zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Přerušení dodávky elektřiny
24.8.2017 22:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Z důvodu přerušení dodávky elektřiny ve čtvrtek dne 31. 8. 2017 v důsledku provádění plánovaných prací na zařízení distribuční soustavy ČEZ dojde v době od 7:30 do 10:30 hodin k omezení provozu Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov. Provoz by měl být v plném rozsahu obnoven ještě téhož dne v pozdějších hodinách.Za způsobené problémy se uživatelům služeb katastru nemovitostí omlouváme.
Přerušení dodávky elektřiny
24.8.2017 22:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Trutnov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Preruseni-dodavky-elektrinyEmbracing BIM for Capital Project Delivery
24.8.2017 20:08 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
EE Publishers, South Africa
Read the articlePrvní státní hackathon pod taktovkou NKÚ
24.8.2017 16:18 GeoBusinessRoční provoz e-governmentu vyjde na 25 miliard korun. Národní kontrolní úřad proto vyhlásil první státní hackathon, aby v něm „externisté“ ukázali, jak by se s daty dalo lépe pracovat. Na…
The post První státní hackathon pod taktovkou NKÚ appeared first on GeoBusiness.
24.8.2017
24.8.2017 12:45Realizovali jsme Kalendář akcí, více se dozvíte na následujících odkazech akcezde.cz a zde.
Vytvářeli jsme pro Řízení letového provozu unikátní pohledy u věže Letiště Praha
24.8.2017 11:53 UpVision Vytvářeli jsme pro Řízení letového provozu unikátní panoramatické pohledy vedle věže u Letiště Praha, vše s potřebnými povoleními a zvláštní koordinací Letiště a ŘLP.Zde náhled na řídící věž:
https://plus.google.com/u/0/b/115833877689730865211/+UpvisionCz1/posts/hrb7ELse6c3
Přehled: Software pro podporu správy majetku a facility management
24.8.2017 11:24 GeoBusinessFacility management software se používá jako informační podpora při komplexních řešeních správy budov a majetku. Přinášíme představení čtyř firem, které řešení pro FM poskytují. Správa majetku na mapě (Cleerio) Online…
The post Přehled: Software pro podporu správy majetku a facility management appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Opportunities abound in Taiwan
24.8.2017 10:31 European GNSS Agency
In recent years, Taiwan has emerged as a world-leading GNSS receiver and chipset manufacturer. In fact, Taiwan-based Mediatek is now positioned as one of the top 3 mobile chipset manufacturers and the country is also home to leading OEMs for LBS and automotive navigation equipment.
The GSA-funded GNSS.asia project is dedicated to developing and implementing GNSS industrial cooperation between European and Asia-Pacific GNSS industries, with a focus on the downstream market and has been actively working with Taiwanese stakeholders, including Mediatek.
“GNSS.asia in Taiwan has built a good network with key Taiwanese counterparts from both the public and private sectors,” says European Chamber of Commerce in Taiwan EU Programme & Technology Committee Assistant Director Angela Hsiao. “Our team has significant knowledge about the international and national policy frameworks relevant to industrial cooperation and high-tech businesses.” According to Hsiao, GNSS.asia is working closely with the governmental agencies under Taiwan’s Ministry of Transportation and Communications (MOTC) and Ministry of Economic Affairs (MOEA), as well as key industrial associations and research institutions operating in various GNSS fields.
Multiple opportunities
Unlike its neighbouring countries, Taiwan is not developing its own GNSS system. Instead, it has positioned itself as an ideal testbed for multi-GNSS applications and services. “The size of Taiwan’s population, the plethora of tall buildings in Taipei and the variety of geographical characteristics of the island provide diverse challenges for GNSS applications to innovate solutions to,” explains Hsiao. “Key technologies, including smart transportation, telematics, autonomous driving, disaster prevention and search and rescue, all of which require GNSS applications, are being developed here in Taiwan.”
Clearly, multi-GNSS is an essential opportunity that Taiwan wants to pursue. “Taiwan, which has a limited domestic market, has done an excellent job at positioning itself in the global high-tech industry,” says Hsiao. “As a result, it is now home to some of the largest chip manufacturers and semiconductor board integrators.”
Other areas of interest to both Taiwan and the EU are car communications, the Internet of Things (IoT) and sensor fusion. “In Taiwan, the shift from a focus on computers to mobile devices has resulted in a steady decline in computer and related industries, such as display, power and memory,” says Hsiao. “However, the advance of digitisation is bringing new opportunities that are re-inventing the landscape of information technology.”
Hsiao notes that although this transition will take time, progress is already being seen in the IoT, car communications and robotics sectors. “The evolution has in any case started and has been made possible by the availability of sensors in large volumes at low cost, by the continuous progress of Taiwan’s connectivity and by the power of computation that is brought about by faster and lower power micro-controllers,” she says.
An ICT powerhouse
In just 30 years, Taiwan has become a strategic player in the design, testing and manufacturing of ICT products. This achievement was made possible because of a successful combination of public and private commitment to ensuring a high level of R&D spending, the strong entrepreneurial drive of Taiwanese businesspeople and an innovative business and industrial ecosystem.
As a result, today ICT is another important field for R&D cooperation between European and Taiwanese entities, with many new areas of cooperation quickly emerging. For example, since the micro- and nano-electronics sectors were identified as major fields of joint interest in 2015, a series of novel and disruptive technologies aiming to address new applications and market segments (such as ICT for healthcare and robotics) have emerged. “Major trends such as IoT and Wearable Technologies are also driving innovation worldwide, and should be considered as major triggers to mobilise all players in Taiwan, both from the public and private sectors, to look for collaboration with Europe,” says Hsiao.
Keeping the momentum going
Looking ahead, Hsiao sees car communications, IoT, autonomous driving, disaster prevention, search and rescue and healthcare services as the key future trends in the Taiwan market where GNSS applications can play an important role. “Future GNSS.asia activities in Taiwan will keep the momentum going, gathering key partners from the public and private sectors to share best practices on innovating GNSS applications,” she says. “As this happens, the GNSS.asia Taiwan team will continue to support industrial relations between the EU and Taiwan and facilitate EGNSS breakthroughs via effective and efficient communication.”
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Jak je každá z družic Galileo před startem testována
24.8.2017 8:14 Český Kosmický PortálKaždá družice Galileo musí před cestou do vesmíru projít náročnou testovací kampaní, která zajistí její připravenost na start, vakuum a teplotní extrémy na oběžné dráze Země.
Jak je každá z družic Galileo před startem testována
24.8.2017 8:14 Český Kosmický PortálKaždá družice Galileo musí před cestou do vesmíru projít náročnou testovací kampaní, která zajistí její připravenost na start, vakuum a teplotní extrémy na oběžné dráze Země.
Státní pozemkový úřad na agrosalonu Země živitelka
24.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Ve dnech 24. až 29. srpna 2017 se Státní pozemkový úřad prezentuje na mezinárodním agrosalonu Země živitelka v Českých Budějovicích.Oznámení o přerušení provozu Pobočky Frýdek-Místek
24.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Z důvodu přerušení dodávky vody (havárie na vodovodní síti) bude v pátek 25. 8. 2017 přerušen provoz na Pobočce Frýdek-Místek (KPÚ pro Moravskoslezský kraj).Design and Analysis Software Adapted for Offshore US Wind Farm Engineering
23.8.2017 19:56 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Offshore Oil & Gas Magazine, USA
Read the articleChange Leader: Overcoming Budget Constraints at State DOTs
23.8.2017 19:51 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
AEC Magazine
Read the articleRobin Partington & Partners Implements Federated BIM Workflow to Design Westminster Borough's Iconic Tower
23.8.2017 17:55 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
MicroStation Connections, USA
Read the articleRobin Partington & Partners Implements Federated BIM Workflow to Design Westminster Borough's Iconic Tower
23.8.2017 17:55 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
MicroStation Connections, USA
Read the article20170823 - volné místo - Odborný referent v OD KP Litoměřice
23.8.2017 14:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20170816-volne-misto-Odborny-referent-v-OAaD-K-(3)20170823 - volné místo - Odborný referent v OD KP Litoměřice
23.8.2017 14:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného pracovního místa - Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20170823 - volné místo - Odborný rada-právník v OPV KP Rumburk
23.8.2017 14:16 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20170816-volne-misto-Odborny-referent-v-OAaD-K-(2)20170823 - volné místo - Odborný rada-právník v OPV KP Rumburk
23.8.2017 14:16 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného pracovního místa - Odborný rada - právník v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20170823 - volné místo - Odborný rada v OAaD KP Rumburk
23.8.2017 14:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného pracovního místa - Odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20170823 - volné místo - Odborný rada v OAaD KP Rumburk
23.8.2017 14:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20170816-volne-misto-Odborny-referent-v-OAaD-K-(1)Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu
23.8.2017 14:10 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřaduOdborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu
23.8.2017 14:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Litoměřicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Litoměřice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný rada - právník v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk n
23.8.2017 14:06 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-rada-pravnik-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahuOdborný rada - právník v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk n
23.8.2017 14:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada - právník v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný rada - právník v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk n
23.8.2017 14:06 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada - právník v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk nOdborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrální
23.8.2017 13:58 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburk vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na KatastrálníOdborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrální
23.8.2017 13:58 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rumburkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný rada v oddělení aktualizace a dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Rumburk na Katastrální
23.8.2017 13:58 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-a-dokumentaceASOCIACE PODNIKATELŮ V GEOMATICE
23.8.2017 13:08 Komora geodetů a kartografů ČR ASOCIACE PODNIKATELŮ V GEOMATICE (APG) Komora geodetů kartografů, od 24. listopadu 2016 nesoucí název Česká komora zeměměřičů, usilující od svého vzniku v roce 1991 stát se komorou ze zákona s povinným členstvím pro všechny úředně oprávněné zeměměřické inženýry se po třetím nezdařeném pokusu dosáhnout svého cíle – tentokrát novelou stávajícího zákona 360/1992, kterým vznikla Česká komora autorizovaných architektů […]Burn scars
23.8.2017 12:00 ESA Observing the Earth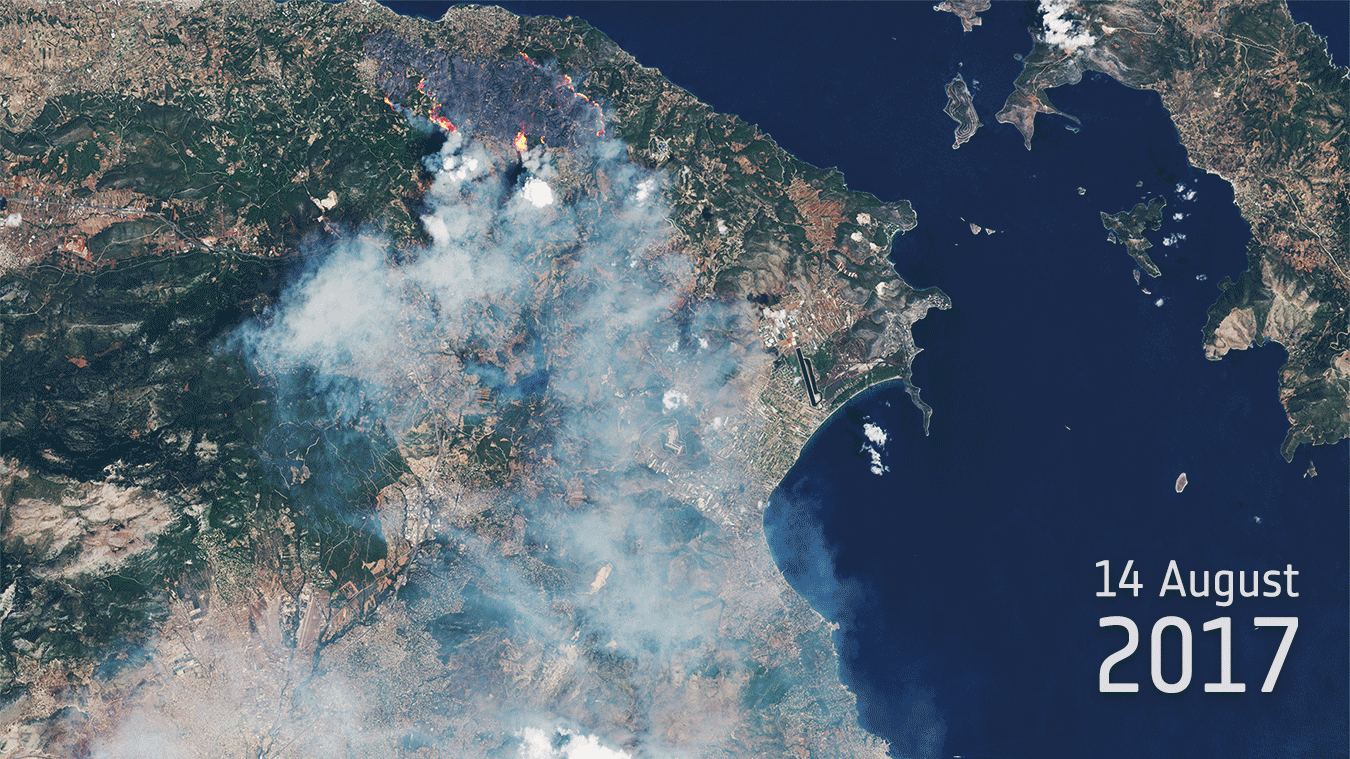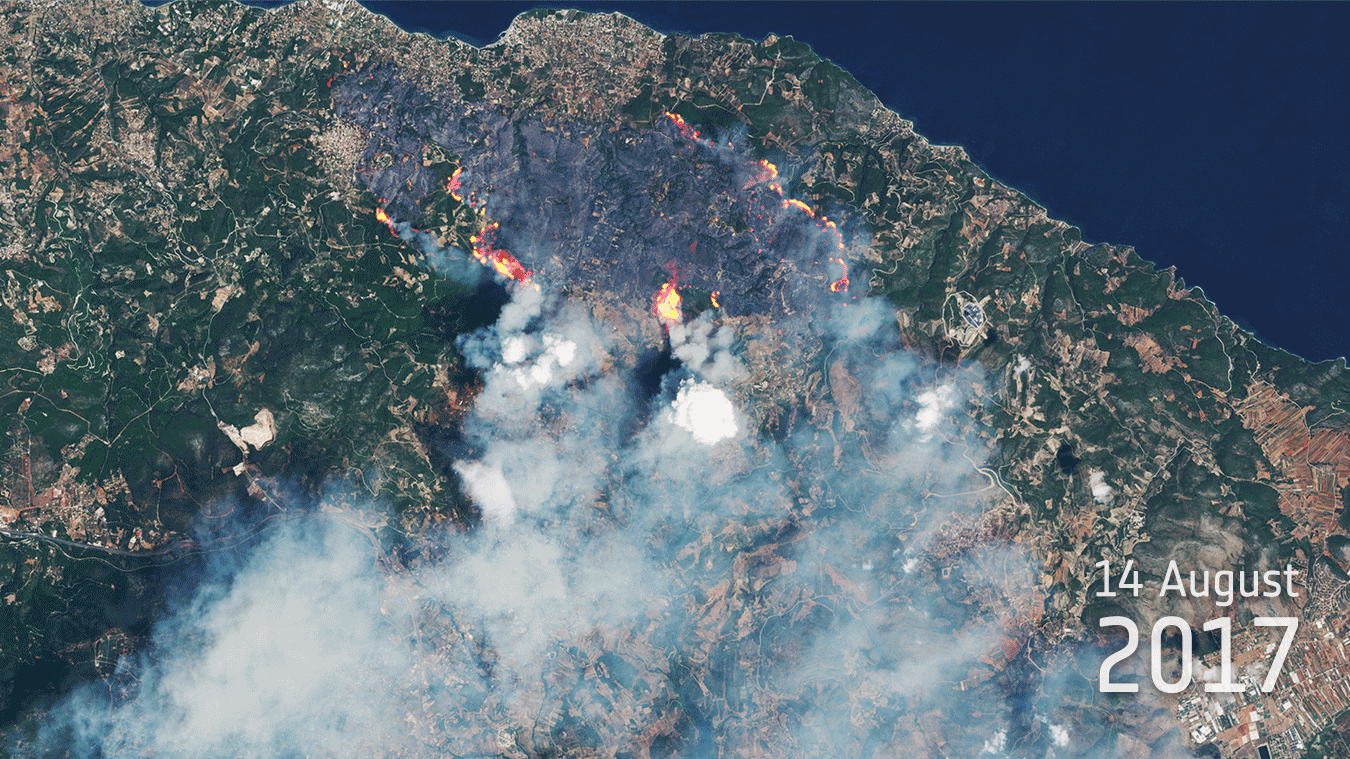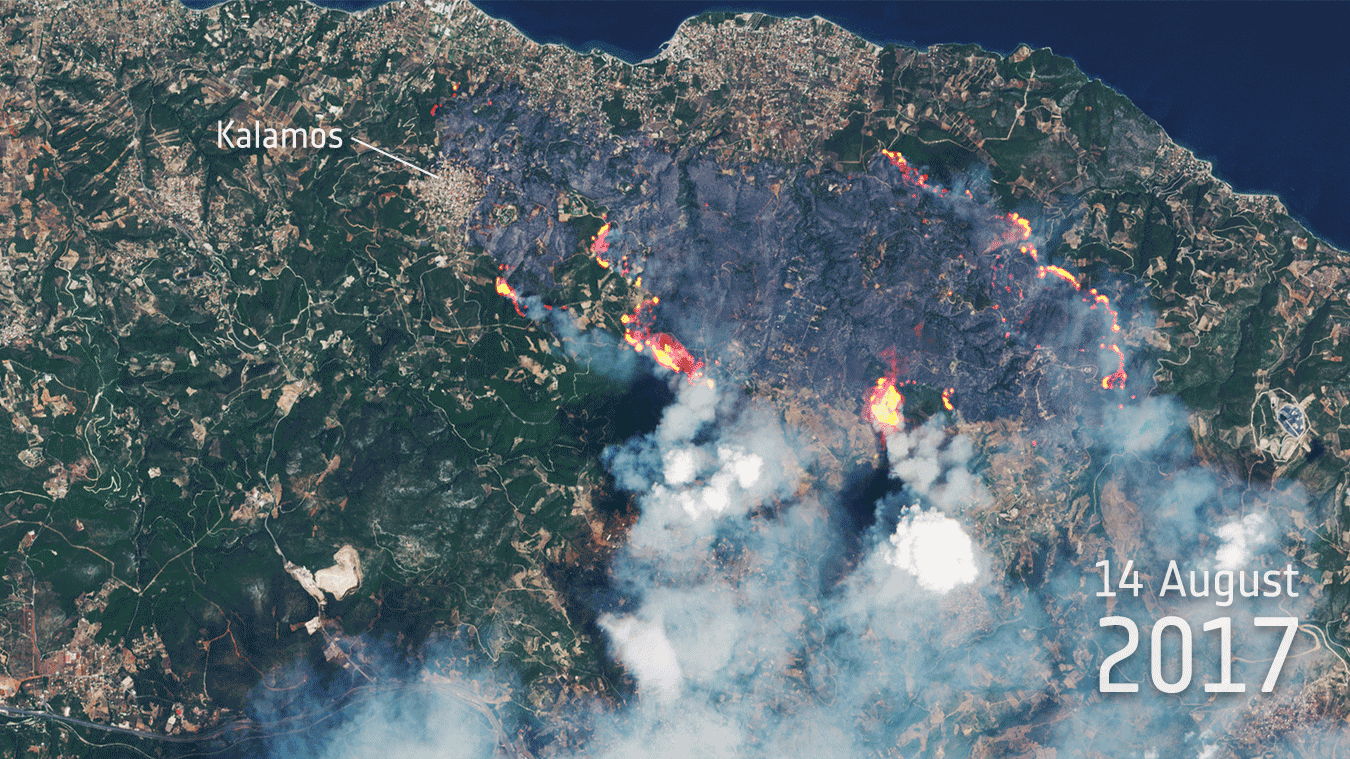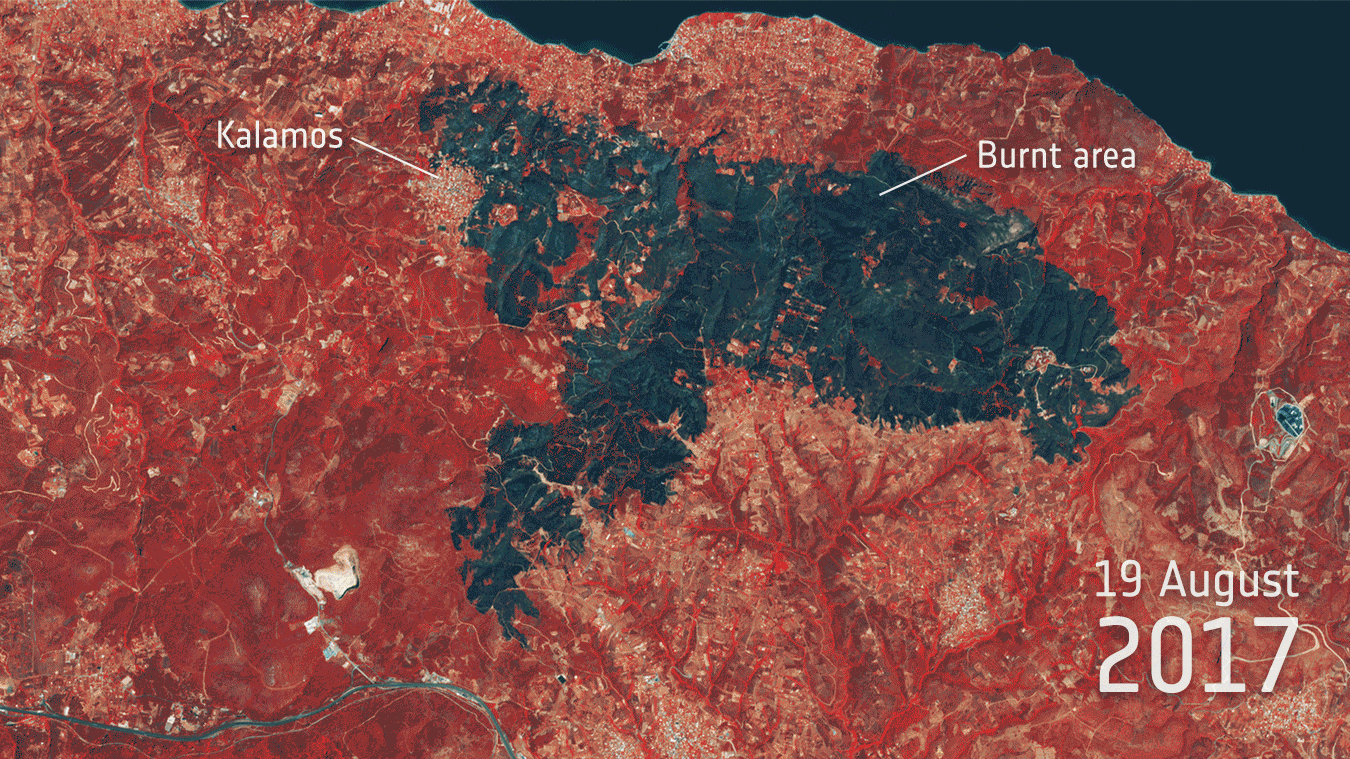
Sentinel-2 shows blazes and dramatic burn scars from wildfires in Greece
V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kra
23.8.2017 12:00 Ústecký kraj V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kraje byla provedena aktualizace údajů pro poskytovatele AOPK – jev 27, 28, 29, 31, 32 (NPR včetně OP, PR včetně OP, zákonná OP MZCHU, památné stromy)Mapová aplikace a mapová apli
23.8.2017 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace a mapová aplikace byly aktualizovány k 22.8.2017.Mapová aplikace Technická infr
23.8.2017 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Technická infrastruktura a mapová aplikace Zastavěné území byly aktualizovány k 22.8.2017.20170823 Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí
23.8.2017 9:57 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20161013Rada-odborny-rada-–-informatik-(4)20170823 Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí
23.8.2017 9:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nem. V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení systemizovaného místa Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí"Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí
23.8.2017 9:50 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obnovy-aOdborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí
23.8.2017 9:50 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostíOdborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí
23.8.2017 9:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru
Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize katastru nemovitostí
Nová nabídka práce v Brně/Praze
23.8.2017 9:24 GISportal.cz CEDA hledá programátora a architekta mapových aplikací.Letní škola GIS v Olomouci
23.8.2017 7:42 GeoBusinessV létě většina studentů odpočívá, cestuje nebo pracuje. Pro zvídavé je určena týdenní škola GISu, kterou v červenci pořádala katedra geoinformatiky na Univerzitě Palackého v Olomouci společně s dalšími zahraničními…
The post Letní škola GIS v Olomouci appeared first on GeoBusiness.
CEDA hledá Google Maps Developera
23.8.2017 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformaceProgramátor a Google Maps Developer
Programátor a architekt mapových aplikací, certifikovaný Google Maps Developer
CEDA jako autorizovaný Google Maps Reseller pro oblast střední a východní Evropy hledá kolegu, jenž bude zastávat také roli certifikovaného Google Maps Developera pro podporu návrhu zákaznických projektů, samostatný návrh a vývoj aplikací s Google Maps
Linky MHD dnes
23.8.2017 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Linky a zastávky MHD provozované dnes v hl. m. PrazeMise ESA Proba-3 vytvoří umělé zatmění Slunce
22.8.2017 20:58 Český Kosmický PortálV polovině srpna společně sledovali astrofyzikové a příležitostní pozorovatelé totální zatmění Slunce nad Severní Amerikou. Zatmění trvalo řádově jen minuty, ale už v příští dekádě budou mít vědci možnost sledovat zatmění trvající hodiny. A to díky průkopnické misi ESA.
Program konference Hexagonu v září 2017 ve Valči
22.8.2017 17:19 GeoBusinessKaždoroční konference firmy Hexagon, známé původně jako Intergraph, se letos bude konat v září v nádherném prostředí hotel-zámku Valeč. 18. ročník uživatelské konference HxGN LOCAL GEOFORUM CS 2017 bude letos…
The post Program konference Hexagonu v září 2017 ve Valči appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Dodatečné výběrové řízení Erasmus+
22.8.2017 16:33 Katedra geografie UP Olomouc Katedra geografie vyhlašuje na středu 4. října 2017 dodatečné výběrové řízení na studentské mobility v rámci programu Erasmus+ na letní semestr akademického roku 2017/18. Výběrové řízení se bude konat v hlavní budově Přírodovědecké fakulty (17. listopadu 12) na učebně 2.025 v 10.00. Podrobnosti k přihlášce naleznete v prostředí aplikace erasmusplus.upol.cz (přihlášení jako do STAGu), v případě dotazů kontaktujte dr. Šimáčka. Kromě již tradičních destinací jsou v nabídce také Srbsko nebo Izrael, pro které jsou i výhodnější finanční podmínky. Uzávěrka možnosti podat přihlášku je 3. října 2017, tak svou šanci nepropásněte.Pokud žádná země z nabídky Katedry geografie nevyhovuje vašim představám, je možné se přihlásit na výběrová řízení jiných kateder, případně prostudovat možnosti mobilit na stránkách Zahraničního oddělení UP. Mobility mimo program Erasmus+ najdete v menu Výměnné programy.
Vědecká výzva IBER 2017
22.8.2017 14:48 Česká kosmická kancelářEvropská kosmická agentura vyhlásila výzvu IBER na návrh experimentů sledujících dopad kosmického záření na živé organismy. Pochopení této problematiky je jedním z hlavních úkolů přípravy dlouhodobých pilotovaných misí mimo nízkou oběžnou dráhu kolem Země. Projektové záměry je nutné odevzdat do 27. října 2017.
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
22.8.2017 14:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztah-(1)Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
22.8.2017 14:07 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vyškov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostemVrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
22.8.2017 14:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vyškovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Hledáme nového kolegu na pozici Programátor a architekt mapových aplikací, certifikovaný Google Maps Developer
22.8.2017 13:35 CEDA Maps a.s. CEDA jako autorizovaný Google Maps Reseller pro oblast střední a východní Evropy hledá kolegu, jenž bude zastávat také roli certifikovaného Google Maps Developera pro podporu návrhu zákaznických projektů, samostatný návrh a vývoj aplikací s Google Maps API, Google Cloud Platform a dalšími mapovými a cloudovými službami.ESA otevře element InCubed pro podávání inovativních návrhů v oblasti EO
22.8.2017 13:34 Český Kosmický PortálAktualizace: živý přenos proběhne dne 6. září 2017 od 10:30 (CET), stream bude dostupný na adrese https://livestream.com/ESA/incubed
Dne 6. září 2017 se otevře výzva na předkládání návrhů projektů do elementu InCubed v programu Evropské kosmické agentury (ESA) Earth Watch, do něhož ČR vložila na ministerské radě ESA 2016 částku 1,5 MEUR. Cílem elementu je podpořit inovativní řešení s vysokým potenciálem komerčního uplatnění v oblasti pozorování Země. Do výzvy bude možné předložit projekty směřující jak k přípravě inovativních aplikací, tak i technologických řešení z oblasti pozorování Země. Element cílí především na firmy, avšak součástí konsorcia mohou být i akademické subjekty.
Podrobnosti výzvy budou následně vyvěšeny v tendrovém systému ESA EMITS.
ESA otevře element InCubed pro podávání inovativních návrhů v oblasti EO
22.8.2017 13:34 Český Kosmický PortálZáznam z otevření elementu InCubed je dostupný na adrese https://livestream.com/ESA/incubed
Dne 6. září 2017 se otevře výzva na předkládání návrhů projektů do elementu InCubed v programu Evropské kosmické agentury (ESA) Earth Watch, do něhož ČR vložila na ministerské radě ESA 2016 částku 1,5 MEUR. Cílem elementu je podpořit inovativní řešení s vysokým potenciálem komerčního uplatnění v oblasti pozorování Země. Do výzvy bude možné předložit projekty směřující jak k přípravě inovativních aplikací, tak i technologických řešení z oblasti pozorování Země. Element cílí především na firmy, avšak součástí konsorcia mohou být i akademické subjekty.
Podrobnosti výzvy budou následně vyvěšeny v tendrovém systému ESA EMITS.
ESA otevře element InCubed pro podávání inovativních návrhů v oblasti EO
22.8.2017 13:34 Český Kosmický PortálDne 6. září 2017 se otevře výzva na předkládání návrhů projektů do elementu InCubed v programu Evropské kosmické agentury (ESA) Earth Watch, do něhož ČR vložila na ministerské radě ESA 2016 částku 1,5 MEUR. Cílem elementu je podpořit inovativní řešení s vysokým potenciálem komerčního uplatnění v oblasti pozorování Země. Do výzvy bude možné předložit projekty směřující jak k přípravě inovativních aplikací, tak i technologických řešení z oblasti pozorování Země. Element cílí především na firmy, avšak součástí konsorcia mohou být i akademické subjekty.
Podrobnosti výzvy budou následně vyvěšeny v tendrovém systému ESA EMITS.
ESA otevře element InCubed pro podávání inovativních návrhů v oblasti EO
22.8.2017 13:34 Český Kosmický PortálDne 6. září 2017 se otevře výzva na předkládání návrhů projektů do elementu InCubed v programu Evropské kosmické agentury (ESA) Earth Watch, do něhož ČR vložila na ministerské radě ESA 2016 částku 1,5 MEUR. Cílem elementu je podpořit inovativní řešení s vysokým potenciálem komerčního uplatnění v oblasti pozorování Země. Do výzvy bude možné předložit projekty směřující jak k přípravě inovativních aplikací, tak i technologických řešení z oblasti pozorování Země. Element cílí především na firmy, avšak součástí konsorcia mohou být i akademické subjekty.
Podrobnosti výzvy budou následně vyvěšeny v tendrovém systému ESA EMITS.
Ample opportunities in Korea
22.8.2017 11:58 European GNSS Agency
Considering that Korea and the EU are amongst the largest car manufacturing regions in the world, there is immense potential for collaboration in the automotive telematics industry. The commercial vehicle telematics market experienced a growth rate of 5% over the last five years, as Hyundai and KIA increasingly turn to GNSS as an integral part of future Information Technology Services (ITS).
Korea also has one of the world’s most advanced LBS portfolios, driven by the country’s superior IT infrastructure, commercial based services and favourable regulatory environment.
Furthermore, the EU-South Korea Free Trade Agreement has eliminated duties for most industrial goods, further enhancing the business environment for European entities.
Add all of this up and you get ample opportunities in Korea for European GNSS companies.
Collaboration is key
In the road sector, many Korean automobile manufacturers and their IT/electronic partners are turning to European made chips and devices. The sector is also relying on EU experts for help with certification, testing and implementing – particularly as the country works towards adopting an eCall system of their own. And in the LBS sector, several Korean smartphone and electronic manufacturers are implementing Galileo capability into their devices.
To ensure European industry is able to take full advantage of opportunities like these, the GNSS.asia Korea team is on the ground working with companies and collaborating with organisations. The GSA-funded GNSS.asia project is dedicated to developing and implementing GNSS industrial cooperation between European and Asia-Pacific GNSS industries, with a focus on the downstream market. The initiative is part of the EU-Korea GNSS Cooperation Agreement of 2006.
For example, the team has a strong partnership with the Institute of Positioning, Navigation and Timing (IPNT) (formerly the Korean GNSS Society (KGS)), an organisation established to stimulate the GNSS field in academia and business. The two meet monthly to discuss national and international multi-GNSS activities and how they can better collaborate to address these issues.
One of the key outcomes of this partnership is an intensive match making programme between European companies and Korean customers and partners. Such companies as NavCert, Syntony F, 3M Systems, Thales, Catapult, Easymile and Enertopia have all benefited from this valuable initiative. GNSS.asia also helps European companies engage with Korean government officials and navigate the complex bureaucratic system.
Thanks to this close collaboration, several business results have been achieved. For instance, as Korea looks to implement their own eCall system, modelled off the European system, the two partners have successfully positioned the multi-constellation, Galileo-enabled chipset as the standard. They have also actively supported Korea SBAS to adopt European structures and systems – including getting Korea SBAS to choose Thales as their system provider.
Just getting started
The successes that EU companies are seeing in Korea are testament to the power of collaboration – and this is only the tip of the iceberg. “As the multi-GNSS initiatives in Korea continue to mature, we will see more and more opportunities for European businesses, particularly in the areas of Korea SBAS, eCall and eLoran,” says GNSS.asia Managing Director Hyemi Hwang. “And we’re just getting started.”
According to Hwang, in order to implement Korea SBAS, the Korean government and industry have a preference for European technology and applications. “This is why they ultimately chose to partner with Thales,” she says. “The Korean government is confident that this partnership will result in the introduction and implementation of massive, real-life applications in the area of autonomous driving, maritime security and safety, and LBS-based drones for security, agriculture, logistics, mapping, and media/entertainment.” Hwang adds that the Korean government is also leveraging EGNOS and European applications to help make their aviation sector more efficient.
Likewise, as the country works towards implementing eCall, it regularly refers to the European system as the standard and is constantly on the lookout for chances to collaborate more closely. “European companies should look to Korean partners in order to take full advantage of this unique business opportunity,” adds Hwang. “To get started, all you have to do is contact your GNSS.asia team here in Korea.”
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
20170822-VŘ Ředitel SCD
22.8.2017 10:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo Ředitel sekce centrální databáze katastru nemovitostí.Ředitel sekce centrální databáze katastru nemovitostí
22.8.2017 9:50 ČÚZK /Urady/Cesky-urad-zememericky-a-katastralni/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Reditel-sekce-centralni-databaze-katastru-nemovitoŘeditel sekce centrální databáze katastru nemovitostí
22.8.2017 9:50 ČÚZK - volná místa Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Ředitel sekce centrální databáze katastru nemovitostíŘeditel sekce centrální databáze katastru nemovitostí
22.8.2017 9:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnívypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Ředitel sekce centrální databáze katastru nemovitostí
Nedostupnost INSPIRE UML modelů
22.8.2017 8:01 CENIA - národní geoportál INSPIRE Ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 12:00 do 15:00 nebude z důvodu plánované údržby dostupný SVN sklad UML modelů datových specifikací INSPIRE.Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin v DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/187646Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že z technických důvodů nebudou ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopeníPřerušení provozu Sbírka listin DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že z technických důvodů nebudou ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopeníPřerušení provozu Sbírky listin DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že z technických důvodů nebudou ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopeníPřerušení provozu Sbírky listin v DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že z technických důvodů nebudou ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopeníPřerušení provozu Sbírky listin v DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že z technických důvodů nebudou ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopeníPřerušení provozu Sbírka listin DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/187646Přerušení provozu Sbírka listin DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že z technických důvodů nebudou ve čtvrtek 24.8.2017 od 16:30 do cca 22:00 dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopeníPřerušení provozu Sbírky listin DP 24.8.2017.
22.8.2017 6:52 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/187646Oznámení o částečném omezení provozu Pobočky Trutnov
22.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Z důvodu přerušení dodávky elektřiny bude ve čtvrtek 31. 8. 2017 od 7:30 do 10:30 hod. částečně omezen provoz Pobočky Trutnov (KPÚ pro Královéhradecký kraj).Zemřel Ing. Jiří Antropius.
21.8.2017 23:50 Zeměměřič Poslední rozloučení bude ve středu 23. srpna 2017 ve 14 hodin v malé obřadní síni krematoria v Praze - Stranicích.Sdílení kritických informací v rámci integrovaného záchranného systému
21.8.2017 15:35 T-MAPYThe post Sdílení kritických informací v rámci integrovaného záchranného systému appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
odborný referent/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu, Technický odbor
21.8.2017 12:56 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-–-obnova-katastraodborný referent/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu, Technický odbor
21.8.2017 12:56 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu, Technický odborodborný referent/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu, Technický odbor
21.8.2017 12:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu, Technický odbor
Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů
21.8.2017 9:13 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-(2)Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů
21.8.2017 9:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů
Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahů
21.8.2017 9:13 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Liberec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení právních vztahůMetroprojekt testuje automatizaci v inženýringu
21.8.2017 7:50 GeoBusinessProjekční firma Metroprojekt Praha testuje v pilotním provozu automatizovanou komunikaci s vlastníky pozemků při projektování staveb. Před výstavbou předchází často komplikovaná korespondence s vlastníky pozemků a nemovitostí, kterých se bude budoucí stavba…
The post Metroprojekt testuje automatizaci v inženýringu appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Kam jezdí stále více turistů v Česku?
21.8.2017 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Datoví žurnalisté z Českého rozhlasu čas od času publikují geodata v zajímavých souvislostech. V jednom ze svých posledních příspěvků se zaměřili na vývoj návštěvnosti českých regionů za posledních 5 let, a to na základě dat ČSÚ o počtu přenocování hostů ubytovacíchPrvní Hackathon veřejné správy
21.8.2017 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformaceV pátek 15. a v sobotu 16. září 2017 se v budově Nejvyššího kontrolního úřadu (Jankovcova 1518/2, 170 04 Praha 7) uskuteční první Hackathon veřejné správy, na jehož organizaci se podílí několik státních institucí.
Registrovat je možné se přímo na webu akce, na kterém nalezete rovněž program na oba dva dny a seznam datových sad, které budou účastníkům
Památky Jihomoravského kraje
21.8.2017 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Památky UNESCO, Národní kulturní památky, Kulturní památky, Památkové zóny a rezervace, Krajinné památkové zóny, Muzea a galerieOznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení metodiky pozemkových úprav
21.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Ústřední ředitelka Státního pozemkového úřadu, jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě (dále jen „zákon“), vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení metodiky pozemkových úprav.Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení správy majetku státu, Krajský pozemkový úřad pro Plzeňský kraj
21.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Ústřední ředitelka Státního pozemkového úřadu, jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě (dále jen „zákon“), vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení správy majetku státu, Krajský pozemkový úřad pro Plzeňský kraj.Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení výkonu auditu
21.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Ústřední ředitelka Státního pozemkového úřadu, jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě (dále jen „zákon“), vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení výkonu auditu.Vrchní odborný referent specialista oddělení investičních činností a programového financování
21.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Státní pozemkový úřad přijme zaměstnance na pozici vrchní odborný referent specialista oddělení investičních činností a programového financování.Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada, Pobočka Jeseník
21.8.2017 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Ústřední ředitelka Státního pozemkového úřadu, jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě (dále jen „zákon“), vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo rada/odborný rada, Pobočka Jeseník.Zaměření podzemních kolektorů v areálu cementárny Radotín
18.8.2017 14:30 HrdličkaSíť podzemních elektrokanálů byla v areálu cementárny budována postupně v průběhu několika desítek let. Bohužel se od nich nezachovala prakticky žádná použitelná dokumentace, což se ukázalo jako velmi problematické v okamžiku, kdy bylo třeba zpracovat nový požární plán závodu. Do značně rozvětvené sítě podzemních tunelů v délce přes půl kilometru existují dva hlavní vstupy, které... View Article
The post Zaměření podzemních kolektorů v areálu cementárny Radotín appeared first on HRDLIČKA spol. s r.o. - komplexní služby v oblasti geodézie.
V mapové aplikaci Územně pláno
18.8.2017 12:00 Jihočeský kraj V mapové aplikaci Územně plánovací dokumentace obcí byla aktualizována územně plánovací dokumentace obcí Bechyně, Borek, Hlavatce (Soběslav), Veselí nad Lužnicí a Strážný.V mapové aplikaci byla aktual
18.8.2017 12:00 Jihočeský kraj V mapové aplikaci byla aktualizována územně plánovací dokumentace obcí Bechyně, Borek, Hlavatce (Soběslav), Veselí nad Lužnicí a Strážný.20170818 - volné místo - Odborný referent v oddělení podpory ICT v technickém odboru
18.8.2017 10:51 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-podpory-ICT-v-technick20170818 - volné místo - Odborný referent v oddělení podpory ICT v technickém odboru
18.8.2017 10:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného pracovního místa - Odborný referent v oddělení podpory ICT v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký krajOdborný referent v oddělení podpory ICT v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
18.8.2017 10:48 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení podpory ICT v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký krajPracovní příležitosti
17.8.2017 16:59Hledáme absolventy SŠ a VŠ na pozice:
• projektant dopravních staveb (polní cesty, místní komunikace)
• projektant vodohospodářských staveb (malé vodní nádrže, poldry ...)
• operátor letecké měřické kamery
Nabízíme práci v mladém kolektivu se špičkovým vybavením a možností seberealizace. V případě vašeho zájmu piště nebo volejte na:
e-mail: georeal@georeal.cz
Tel.: 377 237 343
GSM: 602 452 607
Pracovní příležitosti
17.8.2017 16:59Hledáme absolventy SŠ a VŠ na pozice:
• projektant dopravních staveb (polní cesty, místní komunikace)
• projektant vodohospodářských staveb (malé vodní nádrže, poldry ...)
• operátor letecké měřické kamery
Nabízíme práci v mladém kolektivu se špičkovým vybavením a možností seberealizace. V případě vašeho zájmu piště nebo volejte na:
e-mail: georeal@georeal.cz
Tel.: 377 237 343
GSM: 602 452 607
Pracovní příležitosti
17.8.2017 16:59Hledáme absolventy SŠ a VŠ na pozice:
• projektant dopravních staveb (polní cesty, místní komunikace)
• projektant vodohospodářských staveb (malé vodní nádrže, poldry ...)
• geodet (SŠ, VŠ) ...
• projektant krajinného inženýrství a vodního hospodářství (VŠ)
• operátor letecké měřické kamery
Nabízíme práci v mladém kolektivu se špičkovým vybavením a možností seberealizace. V případě vašeho zájmu piště nebo volejte na:
Sentinel-1 speeds up crop insurance payouts
17.8.2017 13:51 ESA Observing the Earth
For the first time in India, a state government is using satellites to assess lost crops so that farmers can benefit from speedy insurance payouts.
V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kra
17.8.2017 12:00 Ústecký kraj V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kraje byla provedena aktualizace údajů pro poskytovatele NET4GAS, s.r.o. – jev 73, 74, 75, 82, Česká telekomunikační infrastruktura a.s. – jev 81, 82, ČEZ Distribuce, a. s. – jev 72, 73, Telco Pro Services, a. s. – jev 82Obnovení provozu Sbírky listin v DP.
17.8.2017 9:52 Dálkový přístup k údajům KN ČR Vážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že provoz poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin byl obnoven. Za komplikace přerušením provozu způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.Obnovení provozu Sbírky listin v DP.
17.8.2017 9:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníVážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že provoz poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin byl obnoven. Za komplikace přerušením provozu způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Obnovení provozu Sbírka listin DP.
17.8.2017 9:52 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/187102Obnovení provozu Sbírka listin DP.
17.8.2017 9:52 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníVážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že provoz poskytování dokumentů ze Sbírky listin byl obnoven. Za komplikace přerušením provozu způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
Obnovení provozu Sbírky listin v DP.
17.8.2017 9:52 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/187102Připomeňte si poslední tipy a triky
17.8.2017 9:51 ARCDATATým technické podpory se v posledních týdnech věnoval celé řadě zajímavých témat, jako byly hostované feature služby, možnosti úpravy vyskakovacích oken pomocí jazyka Arcade nebo definice umístění obrázku, využití prémiového obsahu ve vlastních aplikacích a dalšímu.
- Jak obnovit obsah ArcGIS Enterprise ze zálohy
- Jak umístit obrázek do horní části vyskakovacího okna
- Synchronizace parametru OPEN_CURSORS mezi Oracle a geodatabází 10.5
- Změna schématu hostované feature služby na ArcGIS Online
- Prémiový obsah v aplikaci Web AppBuilder for ArcGIS
- Výrazový jazyk Arcade ve vyskakovacích oknech ArcGIS Online
- Automatické publikování rastrových dlaždic z vrstvy prvků
Odborný rada - inspektor (technik) ZKI v Praze
17.8.2017 9:29 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Praze vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada - inspektor (technik) ZKI v PrazeOdborný rada - inspektor (technik) ZKI v Praze
17.8.2017 9:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Praze/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-rada-inspektor-(technik)-ZKI-v-PrazeOdborný rada - inspektor (technik) ZKI v Praze
17.8.2017 9:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Prazevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada - inspektor (technik) ZKI v Praze
Odborný rada - inspektor (právník) ZKI v Praze
17.8.2017 9:28 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Praze/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-rada-inspektor-(pravnik)-ZKI-v-PrazeOdborný rada - inspektor (právník) ZKI v Praze
17.8.2017 9:28 ČÚZK - volná místa Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Praze vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný rada - inspektor (právník) ZKI v PrazeOdborný rada - inspektor (právník) ZKI v Praze
17.8.2017 9:28 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Prazevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný rada - inspektor (právník) ZKI v Praze
Sledování sluneční erupce napříč Sluneční soustavou
17.8.2017 8:12 Český Kosmický PortálDeset kosmických sond od Venus Express (ESA) až po Voyager 2 (NASA) pocítilo následky sluneční erupce, která se prohnala naší Sluneční soustavou. Další tři družice pak událost sledovaly. Všechny dohromady pak nabídly unikátní pohled na tento jev kosmického počasí.
Sledování sluneční erupce napříč Sluneční soustavou
17.8.2017 8:12 Český Kosmický PortálDeset kosmických sond od Venus Express (ESA) až po Voyager 2 (NASA) pocítilo následky sluneční erupce, která se prohnala naší Sluneční soustavou. Další tři družice pak událost sledovaly. Všechny dohromady pak nabídly unikátní pohled na tento jev kosmického počasí.
Přerušení provozu Sbírka listin DP.
17.8.2017 7:37 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/186996Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin v DP.
17.8.2017 7:37 ČÚZK /Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Aplikace-DP-do-KN/Archiv-DP/186996Přerušení provozu Sbírky listin v DP.
17.8.2017 7:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníVážení uživatelé, oznamujeme, že ve čtvrtek 17.8.2017 nejsou z provozních důvodů dostupné dokumenty ze Sbírky listin. Na obnovaní provozu intenzivně pracujeme. Za komplikace tímto způsobené se omlouváme a děkujeme za pochopení.
















