nás spojuje: 30 českých dětí bude přemýšlet o nové kosmické stanici na oběžné dráze Měsíce
1.8.2018 13:28 Český Kosmický PortálBadatelé a inženýři z vesmírných agentur po celém světě již dlouho a aktivně diskutují nad projektem vesmírné stanice na oběžné dráze Měsíce. Pořadatelé česko-ruské soutěže Vesmír nás spojuje vyhlásili úkol 2. kola soutěže pro 30 dětí z Česka a 30 dětí z Ruska. Budou natáčet video o nové vesmírné stanici.
Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
1.8.2018 12:20 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Klobouky vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KNOdborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
1.8.2018 12:20 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Klobouky vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KNOdborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
1.8.2018 12:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Kloboukyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
1.8.2018 12:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-v-(2)Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
1.8.2018 12:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Valašské Kloboukyvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
Odborný rada – obnova katastrálního operátu v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN
1.8.2018 12:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-rada-–-obnova-katastralniho-operatu-v-(2)Sonda ESA detekovala vodu v kapalném stavu u jižního pólu Marsu
1.8.2018 11:26 Český Kosmický PortálRadarová data získaná sondou ESA Mars Express ukazují na jezero kapalné vody nacházející se pod vrstvami ledu a prachu v oblasti jižního pólu planety Mars.
Plán plošného pokrytí kraje prostředky zdravotnické záchranné služby
1.8.2018 10:57 T-MAPYThe post Plán plošného pokrytí kraje prostředky zdravotnické záchranné služby appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
EGNSS funding opportunities – what’s on offer?
1.8.2018 9:36 European GNSS Agency
With four topics under the Horizon 2020 EGNSS MARKET UPTAKE 2019 call for proposals set to open on 16 October 2018, now is a good time to take a look at the many EU R&D funding opportunities that the GNSS community can take advantage of.
The EGNSS-related call that is set to open in October supports key EU priorities – leveraging innovation to energise economic growth and support environmental sustainability, particularly in Europe’s cities. The new call will foster the emergence of new innovative downstream applications based on either Galileo and/or EGNOS and support the EU GNSS industry, SMEs, universities, research organisations and public bodies.
The specific challenge of the first topic of the call is to address the EGNSS applications fostering green, safe and smart mobility, with the objective of developing innovative EGNSS-based applications that lead to low-emission, safer, more cost-effective and higher performance mobility and transport solutions, responding to the growing mobility needs of people and goods.
Mass market and the environment
The second topic of the call addresses EGNSS applications fostering digitisation, and its main challenge is to develop EGNSS applications contributing to digitisation of products and services that will, among its other goals, foster the adoption of EGNOS and Galileo in mass markets and provide benefits to users.
The third topic, on EGNSS applications fostering societal resilience and protecting the environment, aims to develop innovative EGNSS applications to support societal resilience, safeguard the wellbeing of EU citizens, improve emergency and disaster management as a response to climate-related natural and man-made disasters, and promote green growth.
Finally, the last topic of Awareness raising and capacity building, aims to build a mechanism to leverage EGNSS excellence, to provide opportunities for the creation of networks of industrial relationships in Europe and also globally , and facilitate EGNSS investments.
For more information on all of these calls, click here.
H2020 Information Day in PragueThe European GNSS Agency (GSA) is organising a Horizon 2020 International Space Information Day and Brokerage Event at its headquarters in Prague on 11-12 October to provide information on space opportunities in Horizon 2020 and beyond and on the next H2020 Space Call, with a special focus on Galileo calls. In addition to learning about space opportunities in H2020, this event will be an opportunity to meet with potential partners for the upcoming 2019-2020 space calls. To register to attend, click here. |
Other opportunities
Other upcoming H2020 calls in different sectors but with specific reference to EGNSS are:
Transport
A number of calls in the transport sector make reference to EGNOS and Galileo-based applications – we will cover some of them here (a more comprehensive list is available below). The topic Integrated multimodal, low-emission freight transport systems and logistics aims to speed up the transition towards the Physical Internet paradigm, demonstrating how different technologies, business cases and standards come together in real-world applications.
The topic Moving freight by water: sustainable infrastructure and innovative vessels aims to make operations at inland waterways and/or port infrastructure more efficient through the use of smart systems and automation. Meanwhile, Innovative applications of drones for safety in transport aims to develop and test technologies and operational and business models for the application of drones to increase the safety, security, and overall efficiency of air, waterborne and surface transport.
Finally, proposals under the topic Developing and testing shared, connected and cooperative automated vehicle fleets in urban areas for the mobility of all should make best use of EGNOS and Galileo to allow communication and cooperation between vehicles and infrastructure and with other road users, and enable automated, smart mobility services, innovative fleet management concepts and higher performance of automated vehicle functions.
Energy
The call Research on advanced tools and technological development targets the development and testing of a number of tools and future technologies, including GNSS timing and synchronisation for smart grids, to cover gaps and to prepare for the energy system of 2030 and beyond.
Health/ Climate Change
The use of advanced IT technologies such as high performance computing and geo-localisation data is anticipated in the topic Mining big data for early detection of infectious disease threats driven by climate change and other factors, to enable the rapid and personalised treatment of patients, and bolster the detection, tracking and control of infectious disease outbreaks.
EGNSS-RELATED CALLS AT A GLANCELeadership in Enabling and Industrial Technologies-ICT
Societal challenge 1 – Health
Societal challenge 2 – Energy
Societal challenge 4 - Transport
Galileo activities are also supported via the Fundamental Elements funding mechanism. |
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Launches Concept3D Interactive Map and Virtual Tour Platform
1.8.2018 9:10 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Platform Creates Immersive Campus Experience for Exploring, Wayfinding, and to Support Marketing and CommunicationsDENVER – July 31, 2018 …
USGIF Announces Two New Board Members
1.8.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Al Di Leonardo and Patty Mims join the Foundation’s Board of DirectorsHerndon, Virginia (July 31, 2018)—The United States Geospatial …
Interview with Scott Hamilton, Dell Industry Strategist at ESRI UC 2018
1.8.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsNevada launches Drone Center of Excellence for Public Safety to mitigate rogue drone airspace incursions
1.8.2018 0:56 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars LAS VEGAS, July 31, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — The Nevada Institute for Autonomous Systems (NIAS) today announced the launch of the …Na Českém rozhlasu jsme komentovali detekční systémy na drony které testujeme
31.7.2018 21:09 UpVision Zařídili jsme a komentovali pro Český Rozhlas ukázku detekčního systému na drony, kde dlouhodobě spolupracujeme na testech systémů od největších výrobců a na rozvoji jejich případných nasazení.Více zde:
https://radiozurnal.rozhlas.cz/zamerit-a-zneskodnit-je-ukol-antidronovych-systemu-chrani-letiste-i-jaderne-7563782
Rise in Home Prices Remains Steady at 6.4% According to S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller Index
31.7.2018 20:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, July 31, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — S&P Dow Jones Indices today released the latest results for the S&P CoreLogic …Berlin bakes
31.7.2018 18:05 ESA Observing the Earth
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite has imaged signs of drought around Berlin, Germany
Berlin bakes
31.7.2018 16:00 ESA Observing the Earth
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellite has imaged signs of drought around Berlin, Germany
Harris Corporation Reports Strong Fourth Quarter and Fiscal 2018 Results...Well Positioned to Accelerate Growth
31.7.2018 15:57 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 4Q18 revenue up 8% to $1.7 billion; orders up 18%; book-to-bill 1.14Q18 GAAP EPS from continuing operations up 29% to $1.74; …
Maxar Technologies reports second quarter 2018 results, declares quarterly dividend
31.7.2018 15:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsEsri Enters Into Memorandum of Understanding with World Bank
31.7.2018 15:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New Agreement Integrates Location Intelligence into World BankSoftware and Initiatives
REDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) …
Alibaba Became the First Partner of UNWGIC
31.7.2018 13:12 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars July 31, 2018 - The first partnership communication meeting of United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC) was held in Deqing, …20180731 - Aktualizace změn VFK z důvodu nové verze ISKN 8.2
31.7.2018 11:00 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKNPředchozí verze:
20180731 - Aktualizace změn VFK z důvodu nové verze ISKN 8.2
31.7.2018 11:00 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKNPředchozí verze:
20180731 - Aktualizace změn VFK z důvodu nové verze ISKN 8.2
31.7.2018 11:00 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKNPředchozí verze:
20180731 - Aktualizace změn VFK z důvodu nové verze ISKN 8.2
31.7.2018 11:00 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKN Aktualizovaná verze popisu změn VF v souvislosti s Nařízením Evropského parlamentu a Rady (EU) na ochranu osobních údajů (General Data Protection Regulation „GDPR“). (Předchozí verze:
Dopady_GDPR_na_data_a_sluzby_CUZK_18052018 (
20180731 - Aktualizace změn VFK z důvodu nové verze ISKN 8.2
31.7.2018 11:00 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKNPředchozí verze:
20180731 - Aktualizace změn VFK z důvodu nové verze ISKN 8.2
31.7.2018 11:00 ČÚZK - Výměnný formát ISKN Aktualizovaná verze popisu změn VF v souvislosti s Nařízením Evropského parlamentu a Rady (EU) na ochranu osobních údajů (General Data Protection Regulation „GDPR“). (Předchozí verze:
Dopady_GDPR_na_data_a_sluzby_CUZK_18052018 (
Interview with Matt Kochanowski, Epson Product Manager at ESRI UC 2018
31.7.2018 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsNabídka nepotřebné ICT techniky
31.7.2018 6:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Nabídka nepotřebné ICT techniky
Nabídka nepotřebné ICT techniky
31.7.2018 6:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Nabidka-nepotrebne-ICT-technikyNabídka nepotřebné ICT techniky
31.7.2018 6:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Nabidky-majetku/Nabidka-nepotrebne-ICT-technikyNabídka nepotřebné ICT techniky
31.7.2018 6:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníKatastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Nabídka nepotřebné ICT techniky
Litogeochemická dokumentace
31.7.2018 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE ArcGIS Server služba zobrazující dokumentační body, které obsahují analytické údaje o chemickém složení více než 13 tisíc vzorků hornin odebraných na území ČR.Výňatky z Informace OMPÚ č. 2/2018
30.7.2018 20:12 Asociace poskytovatelů služeb v pozemkových úpravách Výňatky z Informací Odboru metodiky pozemkových úprav Přílohy Poslední aktualizace Výňatky z Informace OMPÚ č. 2/2018 9.7.2018Výňatky z Informace OMPÚ č. 2/2018
30.7.2018 20:12 Asociace poskytovatelů služeb v pozemkových úpravách Výňatky z Informací Odboru metodiky pozemkových úprav Přílohy Poslední aktualizace Výňatky z Informace OMPÚ č. 2/2018 9.7.2018Výňatky z Informace OMPÚ č. 2/2018
30.7.2018 20:12 Asociace poskytovatelů služeb v pozemkových úpravách Výňatky z Informací Odboru metodiky pozemkových úprav Přílohy Poslední aktualizace Výňatky z Informace OMPÚ č. 2/2018 9.7.2018ARC Research Indicates Geographic Information Systems are Moving to the Cloud
30.7.2018 19:20 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DEDHAM, Mass. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — July 30, 2018 —New ARC Advisory Group research on the geographic information
…
Sphere Drones to Offer Microdrones UAV Solutions
30.7.2018 19:20 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Rome, NY, July 30, 2018 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Sphere Drones, a leading Australian provider of drone solutions for commercial applications, will …Thales Alenia Space and Maxar Technologies' SSL Form Consortium to Further Design and Develop Telesat's LEO Satellite Constellation
30.7.2018 16:29 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars CANNES, France and WESTMINSTER, CO, July 30, 2018 — (PRNewswire) — Thales Alenia Space, a Joint Venture between Thales (67 %) and …Uklízeč/ka
30.7.2018 14:06 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Uklízeč/ka
Uklízeč/ka
30.7.2018 14:06 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Uklízeč/kaUklízeč/ka
30.7.2018 14:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Uklízeč/ka
Geograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Geograf - Brno
Geograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Geograf - Brno
Geograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 Zeměměřický úřad Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Geograf - Brno
Geograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Geograf - BrnoGeograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/GeografGeograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický úřadvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Geograf - Brno
Geograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický úřad vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Geograf - BrnoGeograf - Brno
30.7.2018 13:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericky-urad/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/GeografSentinel-1 maps flash floods in Laos
30.7.2018 12:30 ESA Observing the Earth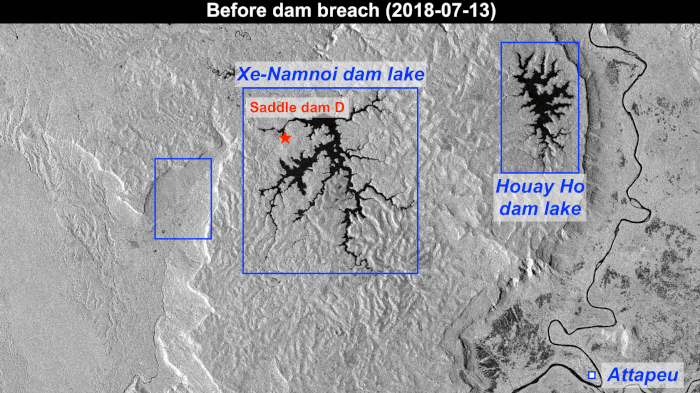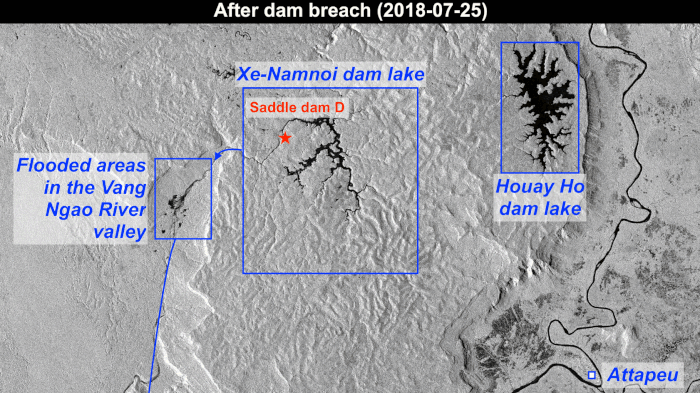
Copernicus Sentinel-1 data are highlighting the collapse of the Xe-Pian Xe-Namnoy dam in the southeastern province of Attapeu in Laos. The collapse has led to flash floods that have claimed several lives and left many more people missing, according to local news reports.















