zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Ve dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP
27.2.2023 21:19 Společnost pro fotogrammetrii a dálkový průzkum Ve dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP v novém kampusu Univerzity J. E. Purkyně v Ústí nad Labem. Účastníky přivítal děkan Fakulty životního prostředí představením fakulty a pracoviště Katedry informatiky a geoinformatiky (KGI). Následovala prezentace techniky a praktických výstupů výzkumu v prostorách KGI, dále prohlídka nového kampusu. Po obědě proběhl cyklus velice zajímavých odborných přednášek, zaměřených na prezentaci výzkumu na katedře. Pozdní odpoledne a večer proběhl společenský večer v prostorách Univerzity, kde jsme oslavili prezidenství paní prof. Leny Halounové z NICE. Ve středu proběhla plánovaná plavba lodí kaňonem Labem včetně občerstvení, část účastníků se do přístavu dostala trasou z OC Fóra lanovkou na výletní zámeček Větruše a do přístavu chůzí po NS Větruše – Vrkoč přes Vaňovské vodopády (délka trasy ca 5.5 km).Ve dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP
27.2.2023 21:19 Společnost pro fotogrammetrii a dálkový průzkumVe dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP v novém kampusu Univerzity J. E. Purkyně v Ústí nad Labem. Účastníky přivítal děkan Fakulty životního prostředí představením fakulty a pracoviště Katedry informatiky a geoinformatiky (KGI). Následovala prezentace techniky a praktických výstupů výzkumu v prostorách KGI, dále prohlídka nového kampusu. Po obědě proběhl cyklus velice zajímavých odborných přednášek, zaměřených na prezentaci výzkumu na katedře. Pozdní odpoledne a večer proběhl společenský večer v prostorách Univerzity, kde jsme oslavili prezidenství paní prof. Leny Halounové z NICE. Ve středu proběhla plánovaná plavba lodí kaňonem Labem včetně občerstvení, část účastníků se do přístavu dostala trasou z OC Fóra lanovkou na výletní zámeček Větruše a do přístavu chůzí po NS Větruše – Vrkoč přes Vaňovské vodopády (délka trasy ca 5.5 km).
The post Ve dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP appeared first on SFDP.
Ve dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP
27.2.2023 21:19 Společnost pro fotogrammetrii a dálkový průzkum Ve dnech 21. – 22. 6. 2022 proběhlo 83. setkání pražských fotogrammetrů a členů SFDP v novém kampusu Univerzity J. E. Purkyně v Ústí nad Labem. Účastníky přivítal děkan Fakulty životního...Antarctic Peninsula glaciers on the run
27.2.2023 17:00 ESA Observing the Earth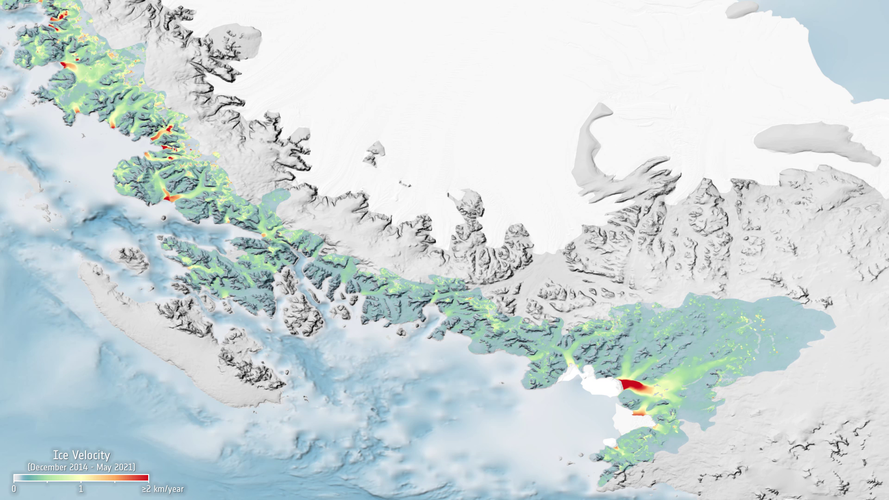
Like many places, the Antarctic Peninsula is falling victim to rising temperatures. However, when scientists used radar images from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission acquired between 2014 and 2021, they were taken aback to discover just how the fast 105 glaciers on the west coast are flowing in the summer months.
Telling time on the Moon
27.2.2023 14:30 ESA Navigation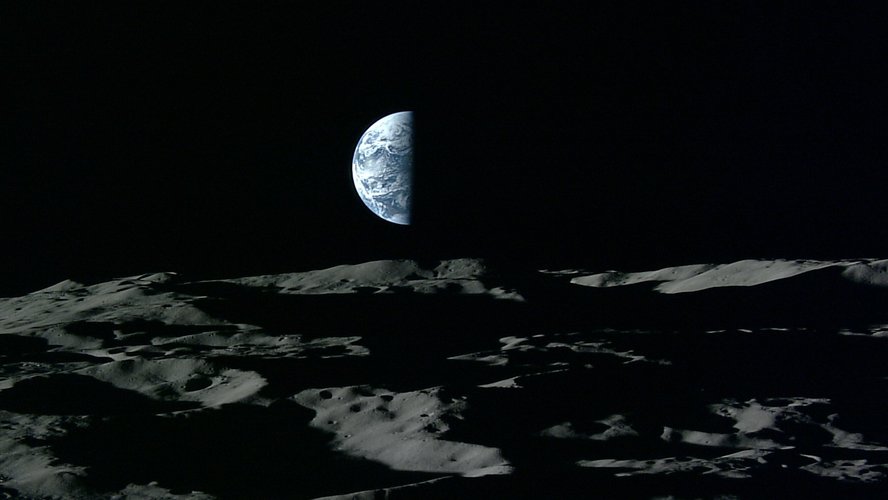
A new era of lunar exploration is on the rise, with dozens of Moon missions planned for the coming decade. Europe is in the forefront here, contributing to building the Gateway lunar station and the Orion spacecraft – set to return humans to our natural satellite – as well as developing its large logistic lunar lander, known as Argonaut. As dozens of missions will be operating on and around the Moon and needing to communicate together and fix their positions independently from Earth, this new era will require its own time.
Leica Tour 6.-16.3.2023
27.2.2023 14:16 GEFOS Pozvánka na tradiční prezentační akci technologií Leica Geosystems AG. 8 prezentací v 8-mi městech. Přijďte se podívat!Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Vyškov
27.2.2023 14:11 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vrchni-referent-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Vyškov
27.2.2023 14:11 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Vyškov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti VyškovVrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Vyškov
27.2.2023 14:11 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Vyškovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Vyškov
25. jednání KRS
27.2.2023 12:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 22. března 2023 proběhne distančně 25. jednání Koordinační rady správců DMVS a DTM.Připomínka kartografického dne
27.2.2023 9:21 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucPřipomeňte si páteční 17. Kartografický den Olomouc krátkém video spotu a fotografiích od Davida Motlíčka: dejfix.cz/17KDO Všem děkujeme za krásný den plný map a zajímavých informací ze zpravodajství ☺️
The post Připomínka kartografického dne appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 9:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Rada/odborný rada v právním oddělení č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
27.2.2023 8:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-městovypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada v právním oddělení č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
Rada/odborný rada v právním oddělení č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
27.2.2023 8:32 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Brno-město vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada v právním oddělení č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - městoRada/odborný rada v právním oddělení č.1 na Katastrálním pracovišti Brno - město
27.2.2023 8:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-v-pravnim-oddeleni-c-1-na-Ka-(1)Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 8:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 8:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 8:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 8:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
Novinky v aplikacích
27.2.2023 8:05 ČÚZK - Geoportál Novinky v aplikacích- Aplikace Geoprohlížeč, Archiv, Analýzy výškopisu a Jména světa fungují na nové verzi API 4.26. Došlo ke změně názvu API z "ArcGIS API for Javascript" na "ArcGIS Maps SDK for JavaScript".
- Ve všech aplikacích je dostupný nový widget Nastavení, který dává různým aplikacím různé možnosti uživatelského prostředí nebo chování po spuštění, například lze nastavit výchozí zdroj vyhledávání či měnit jazykové verze. V Geoprohlížeči si lze přizpůsobit výchozí obsah Seznamu vrstev.
- V aplikaci Geoprohlížeč je Hlášení chyb k dispozici přímo z vyskakovacího okna po kliknutí do mapy.
- V mapových kompozicích Geoprohlížeče se již nepoužívá prohlížecí služba Vektorového souboru správních hranic (VSH), je nahrazena službou z dat RÚIAN. Služba VSH již nebude od 1. 4. 2023 publikována.
- V aplikaci Archiv lze jako Doplněk pro Archivní mapy zapnout mapu Slovenské republiky, což usnadní vyhledávání některých archivních fondů.
DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo
26.2.2023 13:39 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
máme pro Vás akční nabídku propojení DAEX CUT Optimalizátor Professional s pilou Altendorf HAND CUARDE a Altendorf Elmo.
DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo
26.2.2023 13:39 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
máme pro Vás připraveno akční nabídku propojení DAEX CUT Optimalizátor Professional s pilou Altendorf HAND CUARDE a Altendorf Elmo.
The post DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo
26.2.2023 13:39 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
máme pro Vás akční nabídku propojení DAEX CUT Optimalizátor Professional s pilou Altendorf HAND CUARDE a Altendorf Elmo.
The post DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo
26.2.2023 13:39 ŠPINAR - softwareVážení zákazníci,
máme pro Vás připraveno akční nabídku na upgrade programů TurboCAD Platinum 28 CZ a TurboCAD Deluxe CZ.
The post DAEX CUT Optimalizátor – efektivní propojení s pilou Altendorf HAND GUARDE a Altendorf Elmo appeared first on ŠPINAR – software.
Zm�na cen software a slu�eb spole�nosti GISOFT (17.1.2023)
24.2.2023 17:44 GISoftV souvislosti se v�eobecnou situac� jsme nuceni p�istoupit k �prav� cen na�ich softwar�. Nov� ceny naleznete v na�em cen�ku.
Zm�na cen software a slu�eb spole�nosti GISOFT (17.1.2023)
24.2.2023 17:44 GISoftV souvislosti se v�eobecnou situac� jsme nuceni p�istoupit k �prav� cen na�ich softwar�. Nov� ceny naleznete v na�em cen�ku.
Zaměření a zpracování dat z dronu pro měřické práce v geodézii.
24.2.2023 13:17 3gon Zveme každého zájemce, který se zajímá o problematiku bezpilotních letounů DJI Enterprise na workshop organizovaný společností 3gon positioning. AkceZaměření a zpracování dat z dronu pro měřické práce v geodézii.
24.2.2023 13:17 3gon Zveme každého zájemce, který se zajímá o problematiku bezpilotních letounů DJI Enterprise na workshop organizovaný společností 3gon positioning. Akce se konáZaměření a zpracování dat z dronu pro měřické práce v geodézii.
24.2.2023 13:17 3gon Zveme každého zájemce, který se zajímá o problematiku bezpilotních letounů DJI Enterprise na workshop organizovaný společností 3gon positioning.ESA invites you to satnav summer school in Sweden
24.2.2023 13:17 ESA Navigation
This year’s ESA/JRC International Summer School on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) will take place in July in Kiruna, Sweden.
Servery
24.2.2023 12:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatřeníČeský úřad zeměměřický a katastrální nabízí nepotřebný majetek k odkupu. Jedná se o
Servery
Metodické pomůcky v oboru zeměměřictví a katastru
24.2.2023 10:22 ČÚZK /Zememerictvi/Zememericke-cinnosti/Aktuality-pro-zememerice/2023/Metodicke-pomucky-v-oboru-zememerictvi-a-katastruMetodické pomůcky v oboru zeměměřictví a katastru
24.2.2023 10:22 ČÚZK - RSS kanál pro zeměměřiče Oznamujeme, že byla zveřejněna verze 1.2 Metodické pomůcky Vzory geometrických plánů. Metodická pomůcka je nově umístěna na stránce Metodické pomůcky v oboru zeměměřictví a katastru, kde budou společně zveřejňovány vybrané metodické pomůcky, a budou tak pro lepší orientaci vedeny odděleně od stanovisek k aplikaci katastrální vyhlášky. Odkaz na stránku najdete rovněž v sekci "Zeměměřictví/Zeměměřické činnosti" pod částí "Právní a technické předpisy".Metodické pomůcky v oboru zeměměřictví a katastru
24.2.2023 10:22 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznamujeme, že byla zveřejněna verze 1.2 Metodické pomůcky Vzory geometrických plánů. Metodická pomůcka je nově umístěna na stránce Metodické pomůcky v oboru zeměměřictví a katastru, kde budou společně zveřejňovány vybrané metodické pomůcky, a budou tak pro lepší orientaci vedeny odděleně od stanovisek k aplikaci katastrální vyhlášky. Odkaz na stránku najdete rovněž v sekci "Zeměměřictví/Zeměměřické činnosti" pod částí "Právní a technické předpisy".Earth from Space: The Triple Frontier
24.2.2023 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth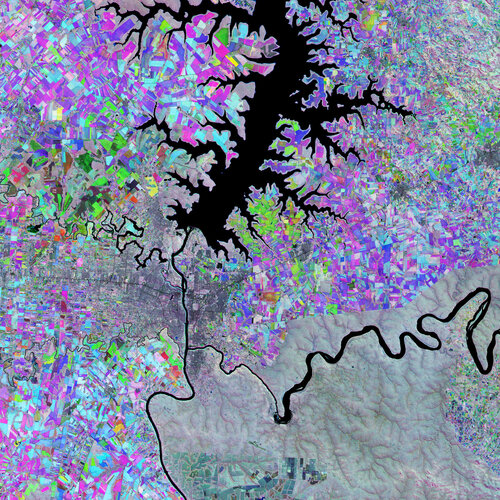 Image:
The Triple Frontier, a region where Paraguay, Brazil and Argentina meet, is featured in this false-colour image, captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Image:
The Triple Frontier, a region where Paraguay, Brazil and Argentina meet, is featured in this false-colour image, captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Vyšla aktualizovaná verze ArcGIS Pro 3.1
24.2.2023 9:50 ARCDATATento týden vyšla aktualizace ArcGIS Pro 3.1. Obsahuje mnoho vylepšení a také na 60 zapracovaných nápadů, které uživatelé navrhují na stránkách ArcGIS Ideas. Instalační soubory si můžete stáhnout na stránce My Esri v sekci Stahování.
Co nového v této verzi například najdete?
Vrstvy katalogu (Catalog layers)
Vrstva katalogu je kolekce odkazů na různorodé typy datových zdrojů, které se pak chovají jako jedna logická vrstva. Umožňuje tak pohodlněji pracovat s daty uloženými na několika místech a v různých formátech. Vrstvám v katalogu můžete zobrazit jejich rozsahy, aplikovat na ně různé filtry a podobně. Více si přečtěte na stránce o Catalog layers.
Okno Lupa
Oblíbenou funkcionalitu z aplikace ArcMap naleznete už i v ArcGIS Pro. Můžete si vyvolat okno, které zobrazí určité území ve větším detailu. Budou v něm fungovat nástroje pro výběr, měření a editaci. (Ikonu pro otevření okna lupy naleznete zcea vpravo na kartě nástrojů View.)
Snazší přístup ke složkám
V okně Katalogu přibyla záložka Počítač (Computer), ve které najdete přístup ke všem složkám v počítači včetně zkratek, jako jsou např. Dokumenty.
Podpora času ve vrstvách scény
Co je nového v časových datech? S časem můžete nyní pracovat i ve vrstvách scén s 3D body, 3D objekty a budovami. Můžete také ve scéně nastavit meze posuvníku rozsahu (Range) v různých časových intervalech, lze definovat preferovanou časovou zónu při publikaci vrstvy na portál a také je možné nastavit fixní čas pro celou vrstvu, která nemá žádné atributové pole, které by se dalo použít k definici času.
Duplikování výkresu
Tato novinka se může hodit každému, kdo potřebuje vytvořit mapu v různých velikostech. Zjednodušilo se duplikování výkresu, a navíc je možné duplikát vytvořit na jiném formátu papíru. A pokud budete chtít, automaticky se přizpůsobí i velikost všech symbolů.
Vylepšení v nastavení symbolů
Mezi zajímavé novinky v nastavení symbolů patří například možnost určit pořadí, v jakém se prvky ve vrstvě vykreslují. Pořadí se může řídit numerickým nebo textovým polem i časovým údajem.
Tvorbu symbolu usnadní i možnost importovat vrstvu z jiného symbolu uloženého ve stylu. Výplň vzorkem má nový parametr, který umožní zarovnat vzorek nikoli podle mapy, ale podle rotace okna, což se může hodit například při tvorbě mapové série. A již je možné manuálně přidávat kontrolní body, což jsou specifické body, které řídí symboliku (například se chovají jako „rohy“ pro přerušované čáry). To mimo jiné usnadní migraci kartografických reprezentací.
Při tvorbě legendy je nyní možné zobrazit pásek s barevným gradientem vodorovně a proporcionální symboly zobrazit „v sobě“.
Editace střech ve 3D
Díky novým nástrojům pro tvorbu střechy můžete hranatý model budovy snadno upravit na tvar, který více odpovídá skutečnosti.
Změna velikosti popisků v závislosti na měřítku
V rámci jediné třídy popisku můžete definovat velikosti popisku v různých měřítkách.
Vychytávky v geoprocessingu
V rolovací nabídce s výpisem atributových polí, kterou najdeme v mnoha nástrojích geoprocessingu, je nyní možné pole seřadit podle abecedy a vybrat, zda se budou ukazovat jména polí, nebo jejich aliasy.
U většiny nástrojů spotřebovávajících kredity si uživatel může nechat ukázat množství kreditů, které daná úloha spotřebuje. Nyní se může objevit i upozornění, že tato úloha může přečerpat dostupné množství kreditů.
V ModelBuilderu dostane každé okno s modelem vlastní malou nástrojovou lištu s nejpoužívanějšími příkazy.
Jednotlivé nástroje, pokud je otevřeme v samostatném okně, si pamatují polohu svého okna.
Zmínit také můžeme, že nástroj Append nově dovolí i aktualizovat prvky.
Podrobnosti o souřadnicovém systému
V informacích o souřadnicovém systému naleznete i grafické znázornění území, pro které je souřadnicový systém určený.
Něco pro administrátory
Administrátoři mohou omezit změny mnoha nastavení – například pro tvorbu indexů, styl metadat, engine pro popisky, způsob tvorby a umístění cache, cesty, výchozí databáze a sady nástrojů, šablony pro výkresy a mnoho dalšího. Je tak pro ně snazší udržovat větší množství ArcGIS Pro ve správném stavu.
Určitě si pročtěte stránku What's new in ArcGIS Pro 3.1, kde naleznete podrobný výpis všech novinek. Hodně se toho totiž do našeho přehledu nedostalo. Vydání české lokalizace pro ArcGIS Pro 3.1 je plánováno na konec března.
Pro další návody a tipy vám doporučujeme navštívit příspěvky kolegů z Technické podpory na platformě Esri Community.
Vyšla aktualizovaná verze ArcGIS Pro 3.1
24.2.2023 9:50 ARCDATATento týden vyšla aktualizace ArcGIS Pro 3.1. Obsahuje mnoho vylepšení a také na 60 zapracovaných nápadů, které uživatelé navrhují na stránkách ArcGIS Ideas. Instalační soubory si můžete stáhnout na stránce My Esri v sekci Stahování.
Co nového v této verzi například najdete?
Vrstvy katalogu (Catalog layers)
Vrstva katalogu je kolekce odkazů na různorodé typy datových zdrojů, které se pak chovají jako jedna logická vrstva. Umožňuje tak pohodlněji pracovat s daty uloženými na několika místech a v různých formátech. Vrstvám v katalogu můžete zobrazit jejich rozsahy, aplikovat na ně různé filtry a podobně. Více si přečtěte na stránce o Catalog layers.
Okno Lupa
Oblíbenou funkcionalitu z aplikace ArcMap naleznete už i v ArcGIS Pro. Můžete si vyvolat okno, které zobrazí určité území ve větším detailu. Budou v něm fungovat nástroje pro výběr, měření a editaci. (Ikonu pro otevření okna lupy naleznete zcela vpravo na kartě nástrojů View.)
Snazší přístup ke složkám
V okně Katalogu přibyla záložka Počítač (Computer), ve které najdete přístup ke všem složkám v počítači včetně zkratek, jako jsou např. Dokumenty.
Podpora času ve vrstvách scény
Co je nového v časových datech? S časem můžete nyní pracovat i ve vrstvách scén s 3D body, 3D objekty a budovami. Můžete také ve scéně nastavit meze posuvníku rozsahu (Range) v různých časových intervalech, lze definovat preferovanou časovou zónu při publikaci vrstvy na portál a také je možné nastavit fixní čas pro celou vrstvu, která nemá žádné atributové pole, které by se dalo použít k definici času.
Duplikování výkresu
Tato novinka se může hodit každému, kdo potřebuje vytvořit mapu v různých velikostech. Zjednodušilo se duplikování výkresu, a navíc je možné duplikát vytvořit na jiném formátu papíru. A pokud budete chtít, automaticky se přizpůsobí i velikost všech symbolů.
Vylepšení v nastavení symbolů
Mezi zajímavé novinky v nastavení symbolů patří například možnost určit pořadí, v jakém se prvky ve vrstvě vykreslují. Pořadí se může řídit numerickým nebo textovým polem i časovým údajem.
Tvorbu symbolu usnadní i možnost importovat vrstvu z jiného symbolu uloženého ve stylu. Výplň vzorkem má nový parametr, který umožní zarovnat vzorek nikoli podle mapy, ale podle rotace okna, což se může hodit například při tvorbě mapové série. A již je možné manuálně přidávat kontrolní body, což jsou specifické body, které řídí symboliku (například se chovají jako „rohy“ pro přerušované čáry). To mimo jiné usnadní migraci kartografických reprezentací.
Při tvorbě legendy je nyní možné zobrazit pásek s barevným gradientem vodorovně a proporcionální symboly zobrazit „v sobě“.
Editace střech ve 3D
Díky novým nástrojům pro tvorbu střechy můžete hranatý model budovy snadno upravit na tvar, který více odpovídá skutečnosti.
Změna velikosti popisků v závislosti na měřítku
V rámci jediné třídy popisku můžete definovat velikosti popisku v různých měřítkách.
Vychytávky v geoprocessingu
V rolovací nabídce s výpisem atributových polí, kterou najdeme v mnoha nástrojích geoprocessingu, je nyní možné pole seřadit podle abecedy a vybrat, zda se budou ukazovat jména polí, nebo jejich aliasy.
U většiny nástrojů spotřebovávajících kredity si uživatel může nechat ukázat množství kreditů, které daná úloha spotřebuje. Nyní se může objevit i upozornění, že tato úloha může přečerpat dostupné množství kreditů.
V ModelBuilderu dostane každé okno s modelem vlastní malou nástrojovou lištu s nejpoužívanějšími příkazy.
Jednotlivé nástroje, pokud je otevřeme v samostatném okně, si pamatují polohu svého okna.
Zmínit také můžeme, že nástroj Append nově dovolí i aktualizovat prvky.
Podrobnosti o souřadnicovém systému
V informacích o souřadnicovém systému naleznete i grafické znázornění území, pro které je souřadnicový systém určený.
Něco pro administrátory
Administrátoři mohou omezit změny mnoha nastavení – například pro tvorbu indexů, styl metadat, engine pro popisky, způsob tvorby a umístění cache, cesty, výchozí databáze a sady nástrojů, šablony pro výkresy a mnoho dalšího. Je tak pro ně snazší udržovat větší množství ArcGIS Pro ve správném stavu.
Určitě si pročtěte stránku What's new in ArcGIS Pro 3.1, kde naleznete podrobný výpis všech novinek. Hodně se toho totiž do našeho přehledu nedostalo. Vydání české lokalizace pro ArcGIS Pro 3.1 je plánováno na konec března.
Pro další návody a tipy vám doporučujeme navštívit příspěvky kolegů z Technické podpory na platformě Esri Community.
Gardelsovu cenu získal Steve Liang, průkopník používání webových standardů pro geodata
23.2.2023 22:02 GeoBusinessNa zasedání členů konsorcia Open Geospatial (OGC, Open Geospatial Consorcium), které se tentokrát konalo 23. února v italském Frascati, byla Stevu Liangovi udělena prestižní cena OGC Kenneth D. Gardels Award. Gardelsova cena je od roku 1999 udělována osobnosti, která se mimořádně zasloužila o rozvoj vize OGC. Steve Liang, profesor a Rogers IoT Research Chair na […]
The post Gardelsovu cenu získal Steve Liang, průkopník používání webových standardů pro geodata appeared first on GeoBusiness.
rada/odborný rada - rozhodování o povolení vkladu v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katas
23.2.2023 14:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jindřichův Hradecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
rada/odborný rada - rozhodování o povolení vkladu v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Jindřichův Hradec (ID SM: 30000179/30003803)
Zpravodaj ČKS 1/2023
23.2.2023 14:34 Česká kartografická společnostPřinášíme první číslo Zpravodaje 2023.
The post Zpravodaj ČKS 1/2023 first appeared on Česká kartografická společnost.
ESA’s forest satellite robust for launch
23.2.2023 14:00 ESA Observing the Earth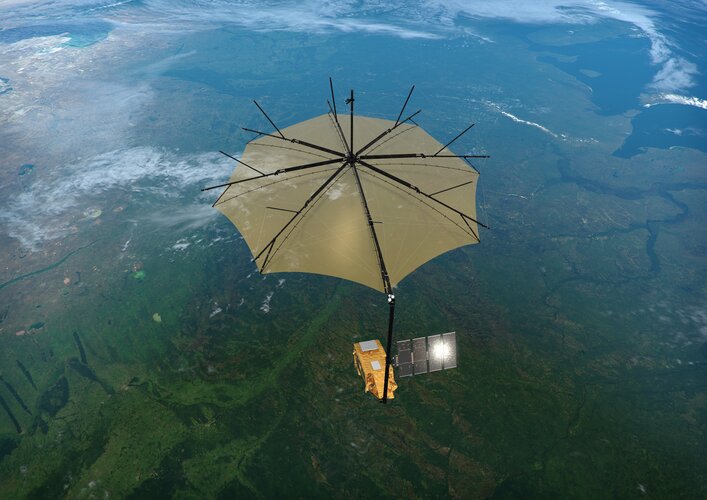
Over the last few months, ESA’s Earth Explorer Biomass satellite has been going through a punishing series of tests to make sure that it will survive the unavoidable blasts of noise and shuddering during liftoff. Engineers have now also tested that it will unfold its solar wing in the correct sequence. Coming through all of this with flying colours, Biomass is a few steps closer to its mission in orbit: to deliver completely new information on our precious forests and the carbon they store.
Ukončení provozu vybraných georeportů
23.2.2023 13:54 CENIA - národní geoportál INSPIRE Vážení uživatelé Národní geoportálu INSPIRE, tímto Vám oznamujeme, že od 23. 2. 2023 byl na Národním Geoportálu INSPIRE ukončen provoz georeportů zaměřených na oblast životního prostředí. Důvodem je stáří aplikace, kterou již nebylo možné aktualizovat. Děkujeme za pochopení.návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec (ID SM
23.2.2023 13:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jindřichův Hradecvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec (ID SM 30000190/30003814)
návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec (ID SM
23.2.2023 13:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/navrh-zapisu-v-katastru-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-KN-návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec (ID SM
23.2.2023 13:45 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo návrh zápisu v katastru v oddělení aktualizace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Jindřichův Hradec (ID SMThe ozone layer: a hole new world
23.2.2023 13:00 ESA Observing the Earth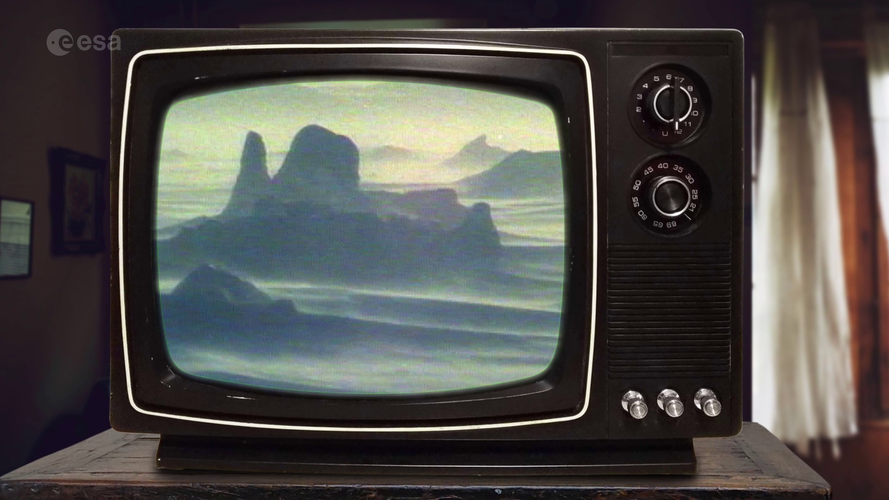 Video:
00:08:47
Video:
00:08:47
In the 1980s, scientists discovered a gaping hole in Earth's ozone layer, caused by humanmade chemicals. But thanks to the historical Montreal Protocol, the world came together to take bold action to save our planet. Decades later, we can see the steady recovery of the ozone hole. How did we do it? And what does space have to do with it? Join us as we explore the journey of the ozone hole, from its alarming discovery to the incredible strides made to fix it, and how satellites are helping us track its recovery.
The ozone layer: a whole new world
23.2.2023 13:00 ESA Observing the Earth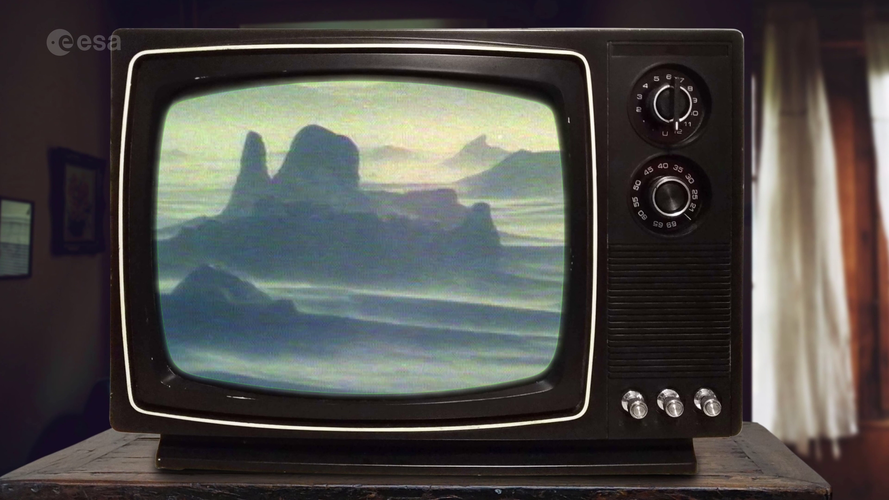 Video:
00:08:47
Video:
00:08:47
In the 1980s, scientists discovered a gaping hole in Earth's ozone layer, caused by humanmade chemicals. But thanks to the historical Montreal Protocol, the world came together to take bold action to save our planet. Decades later, we can see the steady recovery of the ozone hole. How did we do it? And what does space have to do with it? Join us as we explore the journey of the ozone hole, from its alarming discovery to the incredible strides made to fix it, and how satellites are helping us track its recovery.
Krátka správa č. 9/2023
23.2.2023 12:51 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 9/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Krátka správa č. 8/2023
23.2.2023 12:49 Komora geodetů a kartografů SRThe post Krátka správa č. 8/2023 appeared first on Komora geodetov a kartografov.
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
23.2.2023 11:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok
2023
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
23.2.2023 11:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2023Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2022
23.2.2023 11:40 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok
2022
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2022
23.2.2023 11:40 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2022Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2021
23.2.2023 11:39 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2021Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2021
23.2.2023 11:39 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok
2021
20230223_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
23.2.2023 11:01 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN"20230223_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení obnovy a revize KN
23.2.2023 11:01 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(5)Obsazení služebního místa
23.2.2023 9:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj oznamuje, že obsazuje služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu OKO0317 v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu 03040 na Odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu.Služební místo je obsazováno na dobu určitou v režimu pracovního poměru jako zástup po dobu pracovní neschopnosti.
Místem výkonu práce je Plzeň. Předpokládaný nástup: ihned nebo dle dohody. Služební místo je zařazeno do 9. platové třídy.
Obsazení služebního místa
23.2.2023 9:44 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Obsazeni-sluzebniho-mistaOznámení o výběru zástupu na služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu,
23.2.2023 9:35 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Oznámení o výběru zástupu na služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu,Oznámení o výběru zástupu na služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu,
23.2.2023 9:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj odbor obnovy katastrálního operátuvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Oznámení o výběru zástupu na služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu, KÚ pro Plzeňský kraj, Odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu
Oznámení o výběru zástupu na služební místo odborný/vrchní referent – obnova katastrálního operátu,
23.2.2023 9:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Volna-mista/DMS/Oznameni-o-vyberu-zastupu-na-sluzebni-misto-odbornBřeznový den s CAD/PDM expertem – bezplatná konzultace pro vaši firmu
22.2.2023 13:00 Arkance Systems17. března 2023 - přihlaste se na nový termín akce společnosti Arkance Systems. Těšíme se na vás.
Zpráva Březnový den s CAD/PDM expertem – bezplatná konzultace pro vaši firmu pochází z arkance-systems.cz.
Congrats to the first-round winners of the #myEUspace competition!
22.2.2023 12:35 European GNSS Agency
This year EUSPA’s signature competition had a new format. It invited entrepreneurs, innovators and start uppers to submit an idea, prototype, or commercial product. While the challenge was the same, to leverage EU space data and services from the EU space programme, this tweak in the rules of the competition incentivised more innovators to apply.
The #myEUspace competition is open to teams from all EU Member States plus Switzerland, Norway and Iceland and has a total prize of nearly EUR 1 million. In addition to the cash prize, the competition provides support to entrepreneurs throughout the entire innovation cycle, from early-stage start-ups to scale-ups.
Depending on the maturity of the solution at the time of submission, entrepreneurs can compete and win in three different innovation areas: Space My Life, Our Green Planet and Dive in Deep Tech.
‘’Our jury spent hours evaluating the first round of #myEUSpace which saw almost 100 ideas submitted. The stakes were high, and we saw many trailblazing ideas with great market potential,’’ says Justyna Redelkiewicz, Market, Downstream and Innovation department, EUSPA. ‘’Congratulations, not only to the winners, but also to those who had a go at our competition. More opportunities are coming, so don’t be disappointed.’’ she concludes.
Today, EUSPA announces the winners of the first #myEUspace track "Submission of an Idea". This track consists of promising theoretical ideas that leverage EU space data and have a high market potential. The best 15 ideas will receive a cash prize of EUR 10K each.
While the evaluation of the Prototypes’ track is ongoing, the competition remains open for the last track #myEUspace track "Submission of Products" with applications’ deadline 25 April 2023.See the full list of winners by area of innovation:
See the full list of winners by area of innovation:
Our Green Planet
- Spillalert: Intuitive web interface for oil spills and blackwater tank detection
- BugBit: Risk analysis platform for predicting and alerting of bark beetle outbreaks
- Push4CleanAir: SaaS pollution monitoring platform
- Detritus: Online platform and mobile app for waste-crime detection
- Orioos: Autonomous robotic solution for monitoring woody perennial crops
- Vantu: Van-lifers’ companion app to discover ‘off the beaten track’ sites to camp for the night
Dive in Deep Tech
- DeGenS: Decentralized Space-to-Ground Data Availability for AI using Blockchain
- Climate AI for Web3: Real-world portable climate API for virtual worlds powered by AI and satellite data
- Latitudo Supersar: AI analysis, classification and interpretation of multi-sensor and multi-mission images
- WhisperCash: Person to person payments via satellite for isolated regions
- Kyck: Geospatial metaverse platform for exploring and sharing AR experiences in the physical world
Space My Life
- Foremca: Cryptographic methodology providing forensic digital proof
- MicroPURA: Microbial Purity to detect levels of microbial contamination in the air
- Space4CC: Monitoring actions to safeguard cultural heritage in conflict areas
- Oasis City Lab: AI tool to track urban threats
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the EUSPA website (http://www.euspa.europa.eu).
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
22.2.2023 12:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2023Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2023
22.2.2023 12:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok
2023
Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2022
22.2.2023 12:24 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Rozpocet/Rozpocet-uradu-za-rok-2022Rozpočet úřadu za rok 2022
22.2.2023 12:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský krajvystavuje rozpočet úřadu za rok
2022
20232022_Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN
22.2.2023 12:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN"20232022_Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN
22.2.2023 12:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kolin/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizace-(1)Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN
22.2.2023 12:06 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Kolín vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KNOdborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN
22.2.2023 12:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Kolínvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent oddělení dokumentace KN
20230222_Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230208_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obno-(2)20230222_Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN"Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:39 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vrchni-referent-rada-oddeleni-obnovy-a-revize-KN-(Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:39 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:39 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KNZveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 20
22.2.2023 11:30 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Brnězveřejňuje obsah informace poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok
2023
Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 20
22.2.2023 11:30 ČÚZK /Urady/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericke-a-katastralni-inspektoraty/Zememericky-a-katastralni-inspektorat-v-Brne/Casto-hledane-informace/Poskytovani-informaci-106-1999-Sb/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(1)/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(7)20230222_Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN"20230222_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
22.2.2023 11:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230208_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obno-(1)20230222_Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
22.2.2023 11:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN "20230222_Vrchní referent / rada oddělení obnovy a revize KN
22.2.2023 11:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20230208_Odborny-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-obno-(1)Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
22.2.2023 11:10 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KNOdborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
22.2.2023 11:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
Odborný / vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace GI KN
22.2.2023 11:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Vrchni-referent-rada-oddeleni-obnovy-a-revize-KN20230222 - výběrové řízení na ředitele KP Ústí nad Labem
22.2.2023 9:56 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa ředitele/ ředitelky Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem.20230222 - výběrové řízení na ředitele KP Ústí nad Labem
22.2.2023 9:56 ČÚZK - aktuality v resortu Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa ředitele/ ředitelky Katastrálního pracoviště Ústí nad Labem.20230222 - výběrové řízení na ředitele KP Ústí nad Labem
22.2.2023 9:56 ČÚZK /Aktuality-resort/2023/20230222G++ (pozvánka)
22.2.2023 8:43 GISportal.cz
Studenti Geodézie a kartografie an ČVUT srdečně zvou na každoročně pořádanou kultovní geodetickou akci nazvanou G++, kterou pořádají studenti 1. ročníku magisterského studijního programu Geodézie a kartografie z Fakulty stavební ČVUT v Praze. Tato tradice vznikla již v roce 1991 a koná se pravidelně, pouze s pauzami v období 1995 až 2001 a 2020 až […]
The post G++ (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
G++ (pozvánka)
22.2.2023 8:43 GISportal.cz
Studenti Geodézie a kartografie an ČVUT srdečně zvou na každoročně pořádanou kultovní geodetickou akci nazvanou G++, kterou pořádají studenti 1. ročníku magisterského studijního programu Geodézie a kartografie z Fakulty stavební ČVUT v Praze. Tato tradice vznikla již v roce 1991 a koná se pravidelně, pouze s pauzami v období 1995 až 2001 a 2020 až […]
The post G++ (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Digitalizační centrum Ústřední knihovny UK [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
22.2.2023 0:00 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Digitalizační centrum Ústřední knihovny UK nabízí své služby interním i externím zákazníkům. Jedná se o digitalizaci dokumentů, metodickou podporu a školení a další doplňkové služby (např. čištění knih, ořez dokumentu a další).Digitalizační centrum Ústřední knihovny UK [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
22.2.2023 0:00 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Digitalizační centrum Ústřední knihovny UK nabízí služby interním i externím zákazníkům. Jedná se o služby digitalizace, metodické podpory a školení a další doplňkové služby (např. čištění knih, ořez dokumentu a další).20230221_odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nem.
21.2.2023 17:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(4)20230221_odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nem.
21.2.2023 17:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nemovitostem"odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
21.2.2023 17:44 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-popisn-(1)odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
21.2.2023 17:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
21.2.2023 17:44 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů20230221_odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nem.
21.2.2023 17:38 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nemovitostem"20230221_odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů k nem.
21.2.2023 17:38 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20210922_Odborny-referent-oddeleni-aktualizac-(3)odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
21.2.2023 17:37 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
21.2.2023 17:37 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-popisnych-odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahů
21.2.2023 17:37 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo odborný referent v oddělení aktualizace popisných informací odboru právních vztahůPředstavujeme nový produkt DTM Connect
21.2.2023 13:57 ARCDATAO projektu Digitální technické mapy České republiky pravděpodobně slyšela již většina z vás. Jedná se o centrální systém pro správu a využívání údajů o technické infrastruktuře pro území celé ČR a její příchod se rychle blíží. Využijte ji naplno i ve svém GIS díky našemu novému produktu DTM Connect.
Naše řešení poskytuje nástroje pro stažení dat DTM z Informačního systému Digitální mapy veřejné správy (IS DMVS) do ArcGIS a pro jejich nahrání zpět. Po načtení dat DTM do prostředí ArcGIS s nimi můžete pracovat stejně, jako s jakýmkoli jiným zdrojem dat. Můžete je využít k libovolným analýzám a vizualizacím (i ve 3D), při jejich správě a editaci se můžete spolehnout na pokročilé nástroje hlídající jejich topologickou správnost a díky mobilním aplikacím si je můžete vzít i do terénu.
Co vše DTM Connect dokáže?
- Na základě definičních souborů XSD Jednotného výměnného formátu DTM vytvořit souborovou geodatabázi obsahující datový model DTM.
- Import stavových i změnových dat (import dat lze prostorově omezit).
- Obohatit již existující data o další třídy prvků nebo kategorie.
- Zajistit import XML souborů, které jsou v odpovídající verzi Jednotného výměnného formátu DTM.
- Exportovat data z datového modelu DTM do XML souboru dle specifikace JVF DTM a odeslat je do DTM kraje prostřednictvím služeb IS DMVS.
Řešíte problematiku DTM ČR?
Více informací k připravovanému produktu DTM Connect získáte na samostatné stránce.
Rádi odpovíme na vaše dotazy a poradíme vám, jak situaci týkající se příchodu DTM ČR ve vašem konkrétním případě nejlépe řešit. Se svými dotazy se na nás můžete obracet prostřednictvím e-mailu nebo na sociální platformě Esri Community.
Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2023
21.2.2023 11:03 ČÚZK /Urady/Cesky-urad-zememericky-a-katastralni/Casto-hledane-informace/Poskytovani-informaci-106-1999-Sb/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(1)/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(5)Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2023
21.2.2023 11:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnízveřejňuje obsah informace poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok
2023
Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2023
21.2.2023 11:03 ČÚZK /Urady/Cesky-urad-zememericky-a-katastralni/Casto-hledane-informace/Poskytovani-informaci-106-1999-Sb/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(1)/Rok2008-2013/Zverejneni-obsahu-informaci-poskytnutych-na-za-(5)Zveřejnění obsahu informací poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 2023
21.2.2023 11:03 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrálnízveřejňuje obsah informace poskytnutých na žádost dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok
2023
Copernicus Sentinel-2 helps explorers unearth rare 7.6 kg meteorite in Antarctica
21.2.2023 11:03 ESA Observing the Earth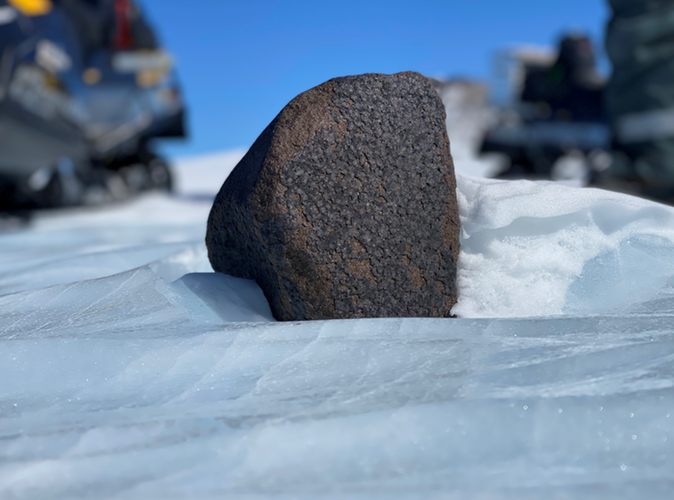
Copernicus Sentinel-2 helps explorers unearth rare meteorite
Slavnostní otevření „Copernicus Academy CZ“ (pozvánka)
21.2.2023 9:39 GISportal.cz
The post Slavnostní otevření „Copernicus Academy CZ“ (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Výroční zpráva dle zákona č. 106/1999 Sb. za rok 20
21.2.2023 9:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Zeměměřický a katastrální inspektorát v Českých Budějovicíchvydává výroční zprávu úřadu za rok
2022























