zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Anglian Water Implements GIS and SAP Integration Module from Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure
24.8.2016 4:00 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureAnglian Water Services Ltd., England’s largest water company by area, has implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s SAP integration module as part of its recent enterprise GIS upgrade. Taking advantage of the latest in web services technology, Hexagon’s SAP integration module provides a seamless connection between Anglian Water’s utility GIS, built on Hexagon’s Intergraph G/Technology, and SAP’s enterprise application integration software, SAP Process Integration (PI).
The combined Hexagon GIS and SAP solution enables Anglian Water to manage its entire water and wastewater networks through an integrated view of assets and activities.
“The integration between Hexagon’s GIS and SAP provides us with a single solution to help manage our assets and work,” said Chris Bodley, Anglian Water’s IS Service Delivery Manager. “The combination provides an important source of reliable information to help us deliver our customer promises through a better understanding of the networks and how they are changing.”
Hexagon’s SAP integration module improves the integration and management of core IT processes and business functions, including asset and work management. The web services-based module removes the need for point-to-point interfaces between systems, which are costly to implement, maintain and upgrade.
Anglian Water’s GIS provides detailed, connected network information to personnel handling key aspects of the company’s day-to-day business operations, including customer services call-takers, network technicians in the field, analysts in asset planning and duty managers in the company’s Operations Management Centre. Anglian Water’s GIS also uses Hexagon’s G/WaterUK, an extension to Intergraph G/Technology that provides capabilities required by U.K. water companies. G/WaterUK originated from a business collaboration between Anglian Water and Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure (then called Intergraph’s Security, Government & Infrastructure division) in 2006.
Hexagon’s SAP integration module was delivered working in partnership with CapGemini, one of Anglian Water’s IT framework partners.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps utilities and communications companies achieve greater reliability, increase efficiency and fulfill the expectations of customers, shareholders and regulators. A pioneer in the development and application of location-based technology, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure provides solutions to hundreds of utilities and communications customers around the globe, supporting network engineering, network operations, customer services, sales and marketing and physical security.
Stav útvarů podzemních vod
24.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Evidence obsahuje údaje o vyhodnocení stavu útvarů podzemních vod v ČR. Stavem podzemních vod vodní zákon rozumí obecné vyjádření stavu útvaru podzemní vody určené kvantitativním nebo chemickým stavem, podle toho, který je horší. Dobrým stavem podzemních vod se rozumí takový stav útvaru podzemních vod, kdy je jeho kvantitativní i chemický stav přinejmenším dobrý. Dobrým chemickým stavem podzemních vod se rozumí chemický stav potřebný pro dosažení cílů ochrany vod jako složky životního prostředí (§ 23a), při kterém koncentrace znečišťujících látek nepřekračují normy environmentální kvality. Normou environmentální kvality se rozumí koncentrace znečišťující látky nebo skupiny látek ve vodě, sedimentech nebo živých organismech, která nesmí být překročena z důvodů ochrany lidského zdraví a životního prostředí. Kvantitativním stavem podzemních vod se rozumí vyjádření míry ovlivnění útvaru podzemních vod přímými a nepřímými odběry. Hodnocení stavu útvarů podzemních vod spočívá v hodnocení jejich chemického a kvantitativního stavu. Pro hodnocení stavu útvarů podzemních vod se využívají výsledky získané ze sítě zjišťování stavu podzemních vod, analýz všeobecných a vodohospodářských charakteristik povodí a hodnocení dopadů lidské činnosti na stav útvarů podzemních vod. Stav vodních útvarů je hodnocen v rámci zpracování plánů povodí. Stav útvarů podzemních vod se eviduje v rozsahu údajů o jejich identifikátoru a klasifikaci jejich chemického a kvantitativního stavu.Útvary podzemních vod
24.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Evidence obsahuje údaje o vymezení a charakteristikách útvarů podzemních vod v ČR. Vodní útvar je dle vodního zákona definován jako vymezené významné soustředění povrchových nebo podzemních vod v určitém prostředí charakterizované společnou formou jejich výskytu nebo společnými vlastnostmi vod a znaky hydrologického režimu. Vodní útvary se člení na útvary povrchových vod a útvary podzemních vod. Útvar podzemní vody je vymezené soustředění podzemní vody v příslušném kolektoru nebo kolektorech; kolektorem se rozumí horninová vrstva nebo souvrství hornin s dostatečnou propustností, umožňující významnou spojitou akumulaci podzemní vody nebo její proudění či odběr. Útvary podzemních vod jsou vymezeny v hloubkové svrchní, základní a hlubinné vrstvě a jsou zjednodušeně vyjádřeny plochami ve třech vrstvách hydrogeologických rajónů (svrchní vrstvy kvartérních sedimentů a coniaku, základní vrstvy a hlubinné vrstvy bazálního křídového kolektoru). Útvary podzemních vod se evidují v rozsahu údajů o jejich územní identifikaci, názvu a číselném identifikátoru, názvu a číselném identifikátoru hydrogeologického rajonu, a jejich příslušnosti k mezinárodní oblasti povodí, dílčímu povodí, správci povodí, správnímu obvodu kraje, popřípadě krajů.. Aktuální vymezení útvarů povrchových vod je určeno vyhláškou č. 5/2011 Sb., o vymezení hydrogeologických rajonů a útvarů podzemních vod, způsobu hodnocení stavu podzemních vod a náležitostech programů zjišťování a hodnocení stavu podzemních vod, ve znění pozdějších předpisů.Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný rada, oddělení řízení restitučních náhrad a přímých restitucí, odbor řízení restitucí
24.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Ústřední ředitelka Státního pozemkového úřadu, jako služební orgán příslušný podle § 10 odst. 1 písm. f) zákona č. 234/2014 Sb., o státní službě (dále jen „zákon“), vyhlašuje výběrové řízení na služební místo odborný rada oddělení řízení restitučních náhrad a přímých restitucí, odbor řízení restitucí.Svatava Maradová: Pozemkový úřad řeší sucho, erozi půdy i závlahy. Jen do pozemkových úprav v krajině šly 4,5 miliardy.
24.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Praha, 24. srpna 2016 – Státní pozemkový úřad dnes představil nové činnosti, kterými rozšiřuje svoji agendu v souvislosti s novelou zákona o Státním pozemkovém úřadu. Nově bude úřad spravovat závlahové soustavy v majetku státu. Na tiskové konferenci byl ředitelkou SPÚ Svatavou Maradovou a profesorem Zdeňkem Žaludem z Akademie věd představen také společný projekt Intersucho.Sme spoľahlivý podnik
23.8.2016 21:08 Geotronics.skGeotronics Slovakia, s.r.o. získal začiatkom júna Pečať spoľahlivosti, ktorú udelilo Národné informačné stredisko Slovenskej republiky. V roku 2016 bolo hodnotených viac ako 12 tisíc dodávateľov a iba 28,9% z nich toto ocenenie získalo. Medzi nimi aj Geotronics Slovakia, s.r.o. Kritériá hodnotenia boli zamerané na posudzovanie dodržania zmluvne deklarovaných požiadaviek, počtu reklamácií a dodržiavania spôsobu a kvality […]
Príspevok Sme spoľahlivý podnik zobrazený najskôr Geotronics Slovakia.
Čerpanie peňazí z PRV SR na roky 2014 až 2020.
23.8.2016 17:42 Komora pozemkových úprav SRČerpanie peňazí z Programu rozvoja vidieka SR na roky 2014 až 2020, ktoré ovplyvňuje aj zadávanie nových projektov pozemkových úprav ako vyšlo v Hospodárskych novinách
Čerpanie peňazí z PRV SR na roky 2014 až 2020
23.8.2016 17:42 Komora pozemkových úprav SR Čerpanie peňazí z Programu rozvoja vidieka SR na roky 2014 až 2020, ktoré ovplyvňuje aj zadávanie nových projektov pozemkových úprav ako vyšlo v Hospodárskych novináchSme spoľahlivý podnik
23.8.2016 16:43 Geotronics.sk Geotronics Slovakia, s.r.o. získal začiatkom júna Pečať spoľahlivosti, ktorú udelilo Národné informačné stredisko Slovenskej republiky. V roku 2016 bolo hodnotených viac ako 12 tisíc dodávateľov a iba 28,9% z nich toto ocenenie získalo. Medzi nimi aj Geotronics Slovakia, s.r.o. Kritériá hodnotenia boli zamerané na posudzovanie dodržania zmluvne deklarovaných požiadaviek, počtu reklamácií a dodržiavania spôsobu a kvality plnenia [...]Sme spoľahlivý podnik
23.8.2016 16:43 Geotronics.sk Geotronics Slovakia, s.r.o. získal začiatkom júna Pečať spoľahlivosti, ktorú udelilo Národné informačné stredisko Slovenskej republiky. V roku 2016 bolo hodnotených viac ako 12 tisíc dodávateľov a iba 28,9% z nich toto ocenenie získalo. Medzi nimi aj Geotronics Slovakia, s.r.o. Kritériá hodnotenia boli zamerané na posudzovanie dodržania zmluvne deklarovaných požiadaviek, počtu reklamácií a dodržiavania spôsobu a kvality plnenia [...]Jak vysvětlit vrstevnice? Virtuální realitou!
23.8.2016 14:03 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČU Pěkná aplikace (nejen) na výuku vrstevnic. Zajímavé využití virtuální reality, já si ještě pamatuju, jak se vrstevnice vysvětlovaly krájením brambor - pokrok nezastavíš ;-).odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN (1)
23.8.2016 12:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření
Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na Katastrálním pracovišti Třebíč, místo výkonu služby Třebíč zde.
odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN (1)
23.8.2016 12:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Trebic/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-(1)Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN. (1)
23.8.2016 12:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Třebíčvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN.
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN. (1)
23.8.2016 12:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-(2)Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN. (1)
23.8.2016 12:26 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu, Katastrální pracoviště Třebíč vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace KN. (1)V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kra
23.8.2016 12:00 Ústecký kraj V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kraje byla provedena aktualizace údajů pro poskytovatele Povodí Ohře, státní podnik – jev 53Mapová aplikace byla aktualiz
23.8.2016 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace byla aktualizována k 22. 8. 2016.Mapová aplikace Územně analyti
23.8.2016 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Územně analytické podklady byla aktualizována k 22. 8. 2016.Seriál videoseminářů technické podpory 2016
23.8.2016 10:43 ARCDATATaké letos si pro vás oddělení technické podpory připravilo seriál krátkých videoseminářů, jejichž prostřednictvím se seznámíte se zajímavou funkcionalitou a novinkami napříč celou platformou ArcGIS. V průběhu následujících čtyř týdnů se budeme postupně zabývat například správou rastrových dat, přípravou zajímavé prezentace prostřednictvím šablon Story Maps či prací s vektorovými dlaždicemi.
V dnešním, prvním dílu se seznámíme s možnostmi optimalizace mapového dokumentu pro účely jeho publikace formou mapové služby, která bude následně využívána aplikací Web AppBuilder for ArcGIS.
Odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu II. v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřa
23.8.2016 9:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu II. v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu II. v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřa
23.8.2016 9:08 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj, vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu II. v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřaOdborný referent v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu II. v technickém odboru na Katastrálním úřa
23.8.2016 9:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-obnovy-katastralni-(1)Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Teplice na Kat
23.8.2016 8:55 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Teplice vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Teplice na KatOdborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Teplice na Kat
23.8.2016 8:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj Katastrální pracoviště Teplicevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Teplice na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj
Odborný referent v oddělení dokumentace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Teplice na Kat
23.8.2016 8:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-dokumentace-katast-(1)Archivní ortofoto České republiky barevné
23.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Archivní ortofoto České republiky, barevné. Snímkování od r. 2002 (zkušební), pravidelné snímkování třetiny území ČR od r. 2003, poloviny území ČR od r. 2012. Pro snímkování do roku 2008 včetně je velikost pixelu 50 cm. Pro snímkování od roku 2009 je velikost pixelu 25 cm.Metodický průvodce návrhem a realizací vozovek nízkokapacitních komunikací
22.8.2016 18:49 Asociace poskytovatelů služeb v pozemkových úpravách Nabízíme certifi kovanou metodiku, která je zaměřena na postup při navrhování a provádění, na kontrolu, popř. údržbu vozovek nízkokapacitních komunikací (především vozovek lesních a polních cest). Metodika se zabývá problematikou geotechnického průzkumu, postupů při vlastním návrhu vozovky, doporučení a pokynů pro provádění, kontrolu a dozor při výstavbě. Důraz je kladen zejména na posouzení podloží vozovky a jeho případných úprav, výběru vhodné skladby vozovky s ohledem na kategorii podloží vozovky ve vztahu k úrovni zatížení.Ukončení spolupráce se společností Aponia Software
22.8.2016 17:00 CEDA Maps a.s. Praha, 22. srpna 2016 – Společnost CEDA oznamuje ukončení spolupráce s firmou Aponia Software, s.r.o. z důvodu nedodržování smluvních závazků. Aponia Software, s.r.o. je povinna vrátit všechna používaná data poskytovaná společností CEDA a odstranit je ze své produktové nabídky, což i po opakovaných výzvách doposud neučinila.O víkendu byl rozhovor s Jakubem v anglickém pořadu Czech Life na Českém Rozhlasu Praha
22.8.2016 10:09 UpVision O víkendu byl na Českém Rozhlasu Praha v anglickém pořadu Czech Life rozhovor o dronech s Jakubem.Více zde:
http://www.radio.cz/en/section/czech-life/discussing-the-positives-but-also-danger-of-drones
odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem (1)
22.8.2016 9:53 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření
Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem na Katastrálním pracovišti Jihlava, místo výkonu služby Jihlava zde.
odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem (1)
22.8.2016 9:53 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Jihlava/O-uradu/Aktuality/odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-pravni-vztahy-k-ne-(1)Odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem. (1)
22.8.2016 9:50 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Vysocinu/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-v-oddeleni-pravni-vztahy-k-ne-(3)Odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem. (1)
22.8.2016 9:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu Katastrální pracoviště Jihlavavypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem.
Odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem. (1)
22.8.2016 9:50 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Vysočinu, Katastrální pracoviště Jihlava vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent v oddělení právní vztahy k nemovitostem. (1)Mise Proba-3 si prohlédne sluneční koronu
22.8.2016 9:35 Český Kosmický PortálKaždých zhruba osmnáct měsíců se vědci i lovci senzací shromáždí na některých místech Země, kde mají možnost na vlastní oči spatřit dechberoucí sluneční zatmění. Měsíc totiž na krátkou dobu zablokuje - při pohledu ze Země - Slunce, a tím odhalí tajemství jeho vnější atmosféry, korony. Ale co kdyby výzkumníci dokázali vytvářet podobná zatmění doslova „na přání“?
Mapa vína a vinohradů na webu
22.8.2016 8:32 GISportal.cz Jaká vína se pěstují v jednotlivých katastrech či kolik hektarů vinohradů tam najdeme a další informace lze snadno zjistit z nové webové mapové aplikace, kterou připravili Jan Miklín a Kateřina Gajdošová z Katedry fyzické geografie a geoekologie Ostravské ...Nabídka služebního místa odborný referent/ vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na KP Blansko
22.8.2016 8:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Blanskonabídka služebního místa
Nabídka služebního místa odborný referent/ vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na KP Blansko
Nabídka služebního místa odborný referent/ vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na KP Blansko
22.8.2016 8:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihomoravsky-kraj/Volna-mista/Nabidka-sluzebniho-mista-odborny-referent-vrchni-rNabídka služebního místa odborný referent/ vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na KP Blansko
22.8.2016 8:25 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihomoravský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Blansko vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Nabídka služebního místa odborný referent/ vrchní referent v oddělení dokumentace KN na KP BlanskoSrpnový mapathon s Lékaři bez hranic opět v Praze…
22.8.2016 8:19 GISportal.cz V Praze s bude konat již čtvrtý mapathon pořádaný humanitární organizací Lékaři bez hranic. Přijďte a podpořte práci Lékařů bez hranic tím, že pomůžete zmapovat místa, která jsou nejvíce ohrožena humanitárními krizemi. Není potřeba mít předchozí ...Nedostupnost webových stránek
22.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Z důvodu údržby web-serverů budou ve středu 24. 8. 2016 od 18.30 do 19.00 dočasně nedostupné webové stránky SPÚ.Děkujeme za pochopení.
Nedostupnost webových stránek
22.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Vážení,z důvodu údržby web-serverů budou ve středu 24.8.2016 od 18:30 do 19:00 dočasně nedostupné webové stránky SPÚ.
Děkujeme za pochopení
Příběhy míst pomozte se sběrem příběhů z Liberecka
21.8.2016 13:08 Zeměměřič Projekt Příběhy míst si klade za cíl sesbírat historické informace o místech v regionu, sahajícím od německé itavy a po Vrchlabí. V jeho druhé fázi, v roce 2016, je sběr rozířen z informací o vrcholech na jakákoli místa. Jako podklad byla vybrána iroce oblíbená turistická mapa z roku 1927 od libereckého kartografa Josefa Matouscheka.Olympijské běhy ve Vašem okolí?
21.8.2016 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Jak daleko byste museli běžet z Vašeho domu, abyste uběhli maraton? Zadejte libovolnou lokaci v interaktivní mapě, kterou publikoval deník The New York Times a dostanete představu o vzdálenosti olympijských běhů ve Vašem okolí spolu s časy, ve kterých uběhli tuto vzdálenost olympijští vítězové vVyužití otevřených dat v geomatice
21.8.2016 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Další ročník konference Geoinformatics proběhne ve dnech 12. a 13. září 2016 v místnosti B - 169 na Stavení fakultě ČVUT v Praze.Hlavním tématem konference je Využití otevřených dat v Geomatice. Mezi přednášejícími budou zástupci poskytovatelů i uživatelů otevřených dat. Mezi poskytovateli dat budou dobře známí poskytovatelé otevřených dat jako Český úřadV sekci Směrnice a metodiky (h
19.8.2016 12:00 Plzeňský kraj V sekci Směrnice a metodiky (http://geoportal.plzensky-kraj.cz/gs/smernice-a-metodiky/) je k dispozici aktualizovaný dokument Vizualizace jevů Územně analytických podkladů a Územních plánů Datového modelu T-MAPY verze 3.4. O samotnou vizualizaci pro ArcGIS mohou registrovaní uživatelé požádat prostřednictvím aplikace HelpDesk (https://geoportal.plzensky-kraj.cz/tw/ost/gp/helpdesk/requirements).V sekci Směrnice a metodiky je
19.8.2016 12:00 Plzeňský kraj V sekci Směrnice a metodiky je k dispozici aktualizovaný dokument Vizualizace jevů Územně analytických podkladů a Územních plánů Datového modelu T-MAPY verze 3.4. O samotnou vizualizaci pro ArcGIS mohou registrovaní uživatelé požádat prostřednictvím aplikace HelpDesk.Blíží se 2. konference Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl
19.8.2016 10:02 UpVision A je tu zase po roce druhý ročník Konference Aliance pro bezpilotní letecký průmysl, která se koná 14.9.2016 v Praze na ČZU. Součástí letošní konference bude i expozice nejnovějších řešení členů Aliance.Podrobný program konference naleznete na www.uava.cz/konference, v případě dotazů nás neváhejte kontaktovat na info@uava.cz.
Registrovat se můžete na http://uava-konference-1-2016.takeplace.eu/cs
Přijďte nás navštívit, budeme se těšit.
Jakub bude na pozvání speaker v Londýně na Commercial UAV Show 2016
19.8.2016 10:02 UpVision Letos v říjnu bude Jakub na pozvání speaker v Londýně na jedné z největších světových UAV Show, konkrétně na Commercial UAV Show 2016.Více zde:
http://www.terrapinn.com/exhibition/the-commercial-uav-show/speaker-jakub-KARAS.stm
Příběhy míst – pomozte se sběrem příběhů z Liberecka
19.8.2016 8:29 GISportal.cz Projekt „Příběhy míst“ si klade za cíl sesbírat historické informace o místech v regionu, sahajícím od německé Žitavy až po Vrchlabí. V jeho druhé fázi, v roce 2016, je sběr rozšířen z informací o vrcholech ...INSPIRE prohlížecí služba pro téma Využití území - kraj Plzeňský
19.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Uveřejnění zásad územního rozvoje Plzeňského kraje formou vektorové prohlížecí - mapové služby.Referent/referentka, Pobočka Brno
19.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Státní pozemkový úřad přijme zaměstnance na pozici referent/referentka, Pobočka Brno.Máte nápad jak využít kosmické technologie a přetavit je v komerční úspěch? Využijte příležitost a přihlaste se do historicky první výzvy podnikatelského inkubátoru ESA BIC Prague!
18.8.2016 16:47 Český Kosmický PortálZískejte 50 000 € a rozjeďte své podnikání! Pokud máte nápad na startup, který ve svých komerčních produktech či službách využije kosmické technologie nebo systémy, neváhejte a přihlaste se do aktuálně otevřené výzvy inkubátoru ESA BIC Prague.
20160818-Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí-KP Benešov
18.8.2016 10:53 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Benesov/O-uradu/Aktuality/20160728-Oznameni-o-vyhlaseni-vyberoveho-rizen-(1)20160818-Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí-KP Benešov
18.8.2016 10:53 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Na úřední elektronické desce Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj, v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí, Katastrální pracoviště Benešov"20160818Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce-KÚ SČK
18.8.2016 10:50 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20150901Oznameni-o-vyhlaseni-vyberoveho-rizeni-(9)20160818Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce-KÚ SČK
18.8.2016 10:50 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj"20160818-Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí-KP Benešov
18.8.2016 10:46 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na služební místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí KP Benešov"20160818-Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí-KP Benešov
18.8.2016 10:46 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20160728-Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-odde-(1)Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí (1)
18.8.2016 10:44 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-vrchni-referent-oddeleni-aktu-(2)Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí (1)
18.8.2016 10:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Benešovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nem
Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí
Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí (1)
18.8.2016 10:44 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Benešov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent/vrchní referent oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí (1)Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce
18.8.2016 10:43 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj, vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekceOdborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce
18.8.2016 10:43 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-odboru-obnovy-katastralniho-operaOdborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce
18.8.2016 10:43 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sek
Odborný referent odboru obnovy katastrálního operátu Technické sekce
Geoinformatics (pozvánka na konferenci)
18.8.2016 8:25 GISportal.cz Další ročník konference Geoinformatics proběhne ve dnech 12. a 13. září 2016 v místnosti B – 169 na Stavení fakultě ČVUT v Praze. Hlavním tématem konference je Využití otevřených dat v Geomatice. Mezi přednášejícími budou ...Vrchní referent/rada oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Tábor
18.8.2016 6:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj Katastrální pracoviště Táborvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent/rada oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Tábor
Vrchní referent/rada oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Tábor
18.8.2016 6:51 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Jihocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-oddeleni-dokumentace-KN-KatasVrchní referent/rada oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště Tábor
18.8.2016 6:51 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Jihočeský kraj, Katastrální pracoviště Tábor vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent/rada oddělení dokumentace KN Katastrálního pracoviště TáborVýpadek sítě.
17.8.2016 16:59 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 18.8.2016 bude Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem z technických důvodů uzavřeno. Důvodem je oprava sítě WAN dodavatelem telekomunikačních služeb O2 Czech Republic a.s. Omlouváme se za případné komplikace a děkujeme za pochopení.Výpadek sítě.
17.8.2016 16:59 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vypadek-siteVýpadek sítě.
17.8.2016 16:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Dne 18.8.2016 bude Katastrální pracoviště Ústí nad Labem z technických důvodů uzavřeno. Důvodem je oprava sítě WAN dodavatelem telekomunikačních služeb O2 Czech Republic a.s. Omlouváme se za případné komplikace a děkujeme za pochopení.Výpadek sítě.
17.8.2016 16:44 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Usti-nad-Labem/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vypadek-siteOznámení - stavbení úpravy KP Česká Lípa
17.8.2016 16:08 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Liberecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Ceska-Lipa/O-uradu/Aktuality/Oznameni-stavbeni-upravy-KP-Ceska-LipaOznámení - stavbení úpravy KP Česká Lípa
17.8.2016 16:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení klienti,na Katastrálním pracovišti Česká Lípa probíhá od poloviny srpna roku 2016 akce "Vybudování kompresskříní". V této souvislosti může docházet k mírnému omezení ve veřejně přístupných prostorách budovy KP Česká Lípa, zejména při stěhování dokumentů, nábytku a při pohybu zaměstnanců stavební firmy. Funkce podatelny a přepážek informací však budou bez omezení a dostupné v úředních dnech a hodinách.
Děkujeme za pochopení
Ing. Bc. Miroslav Vilímek, ředitel KP Česká Lípa
Oznámení - stavbení úpravy KP Česká Lípa
17.8.2016 16:08 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Vážení klienti,na Katastrálním pracovišti Česká Lípa probíhá od poloviny srpna až do konce roku 2016 akce "Vybudování kompresskříní". V této souvislosti může docházet k mírnému omezení ve veřejně přístupných prostorách budovy KP Česká Lípa, zejména při stěhování dokumentů, nábytku a při pohybu zaměstnanců stavební firmy. Funkce podatelny a přepážek informací však budou bez omezení a dostupné v úředních dnech a hodinách.
Děkujeme za pochopení
Ing. Bc. Miroslav Vilímek, ředitel KP Česká Lípa
20160817-Nový dokument - Hromadné operace
17.8.2016 13:57 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V sekci Uživatelské postupy v ISÚI byl zveřejněn nový dokument "Hromadné operace s prvky" pro editory ISÚI.Zveřejněno 17. 8. 2016
20160817-Nový dokument - Hromadné operace
17.8.2016 13:57 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/RUIAN-novinky/2016/20160817-Novy-dokument-Hromadne-operace20160817-Nový dokument - Hromadné operace
17.8.2016 13:57 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/RUIAN-novinky/2016/20160817-Novy-dokument-Hromadne-operace20160817-Inzerát-Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, OOKO-KÚ pro Středočeský kr
17.8.2016 13:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V části "Volná místa" byl vystaven inzerát na pracovní pozici "Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj"20160817-Inzerát-Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, OOKO-KÚ pro Středočeský kr
17.8.2016 13:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20160817Inzerat-Odborny-referent-katastru-nemovito20160817Inzerát-Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, OOKO-KÚ pro Středočeský kra
17.8.2016 13:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření V části "Volná místa" byl vystaven inzerát na pracovní pozici "Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj"Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu
17.8.2016 13:20 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj, vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátuOdborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu
17.8.2016 13:20 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-katastru-nemovitosti-Technicke-seOdborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu
17.8.2016 13:20 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent katastru nemovitostí - Technické sekce, odbor obnovy katastrálního operátu
Telefonní ústředna - porucha
17.8.2016 12:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Provozní informace,z důvodu poruchy telefonní ústředny je telefonní spojení na Katastrální pracoviště Olomouc a Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj přerušeno. Na odstranění závady intenzivně pracujeme.
Omlouváme se za vzniklé komplikace. Děkujeme za pochopení.
Telefonní ústředna - porucha
17.8.2016 12:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Olomouc/O-uradu/Aktuality/Telefonni-ustredna-poruchaTelefonní ústředna - porucha
17.8.2016 12:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Provozní informace,z důvodu poruchy telefonní ústředny je telefonní spojení na Katastrální pracoviště Olomouc a Katastrální úřad pro Olomoucký kraj přerušeno. Na odstranění závady intenzivně pracujeme.
Omlouváme se za vzniklé komplikace. Děkujeme za pochopení.
Telefonní ústředna - porucha
17.8.2016 12:23 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Olomoucky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Telefonni-ustredna-poruchaMapová aplikace Investiční akc
17.8.2016 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Investiční akce 2016 (http://geoportal.kraj-jihocesky.gov.cz/gs/doprava/) byla doplněna o informace k uzavírkám silnic II/135 v obci Svinky a II/157 v obci Trhové Sviny.Mapová aplikace Investiční akc
17.8.2016 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Investiční akce 2016 (http://geoportal.kraj-jihocesky.gov.cz/gs/doprava/) byla doplněna o informace k uzavírkám silnic II/135 v obci Svinky a II/157 v obci Trhové SvinyMapová aplikace Investiční akc
17.8.2016 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Investiční akce 2016 (http://geoportal.kraj-jihocesky.gov.cz/gs/doprava/) byla doplněna o informace k uzavírkám v důsledku rekonstrukcí silnic II/135 v obci Svinky a II/157 v obci Trhové SvinyMapová aplikace Investiční akc
17.8.2016 12:00 Jihočeský kraj Mapová aplikace Investiční akce 2016 byla doplněna o informace k uzavírkám silnic II/135 v obci Svinky a II/157 v obci Trhové Sviny.Přehledná správa majetku zvyšuje výnosy z pachtu
17.8.2016 10:16Vlastníte zemědělskou půdu? V tom případě jistě víte, jakou administrativní zátěž to přináší. Každoroční daňová přiznání, hlídání vývoje cen půdy, vyjednávání s jednotlivými zemědělci, správa pachtovních smluv. Pokud vlastníte pozemky ve více katastrálních územích, může se jednoduše stát, že ztratíte přehled, zda pronajímáte a dostáváte pachtovné za skutečně všechny své pozemky a zda máte vše řádně smluvně ošetřeno v pachtovních smlouvách.
CleverAssets, aplikace pro správu zemědělské půdy, veškerou agendu týkající se správy majetku výrazně zjednodušuje. Jde o online aplikaci, která díky průběžné aktualizaci s katastrem nemovitostí zajišťuje aktuální online přehled o smluvních vztazích, pomáhá automaticky generovat pachtovní smlouvy a podklady pro dotace ke každému pozemku a vytvoření daňového přiznání je záležitostí na pár minut. Díky grafickým výstupům vše vidíte jasně a přehledně, navíc bez složitých instalací nového softwaru.
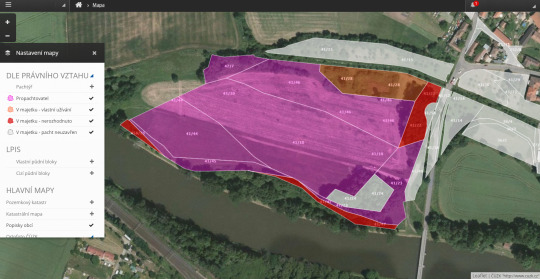
Vlastníkům zemědělské půdy jsme schopni připravit kompletní analýzu jejich vlastnictví a doporučit konkrétní kroky pro zvýšení výnosů z pachtů. Díky mnoholetým zkušenostem s katastrem nemovitostí a vlastním průzkumům trhu nabízíme také poradenství v oblasti nákup a prodej půdy a zajištění potřebné agendy.

Aplikace je určena nejen vlastníkům půdy, ale také hospodařícím zemědělcům, kterým hlídá změny ve vlastnictví půdy, automaticky vyplácí pacht, zjednodušuje směny pozemků a mnoho dalšího.
Pořádek v pachtovních smlouvách přispívá k nastavení tržní ceny pachtů a férovému jednání mezi vlastníkem a zemědělcem, což je klíčem pro zachování kvality půdy pro budoucí generace.
Více o tom, jak aplikace funguje, také na www.cleverassets.cz.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureNorth Wales Police has successfully implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s Known Callers contact management module as part of its Intergraph Computer-Aided Dispatch (I/CAD) incident management system. The new module helps North Wales Police satisfy a crucial requirement of providing the ability to identify repeat and vulnerable callers at the point of contact.
Addressing caller vulnerabilities is a key requirement for North Wales Police and other forces throughout the UK, a need cited by Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary (HMIC), which independently assesses police forces in England and Wales on how effectively they protect vulnerable people from harm and support victims. The solution also aids police force safety by automatically alerting operators to any potential risk of dispatching officers to premises where legally held firearms may be present. The new module builds upon North Wales Police’s existing I/CAD system from Hexagon, a suite of industry-leading incident management software that features complete, integrated capabilities for call handling and dispatching, field communications and more.
The new Hexagon solution improves the collection of information from the caller through a configurable workflow that supports the principle of “collect once, use many times”. It uses a specialised rules engine that supports structured dialogue and helps avoid double entry of information. It also automates the search of data already held by the force, reducing the time spent by the communications operator on basic checking of intelligence. This consistent approach provides more effective support to those in greatest need of the police’s protection and support.
Paul Shea, North Wales Police Control Room Manager, said, “Hexagon has provided North Wales Police with a solution which assists communications operators to identify caller’s vulnerabilities at the point of contact, while also providing a comprehensive history of calls. Following work by the Hexagon team to meet our organisations’ specific needs at the point of call, the solution has far exceeded our initial expectations.”
Ian Holmes, Public Safety and Security Sales Manager, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure, said, “Hexagon is pleased to assist North Wales Police by improving call-handling performance as identified by HMIC. Building from our long-term commitment and relationship, we will continue to work in partnership together for a safer North Wales.”
The global leader in public safety and security solutions, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps protect 1 in 12 people worldwide. By improving the quality, accuracy and availability of critical information, Hexagon’s integrated solutions increase public safety and security performance and productivity, while reducing the total cost of ownership for mission-critical IT investments.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureNorth Wales Police has successfully implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s Known Callers contact management module as part of its Intergraph Computer-Aided Dispatch (I/CAD) incident management system. The new module helps North Wales Police satisfy a crucial requirement of providing the ability to identify repeat and vulnerable callers at the point of contact.
Addressing caller vulnerabilities is a key requirement for North Wales Police and other forces throughout the UK, a need cited by Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary (HMIC), which independently assesses police forces in England and Wales on how effectively they protect vulnerable people from harm and support victims. The solution also aids police force safety by automatically alerting operators to any potential risk of dispatching officers to premises where legally held firearms may be present. The new module builds upon North Wales Police’s existing I/CAD system from Hexagon, a suite of industry-leading incident management software that features complete, integrated capabilities for call handling and dispatching, field communications and more.
The new Hexagon solution improves the collection of information from the caller through a configurable workflow that supports the principle of “collect once, use many times”. It uses a specialised rules engine that supports structured dialogue and helps avoid double entry of information. It also automates the search of data already held by the force, reducing the time spent by the communications operator on basic checking of intelligence. This consistent approach provides more effective support to those in greatest need of the police’s protection and support.
Paul Shea, North Wales Police Control Room Manager, said, “Hexagon has provided North Wales Police with a solution which assists communications operators to identify caller’s vulnerabilities at the point of contact, while also providing a comprehensive history of calls. Following work by the Hexagon team to meet our organisations’ specific needs at the point of call, the solution has far exceeded our initial expectations.”
Ian Holmes, Public Safety and Security Sales Manager, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure, said, “Hexagon is pleased to assist North Wales Police by improving call-handling performance as identified by HMIC. Building from our long-term commitment and relationship, we will continue to work in partnership together for a safer North Wales.”
The global leader in public safety and security solutions, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps protect 1 in 12 people worldwide. By improving the quality, accuracy and availability of critical information, Hexagon’s integrated solutions increase public safety and security performance and productivity, while reducing the total cost of ownership for mission-critical IT investments.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureNorth Wales Police has successfully implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s Known Callers contact management module as part of its Intergraph Computer-Aided Dispatch (I/CAD) incident management system. The new module helps North Wales Police satisfy a crucial requirement of providing the ability to identify repeat and vulnerable callers at the point of contact.
Addressing caller vulnerabilities is a key requirement for North Wales Police and other forces throughout the UK, a need cited by Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary (HMIC), which independently assesses police forces in England and Wales on how effectively they protect vulnerable people from harm and support victims. The solution also aids police force safety by automatically alerting operators to any potential risk of dispatching officers to premises where legally held firearms may be present. The new module builds upon North Wales Police’s existing I/CAD system from Hexagon, a suite of industry-leading incident management software that features complete, integrated capabilities for call handling and dispatching, field communications and more.
The new Hexagon solution improves the collection of information from the caller through a configurable workflow that supports the principle of “collect once, use many times”. It uses a specialised rules engine that supports structured dialogue and helps avoid double entry of information. It also automates the search of data already held by the force, reducing the time spent by the communications operator on basic checking of intelligence. This consistent approach provides more effective support to those in greatest need of the police’s protection and support.
Paul Shea, North Wales Police Control Room Manager, said, “Hexagon has provided North Wales Police with a solution which assists communications operators to identify caller’s vulnerabilities at the point of contact, while also providing a comprehensive history of calls. Following work by the Hexagon team to meet our organisations’ specific needs at the point of call, the solution has far exceeded our initial expectations.”
Ian Holmes, Public Safety and Security Sales Manager, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure, said, “Hexagon is pleased to assist North Wales Police by improving call-handling performance as identified by HMIC. Building from our long-term commitment and relationship, we will continue to work in partnership together for a safer North Wales.”
The global leader in public safety and security solutions, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps protect 1 in 12 people worldwide. By improving the quality, accuracy and availability of critical information, Hexagon’s integrated solutions increase public safety and security performance and productivity, while reducing the total cost of ownership for mission-critical IT investments.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Hexagon solution aids police in satisfying key public and police safety requirementsHexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Hexagon solution aids police in satisfying key public and police safety requirementsHexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureNorth Wales Police has successfully implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s Known Callers contact management module as part of its Intergraph Computer-Aided Dispatch (I/CAD) incident management system. The new module helps North Wales Police satisfy a crucial requirement of providing the ability to identify repeat and vulnerable callers at the point of contact.
Addressing caller vulnerabilities is a key requirement for North Wales Police and other forces throughout the UK, a need cited by Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary (HMIC), which independently assesses police forces in England and Wales on how effectively they protect vulnerable people from harm and support victims. The solution also aids police force safety by automatically alerting operators to any potential risk of dispatching officers to premises where legally held firearms may be present. The new module builds upon North Wales Police’s existing I/CAD system from Hexagon, a suite of industry-leading incident management software that features complete, integrated capabilities for call handling and dispatching, field communications and more.
The new Hexagon solution improves the collection of information from the caller through a configurable workflow that supports the principle of “collect once, use many times”. It uses a specialised rules engine that supports structured dialogue and helps avoid double entry of information. It also automates the search of data already held by the force, reducing the time spent by the communications operator on basic checking of intelligence. This consistent approach provides more effective support to those in greatest need of the police’s protection and support.
Paul Shea, North Wales Police Control Room Manager, said, “Hexagon has provided North Wales Police with a solution which assists communications operators to identify caller’s vulnerabilities at the point of contact, while also providing a comprehensive history of calls. Following work by the Hexagon team to meet our organisations’ specific needs at the point of call, the solution has far exceeded our initial expectations.”
Ian Holmes, Public Safety and Security Sales Manager, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure, said, “Hexagon is pleased to assist North Wales Police by improving call-handling performance as identified by HMIC. Building from our long-term commitment and relationship, we will continue to work in partnership together for a safer North Wales.”
The global leader in public safety and security solutions, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps protect 1 in 12 people worldwide. By improving the quality, accuracy and availability of critical information, Hexagon’s integrated solutions increase public safety and security performance and productivity, while reducing the total cost of ownership for mission-critical IT investments.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureNorth Wales Police has successfully implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s Known Callers contact management module as part of its Intergraph Computer-Aided Dispatch (I/CAD) incident management system. The new module helps North Wales Police satisfy a crucial requirement of providing the ability to identify repeat and vulnerable callers at the point of contact.
Addressing caller vulnerabilities is a key requirement for North Wales Police and other forces throughout the UK, a need cited by Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary (HMIC), which independently assesses police forces in England and Wales on how effectively they protect vulnerable people from harm and support victims. The solution also aids police force safety by automatically alerting operators to any potential risk of dispatching officers to premises where legally held firearms may be present. The new module builds upon North Wales Police’s existing I/CAD system from Hexagon, a suite of industry-leading incident management software that features complete, integrated capabilities for call handling and dispatching, field communications and more.
The new Hexagon solution improves the collection of information from the caller through a configurable workflow that supports the principle of “collect once, use many times”. It uses a specialised rules engine that supports structured dialogue and helps avoid double entry of information. It also automates the search of data already held by the force, reducing the time spent by the communications operator on basic checking of intelligence. This consistent approach provides more effective support to those in greatest need of the police’s protection and support.
Paul Shea, North Wales Police Control Room Manager, said, “Hexagon has provided North Wales Police with a solution which assists communications operators to identify caller’s vulnerabilities at the point of contact, while also providing a comprehensive history of calls. Following work by the Hexagon team to meet our organisations’ specific needs at the point of call, the solution has far exceeded our initial expectations.”
Ian Holmes, Public Safety and Security Sales Manager, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure, said, “Hexagon is pleased to assist North Wales Police by improving call-handling performance as identified by HMIC. Building from our long-term commitment and relationship, we will continue to work in partnership together for a safer North Wales.”
The global leader in public safety and security solutions, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps protect 1 in 12 people worldwide. By improving the quality, accuracy and availability of critical information, Hexagon’s integrated solutions increase public safety and security performance and productivity, while reducing the total cost of ownership for mission-critical IT investments.
Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure Helps North Wales Police Identify Vulnerable Callers
17.8.2016 2:30 Hexagon Safety & InfrastructureNorth Wales Police has successfully implemented Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure’s Known Callers contact management module as part of its Intergraph Computer-Aided Dispatch (I/CAD) incident management system. The new module helps North Wales Police satisfy a crucial requirement of providing the ability to identify repeat and vulnerable callers at the point of contact.
Addressing caller vulnerabilities is a key requirement for North Wales Police and other forces throughout the UK, a need cited by Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary (HMIC), which independently assesses police forces in England and Wales on how effectively they protect vulnerable people from harm and support victims. The solution also aids police force safety by automatically alerting operators to any potential risk of dispatching officers to premises where legally held firearms may be present. The new module builds upon North Wales Police’s existing I/CAD system from Hexagon, a suite of industry-leading incident management software that features complete, integrated capabilities for call handling and dispatching, field communications and more.
The new Hexagon solution improves the collection of information from the caller through a configurable workflow that supports the principle of “collect once, use many times”. It uses a specialised rules engine that supports structured dialogue and helps avoid double entry of information. It also automates the search of data already held by the force, reducing the time spent by the communications operator on basic checking of intelligence. This consistent approach provides more effective support to those in greatest need of the police’s protection and support.
Paul Shea, North Wales Police Control Room Manager, said, “Hexagon has provided North Wales Police with a solution which assists communications operators to identify caller’s vulnerabilities at the point of contact, while also providing a comprehensive history of calls. Following work by the Hexagon team to meet our organisations’ specific needs at the point of call, the solution has far exceeded our initial expectations.”
Ian Holmes, Public Safety and Security Sales Manager, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure, said, “Hexagon is pleased to assist North Wales Police by improving call-handling performance as identified by HMIC. Building from our long-term commitment and relationship, we will continue to work in partnership together for a safer North Wales.”
The global leader in public safety and security solutions, Hexagon Safety & Infrastructure helps protect 1 in 12 people worldwide. By improving the quality, accuracy and availability of critical information, Hexagon’s integrated solutions increase public safety and security performance and productivity, while reducing the total cost of ownership for mission-critical IT investments.
Natura 2000 - Krajinný pokryv (E-shop - předpřipravená datová sada)
17.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Vrstva Natura 2000 je součástí služby Copernicus pro monitorování území. Obsahuje podrobné informace o využití území v chráněných oblastech soustavy Natura 2000 (spolu s 2km obalovou zónou) ve 39 evropských státech. Jedná se o vektorová data v měřítku cca 1 : 10 000, aktuálně dostupná za roky 2006 a 2012.Mapa osídlení (E-shop - předpřipravená datová sada)
17.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Mapa evropského osídlení je součástí služby Copernicus pro monitorování území. Jedná se o rastr vytvořený na základě družicových snímků SPOT5 a SPOT6, který zobrazuje procento zastavěného území na prostorovou jednotku. Aktuálně jsou k dispozici data za r. 2014 se 100metrovým prostorovým rozlišením a za r. 2016 s 10metrovým rozlišením.Zásady územního rozvoje - využití území - WFS
17.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Zásady územního rozvoje - využití území - WMSRiparian Zones (E-shop - předpřipravená datová sada)
17.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Riparian Zones (Břehové zóny) jsou součástí služby Copernicus pro monitorování území. Obsahuje podrobné informace o využití území v okolí vodních toků a zmapovaných zelených lineárních prvků (Green Linear Elements) ve 39 evropských státech. Jedná se o vektorová data v měřítku cca 1 : 10 000, aktuálně dostupná za období 2010 - 2013.Zásady územního rozvoje - využití území - WMS
17.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Zásady územního rozvoje - využití území - WMSHigh Resolution Layers 2012 (E-shop - předpřipravená datová sada)
17.8.2016 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE High Resolution Layers (HRL) jako součást služby evropského programu Copernicus pro monitorování území obsahují informace z pěti různých tématických oblastí – nepropustnost povrchu, lesy (hustota a typ lesních porostů), přírodní a polopřírodní louky (v současnosti není dostupná ke stažení a je přepracovávána), mokřady a trvalé vodní plochy. Jedná se o rastrová data o prostorovém rozlišení 20 metrů, která jsou vytvářena poloautomatickými postupy nad družicovými snímky každé 3 roky (aktuálně za r. 2012).Data vznikala řízenou klasifikací nad družicovými snímky a následnou manuální editací. Původní prostorové rozlišení je 20 metrů, validované produkty budou převzorkovány na 100metrové rozlišení. Data nebyla validována.Ministr zemědělství Marian Jurečka pracovně navštívil Státní pozemkový úřad
17.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Praha, 16. srpna 2016 – Ministr zemědělství Marian Jurečka dnes pracovně navštívil ústředí Státního pozemkového úřadu (SPÚ). Zúčastnil se zde porady krajských ředitelů a vedení SPÚ.Státní pozemkový úřad zahájil 10. ročník soutěže Společné zařízení roku
17.8.2016 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Praha, 17. srpna 2016 – Státní pozemkový úřad dnes zahájil jubilejní ročník soutěže o nejkvalitnější realizovaná společná zařízení navrhovaná v pozemkových úpravách.Zemřel Ing. Zdeněk Konečný
16.8.2016 18:57 Zeměměřič Ing. Zdeněk Konečný zemřel 11. srpna 2016 ve věku 65 let.Oprava pádu ArcMap 10.4 a 10.4.1 při otevření mapového dokumentu
16.8.2016 14:35 ARCDATASpolečnost Esri obdržela od uživatelů chybová hlášení, že po aktualizaci na ArcGIS 10.4 nebo 10.4.1 for Desktop dochází k pádu aplikace ArcMap při otevření mapového dokumentu. Zjistilo se, že toto chování je spojeno s uložením dat v enterprise geodatabázi s MS SQL Server 2008, 2008 R2, 2012 a 2014, pokud geodatabáze obsahuje kombinaci tříd prvků s nízkou a vysokou přesností ukládání souřadnic. Uživatelé používající jiný typ databáze tímto problémem nebyli zasaženi.
Uživatelům, kteří ve své enterprise geodatabázi s MS SQL Server používají oba typy přesnosti ukládání souřadnic, proto doporučujeme instalovat opravný balíček, který je možné stáhnout ze stránek společnosti Esri. Více se o této problematice můžete dočíst v následujícím článku.
















