zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Interview with Rob Wall, account executive at Basis Technology
14.4.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsSnímky z družice Sentinel-5P aneb změna koncentrací NO2 oproti roku 2019 – ČR, Evropa, svět
14.4.2020 8:53 GISportal.cz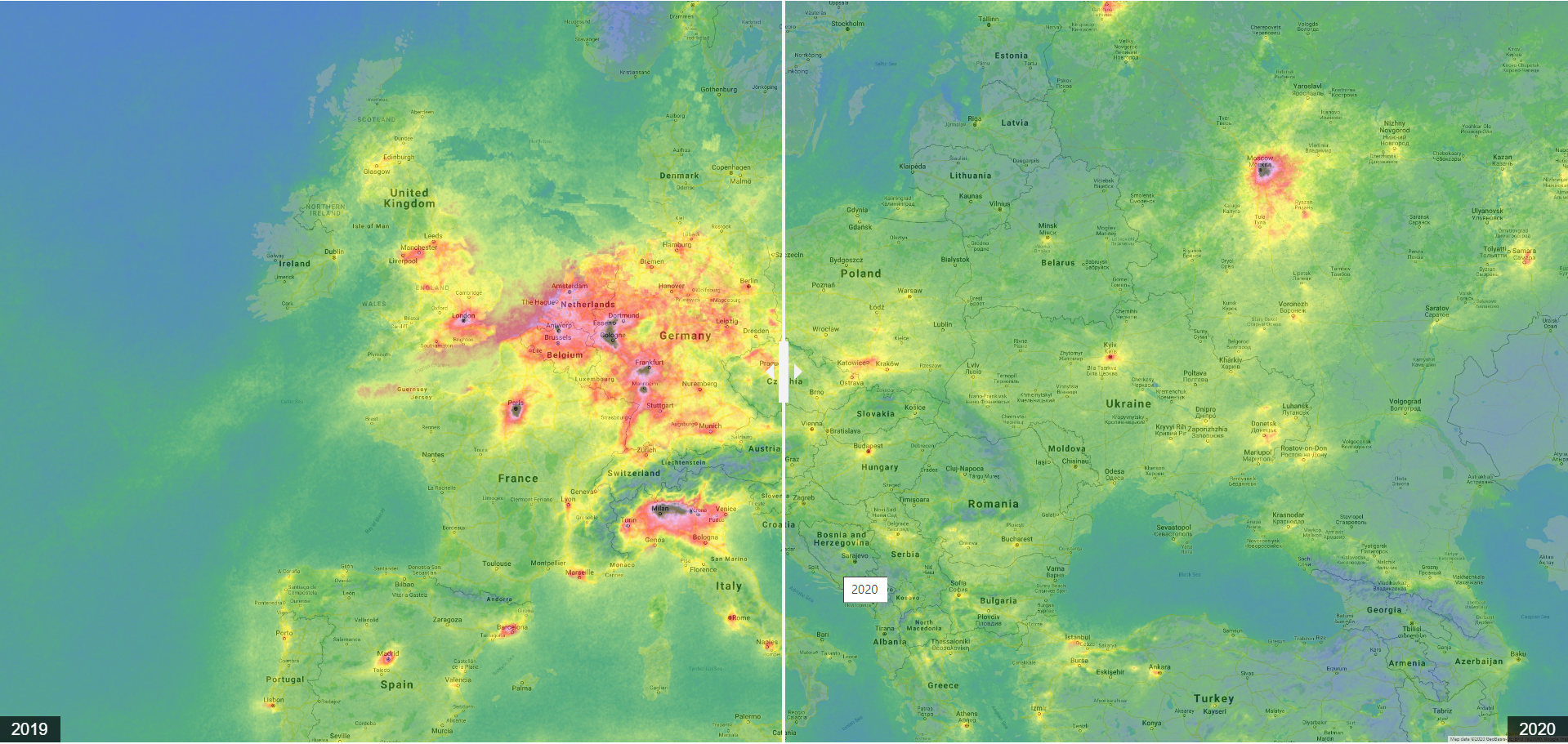
O vlivu opatření proti šíření koronaviru na kvalitu ovzduší jsme zde psali již vícekrát. Nyní se podívejme, jak vypadají opět novější družicové snímky za totožné období v roce 2019 a 2020 a to jak pro Českou republiku, tak pro Evropu a i celý svět. Zaměříme se na koncentrace oxidu dusičitého (NO2). Primárním zdrojem oxidu dusičitého […]
The post Snímky z družice Sentinel-5P aneb změna koncentrací NO2 oproti roku 2019 – ČR, Evropa, svět appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Provádíme podrobné fotodokumentace staveb z dronů
14.4.2020 8:50 UpVisionProvádíme podrobné fotodokumentace staveb z dronů, jako například fotodokumentaci fasády administrativní budovy po dokončení stavby minulý týden, včetně fotodokumentace průběhu výstavby celé budovy. https://www.facebook.com/UpVision.cz/photos/pcb.1229496733905558/1229496417238923/
The post Provádíme podrobné fotodokumentace staveb z dronů appeared first on Upvision.
Provádíme podrobné fotodokumentace staveb z dronů
14.4.2020 8:50 UpVisionProvádíme podrobné fotodokumentace staveb z dronů, jako například fotodokumentaci fasády administrativní budovy po dokončení stavby minulý týden, včetně fotodokumentace průběhu výstavby celé budovy. https://www.facebook.com/UpVision.cz/photos/pcb.1229496733905558/1229496417238923/
The post Provádíme podrobné fotodokumentace staveb z dronů appeared first on Upvision.
Koronavirus 3
14.4.2020 7:25 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V souvislosti s vydáním usnesení vlády ČR č. 399 ze dne 9. 4. 2020 o mimořádných opatřeních Ministerstva zdravotnictví na další období s účinností od 11. 4. 2020 od 6:00 hod. do 19. 4. 2020 do 24:00 hod. platí na všech pracovištích katastrálních úřadů nadále omezený provoz pro veřejnost. Katastrální úřady přijímají bez omezení elektronická podání ve stanovené formě a poštovní zásilky. K získání informací z katastru nemovitostí využijte aplikaci Nahlížení do katastru, která umožňuje vyřízení úplného výpisu z katastru přes e-shop. Neodkladné záležitosti bude možné vyřídit v omezených úředních hodinách v pondělí a ve středu od 8:00 do 11:00 hodin. Prosíme, abyste se před případnou návštěvou řídili pokyny uvedenými na www stránkách příslušných katastrálních pracovišť.Děkujeme za pochopení.
Koronavirus 3
14.4.2020 7:25 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Koronavirus-3Esri COVID-19 zdroje
14.4.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Společnost Esri reaguje na současnou situaci týkající se Koronaviru a zakládá platformu obsahující volně dostupný datasety, aplikace a další zdroje využitelné při mapování a řešení tétoTraditional PC Shipments Saw a Sharp Decline in Q1 2020 Despite Increased Demand to Meet Remote Work and School Needs, According to IDC
14.4.2020 0:39 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars FRAMINGHAM, Mass. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 13, 2020 —The global traditional PC market, comprised of desktops, notebooks, and …
Sanjay Gangal interviews Dr. Michael Flaxman, Spatial Data Science Practice Lead at OmniSci
13.4.2020 21:51 GISCafe.com Webcasts-WebinarsEnhanced COVID-19 Map Shows Deadly Trends In Rural U.S. Counties
13.4.2020 21:07 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Company's data scientists find hot spots for coronavirus among small, close-knit communitiesNASHVILLE, Tenn., April 13, 2020 — (PRNewswire) …
Esri and FEMA Provide Free Access to Data and Mapping Technology in Response to COVID-19
13.4.2020 17:45 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Advanced Software Solutions to Aid Non-Federal Governmental EntitiesREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 13, 2020 —
Esri, …
American Traditions Insurance Company Joins GIC Program
13.4.2020 17:45 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DES PLAINES, Ill., April 13, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — American Traditions Insurance Company, a company dedicated to providing …Volunteers Launch Innovative COVID-19 Resource Mapping
13.4.2020 17:45 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Youth volunteers across the United States have launched a live map (bit.ly/COVID19resourcemapping) visualizing community resources in response to …Kam s pozemkovými úpravami?
13.4.2020 9:03 Komora pozemkových úprav SRAký bude, resp. aký by mohol byť osud pozemkových úprav pod novým vedením rezortu?
Kam s pozemkovými úpravami?
13.4.2020 9:03 Komora pozemkových úprav SRAký bude osud pozemkových úprav pod novým vedením rezortu?
Kam s pozemkovými úpravami?
13.4.2020 9:03 Komora pozemkových úprav SRAký bude, resp. aký by mohol byť osud pozemkových úprav pod novým vedením rezortu?
Kam s pozemkovými úpravami?
13.4.2020 9:03 Komora pozemkových úprav SRAký bude, resp. aký by mohol byť osud pozemkových úprav pod novým vedením rezortu?
Kam s pozemkovými úpravami?
13.4.2020 9:03 Komora pozemkových úprav SRAký bude osud pozemkových úprav pod novým vedením rezortu?
Kam s pozemkovými úpravami?
13.4.2020 9:03 Komora pozemkových úprav SRAký bude, resp. aký by mohol byť osud pozemkových úprav pod novým vedením rezortu?
20200411 - Generování změnových VFR
11.4.2020 22:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele změnových VFR:Od pátku 10. 4. 2020 bylo obnoveno standardní generování změnových VFR. Soubor za 9. 4. 2020 obsahuje i změny za 7. a 8. 4. 2020.
Zveřejněno 11. 4. 2020
20200411 - Generování změnových VFR
11.4.2020 22:05 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele změnových VFR:Generování změnových souborů VFR bylo obnoveno. Soubory 20200407_ST_Z*, které byly původně vystaveny, nebyly kompletní a byly odstraněny. Jejich změny jsou obsaženy v následujících souborech 20200409_ST_Z*. Pokud jste si soubory 20200407_ST_Z* již stáhli, počítejte s tím, že v souborech 20200409_ST_Z* jsou obsaženy stejné změny ještě jednou. Řada návazností v podobě atributu <vf:PredchoziSoubor> se soubory 20200407_ST_Z* nepočítá. Omlouváme se za komplikace.
Aktualizováno 14. 4. 2020
20200411 - Generování změnových VFR
11.4.2020 22:05 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/2-Poskytovani-udaju-RUIAN-ISUI-VDP/Vymenny-format-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-VFR/20200411-Generovani-zmenovych-VFRUIUC’s CyberGIS Center is recruiting a System Engineer
11.4.2020 7:21 The ad and application instruction are available on this webpage: https://cybergis.illinois.edu/career/system-engineer/. This position is expected to join a dynamic team to make significant contributions to innovating big-data and high-performance geospatial computing systems. The position is full-time, permanent, and eligible for attractive benefits. Application deadline is April 13, 2020. Your help for spreading the word would be greatly appreciated.Earth Challenge 2020 World’s Largest Citizen Science Initiative Launched for Earth Day 2020
10.4.2020 22:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars World’s Largest Citizen Science Initiative Launched for Earth Day 2020Individuals Around the Globe Use Smart Phone App to Take Action and …
Microsoft’s Singapore digital twin “offers blueprint for smart buildings of the future”
10.4.2020 21:31 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Global Construction Review, UK
Read the articleStony Brook University: managing energy with data
10.4.2020 21:27 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Chief Sustainability Officer, UK
Read the articleBentley and Schneider build digital twin for Microsoft
10.4.2020 21:24 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
International Construction, UK
Read the articleBentley Systems’ SVP Alan Kiraly Elected to the Board of MIMOSA
10.4.2020 21:20 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
GeoConnexion, UK
Read the articlexyzt.ai Delivers Maritime Location Intelligence at an Unprecedented Scale
10.4.2020 18:21 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 07 April 2020, Leuven, Belgium - AIS or Automatic Identification System is a technology used for vessels to communicate their status, including GPS …4 Earth Intelligence Launches Satellite Land Use Mapping Service
10.4.2020 18:20 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Bristol, UK, 09 April 2020 – Earth observation company 4 Earth Intelligence (4EI) has launched a new land cover mapping service based on …INCATech Receives 2020 Esri® Federal Small Business Specialty Award for Delivery
10.4.2020 18:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars INCATech received the Federal Small Business Specialty Award, Delivery Partner from Esri® for consistent engagement and excellence in delivering …Tennessee River Valley Mapguide Announces New Site Platform
10.4.2020 18:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The Tennessee River Valley Mapguide announces its new website platform showcasing the natural, cultural and historic attractions that define the …HealthAlerts.io Launched to Map COVID-19 Testing Locations and Combat the Coronavirus
10.4.2020 18:19 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Map COVID-19 Testing Sites, Access Local Assessment Tools and Get Real-time Health AlertsVANCOUVER, April 10, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — …
Earth from Space: Wheatbelt, Western Australia
10.4.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:03:23
Video:
00:03:23
In this week's edition of the Earth from Space programme, Copernicus Sentinel-2 takes us over an area in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia.
See also Wheatbelt, Western Australia to download the image.
Wheatbelt, Western Australia
10.4.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth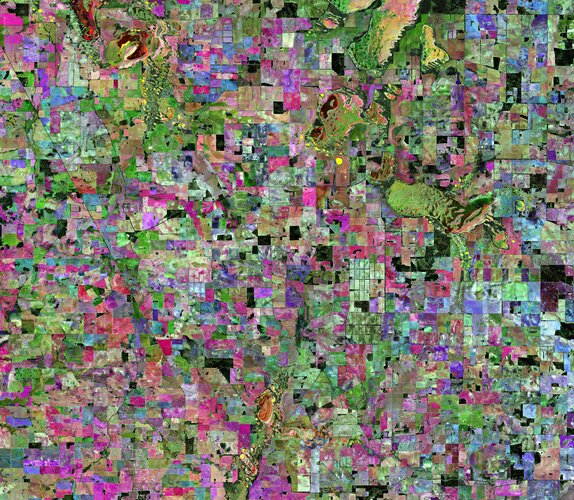 Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features an area in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia.
Image:
This Copernicus Sentinel-2 image features an area in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia.
INSPIRE téma Budovy (BU)
10.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma budovy (BU). Data pochází částečně z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech, a částečně z ISKN (Informační systém katastru nemovistostí). Zdrojem informací o budovách v ISKN je objekt Stavba, v RÚIAN je to Stavební objekt. Většina Staveb je zároveň Stavebními objekty, ale jsou případy, kdy tomu tak není. Kromě Budov datová sada obsahuje i části budov, které jsou pro potřeby INSPIRE vyjádřeny vchody z RÚIAN. Vchody obsahují informace o počtu podlaží, technickoekonomických atributech apod. Datová sada pokrývá celé území české republiky. V datové sadě není uvedeno 1,14%, t.j. 48345 budov (k 06. 04. 2020), protože neobsahují definiční bod ani polygon. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech, ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních, v zákoně 256/2013 Sb., o katastru nemovitostí, v katastrální vyhlášce č. 357/2013 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Buildings v 3.0 z 13.12.2013. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Budovy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
10.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 06. 04. 2020 je to 96,72% území České republiky, t.j. 76 283,59km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.INSPIRE téma Adresy (AD)
10.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma adresy (AD). Vychází především z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze adresní místa a jejich komponenty, kterými jsou stát, obec, část obce, městský obvod v Praze (MOP), městký obvod/městská část (MO/MČ), ulice a pošta a to na území celé České Republiky. Obsahují rozvněž geometrii, která určuje definiční bod adresního místa. V datové sadě nění uvedeno 1,18%, t.j. 34668 adresních míst (k 06. 04. 2020), protože neobsahují definiční bod, podle kterého by je bylo možné prostorově určit. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech a ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních a INSPIRE Data Specification on Addresses v 3.0.1 z 26.4.2010. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Adresy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Parcely (CP)
10.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze katastrální území (pro celou Českou Republiku) a parcely a jejich hranice z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 06. 04. 2020 je to 96,72% území České republiky, t.j. 76 283,59km2). Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Parcely ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě poskytovaná v e-shopu
10.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě je poskytována za úplatu a obsahuje analogovou mapu s kompletní kresbou. Analogová mapa pokrývá 3,03 % území České republiky, což je 2 392,74km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.Katastrální mapa ve formátech DGN a DXF poskytovaná v e-shopu
10.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě je poskytována zdarma ve formátu DGN a DXF a obsahuje prvky Digitální katastrální mapy (DKM) a Katastrální mapy digitalizované (KMD), tedy bodová pole, budovy, další prvky mapy, hranice parcel, katastrální hranice, parcely katastru nemovitostí, prvky orientační mapy a hranice věcného břemene. Z důvodu použití formátu DGN produkt neobsahuje značky na liniích a oblouky jsou nahrazeny lomenými čárami. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě k 06. 04. 2020 pokrývá 96,72% území České republiky, t.j. 76 283,59km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.NearSpace Launch Inc. celebrates 500+ satellite systems in orbit over five years: Now establishing an Indiana STEM education non-profit
10.4.2020 0:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars UPLAND, Ind., April 9, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — NearSpace Launch Inc. (NSL) will be delivering its 500th space system for launch in …OmniSci and Z by HP Accelerate Data-Driven Workflows
10.4.2020 0:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars World's Most Powerful Workstation Now Available with OmniSci Platform to Bring Accelerated Analytics to Individual Technical ProfessionalsSAN …
Suntuity AirWorks and Suntuity University Present Free Multi-Series Webinars to Help First Responders Leverage Drones to Combat COVID-19
10.4.2020 0:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Leveraging Suntuity University's Learning Management Systems and Suntuity AirWorks' enterprise equipment support teams …DroneUp Submits Proposal to the Unicode Consortium for a Drone Emoji
9.4.2020 22:33 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Launching Petition for Industry Participation
Virginia Beach, VA (April 9, 2020) — DroneUp, an end-to-end aerial data solutions …
OGC and buildingSMART International publish discussion paper on the integration of BIM and GIS
9.4.2020 22:18 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New discussion paper aims to coordinate the development of data standards produced by the two leading standards organizationThe Open Geospatial …
Pomáháme hasičům, když jde o vteřiny
9.4.2020 17:15 CEDA Maps a.s. Praha, 9. dubna 2020 - CEDA pomáhá v boji s koronavirem. Abychom podpořili Hasičský záchranný sbor, poskytneme mu zdarma aktualizace profesionálních map.Satellites and machine learning for water management
9.4.2020 17:13 ESA Observing the Earth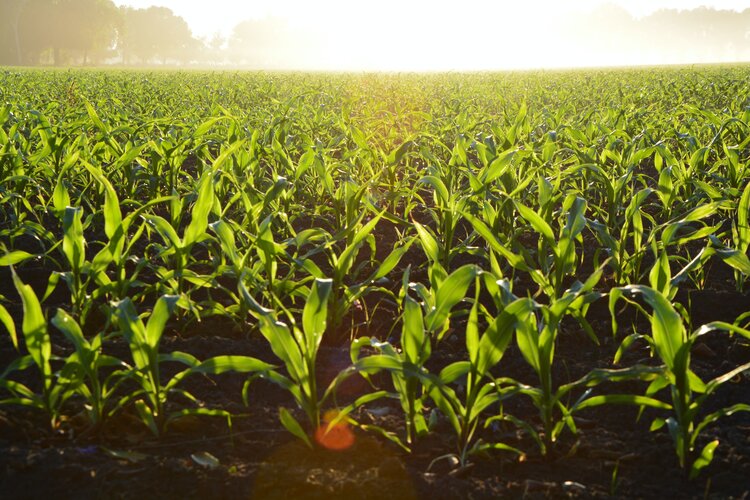
Freshwater is vital to life – but a growing global population, economic development and the effects of climate change are putting mounting pressure on this precious finite resource. Globally, agriculture accounts for 70% of all freshwater consumed, so efficient water management is essential. An ESA project that focuses on fusing data from two different Copernicus Sentinel missions is providing estimates of evapotranspiration, which is not only key for sustainable agriculture, but also important for water resource management and for a number of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
Iconic Space Technology Firm Returns to Canadian Control as Sale of MDA to Northern Private Capital Closes
9.4.2020 16:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars BRAMPTON, ON, April 8, 2020 — (PRNewswire) —BRAMPTON, ON, April 8, 2020 /CNW/ - Effective today, April 8th, the sale transaction …
Esri Announces Online Analytics Platform for Caribbean Community
9.4.2020 16:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New GeoPortal Site Provides Free Location Data and Mapping ResourcesREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 8, 2020 —
Esri, …
Semantic Visons: Visualizing the Spread of COVID-19 in Global Online Media
9.4.2020 16:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Czech-based data analytics and risk assessment firm Semantic Visions (SV) has released to YouTube a dramatic geospatial visualization of the spread …Nový Metadatový profil ČR (verze 4.2)
9.4.2020 14:54 CENIA - národní geoportál INSPIRE KOVIN (Koordinační výbor pro INSPIRE) po svém posledním jednání doporučil k užívání novou verzi Metadatového profilu ČR. Dokument naleznete na stránce Metadata > Vytvořit na Národním geoportálu INSPIRE. Hlavní změny verze 4.1 oproti verzi 3.1: · doplněno vysvětlení rozdílu mezi síťovými službami a interoperabilními službami; · položky CZ-1 a CZ-3 byly přesunuty do INSPIRE...Investiční referent v oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Králové
9.4.2020 12:32 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Investiční referent v oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Královéhradecký kraj
Investiční referent v oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Králové
9.4.2020 12:32 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Investiční referent v oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro KrálovéInvestiční referent v oddělení hospodářské správy kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Králové
9.4.2020 12:32 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Volna-mista/Investicni-referent-v-oddeleni-hospodarske-spr-(1)Využití BIM při rekonstrukci nádraží Čachovice
9.4.2020 11:48 Hrdlička Rekonstrukce kolejiště a nástupišť v nádraží Čachovice spadá do pilotních projektů využití..Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králov
9.4.2020 11:42 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Králové vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec KrálovRada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králov
9.4.2020 11:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Rada-odborny-rada-v-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-(1)Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králov
9.4.2020 11:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Královévypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada v oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem Katastrálního pracoviště Hradec Králové
20200409 Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.4.2020 11:27 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Melnik/O-uradu/Aktuality/20190828-Odborny-rada-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-(5)20200409 Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.4.2020 11:27 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Mělník Vyhlášení výběrového řízení: Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem V části "Úřední deska", v sekci "Oznámení a jiná úřední sdělení" bylo vystaveno "Oznámení o vyhlášení výběrového řízení na obsazení služebního místa Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem"Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.4.2020 11:26 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Mělník vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostemOdborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.4.2020 11:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Mělníkvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
Odborný referent oddělení právních vztahů k nemovitostem
9.4.2020 11:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Odborny-referent-oddeleni-pravnich-vztahu-k-ne-(2)Co přináší nová verze Map s příběhem?
9.4.2020 9:50 ARCDATAOd čtvrtka 9. dubna je k dispozici nová verze Map s příběhem, která s sebou přináší celou řadu dílčích vylepšení i úplně nových funkcí, které se vám v následujícím přehledu pokusíme krátce představit.
Navigační lišta příběhu
Vytvořením navigační lišty, nebo chcete-li „panelu záložek“, se ke všem blokům formátovaným jako nadpis automaticky vytvoří odkazy, jejichž prostřednictvím může čtenář přejít na konkrétní místo v příběhu.
Tuto funkci zapnete v panelu Návrh:
Z nadpisů se pak vytvoří navigační lišta.
Je-li panel záložek širší, než se vejde na obrazovku, lze se v něm posouvat pomocí šipek.
Maximum zobrazených nadpisů je 10. Pokud je název delší než 30 znaků, je automaticky zkrácen použitím výpustky „…“. Navigační lišta se zobrazuje stále nahoře, tedy i během rolování.
Vlastní úpravy navigační lišty
Lištu je dále možné upravovat. Zobrazit můžete například jen vybrané záložky (nadpisy), nebo upravit texty záložek. Tato nastavení můžete provést v nástrojích lišty na kartě Nastavení.
Nové možnosti bočního bloku: plovoucí panel
Při použití panelu „boční blok“ si můžete vybrat mezi dvěma typy zobrazení textové části: ukotveným a plovoucím, který se pohybuje zároveň s rolováním stránky.
Stejně jako do ukotveného verze, i do plovoucí je kromě textu možné přidávat i mapy, fotografie či jiný multimédiální obsah, oddělovače a tlačítka. Můžete si nastavit také jeho velikost a umístění.
Rozvržení bočního bloku snadno změníte v nastavení. Po změně panelu na ukotvenou verzi se tyto dílčí úpravy plovoucího bloku vrátí na výchozí nastavení.
Nová podoba sbírek
Sbírky (aktuálně v beta verzi) byly na základě zpětné vazby od autorů přepracovány. Úpravy se dotkly jak vlastního nástroje pro tvorbu sbírek, tak i stránky s přehledem sbírek. V náhledovém okně můžete zkontrolovat, jak budou vaše sbírky vypadat na počítači, telefonu či tabletu.

Na přehled sbírky se dostanete pomocí postranní lišty na úvodní stránce vpravo. Je na ní uveden název sbírky a položky, kterou si právě prohlížíte. Dále jsou k dispozici tlačítka, kterými se dostanete na předchozí či následující obrázek. Kliknutím na název sbírky se pak dostanete do jejího přehledu.
Duplikování expresních map v bočním bloku či prezentaci
V předchozí verzi bylo možné v bočním bloku či prezentaci duplikovat snímky, které obsahovaly obrázky, videa, webové mapy či scény. Nová verze podporuje i duplikování expresních map. Duplikovanou mapu je možné dále upravovat na panelu nástrojů v kartě úprav.
Zjednodušení tvorby expresních map
V editoru mapy se dá přepínat viditelnost různých vrstev mapy, uložit aktuální přiblížení a zobrazovanou oblast mapy. Tyto změny se vážou k aktuálnímu snímku. Pro úpravy zdrojové expresní mapy (jako je změna podkladové mapy, zákres nových prvků a podobně) použijte tlačítko Upravit mapu.
Nové motivy
Přibyly dva nové motivy: Tidal (modrý) a Slate (šedý). Přibyly také dvě dvojice fontů: Pax + Neue Swift a Ocean Sans + Mahsuri Sans.
V nových motivech jsou pro expresní mapy k dispozici tyto podkladové mapy:
Slate
- Newspaper (základní)
- Human geography dark (alternativní)
Tidal
- Ocean (základní)
- Streets dark (alternativní)
A pro oba ještě také družicové snímky.
Sjednocení nástrojů pro přidávání obrázků a videí
Nová verze sjednotila nástroje pro přidávání obrázků a videí. Soubor nyní můžete buď nahrát přímo z počítače, nebo jej vložit pomocí URL (kromě úvodního obrázku).
Skrytí snímku
Uživatelé mohou snímky nejen duplikovat, ale také skrývat, a to jak v bočním bloku, v prezentaci, tak i v prohlídce s průvodcem.
Skrytý snímek je automaticky přeskakován a při rolování stránkou se nezobrazuje. Skrytím snímku dojde také ke skrytí bodu na mapě, ke kterému snímek odkazoval. Další snímky v pořadí budou automaticky přečíslovány tak, aby na sebe navazovaly.
Vylepšené prohlídky s průvodcem
Do okna lze přidat video nebo obrázek pomocí URL.
Ke každému bodu mohou uživatelé i nadále přidat až 5 obrázků či videí. Jejich pořadí je možné měnit přímo v panelu médií.
Vylepšení se dočkaly také mapy
Uživatelé si mohou vybrat z následujících volitelných doplňků pro expresní či webové mapy a scény:
Vyhledávání
Lokalizace
Vypnutí mapové navigace (skryje tlačítka pro přibližování a posun mapy)
Nový vzhled anotací u expresních map
Panel nástrojů pro úpravu expresních map nabízí možnosti úprav vzhledu anotací a šipek.
Anotace a vodicí čáry
Jednosměrné a obousměrné šipky
Další vylepšení
- K vyhledávání map lze využít všechny kategorie z Living Atlas.
- Zlepšená podpora tisku složitějších bloků.
- Přechody mezi duplikovanými scénami používají stejnou animaci, jako se používá v Prohlížeči scén a v ArcGIS JavaScript API.
- Přetahovat myší se dají i bloky s tlačítky a s oddělovači.
Hromadné prodloužení výpůjček [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
9.4.2020 9:50 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK V souvislosti s prodloužením stavu nouze byly všechny výpůjčky opět prodlouženy, aktuální datum pro vrácení je do 15. 5. 2020.Maps-For-Free představují možnost zobrazení reliéfu po celém světě
9.4.2020 8:07 GISportal.cz
Německý projekt Maps-For-Free je jednoduchá prohlížečka mapových podkladů s relativně základními funkcemi. Co však stojí za pozornost je jejich zobrazení reliéfu celého světa. Pro tvorbu reliéfu používají datové sady USGS (geologická služba USA) a to konkrétně SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) a GTOPO30. Mimo tyto vrstvy jsou k dispozici data z VMap0 od GIS.labu. Na mapě je také k […]
The post Maps-For-Free představují možnost zobrazení reliéfu po celém světě appeared first on GISportal.cz.
KGItalk online
9.4.2020 7:33 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucKGItalk bude pokračovat online ❗️ Díky aktuální situaci jsme se stali experty na online výuku 🖥 Proto padlo rozhodnutí, že od příští středy opět rozběhneme #kgitalk 🥳 Těšit se opět můžete na cestovatelské přednášky ale i na speciály představující, co se skrývá za aktuálními projekty chytré karantény, 3D tisku ochranných pomůcek nebo Corona vizualizací 🤓 […]
The post KGItalk online appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Pobočka Vyškov dokončila realizaci protierozního opatření v k.ú. Drnovice u Vyškova
9.4.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Pobočka Vyškov během podzimu 2019 zabezpečila výsadbu krajinných prvků, sloužících především jako protierozní opatření nad zastavěnou částí obce Drnovice.Obec Drnovice se nachází asi 4 km západním směrem od obce Vyškov. Potřeba vybudovat zde tento prvek společných zařízení vzešla z návrhu komplexních pozemkových úprav (zapsaných do katastru nemovitostí v roce 2013) a z potřeby obce ochránit území před prvním přívalem vody z přilehlých polí, která leží na poměrně svažitých a dlouhých pozemcích. Protože se jedná o plochu v silně návětrném území, bude opatření sloužit také k ochraně před větrnou erozí.
Pobočka Vyškov dokončila realizaci protierozního opatření v k.ú. Drnovice u Vyškova
9.4.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Pobočka Vyškov během podzimu 2019 zabezpečila výsadbu krajinných prvků, sloužících především jako protierozní opatření nad zastavěnou částí obce Drnovice.Obec Drnovice se nachází asi 4 km západním směrem od obce Vyškov. Potřeba vybudovat zde tento prvek společných zařízení vzešla z návrhu komplexních pozemkových úprav (zapsaných do katastru nemovitostí v roce 2013) a z potřeby obce ochránit území před prvním přívalem vody z přilehlých polí, která leží na poměrně svažitých a dlouhých pozemcích. Protože se jedná o plochu v silně návětrném území, bude opatření sloužit také k ochraně před větrnou erozí.
Oh Man…
8.4.2020 23:13 Carlson Software Oh man, oh man, oh man…. Just what the heck is going on? Well, a few weeks ago I had all this stuff going on: getting ready to travel from one coast to another for conferences, preparing class presentations, renewing my passport just in case. Now, even though I’ve spent twice as much on groceries […]Map Into the Void
8.4.2020 23:05 Carlson Software For many mine sites around the world, the juxtaposition of a modern, open pit site with historic underground workings raises concerns of a potentially catastrophic hazard such as ground instability caused by the presence of old cavities underneath current mining operations. It is often the case that very little reliable mapping data survives from historic […]Esri Partners with MCH Strategic Data to Provide School Closure, Reopening, and Instructional Plan Data
8.4.2020 21:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Information on US Education Affected by COVID-19 Available on New DashboardREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 8, 2020 …
Kin Insurance Partners with Cape Analytics to Improve the Insurance Experience with Geospatial, Predictive Property Insights
8.4.2020 20:14 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 8, 2020 —Today, Cape Analytics is announcing that Kin Insurance – a fully …
Happy birthday to a cool satellite
8.4.2020 19:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Airbus-built CryoSat-2 gathering snow and ice data for a decade@AirbusSpace @esa_cryosat @ESA_EO #CryoSat #seaice
Friedrichshafen, 08 April 2020 …
20200408 - Negenerování změnových VFR
8.4.2020 19:35 ČÚZK /Uvod/Produkty-a-sluzby/RUIAN/2-Poskytovani-udaju-RUIAN-ISUI-VDP/Vymenny-format-RUIAN/Archiv-novinek-VFR/20200408-Negenerovani-zmenovych-VFR20200408 - Negenerování změnových VFR
8.4.2020 19:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele změnových VFR:Z technických důvodů bylo dočasně pozastaveno generování změnových VFR. V důsledku tohoto stavu bude do spuštění generování změnových VFR existovat nekonzistentní stav dat RÚIAN a VFR. O nápravě současného stavu vás budeme informovat. Omlouváme se za komplikace.
Zveřejněno 8. 4. 2020
20200408 - Negenerování změnových VFR
8.4.2020 19:35 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Oznámení pro uživatele změnových VFR:Z technických důvodů bylo dočasně pozastaveno generování změnových VFR. V důsledku tohoto stavu bude do spuštění generování změnových VFR existovat nekonzistentní stav dat RÚIAN a VFR. O nápravě současného stavu vás budeme informovat. Omlouváme se za komplikace.
Zveřejněno 8. 4. 2020
OGC members create new ‘OGC API - Styles’ Standards Working Group
8.4.2020 19:07 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Working Group aims to develop a new OGC API that will allow creators to publish and share styles to be used by different users, systems, and datasets …New Indoor Drone Uses UVC Lights for Disinfection of Essential Businesses
8.4.2020 17:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Digital Aerolus, the creators of the Aertos® drone are using its patented artificial intelligence (A.I.) system and mathematical framework for …HERE continues to lead as Counterpoint Research’s top location & mapping platform, ahead of Google and TomTom
8.4.2020 17:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Amsterdam – For the third time in a row, HERE Technologies was named by Counterpoint Research as the world’s number one location platform. The …New Indoor Drone Uses UVC Lights for Disinfection of Essential Businesses
8.4.2020 17:55 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Digital Aerolus, the creators of the Aertos® drone are using its patented artificial intelligence (A.I.) system and mathematical framework for …20200409 – volné místo – Ředitel/ka kanceláře ředitele katastrálního úřadu na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
8.4.2020 13:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Ústecký kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Nabídka volného pracovního místa - na služební místo představeného – Ředitel / ředitelka kanceláře ředitele katastrálního úřadu na Katastrálním úřadu pro Ústecký kraj20200409 – volné místo – Ředitel/ka kanceláře ředitele katastrálního úřadu na KÚ pro Ústecký kraj
8.4.2020 13:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Ustecky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/20200409-–-volne-misto-–-Reditel-ka-kancelare-rediMaintaining EGNSS operations and security in challenging times: the GSA response
8.4.2020 12:34 European GNSS Agency
The coronavirus pandemic has had an impact on organisations, businesses, individuals and their families. As one of the few European Agencies delivering services 24/7, and with centres spread across Europe, the European GNSS Agency (GSA) has put various measures into place to ensure continuity of services and the security of EGNSS infrastructure, while at the same time prioritising the health and safety of staff and contractors.
The GSA is responsible for ensuring business continuity and keeping Galileo and EGNOS secure and operational, and this can only be done by protecting the health and safety of its staff and partners, which remains the Agency’s top priority.
The GSA is helped in this by the fact that, from its Prague headquarters, it is used to working remotely with the different Galileo and EGNOS sites across Europe. At the same time, special measures are being taken to protect the various operators working around the clock, seven days a week. The Agency is currently responding to the different scenarios in each country in order to manage security and operations, while putting measures in place to protect its people.
“These are very challenging times for all of us, requiring us to be flexible and resourceful. I am proud of how the GSA teams across our different sites have quickly adapted to the new situation,” said GSA Acting Executive Director Pascal Claudel. “The spirit of solidarity and cooperation I experience every day has shown me that the GSA’s team is its core asset and a strong foundation upon which to build the future of the Agency,” he said. “The entire European GNSS family has pulled together, and the GSA can rely on the support and commitment of all our partners, including Member States, industry, and SMEs.”
Read this: Are you aware? Beacons save lives!
GSA staff and contractors are learning new ways to work online to continue providing location, navigation and timing services to the user community. This applies equally at GSA headquarters and at the various sites. The Agency is also working with the European Commission, Member States and industry to find new solutions to emerging issues. “With the support of the Member States and industry, the GSA has demonstrated its leadership in this time of crisis, ensuring the continuity of the Galileo and EGNOS services. This is evidence that Europe is stronger together,” said GSA Administrative Board Chair Jean Yves Le Gall.
The GSA’s commitment to helping European industry benefit from EGNOS and Galileo remains as strong as ever, and the Agency is continuing its work on activities that are already underway.
Horizon 2020
The 21 ongoing projects remain on track (with the option of contractual adjustments to help partners impacted by the crisis). The new call with 44 project proposals is in the evaluation phase, for the first time taking place remotely via video conference.
Fundamental Elements
There are 19 projects ongoing and on track (also with contractual flexibility to help partners impacted by the crisis). For later in 2020, 13 more projects are already published or are under evaluation.
Industrial contracts
During the COVID-19 crisis, the GSA is ensuring full support to the EU space industry by agreeing contractual adjustments to be implemented as needed throughout the entire supply chain, from Primes to SMEs.
And this: eCall: 2 years of saving lives
GNSS and the response to COVID-19
Since the outbreak of the coronavirus earlier this year, many apps have been developed that use GNSS precise location to monitor the global spread of the virus and to map outbreaks of the COVID-19 disease. GNSS-apps are also proving their usefulness by helping people to implement social distancing in queues and other public spaces.
To support the EU response to COVID-19, the EC and GSA are also working on the “Galileo Green Lane” app, to facilitate the movement of goods and freight within the EU. The objective of the “Galileo Green Lane” is to relieve borders from the pressure of handling goods and to manage more efficiently the transit of critical goods. At the same time, this Galileo app will provide Member States with a tool to report to the EU on the Green Lanes initiative. A first version of the app is expected in mid-April.
The GSA is compiling a repository of these apps as a knowledge bank of solutions and toolbox that are being used to fight the pandemic and to help authorities, emergency response services, citizens and app developers to understand current needs and available resources.
If you have developed an app that is already working and being used to map the spread of the coronavirus, to monitor incidences of the disease, or to alert users about possible risky contacts, tell us about it and we will include it in our database. We are looking for apps that are already working and available. Submit some information on your solutions in writing to market@gsa.europa.eu and we will feature them on the GNSS4Crisis page.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Maintaining EGNSS operations and security in challenging times: the GSA response
8.4.2020 12:34 European GNSS Agency
The coronavirus pandemic has had an impact on organisations, businesses, individuals and their families. As one of the few European Agencies delivering services 24/7, and with centres spread across Europe, the European GNSS Agency (GSA) has put various measures into place to ensure continuity of services and the security of EGNSS infrastructure, while at the same time prioritising the health and safety of staff and contractors.
The GSA is responsible for ensuring business continuity and keeping Galileo and EGNOS secure and operational, and this can only be done by protecting the health and safety of its staff and partners, which remains the Agency’s top priority.
The GSA is helped in this by the fact that, from its Prague headquarters, it is used to working remotely with the different Galileo and EGNOS sites across Europe. At the same time, special measures are being taken to protect the various operators working around the clock, seven days a week. The Agency is currently responding to the different scenarios in each country in order to manage security and operations, while putting measures in place to protect its people.
“These are very challenging times for all of us, requiring us to be flexible and resourceful. I am proud of how the GSA teams across our different sites have quickly adapted to the new situation,” said GSA Acting Executive Director Pascal Claudel. “The spirit of solidarity and cooperation I experience every day has shown me that the GSA’s team is its core asset and a strong foundation upon which to build the future of the Agency,” he said. “The entire European GNSS family has pulled together, and the GSA can rely on the support and commitment of all our partners, including Member States, industry, and SMEs.”
Read this: Are you aware? Beacons save lives!
GSA staff and contractors are learning new ways to work online to continue providing location, navigation and timing services to the user community. This applies equally at GSA headquarters and at the various sites. The Agency is also working with the European Commission, Member States and industry to find new solutions to emerging issues. “With the support of the Member States and industry, the GSA has demonstrated its leadership in this time of crisis, ensuring the continuity of the Galileo and EGNOS services. This is evidence that Europe is stronger together,” said GSA Administrative Board Chair Jean Yves Le Gall.
The GSA’s commitment to helping European industry benefit from EGNOS and Galileo remains as strong as ever, and the Agency is continuing its work on activities that are already underway.
Horizon 2020
The 21 ongoing projects remain on track (with the option of contractual adjustments to help partners impacted by the crisis). The new call with 44 project proposals is in the evaluation phase, for the first time taking place remotely via video conference.
Fundamental Elements
There are 19 projects ongoing and on track (also with contractual flexibility to help partners impacted by the crisis). For later in 2020, 13 more projects are already published or are under evaluation.
Industrial contracts
During the COVID-19 crisis, the GSA is ensuring full support to the EU space industry by agreeing contractual adjustments to be implemented as needed throughout the entire supply chain, from Primes to SMEs.
And this: eCall: 2 years of saving lives
GNSS and the response to COVID-19
Since the outbreak of the coronavirus earlier this year, many apps have been developed that use GNSS precise location to monitor the global spread of the virus and to map outbreaks of the COVID-19 disease. GNSS-apps are also proving their usefulness by helping people to implement social distancing in queues and other public spaces.
To support the EU response to COVID-19, the EC and GSA are also working on the “Galileo Green Lane” app, to facilitate the movement of goods and freight within the EU. The objective of the “Galileo Green Lane” is to relieve borders from the pressure of handling goods and to manage more efficiently the transit of critical goods. At the same time, this Galileo app will provide Member States with a tool to report to the EU on the Green Lanes initiative. A first version of the app is expected in mid-April.
The GSA is compiling a repository of these apps as a knowledge bank of solutions and toolbox that are being used to fight the pandemic and to help authorities, emergency response services, citizens and app developers to understand current needs and available resources.
If you have developed an app that is already working and being used to map the spread of the coronavirus, to monitor incidences of the disease, or to alert users about possible risky contacts, tell us about it and we will include it in our database. We are looking for apps that are already working and available. Submit some information on your solutions in writing to market@gsa.europa.eu and we will feature them on the GNSS4Crisis page.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Odborný referent – budování podrobných bodových polí v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu Katastr
8.4.2020 11:26 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský krajvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Odborný referent – budování podrobných bodových polí v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský kraj
Odborný referent – budování podrobných bodových polí v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu Katastr
8.4.2020 11:26 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Odborný referent – budování podrobných bodových polí v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu KatastrOdborný referent – budování podrobných bodových polí v oddělení obnovy katastrálního operátu Katastr
8.4.2020 11:26 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Odborny-referent-–-budovani-podrobnych-bodovych-poCEEPUS ve 2020/2021
8.4.2020 11:04 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucBylo potvrzeno, že mobility skrz CEEPUS budou realizovány! V online platformě jsou dostupné informace výměnných pobytech a podrobnostech.
The post CEEPUS ve 2020/2021 appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
CryoSat still cool at 10
8.4.2020 11:00 ESA Observing the Earth
Today marks 10 years since a Dnepr rocket blasted off from an underground silo in the remote desert steppe of Kazakhstan, launching one of ESA’s most remarkable Earth-observing satellites into orbit. Tucked safely within the rocket fairing, CryoSat had a tough job ahead: to measure variations in the height of Earth’s ice and reveal how climate change is affecting the polar regions. Carrying novel technology, this extraordinary mission has led to a wealth of scientific discoveries that go far beyond its primary objectives to measure polar ice. And, even at 10 years old, this incredible mission continues to surpass expectations.
Možnost brigády - anotování české lokalizace pro Natural Language Processing engine firmy D-Tag
8.4.2020 10:43 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČU Švýcarská firma D-Tag Europe Ltd. poptává česky mluvící studenty pro překlad z ENG do CZE za 2000 HUF/hodinu (cca. 6EUR/hod).Popis nabídky:
"D-Tag Europe Ltd. is involved to deliver tasks for query building tasks of different language
contract with external experts who will act as individual consultants (also hereby known as
“Service Providers”) to deliver the tasks by the deadline.
- Translate and localize (using local expressions and language) master source queries
V případě zájmu kontaktujte prosím přímo paní Kinga Dancsházy na "kinga.dancshazy@ditag.eu" s předmětem emailu " CZ annotator student".
Možnost brigády - anotování české lokalizace pro Natural Language Processing engine firmy D-Tag
8.4.2020 10:43 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČU Maďarská firma D-Tag Europe Ltd. poptává česky mluvící studenty pro překlad z ENG do CZE za 2000 HUF/hodinu (cca. 6EUR/hod).Popis nabídky:
"D-Tag Europe Ltd. is involved to deliver tasks for query building tasks of different language
contract with external experts who will act as individual consultants (also hereby known as
“Service Providers”) to deliver the tasks by the deadline.
- Translate and localize (using local expressions and language) master source queries
V případě zájmu kontaktujte prosím přímo paní Kinga Dancsházy na "kinga.dancshazy@ditag.eu" s předmětem emailu " CZ annotator student".
Zrušení setkání Český Těšín
8.4.2020 9:29 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Karvina/O-uradu/Aktuality/Zruseni-setkani-Cesky-TesinZrušení setkání Český Těšín
8.4.2020 9:29 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Karviná zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Důležité upozornění!Setkání pracovníků Katastrálního pracoviště Karviná s vlastníky nemovitostí dotčených revizí údajů katastru nemovitostí v k. ú. Český Těšín, které se mělo konat ve velké zasedací místnosti v budově Městského úřadu Český Těšín dne 20. 4. 2020, se s ohledem na opatření přijatá vládou ČR v souvislosti s novým typem koronaviru Sars-CoV-2 ruší.
Druhý termín stanovený na 22. 6. 2020 zatím zůstává v platnosti.
Maxar Announces Close of MDA Divestiture and Provides Update on Ongoing Support of Critical Customer Missions
8.4.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WESTMINSTER, Colo. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 8, 2020 —Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR), a trusted partner and innovator …
Cenová mapa nemovitostí celé ČR – Atlas cen
8.4.2020 8:01 GISportal.cz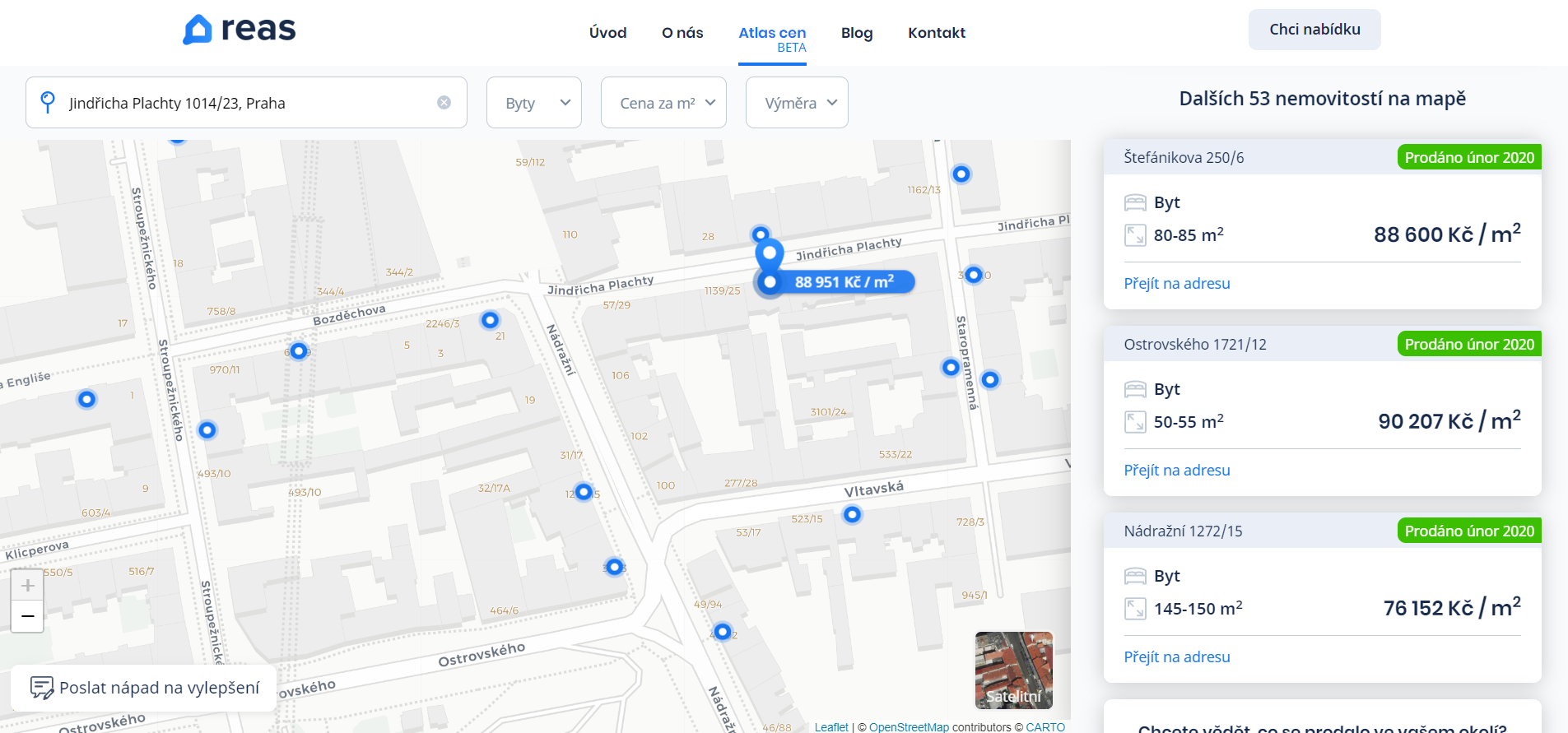
Před několika týdny se objevila první verze Atlasu cen, která ještě obsahovala reálné prodejní ceny, metráž jednotlivých bytů, apod., čímž podle Katastru nemovitostí porušil zákon – více o tom psali např. na CzechCrunch. Nová (7. 4. 2020) publikovaná verze Atlasu cen již obsahuje pouze ceny přepočtené na m2 a údaje o obytné ploše jsou rozděleny […]
The post Cenová mapa nemovitostí celé ČR – Atlas cen appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Esri and United Nations Team to Provide Countries with COVID-19 Data Resources
8.4.2020 2:11 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars UN to Offer Free Access to Smart Mapping Software During Global PandemicREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 7, 2020 …
Quantum-Systems offers the MicaSense Dual Camera System for the Trinity F90+ fixed-wing UAV
7.4.2020 21:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 8th of April 2020: Gilching / Germany: As a manufacturer of advanced VTOL UAV systems for high-precision surveying tasks in the professional field it …Going Digital helped the Government of Malaysia leverage digital twins to deliver trusted information for better project and asset management
7.4.2020 18:58 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
World Highways, UK
Read the articleDigital Twins in Utilities
7.4.2020 18:50 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
PowerGrid Intl, USA
Read the articleCoreLogic Reports February Home Prices Increased by 4.1% Year Over Year
7.4.2020 18:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Annual home price increases in February 2020 reached their highest level in more than a yearAs of February 2020, and prior to the coronavirus …
ConnexiCore Is Supporting Construction Project Safety by Utilizing Drones for Social Distancing
7.4.2020 18:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Construction companies across the US are using drones to safely conduct inspections, gather data, and more, all while protecting workers.MILFORD, …
INDOT Selects Woolpert to Integrate UAS into Operations
7.4.2020 18:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Woolpert will work with INDOT officials to safely and effectively integrate UAS and related technologies into the business operations of multiple …Lemur Pro Esri-based GIS App from Critigen Now Available on SAP® App Center
7.4.2020 18:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Critigen delivers intuitive mobility solution to field workers by integrating Geographic Information System (GIS) with SAP® Asset Manager and SAP® …OMI Announces Drone Disinfection System for Large Indoor Spaces to Kill the Coronavirus
7.4.2020 18:37 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars BELLE CHASSE, La., April 7, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — OMI Environmental Solutions, a K-Solv Group Company, announces Drone …Mikuláš Klaudyán v Dolním Bousově [Knihovna geografie, byTopic]
7.4.2020 18:35 Katedra aplikované geoinformatiky a kartografie Přf UK V období 17. 2. - 31. 3. 2020 byla výstava Mikuláš Klaudyán: první mapa Čech zapůjčena Infocentru Dolní Bousov.Why Utilities Need Digital Twins
7.4.2020 18:29 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
PowerGrid Intl, USA
Read the articleHow Going Digital Can Reverse Your Engineering Challenges
7.4.2020 18:08 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Geo4Construction.com, France/Benelux
Read the articleNa Lupa.cz vyšel Jakubův článek o využití dronů po světě v probíhající pandemii
7.4.2020 10:33 UpVisionDnes vyšel Jakubův článek na Lupě, jak drony pomáhají po světě v probíhající pandemii a jak by mohli více pomoci i v České republice. Více zde: https://www.lupa.cz/clanky/od-sledovani-narusitelu-po-dopravu-leku-jak-se-pri-epidemii-vyuzivaji-drony/
The post Na Lupa.cz vyšel Jakubův článek o využití dronů po světě v probíhající pandemii appeared first on Upvision.
Na Lupa.cz vyšel Jakubův článek o využití dronů po světě v probíhající pandemii
7.4.2020 10:33 UpVisionDnes vyšel Jakubův článek na Lupě, jak drony pomáhají po světě v probíhající pandemii a jak by mohli více pomoci i v České republice. Více zde: https://www.lupa.cz/clanky/od-sledovani-narusitelu-po-dopravu-leku-jak-se-pri-epidemii-vyuzivaji-drony/
The post Na Lupa.cz vyšel Jakubův článek o využití dronů po světě v probíhající pandemii appeared first on Upvision.
Ministryně financí ČR ve Ville Hrdlička
7.4.2020 9:13 Hrdlička Město Česká Lípa pozvalo paní Schillerovou, která strávila celý den s představiteli města.3. díl služby UtilityReport je na světě
7.4.2020 9:12 Hrdlička V 3. díle Vám ukážeme, jaké náležitosti jsou potřeba při vyřízení žádosti o stavební povolení.Ministyně financí ČR ve Ville Hrdlička
7.4.2020 9:08 Hrdlička Město Česká Lípa pozvalo paní Schillerovou, která strávila celý den s představiteli města.Atlas rozvoje venkova
7.4.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace ATLAS Rozvoje venkovaBudoucnost venkova v České republice: Výzvy, vize, rozvojové scénáře a adaptační strategie
Před několika dny byl představen výsledek společného projektu TAČR pracovníků Západočeské univerzity v Plzni a Ostravské univerzity, který řeší přípravu českého venkova na budoucnost. Klíčovou pozornost věnuje otázkám ekonomického rozvoje a





































