zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Elektronická rezervace - pozastavení funkčnosti
23.3.2020 8:06 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Havlickuv-Brod/O-uradu/Aktuality/Elektronicka-rezervace-pozastaveni-funkcnostiElektronická rezervace - pozastavení funkčnosti
23.3.2020 8:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Havlíčkův Brod zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Z důvodu omezení úředních hodin na katastrálním pracovišti byla dočasně vypnuta možnost objednání přes internet.Děkujeme za pochopení
Noví členové APG
23.3.2020 7:14 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Novými členy Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice se staly společnost Hanousek s.r.o., zastoupená jednatelem Ing. Davidem Dohnalem, a společnost AGROPLAN, spol. s r.o., zastoupená jednatelem panem Petrem Kubů. Počet členů Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice stále roste. Členství v APG má celou řadu výhod: + práce v pracovních skupinách + příležitost aktivně ovlivňovat dění + právní služby pro vaše podnikání + diskuse s kolegy […]DTM ČR ve výstavbě II
23.3.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Přípomínáme blížící se seminář DTM ČR ve výstavbě II. Uskuteční se již 1. 4. 2020 formou webináře. Registrace je stále otevřenaAPGEO - NOVÍ ČLENOVÉ APG
23.3.2020 1:00 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Novými členy Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice se staly společnost Hanousek s.r.o., zastoupená jednatelem ..."Flattening the Curve" Analysis Added to U.S. Spread of COVID-19 Map
23.3.2020 0:11 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars
St. Paul, Minnesota, March 22, 2020 – This afternoon, Minnesota based nonprofit SharedGeo updated its online COVID-19 …
Na pomoci se zvládáním epidemie koronaviru se podílejí i studenti GÚ
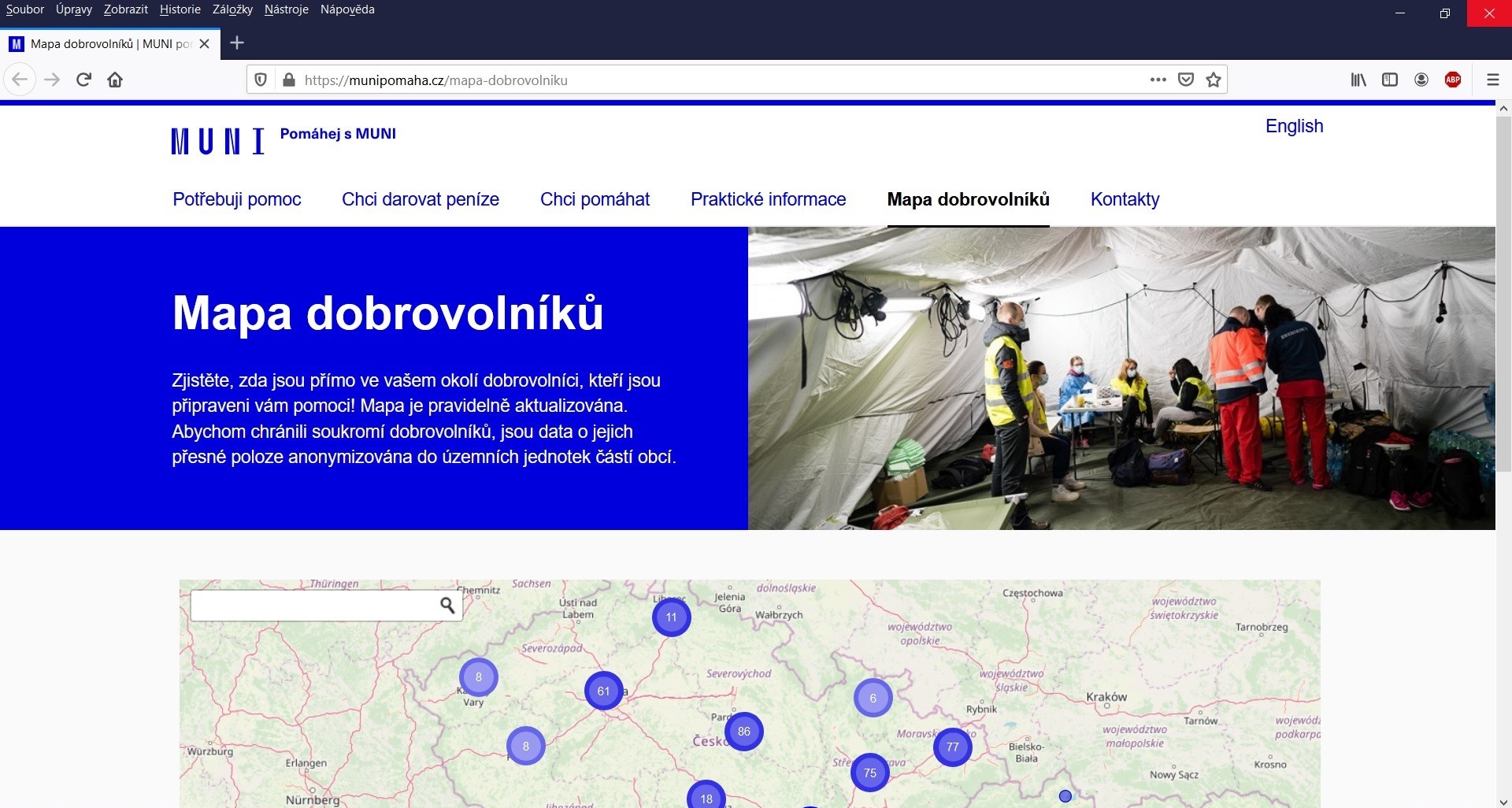
23.3.2020 0:00 Geografický ústav MUMasarykova univerzita disponuje v současné době řadou dobrovolníků, zejména studentů, kteří jsou připraveni pomáhat se zvládáním epidemie koronaviru.
Na organizování této pomoci se podílí také studenti Geografického ústavu Jiří Hladík a Dajana Snopková, kteří spravují Mapu dobrovolníků, díky které je možno zjistit jejich aktuální počet na různých místech v rámci České republiky.
Připomeňte si svoji profesi. Dnes je mezinárodní den zeměměřičů
21.3.2020 10:57 ZeměměřičDnešní den, tedy 21. března, je již potřetí dnem, kdy si svoji profesi mohou oficiálně připomenout oslavou všichni zeměměřiči (a geodeti a geomatici). 21. březen je totiž mezinárodní den zeměměřičů (Global Surveyors‘ Day). Toto celosvětové připomenutí si naší profese poprvé vyhlásila Mezinárodní federace zeměměřičů (FIG) v roce 2018. Své fotografie, pokud budete chuť si naši profesi připomenout, nám posílejte na […]
The post Připomeňte si svoji profesi. Dnes je mezinárodní den zeměměřičů appeared first on Zeměměřič.
Předseda APG jednal s ministryní financí
21.3.2020 7:37 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Ministryně financí Alena Schillerová zavítala na Českolipsko, kde navštívila několik lokalit. Hlavní setkání se starostkou České Lípy Ing. Jitkou Volfovou se konalo v sídle Okresní hospodářské komory Česká Lípa ve Ville Hrdlička. Zde také proběhla diskuze představitelů samospráv a podnikatelské veřejnosti. V rámci diskuze předseda APG Martin Hrdlička vyzdvihl možnosti katastru nemovitostí jako zdroje informací nejen pro veřejnou […]Předseda APG jednal s ministryní financí
21.3.2020 7:37 Asociace podnikatelů v geomatice Ministryně financí Alena Schillerová zavítala na Českolipsko, kde navštívila několik lokalit. Hlavní setkání se starostkou České Lípy Ing. Jitkou Volfovou se konalo v sídle Okresní hospodářské komory Česká Lípa ve Ville Hrdlička. Zde také proběhla diskuze představitelů samospráv a podnikatelské veřejnosti. V rámci diskuze předseda APG Martin Hrdlička vyzdvihl možnosti katastru nemovitostí jako zdroje informací nejen pro […]USAFacts Coronavirus Data Hub and Map Tracking the Daily Spread of the Virus in Every U.S. County Is Now Live
21.3.2020 2:07 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Provides Easy Access to Trusted Data for Journalists, Civic Leaders and Members of the PublicBELLEVUE, Wash. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March …
LiDAR Start-Up Blickfeld Closes Series A Financing Round With Participation of Continental and Wachstumsfonds Bayern
20.3.2020 21:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars MUNICH — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 20, 2020 —Munich-based LiDAR start-up Blickfeld has completed its Series A financing round. The …
GovPilot Makes Software Free During Crisis to Help Local Governments Combat COVID-19
20.3.2020 21:34 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars GovPilot's cloud-based software will enable governments to deploy critical solutions and help non-essential government employees work remotely while …Opatrenia PPA na zníženie rizík podvodov pri podávaní žiadostí o priame podpory
20.3.2020 21:28 Komora pozemkových úprav SRPôdohospodárska platobná agentúra dáva do pozornosti žiadateľom o priame podpory na rok 2020 najčastejšie nedostatky a chyby, ktoré sa prejavujú v súvislosti s plnením podmienok poskytnutia podpory podľa Nariadenia vlády SR č. 342/2014 Z. z....
Opatrenia PPA na zníženie rizík podvodov pri podávaní žiadostí o priame podpory
20.3.2020 21:28 Komora pozemkových úprav SRPôdohospodárska platobná agentúra dáva do pozornosti žiadateľom o priame podpory na rok 2020 najčastejšie nedostatky a chyby, ktoré sa prejavujú v súvislosti s plnením podmienok poskytnutia podpory podľa Nariadenia vlády SR č. 342/2014 Z. z. Konkrétne plnením podmienky, podľa ktorej sa platby...
Celebrating the GNSS surveying community
20.3.2020 21:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) joins the 2020 Global Surveyors Day, to celebrate the men and women of the surveying profession and their valuable work across a wide range of geomatics applications including land surveying (cadastral, construction, mapping and GIS, mining and infrastructure monitoring) and offshore surveying. The surveying industry and community have been an early adopter of Galileo and EGNOS leveraging on the high-precision positioning to develop new services and applications.
The geomatics community has always supported and trusted the European GNSS, and this is confirmed by the gradual penetration of Galileo in GNSS receivers for surveying and mapping. Currently around 55% of GNSS surveying receivers already support Galileo and around 90% are EGNOS-enabled. Moreover, most RTK providers in Europe have already upgraded to Galileo or are starting to do so, and major PPP and PPP-RTK providers are following their example.
The 2019 GSA GNSS Market Report highlights the benefits of GNSS for the geomatics community, noting that geomatics professionals already benefit from EGNSS in a multi-constellation environment, where it provides higher availability, continuity, reliability and better results in harsh conditions.
Watch this: EGNOS and Galileo for Mapping
“Geomatics is a key user segment for EGNSS, in which the added accuracy and reliability that Galileo and EGNOS bring to the table are a key driver of innovative services and solutions,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani. “We are working continuously with this user community to understand their needs and requirements, so we can ensure that future EGNSS evolutions adequately reflect these needs,” she said.
Research and development
A number of Horizon 2020-funded research projects aim to harness the benefits of EGNSS in targeted geomatics solutions. One such project is GIMS, which is building an advanced low-cost system based on EGNSS, Copernicus Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and other in-situ sensors to monitor ground deformations, with a focus on landslides and subsidence.
The project’s goal is to provide detailed and timely knowledge of the geophysical behaviour of parts of the Earth surface, and its impact on structures, in order to prevent injury to the public in the event of landslides, for instance, and to better plan preventative maintenance. The system will report deformations with millimetre-level accuracy and the integration of in-situ accelerometers will give real-time alerts in case of sudden movements.
Another project, GISCAD-OV, covers the entire cadastral value chain and aims to design, develop and validate an innovative and cost-effective High Accuracy Service (HAS) for Cadastral Surveying applications, based on GPS+Galileo E6 HAS and Precise Point Positioning-Ambiguity Resolution (PPP-AR) quick convergence techniques.
It will achieve this by upgrading commercial GNSS receivers for decoding and applying Galileo E6 corrections and integrating them into the PPP solution. It will also use PPP-RTK Multiple Constellation and Multiple Carrier Ambiguity Resolution and instantaneous fixing, along with cost effective solutions using low-cost augmentation services and receivers, paving the way for “Smartphone Surveying”.
Success stories
While ongoing research is set to deliver some exciting developments for the geomatics community, EGNSS is already being successfully used in the sector. One success story is at Eustream, the operator of a high-pressure gas transmission system in the Slovak Republic. The company operates gas pipelines with an overall length of 2,273 km, which are regularly inspected. The operator’s field operators use handheld GNSS devices to directly locate specific pipes with the required precision.
Read this: Galileo and EGNOS: supporting effective disaster management
“Our pipelines are routed through rural areas and there are sites with no GPRS coverage. EGNOS helps us to achieve the required precision and fulfil our task even without Internet connection,” said Branislav Reťkovský, head of Eustream’s GIS department. “For us, EGNOS means a reliable, open and free-of-charge back-up solution that brings confidence to our land survey practice,” he said.
The Portuguese Cycling Federation is also aware of the benefits that EGNOS has to offer and has recommended the use of EGNOS for the creation of cycling tracks and marking of paths, thanks to the higher-precision geolocation it offers, in its Regulation for the Homologation of cycling routes and ‘Cyclin’ Portugal’ Centres”.
Engaging with stakeholders
The GSA engages in a systematic process of consultation with the surveying community, and based on this consultation, it produces The Report on Surveying User Needs and Requirements, which can be downloaded here.
On the occasion of Global Surveyors Day, the GSA would like to congratulate the men and women of the surveying profession. We thank you for your dedicated service and we look forward to our ongoing mutually-beneficial cooperation in the future.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Celebrating the GNSS surveying community
20.3.2020 21:07 European GNSS Agency
The European GNSS Agency (GSA) joins the 2020 Global Surveyors Day, to celebrate the men and women of the surveying profession and their valuable work across a wide range of geomatics applications including land surveying (cadastral, construction, mapping and GIS, mining and infrastructure monitoring) and offshore surveying. The surveying industry and community have been an early adopter of Galileo and EGNOS leveraging on the high-precision positioning to develop new services and applications.
The geomatics community has always supported and trusted the European GNSS, and this is confirmed by the gradual penetration of Galileo in GNSS receivers for surveying and mapping. Currently around 55% of GNSS surveying receivers already support Galileo and around 90% are EGNOS-enabled. Moreover, most RTK providers in Europe have already upgraded to Galileo or are starting to do so, and major PPP and PPP-RTK providers are following their example.
The 2019 GSA GNSS Market Report highlights the benefits of GNSS for the geomatics community, noting that geomatics professionals already benefit from EGNSS in a multi-constellation environment, where it provides higher availability, continuity, reliability and better results in harsh conditions.
Watch this: EGNOS and Galileo for Mapping
“Geomatics is a key user segment for EGNSS, in which the added accuracy and reliability that Galileo and EGNOS bring to the table are a key driver of innovative services and solutions,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani. “We are working continuously with this user community to understand their needs and requirements, so we can ensure that future EGNSS evolutions adequately reflect these needs,” she said.
Research and development
A number of Horizon 2020-funded research projects aim to harness the benefits of EGNSS in targeted geomatics solutions. One such project is GIMS, which is building an advanced low-cost system based on EGNSS, Copernicus Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and other in-situ sensors to monitor ground deformations, with a focus on landslides and subsidence.
The project’s goal is to provide detailed and timely knowledge of the geophysical behaviour of parts of the Earth surface, and its impact on structures, in order to prevent injury to the public in the event of landslides, for instance, and to better plan preventative maintenance. The system will report deformations with millimetre-level accuracy and the integration of in-situ accelerometers will give real-time alerts in case of sudden movements.
Another project, GISCAD-OV, covers the entire cadastral value chain and aims to design, develop and validate an innovative and cost-effective High Accuracy Service (HAS) for Cadastral Surveying applications, based on GPS+Galileo E6 HAS and Precise Point Positioning-Ambiguity Resolution (PPP-AR) quick convergence techniques.
It will achieve this by upgrading commercial GNSS receivers for decoding and applying Galileo E6 corrections and integrating them into the PPP solution. It will also use PPP-RTK Multiple Constellation and Multiple Carrier Ambiguity Resolution and instantaneous fixing, along with cost effective solutions using low-cost augmentation services and receivers, paving the way for “Smartphone Surveying”.
Success stories
While ongoing research is set to deliver some exciting developments for the geomatics community, EGNSS is already being successfully used in the sector. One success story is at Eustream, the operator of a high-pressure gas transmission system in the Slovak Republic. The company operates gas pipelines with an overall length of 2,273 km, which are regularly inspected. The operator’s field operators use handheld GNSS devices to directly locate specific pipes with the required precision.
Read this: Galileo and EGNOS: supporting effective disaster management
“Our pipelines are routed through rural areas and there are sites with no GPRS coverage. EGNOS helps us to achieve the required precision and fulfil our task even without Internet connection,” said Branislav Reťkovský, head of Eustream’s GIS department. “For us, EGNOS means a reliable, open and free-of-charge back-up solution that brings confidence to our land survey practice,” he said.
The Portuguese Cycling Federation is also aware of the benefits that EGNOS has to offer and has recommended the use of EGNOS for the creation of cycling tracks and marking of paths, thanks to the higher-precision geolocation it offers, in its Regulation for the Homologation of cycling routes and ‘Cyclin’ Portugal’ Centres”.
Engaging with stakeholders
The GSA engages in a systematic process of consultation with the surveying community, and based on this consultation, it produces The Report on Surveying User Needs and Requirements, which can be downloaded here.
On the occasion of Global Surveyors Day, the GSA would like to congratulate the men and women of the surveying profession. We thank you for your dedicated service and we look forward to our ongoing mutually-beneficial cooperation in the future.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
A Note from the President’s Desk | March 2020
20.3.2020 20:20 Carlson Software Response to COVID-19 It is times like this when we at Carlson Software feel especially fortunate to be working with the land surveying, mining and construction industries. All involve field work, fresh air and almost built-in “social distancing”. Work takes place on construction sites, at wind-swept mines, in woods, fields and subdivisions, away from large gatherings in […]Satellite Imagery: COVID-19 testing facilities in Munich, Germany
20.3.2020 18:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars European Space Imaging collected imagery yesterday afternoon (March 19 2020) of the COVID-19 drive-through testing facilities currently erected at …Důležitý patch pro Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1
20.3.2020 13:40 ARCDATASpolečnost Esri vydala nový patch pro Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1 – High Availability Licensing Patch. Kromě toho, že nový patch řeší problémy s licencováním v Portálech, které musí zajišťovat vysokou uživatelskou dostupnost, slouží také jako náhrada za již dříve vydaný Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1 Security Patch 2019 Update 2 Patch, u kterého bylo zjištěno, že v některých případech může způsobit nesprávnou instalaci následných patchů.
Důrazně doporučujeme všem, kteří si nainstalovali patch Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1 Security Patch 2019 Update 2 Patch, aby si co nejdříve stáhli a nainstalovali patch nový Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1 High Availability Licensing Patch a vyhnuli se tak případným problémům, které mohou souviset s nesprávnou instalací následně nově vydaných oprav (patche, hot-fixy). U klientů s operačním systémem Windows může instalace této opravy trvat déle, jelikož musí nejprve dojít k odinstalování staršího patche. Uživatelů s operačním systémem Linux se toto omezení netýká. Nový patch zároveň obsahuje veškeré opravy, které byly součástí původní opravy Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1 Security Patch 2019 Update 2 Patch.
Úplný seznam chyb, které nový Portal for ArcGIS 10.7.1 High Availability Licensing Patch řeší, a instalační soubor patche můžete najít na stránce opravy.
Upozornění
20.3.2020 13:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální - Katastrální pracoviště Slaný zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Podání můžete učinit bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné u vchodu do budovy.Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce.
V podání uveďte Váš e-mail, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí a případně Vás vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.
Pokud budete podávat více podání, označte jejich pořadí.
Dále upozorňujeme na možnost elektronického podání s využítím datové schránky. Taková podání musí být převedena z analogové do elektronické pdoby s využitím autorizované konverze dokumentu, opatřena značkou subjektu nebo elektronickým podpisem osoby, která konverzi provedla, a výstup opatřen kvalifikovaným časovým razítkem a musí být zaslán prostřednictvím datové schránky )častníka řízení nebo jeho zástupce (vše na www.cuzk.cz)
Upozornění
20.3.2020 13:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Slany/O-uradu/Aktuality/UpozorneniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 13:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníUpozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné ve vchodu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště!
Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Obálku označte názvem příslušného úřadu. Uveďte v podání Váš email, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.
Schránka je přístupná každý pracovní den od 8 do 13 hod.
Schránku pravidelně vybíráme!
Pokud budete podávat více podání, označte prosím jejich pořadí.
podrobnosti viz celé oznámení
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 13:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníUpozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné ve vchodu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště!
Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Obálku označte názvem příslušného úřadu. Uveďte v podání Váš email, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.
Schránka je přístupná pondělí a středa od 8 do 17 hod a úterý, čtvrtek a pátek od 8 do 13 hod.
Schránku pravidelně vybíráme!
Pokud budete podávat více podání, označte prosím jejich pořadí.
PODROBNOSTI VE SDĚLENÍ
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 13:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Rychnov nad Kněžnou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníUpozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné ve vchodu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště!
Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Obálku označte názvem příslušného úřadu. Uveďte v podání Váš email, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.
Schránka je přístupná každý pracovní den od 8 do 13 hod.
Schránku pravidelně vybíráme!
Pokud budete podávat více podání, označte prosím jejich pořadí.
PODROBNOSTI VE SDĚLENÍ
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 13:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Rychnov-nad-Kneznou/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniSchránka na návrhy
20.3.2020 12:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Benešov zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Upozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné u vchodu do budovy (vstupní mezidveří)! Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Uveďte v podání Váš mail, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet. Schránka je přístupná v pracovní dny od 7 do 15 hod.
Schránka na návrhy
20.3.2020 12:24 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Benesov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Schranka-na-navrhySchránka na návrhy
20.3.2020 12:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Benešov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné u vchodu do budovy (vstupní mezidveří)! Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Uveďte v podání Váš mail, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet. Schránka je přístupná v pracovní dny od 7 do 15 hod.Land-cover maps of Europe from the Cloud
20.3.2020 11:30 ESA Observing the Earth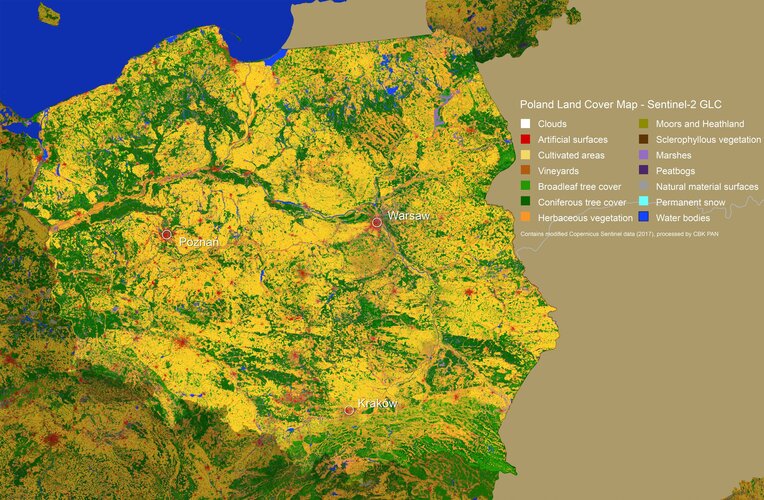
Earth’s land is covered by a range of different types of vegetation, from forest and marsh to crops and bodies of water, as well as the artificial surfaces that are an increasingly common feature of our landscape.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 11:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 11:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podani-(1)Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 11:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Břeclav zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 11:13 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Breclav/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podani20200320 - Probíhající opravy/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik
20.3.2020 10:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele VFR:U obcí bude postupně probíhat oprava/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik (skloňování názvů) dle podkladů od Ústavu pro jazyk český, což se projeví změnou v souborech VFR. Lze tedy očekávat zvýšený výskyt změn obcí ve změnových souborech. Následně budou tyto opravy/doplnění probíhat pro části obce, MOMC a katastrální území.
Zveřejněno 20. 3. 2020
20200320 - Probíhající opravy/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik
20.3.2020 10:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele VFR:U obcí bude postupně probíhat oprava/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik (skloňování názvů) dle podkladů od Ústavu pro jazyk český, což se projeví změnou v souborech VFR. Lze tedy očekávat zvýšený výskyt změn obcí ve změnových souborech. Následně budou tyto opravy/doplnění probíhat pro části obce, MOMC a katastrální území.
(Ukázka doplňovaných dublet/dvojtvarů: „Semicím; Semicům“)
Zveřejněno 20. 3. 2020
20200320 - Probíhající opravy/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik
20.3.2020 10:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele VFR:U obcí bude postupně probíhat oprava/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik (skloňování názvů) dle podkladů od Ústavu pro jazyk český, což se projeví změnou v souborech VFR. Lze tedy očekávat zvýšený výskyt změn obcí ve změnových souborech. Následně budou tyto opravy/doplnění probíhat pro části obce, MOMC a katastrální území.
(Ukázky doplňovaných dublet/dvojtvarů: „Semicím; Semicům“, „Životicím/Životicům u Nového Jičína“)
Zveřejněno 20. 3. 2020
20200320 - Probíhající opravy/doplnění mluvnických charakteristik
20.3.2020 10:23 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/2-Poskytovani-udaju-RUIAN-ISUI-VDP/Vymenny-format-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-VFR/20200320-Probihajici-opravy-doplneni-mluvnickychOdborný/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu OKO0324
20.3.2020 10:14 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu OKO0324Odborný/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu OKO0324
20.3.2020 10:14 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Plzensky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/5-Ozn-o-vyhl-vyberoveho-rizeni-OOKOOdborný/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu OKO0324
20.3.2020 10:14 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Plzeňský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný/vrchní referent - obnova katastrálního operátu OKO0324
Kuwait
20.3.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth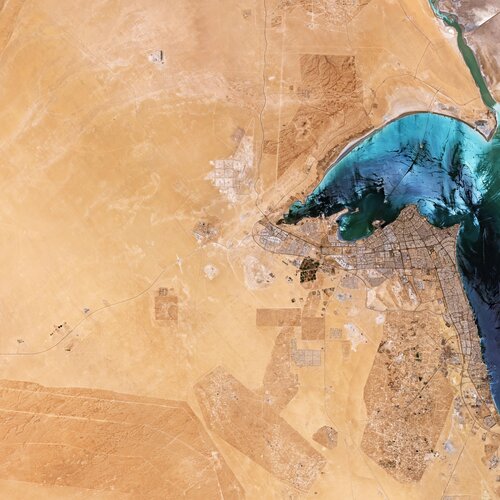 Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kuwait in the Middle East.
Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kuwait in the Middle East.
Earth from Space: Kuwait
20.3.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:03:36
Video:
00:03:36
In this week's edition of the Earth from Space programme, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kuwait in the Middle East.
See also Kuwait to download the image.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 9:12 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Boskovice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 9:12 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Boskovice/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniKoronavirus v českých mapách
20.3.2020 8:13 GISportal.cz
Po příspěvku Coronavirus v grafech, mapách a dashboardech, který se soustředil především na zahraniční mapy a vizualizace, přinášíme přehled některých map s českou tématikou. Pokud víte o podobné mapě či projektu, napište nám, rádi projekt zveřejníme! Mobilní Rozhlas je mobilní i webová aplikace, která slouží pro komunikaci mezi radnicí a občany. Firma již dříve oznámila, […]
The post Koronavirus v českých mapách appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 8:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Blansko/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 8:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Blansko zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Delair and BASF collaborate to accelerate research for agricultural solutions
20.3.2020 8:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Visual intelligence platform from Delair to support agricultural research projects of BASF worldwideDelair.ai platform to streamline and create …
Výsledky GISáček 2020
20.3.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Výsledky studentské soutěže GISáček 2020: https://gisak.vsb.cz/gisostrava/cz/gisacek/vysledky_souteze_2020.pdfMožnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 6:58 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-venkov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 6:58 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Brno-venkov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 6:57 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Hustopece/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 6:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hustopeče zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 6:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hodonín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
20.3.2020 6:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Hodonin/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniKatastrální mapa v rastrové podobě poskytovaná v e-shopu
20.3.2020 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě je poskytována za úplatu a obsahuje analogovou mapu s kompletní kresbou. Analogová mapa pokrývá 3,07 % území České republiky, což je 2 423,90km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.INSPIRE téma Budovy (BU)
20.3.2020 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma budovy (BU). Data pochází částečně z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech, a částečně z ISKN (Informační systém katastru nemovistostí). Zdrojem informací o budovách v ISKN je objekt Stavba, v RÚIAN je to Stavební objekt. Většina Staveb je zároveň Stavebními objekty, ale jsou případy, kdy tomu tak není. Kromě Budov datová sada obsahuje i části budov, které jsou pro potřeby INSPIRE vyjádřeny vchody z RÚIAN. Vchody obsahují informace o počtu podlaží, technickoekonomických atributech apod. Datová sada pokrývá celé území české republiky. V datové sadě není uvedeno 1,15%, t.j. 48458 budov (k 16. 03. 2020), protože neobsahují definiční bod ani polygon. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech, ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních, v zákoně 256/2013 Sb., o katastru nemovitostí, v katastrální vyhlášce č. 357/2013 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Buildings v 3.0 z 13.12.2013. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Budovy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
20.3.2020 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 16. 03. 2020 je to 96,69% území České republiky, t.j. 76 257,96km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.Katastrální mapa ve formátech DGN a DXF poskytovaná v e-shopu
20.3.2020 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě je poskytována zdarma ve formátu DGN a DXF a obsahuje prvky Digitální katastrální mapy (DKM) a Katastrální mapy digitalizované (KMD), tedy bodová pole, budovy, další prvky mapy, hranice parcel, katastrální hranice, parcely katastru nemovitostí, prvky orientační mapy a hranice věcného břemene. Z důvodu použití formátu DGN produkt neobsahuje značky na liniích a oblouky jsou nahrazeny lomenými čárami. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě k 16. 03. 2020 pokrývá 96,69% území České republiky, t.j. 76 257,96km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.INSPIRE téma Adresy (AD)
20.3.2020 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma adresy (AD). Vychází především z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze adresní místa a jejich komponenty, kterými jsou stát, obec, část obce, městský obvod v Praze (MOP), městký obvod/městská část (MO/MČ), ulice a pošta a to na území celé České Republiky. Obsahují rozvněž geometrii, která určuje definiční bod adresního místa. V datové sadě nění uvedeno 1,19%, t.j. 34913 adresních míst (k 16. 03. 2020), protože neobsahují definiční bod, podle kterého by je bylo možné prostorově určit. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech a ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních a INSPIRE Data Specification on Addresses v 3.0.1 z 26.4.2010. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Adresy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Parcely (CP)
20.3.2020 1:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze katastrální území (pro celou Českou Republiku) a parcely a jejich hranice z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 16. 03. 2020 je to 96,69% území České republiky, t.j. 76 257,96km2). Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Parcely ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.Výsledky studentské soutěže GISáček 2020
20.3.2020 0:07 GeoBusinessStudentská soutěžní konference GISáček 2020 se letos uskutečnila 18. března, tentokrát kvůli koronaviru formou videokonference. Soutěže se mohou zúčastnit všichni studenti vysokých škol, kteří na konferenci mohou představit výsledky svých prací, magisterských i bakalářských. Vítězové magisterské kategorie 1. místo: Jakub Seidl, VŠB-TU Ostrava: Využití bezpilotních leteckých prostředků pro monitoring svahových pohybů 2. místo: Přemysl Dratva, […]
The post Výsledky studentské soutěže GISáček 2020 appeared first on GeoBusiness.
Pobočka Jihlava obdržela pochvalu od obce Vílanec
20.3.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Praha, 20. března 2020: Ústřední ředitel Státního pozemkového úřadu obdržel další oceněné pracovníků. Tentokrát pochvalu obdrželi pracovníci Pobočky Jihlava za spolupráci s vedením obce Vílanec.Pozastavení činností v řízení o pozemkových úpravách
20.3.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Do odvolání jsou pozastaveny činnosti všech pracovišť související s nutností osobních aktivit účastníků řízení o pozemkových úpravách.Pozastavení činností v řízení o pozemkových úpravách
20.3.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Do odvolání jsou pozastaveny činnosti všech pracovišť související s nutností osobních aktivit účastníků řízení o pozemkových úpravách.Výsledky studentské soutěže GISáček 2020
19.3.2020 22:03 Přestože letos studentská konference GISáček 2020 změnila na poslední chvíli svou formu z prezenční na videokonferenci, zúčastnilo se jí téměř 70 posluchačů. Přínosem této podoby byla především živá diskuse v chatu videokonference. Odborná porota složená ze zástupců firem ocenila práce následujících studentů: Magisterská kategorie: 1.místo: Jakub Seidl, VŠB-TU Ostrava: Využití bezpilotních leteckých prostředků pro monitoring […]Výsledky studentské soutěže GISáček 2020
19.3.2020 22:03 Přestože letos studentská konference GISáček 2020 změnila na poslední chvíli svou formu z prezenční na videokonferenci, zúčastnilo se jí téměř 40 posluchačů. Přínosem této podoby byla především živá diskuse v chatu videokonference. Odborná porota složená ze zástupců firem ocenila práce následujících studentů: Magisterská kategorie: 1.místo: Jakub Seidl, VŠB-TU Ostrava: Využití bezpilotních leteckých prostředků pro monitoring […]HxGN Content Program provides aerial imagery in response to COVID-19
19.3.2020 20:15 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WASHINTON, D.C., USA (19 March 2020) — Hexagon’s Geosystems division announced today the HxGN Content Program is making its aerial …Doplnění změn územně plánovacích dokumentací
19.3.2020 19:00 Plzeňský kraj Nově bylo uveřejněno dalších 43 změn územně plánovacích dokumentací. Vyhledat příslušnou územně plánovací dokumentaci můžete v sekci Územní plánování » Obce v kraji » Územní plány a další nástroje územního plánování. Nově jsou k dispozici následující změnové dokumentace: Změna č.1 ÚP Babylon, Změna č.1 ÚP Bezvěrov, Změna č.1 ÚP Bolešiny, Změna č.3 ÚP Bor, Změna č.1 ÚP Březina, Změna č.1 ÚP Buková, Změna č.3 ÚP Černošín, Změna č.1 ÚP Dobřany, Změna č.1 ÚP Dobříč, Změna č.1 ÚP Draženov, Změna č.1 ÚP Halže, Změna č.2 ÚP Heřmanova Huť, Změna č.4 ÚP obce Horní Lukavice, Změna č.1 ÚP Chválenice, Změna č.1 ÚP Kasejovice, Změna č.1 ÚP Klenová, Změna č.1 ÚP Kostelec, Změna č.1 ÚP Letkov, Změna č.1 ÚP Líšťany, Změna č.1 ÚP obce Medový Újezd, Změna č.1 ÚP Mirošov, Změna č.1 ÚP Mířkov, Změna č.1 ÚP Mrtník, Změna č.1 ÚP Nýřany, Změna č.3 ÚP Pernarec, Změna č.1 ÚP Planá, Změna č.3 ÚP Prádlo, Změna č.1 ÚP Rybnice, Změna č.1 ÚP Řenče, Změna č.1 ÚP Studánka, Změna č.1 ÚP Třemošná, Změna č.2 ÚP Vejprnice, Změna č.1 ÚP Velhartice, Změna č.1 ÚP Vochov, Změna č.2 ÚP Vrhaveč, Změna č.1 ÚP Zhoř, Změna č.1 ÚP Zruč-Senec, Změny č.1 a č.3 ÚP Žihle, Změna č.2 ÚP sídelního útvaru Spálené Poříčí, Změna č.13 ÚP sídelního útvaru Železná Ruda, Změna č.1 RP Lužany - Obytná zóna 2, Změna č.3 RP města Železná Ruda - Špičák.Doplnění územně plánovacích dokumentací
19.3.2020 18:00 Plzeňský kraj Nově bylo uveřejněno dalších 16 územně plánovacích dokumentací. Vyhledat příslušnou územně plánovací dokumentaci můžete v sekci Územní plánování » Obce v kraji » Územní plány a další nástroje územního plánování. Nově jsou k dispozici následující dokumentace: ÚP Česká Kubice, ÚP Drahotín, ÚP Frymburk, ÚP Hlohová, ÚP Hrádek, ÚP Hradiště, ÚP Ledce, ÚP Liblín, ÚP Loučim, ÚP Mileč, ÚP Rokycany, ÚP Újezd, ÚP Vrčeň, ÚP Ždánov, ÚS Dobřany - obytná zóna jih, ÚS Radnice - lokalita Z3.COVID-19: nitrogen dioxide over China
19.3.2020 16:30 ESA Observing the Earth
Recent data have shown a decline of air pollution over northern Italy coinciding with its nationwide lockdown to prevent the spread of the coronavirus (COVID-19). This new map shows the variation of nitrogen dioxide concentrations over China from December to March – thanks to the Tropomi instrument on board the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite.
COVID-19: nitrogen dioxide over China
19.3.2020 16:30 ESA Observing the Earth
Recent data have shown a decline of air pollution over northern Italy coinciding with its nationwide lockdown to prevent the spread of the coronavirus (COVID-19). This new map shows the variation of nitrogen dioxide emissions over China from December to March – thanks to the Tropomi instrument on board the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite.
Genasys™ Inc. Releases COVID-19 Interactive Map Layer Service
19.3.2020 16:15 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, March 19, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Genasys Inc. (NASDAQ: GNSS), a global provider of critical communications solutions, today released …Esri Provides Free Mapping Software for Organizations Fighting COVID-19
19.3.2020 16:15 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Communities in Need of Resources Can Access Location Intelligence Technology at No CostREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — March 19, …
Sapiens Partners With HazardHub to Integrate Real-time, Geographic Risk Data Into Its P&C Core Suite
19.3.2020 16:15 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Integrating HazardHub's comprehensive data with Sapiens CoreSuite for Property & Casualty will facilitate more accurate underwriting and …Mimo úřední hodiny stanovené krizovým opatřením vlády ČR lze vhodit podání do schránky
19.3.2020 15:13 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Semily zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Mimo úřední hodiny stanovené krizovým opatřením vlády ČR (PO a ST 8:00 - 11:00) lze vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do schránky, která je umístěna vlevo u vstupu do budovy katastrálního pracoviště v Semilech. Schránka je trvale přístupná. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že v míře co největší využijete tuto zcela bezkontaktní možnost.
Mimo úřední hodiny stanovené krizovým opatřením vlády ČR lze vhodit podání do schránky
19.3.2020 15:13 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Semily/O-uradu/Aktuality/Mimo-uredni-hodiny-stanovene-krizovym-opatrenim-vlIndiana School Wins Grand Prize at 28th Annual Future City Competition
19.3.2020 15:10 Bentley Systems Bentley Systems Sponsors the Annual Competition, which Challenges Middle School Students to Design a Future City and Overcome Engineering ChallengesWASHINGTON – March 19, 2020 – Bentley Systems, Incorporated, a leading global provider of comprehensive software and digital twin cloud services for the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure, and DiscoverE, a network of volunteers that introduces students, parents, and educators to engineering and provides hands-on engineering experiences, announced that Yemoja, a city of the future designed by students from Norwell Middle School in Ossian, Indiana, won the Grand Prize at the 2020 Future City Competition.
The competition finals, held at the Hyatt Regency Washington in Washington, D.C., is organized by DiscoverE and sponsored in part by Bentley. Sixth, seventh, and eighth-grade students from 1,500 schools in more than 40 regions, as well as teams from Canada, have imagined, designed, and built cities for the 2019-2020 Future City Competition. This year’s theme, Clean Water: Tap into Tomorrow, challenged students to identify an urban water system threat and develop a futuristic solution to ensure a reliable supply of clean drinking water.
Students from Norwell Middle School, including Jordyn Xayyachack, Teagan Lesley, Madeline McCabe, Nevada Lenwell, Morgan Batdorff, Connor Reed, Cassandra Coyne, Eli Randol, and Lukas Mashuda, paired with educators Bill Bostain, Stephanie Scott, and Bonnie Dickey as well as volunteer mentor Albert Bostain, won a trip to Space Camp at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Ala., as well as $7,500 provided by Bentley, for their school’s STEM program.
Maggie Dressel, program manager of Future City, said the Norwell Middle School team won due to its innovative approach to tackling a problem faced by many real-world cities. “In the course of their research, the team identified plastics as one of the issues,” she said. “In an effort to combat that, they did an in-school campaign on plastic pollution and collected 5,000 plastic bottle caps, melted them down, and used the material to create the model.”
Bentley CIO Claire Rutkowski gave a presentation during the finals that discussed the challenges future cities will face, including urbanization, climate change, water and food scarcity, and population growth. She said some innovations on the way that will improve future cities and help address challenges include digital twins to help design and manage assets, 3D printing to quickly produce individual components and entire buildings, and new high-tech materials, such as concrete that can heal itself through bacteria that generates calcite as it gets wet, or sidewalks that generate power through the kinetic energy of foot pressure.
Rutkowski also had advice for the budding engineers in the room. “Four out of five of you, by the time you graduate from college, will be doing a job that hasn’t even been invented yet,” she said. “Work hard, and don’t be afraid to be the one who steps out and says, ‘Hey, why don’t we try making a sidewalk that creates electricity?’ Be creative and innovative.”
To download videos of the award presentation, please click on the following links.
https://bentley.sharefile.com/d-se108b5d4a6f40e9a
https://bentley.sharefile.com/d-sfef558bba13402d8
To access Claire Rutkowski’s presentation, please click here.
To download images of the winning team, please click on the following links.
https://www.bentley.com/-/media/Images/Press Release Images/2020/Future_Cities_Winning_Team
https://www.bentley.com/-/media/Images/Press Release Images/2020/Future_Cities_Winning_Team_with_Bentley
https://www.bentley.com/-/media/Images/Press Release Images/2020/Future_Cities_First_Place_Team_with_Bentley_Team
About DiscoverE
DiscoverE is leading a growing volunteer movement that inspires and informs present and future generations to discover engineering. Our network of volunteers in the US and abroad is drawn from the DiscoverE coalition of more than 100 professional societies, major corporations and government agencies. Together we meet a vital need: introducing students, parents, and educators to engineering, engaging them in hands-on engineering experiences and making science and math relevant. For more information, visit www.discovere.org.
About Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems is a leading global provider of software solutions to engineers, architects, geospatial professionals, constructors, and owner-operators for the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure. Bentley’s MicroStation-based engineering and BIM applications, and its digital twin cloud services, advance the project delivery (ProjectWise) and the asset performance (AssetWise) of transportation and other public works, utilities, industrial and resources plants, and commercial and institutional facilities.
Bentley Systems employs more than 3,500 colleagues and generates annual revenues of more than $700 million in 172 countries. From inception in 1984, the company has remained majority-owned by its five founding Bentley brothers. www.bentley.com
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:06 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kyjov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kyjov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:06 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kyjov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-město zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 399 ze dne 9.4.2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 17,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-město zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:05 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Brno-mesto/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 13:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Brno-město zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Podání KP Krnov
19.3.2020 13:05 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Krnov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Podani-KP-KrnovPodání KP Krnov
19.3.2020 13:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Krnov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Vážení klienti, z důvodu omezeného rozsahu úředních hodin stanoveného Usnesením Vlády ČR ze dne 15. 3. 2020 č. 217 vám umožňujeme doručovat podání i mimo stanovené úřední hodiny pro veřejnost do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna u vstupu do budovy Katastrálního pracoviště Krnov.Je nutné dodržovat následující:
Vhazujte pouze podání v zalepené obálce.
Podání musí být podepsáno.
Uveďte na své podání e-mail, na který bude přijetí podání potvrzeno a telefonní číslo.
Upozorňujeme vás, že:
Schránka bude vybírána každý pracovní den v 8:00 a 12:00 hodin.
Správní poplatek je možné uhradit převodem na účet na základě výzvy k úhradě.
Okamžikem přijetí podání bude okamžik výběru schránky.
Schránka na podání
19.3.2020 12:15 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Jablonec-nad-Nisou/O-uradu/Aktuality/Schranka-na-podaniSchránka na podání
19.3.2020 12:15 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Jablonec nad Nisou zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Vážení klienti !Přestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky. Na parkovišti Katastrálního úřadu pro Liberecký kraj, Katastrálního pracoviště Jablonec nad Nisou (dále jen úřad) z ulice Uhelná je z tohoto důvodu umístěno služební vozidlo Škoda Fabia combi RZV 3L5 9490 červené barvy, které bude jako schránka pro příjem podání sloužit. Do mezery v okně u jeho pravých zadních dveří lze v zalepené obálce vhazovat podání (návrhy na zápis práv a jiných údajů do katastru), a to i mimo v nouzovém režimu stanovené úřední hodiny. Tato schránka je k dispozici v pracovní dny od 7:00 do 14: 00 hod a vybírá se v 10:00 a v 14:00 hod. Obálky jsou k dispozici v krabici v rohu okna budovy.
Potvrzení o přijetí podání obdržíte na e-mail, který prosím uvádějte v návrhu (podání). Na tento e-mail Vám bude rovněž zaslán podklad pro platbu (v případě, že je podání návrhu zpoplatněno) tak, abyste mohli provést platbu bezhotovostně prostřednictvím Vaší banky.
Pokud potřebujete vyplnit návrh na vklad, případně jiný formulář, doporučujeme Vám jej vyplnit z domova v elektronické aplikaci na adrese: https://www.cuzk.cz/Fornulare-a-elektronicka-podani resp. na adrese: https://nv.cuzk.cz/Web/Uvod.aspx.
Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti, zároveň Vás prosíme, nevhazujte v obálce hotovost, platbu zaplaťte bezhotovostně na výzvu resp. podklad pro platbu, který Vám bude zaslán na e-mail!
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 12:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vyškov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 12:07 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Vyskov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 12:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vyškov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 12:07 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Vyškov zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 11:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Znojmo/O-uradu/Aktuality/Moznost-bezkontaktniho-podaniMožnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 11:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Znojmo zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 11:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Znojmozveřejnil novou aktualitu: Přestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 11:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Znojmo zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailovou adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Možnost bezkontaktního podání
19.3.2020 11:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Znojmo zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Možnost bezkontaktního podáníPřestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8,00 do 11,00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřeného sběrného boxu, který je umístěn vždy u vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Box je zpřístupněn v běžných úředních hodinách. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrného boxu. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.
Úspěch naší studentky v soutěži GISáček [Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie, byTopic]
19.3.2020 10:20 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK Bc. Daniela Valchářová vyhrála se svojí bakalářskou prací Tematický atlas Církve adventistů sedmého dne studentskou soutěž GISáček. Gratulujeme!Schránka pro příjem podání
19.3.2020 10:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Mělník zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V zádveří KP byla umístěna schránka pro příjem podání, která je přístupná době běžných úředních hodin a je pravidelně vybírána.Schránku mohou klienti použít pro vhoz svých podání v obálce.
POZOR!!! je důležité, aby v návrhu na vklad nebo jiného podání byla uvedena funkční mailová adresa (pro potvrzení přijetí podání, pro zaslání podkladu pro platbu).
Schránka pro příjem podání
19.3.2020 10:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Melnik/O-uradu/Aktuality/Schranka-pro-prijem-podaniAurora Police Launch New Hexagon Public Safety Technology to Better Serve Community
19.3.2020 9:00 Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure HxGN OnCall Records provides deeper insights into public safety trends in the community.Důležité upozornění
19.3.2020 8:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Český úřad zeměměřický a katastrální - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Na KP Příbram došlo k omezení úředních hodin. Otevřena je pouze podatelna, vždy v Po a St od 8-11 do odvolání.Informace o průběhu vkladového řízení je možno získat na tel. čísle 318 401 611.
Důležité upozornění
19.3.2020 8:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Na KP Příbram došlo k omezení úředních hodin. Otevřena je pouze podatelna, vždy v Po a St od 8-11 do odvolání.Informace o průběhu vkladového řízení je možno získat na tel. čísle 318 401 611.
Důležité upozornění
19.3.2020 8:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Pribram/O-uradu/Aktuality/Dulezite-upozorneniGISáček 2020 – priebeh a výsledky súťaže
19.3.2020 8:30 GISportal.cz
Dňa 18.3.2020 sa uskutočnila študentská súťaž GISáček. Toto podujatie je primárne určené študentom vysokých škôl, ktorí sa v rámci svojich bakalárskych a magisterských prác venujú témam z oblasti geoinformatiky, geoinformačných technológií a ich aplikácií. Študenti tu majú možnosť prezentovať výsledky svojich prác pred komisiou zloženou z odborníkov z akademickej aj súkromnej sféry, čím zároveň môžu získať kvalitnú spätnú väzbu […]
The post GISáček 2020 – priebeh a výsledky súťaže appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Schránka pro podání
19.3.2020 8:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Moravské Budějovice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Přestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8:00 do 11:00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna ve vestibulu budovy katastrálního pracoviště. Schránka je zpřístupněna v pracovní dny od 8:00 do 14:00 hod. Pokud v podání uvedete e-mailovou adresu, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.Schránka pro podání
19.3.2020 8:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu - Katastrální pracoviště Moravské Budějovice zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Přestože jsou v souladu s usnesením vlády č. 217 ze dne 15. března 2020 úřední hodiny pro veřejnost pouze v pondělí a středu od 8:00 do 11:00 hod., je možné i mimo tyto úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené schránky, která je umístěna ve vestibulu budovy katastrálního pracoviště. Schránka je zpřístupněna v pracovní dny od 8:00 do 14:00 hod. Pokud v podání uvedete e-mailovou adresu, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti.Schránka pro podání
19.3.2020 8:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Moravske-Budejovice/O-uradu/Aktuality/Schranka-pro-podaniRada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro K
19.3.2020 7:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro KRada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro K
19.3.2020 7:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Oznameni-o-vyhlaseni-vyberoveho-rizeni-2-kola-vybRada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro K
19.3.2020 7:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada/odborný rada – vedoucí oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký
schránka
19.3.2020 7:45 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Frydlant/O-uradu/Aktuality/schrankaschránka
19.3.2020 7:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Frýdlant zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Podání na KP Frýdlant lze i mimo omezené úřední hodiny podatelny učinit vložením do okénka u vchodu - sběrné schránky . Schránka se vybírá průběžně každý den v Út až Čt do 14 hod., v Pá do 12 hod. Přijímány jsou veškeré žádosti včetně návrhů na vklad. Uvedete-li e-Mail, zašleme Vám údaje pro bezhotovostní platbu správního poplatku za podání návrhu a potvrzení o převzetí (např. kopii návrhu s naším podacím razítkem). Podání vkládejte v uzavřené obálce až do velikosti A4. Důležité upozornění: zkontrolujte, prosím, zda je Váš návrh na vklad podepsaný. Do obálky nevkládejte hotovost.Prosíme o preferování tohoto způsobu nebo použití pošty. Osobní jednání je vyhrazeno jen pro skutečně nezbytné případy.
Ing. Bc. Skalická
schránka
19.3.2020 7:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Frýdlant zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Podání na KP Frýdlant lze i mimo omezené úřední hodiny podatelny učinit vložením do okénka u vchodu nahrazující schránku . Schránka se vybírá průběžně každý den v Po až Čt do 15 hod., v Pá do 12 hod. Přijímány jsou veškeré žádosti včetně návrhů na vklad. Uvedete-li e-Mail, zašleme Vám údaje pro bezhotovostní platbu a potvrzení o převzetí (např. kopii návrhu s naším podacím razítkem). Podání vkládejte v uzavřené obálce až do velikosti A4. Důležité upozornění: zkontrolujte, prosím, zda je Váš návrh na vklad podepsaný.Do obálky nevkládejte hotovost.Prosíme o preferování tohoto způsobu nebo použití pošty. Osobní jednání je vyhrazeno jen pro skutečně nezbytné případy.
Ing.Bc.Skalická
schránka
19.3.2020 7:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Frýdlant zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Podání na KP Frýdlant lze i mimo omezené úřední hodiny podatelny učinit vložením do okénka u vchodu nahrazující schránku . Schránka se vybírá průběžně každý den v Út až Čt do 15 hod., v Pá do 12 hod. Přijímány jsou veškeré žádosti včetně návrhů na vklad. Uvedete-li e-Mail, zašleme Vám údaje pro bezhotovostní platbu a potvrzení o převzetí (např. kopii návrhu s naším podacím razítkem). Podání vkládejte v uzavřené obálce až do velikosti A4. Důležité upozornění: zkontrolujte, prosím, zda je Váš návrh na vklad podepsaný.Do obálky nevkládejte hotovost.Prosíme o preferování tohoto způsobu nebo použití pošty. Osobní jednání je vyhrazeno jen pro skutečně nezbytné případy.
Ing.Bc.Skalická
schránka
19.3.2020 7:45 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Liberecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Frýdlant zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Podání na KP Frýdlant lze i mimo omezené úřední hodiny podatelny učinit vložením do okénka u vchodu - sběrné schránky . Schránka se vybírá průběžně každý den v Út až Čt do 14 hod., v Pá do 12 hod. Přijímány jsou veškeré žádosti včetně návrhů na vklad. Uvedete-li e-Mail, zašleme Vám údaje pro bezhotovostní platbu správního poplatku za podání návrhu a potvrzení o převzetí (např. kopii návrhu s naším podacím razítkem). Podání vkládejte v uzavřené obálce až do velikosti A4. Důležité upozornění: zkontrolujte, prosím, zda je Váš návrh na vklad podepsaný. Do obálky nevkládejte hotovost.Prosíme o preferování tohoto způsobu nebo použití pošty. Osobní jednání je vyhrazeno jen pro skutečně nezbytné případy.
Děkujeme za pochopení
Mapujeme COVID19
19.3.2020 6:55 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucMapujeme koronavirus v Olomouckém kraji ❗️ Jediné místo koncentrující aktuální informace z různých zdrojů, a navíc i nad mapou 🌎 Podívejte se co naši studenti dokázali za 24 hodin v rámci virtuálního hackathonu 😎 https://gis.upol.cz/covid/ #koronavirus #prehledne #hackathon #geoinformatika #bettermapsbetterworld
The post Mapujeme COVID19 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.