zprávy
zdroje zpráv:Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí ekonomicko – správního oddělení Kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu
3.4.2020 11:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj kancelář ředitelevypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí ekonomicko – správního oddělení Kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu pro Zlínský kraj
Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí ekonomicko – správního oddělení Kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu
3.4.2020 11:44 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Zlínský kraj kancelář ředitele vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Rada / odborný rada – vedoucí ekonomicko – správního oddělení Kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřaduRada / odborný rada – vedoucí ekonomicko – správního oddělení Kanceláře ředitele Katastrálního úřadu
3.4.2020 11:44 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Zlinsky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/DMS/Rada-odborny-rada-–-vedouci-ekonomicko-–-spravniSchránka
3.4.2020 11:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-západ zveřejnil novou aktualitu: umístění sběrného boxu Praha-západ Upozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání Katastrálnímu pracovišti Praha-západ bezkontaktně do sběrného boxu umístěného u vchodu do budovy! Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Pokud uvedete v podání Váš mail, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.Schránka je přístupná v pondělí a středu od 8:00 do 17:00, v úterý a čtvrtek od 8:00 do 15:00 a v pátek do 13hodin.
Schránka
3.4.2020 11:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-zapad/O-uradu/Aktuality/20200313_Coronavirus_nouzovy-stav-(1)Bezpečnostní patch pro ArcGIS Server
3.4.2020 11:07 ARCDATASpolečnost Esri vydala nový bezpečnostní patch pro ArcGIS Server – ArcGIS Server Security 2020 Update 1 Patch. Tento patch řeší zranitelnost ArcGIS Enterprise, konkrétně komponenty ArcGIS Server útokem Server Side Request Forgery (SSRF). Uživatelé ArcGIS Serveru tak mohou být vystaveni riziku získání interních informací neautorizovanou osobou v závislosti na konfiguraci systému. V některých případech mohou útočníci nahlédnout do infrastruktury, nebo nad ní získat administrativní kontrolu.
Toto bezpečností riziko se týká všech verzí před ArcGIS Server 10.8 na operačních systémech Windows a Linux. Z tohoto důvodu společnost Esri všem důrazně doporučuje instalovat tento bezpečnostní patch, který je k dispozici pro verze ArcGIS Serveru 10.4 až 10.7.1.
Úplný seznam chyb, které nový ArcGIS Server Security 2020 Update 1 Patch řeší, a instalační soubor patche můžete najít na stránce opravy: https://support.esri.com/en/download/7775.
Sběrný box - bezkontaktní podání
3.4.2020 10:44 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Sběrný box - bezkontaktní podáníUpozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné vlevo od vstupních dveří do budovy. Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Uveďte v podání Váš mail a na vyžádání Vás budeme informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.
Schránka je přístupná: pondělí a středa 11-17 hod, úterý a čtvrtek 8-14:30 hod, pátek 8-13hod.
Schránka je pravidelně vybírána.
Vrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
3.4.2020 10:24 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Hradec Králové zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Vrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště TrutnovVrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
3.4.2020 10:24 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Trutnov/O-uradu/Aktuality/Vrchni-referent-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-kataVrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
3.4.2020 10:18 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnovvypisuje výběrové řízení na místo
Vrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
Vrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
3.4.2020 10:18 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Kralovehradecky-kraj/Uredni-deska/Oznameni-a-jina-uredni-sdeleni/Volna-mista/Vrchni-referent-rada-v-oddeleni-aktualizace-kataVrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště Trutnov
3.4.2020 10:18 ČÚZK - volná místa Katastrální úřad pro Královéhradecký kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Trutnov vypisuje výběrové řízení na místo Vrchní referent / rada v oddělení aktualizace katastru nemovitostí Katastrálního pracoviště TrutnovCovid-19 - omezení provozu KP Kolín
3.4.2020 10:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kolin/O-uradu/Aktuality/Covid-19-omezeni-provozu-KP-KolinCovid-19 - omezení provozu KP Kolín
3.4.2020 10:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Provozní doba Podatelny KP Kolín: Po + St: 08:00-11:00
Poskytování údajů z KN, ani další jednání vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, nebudou na pracovišti probíhat. Naplánovaná ústní jednání budou zrušena. Náhradní termín jednání bude stanoven po skončení krizového opatření.
Pro získání informací o vkladovém řízení prosím volejte tel. 321 737 014, 321 737 015, 737 017
Covid-19 - omezení provozu KP Kolín
3.4.2020 10:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Provozní doba Podatelny KP Kolín: Po + St: 08:00-11:00
Poskytování údajů z KN, ani další jednání vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, nebudou na pracovišti probíhat. Naplánovaná ústní jednání budou zrušena. Náhradní termín jednání bude stanoven po skončení krizového opatření.
Pro získání informací o vkladovém řízení prosím volejte tel. 321 737 014, 321 737 015, 737 017
Usnesení vlády České Republiky ze dne 15.03 2020 č. 215 o přijetí krizového opatření
Earth from Space: Finistère
3.4.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth Video:
00:00:00
Video:
00:00:00
In this week's edition of the Earth from Space programme, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Finistère – a French department in the west of Brittany.
See also Finistère, France to download the image.
Finistère, France
3.4.2020 10:00 ESA Observing the Earth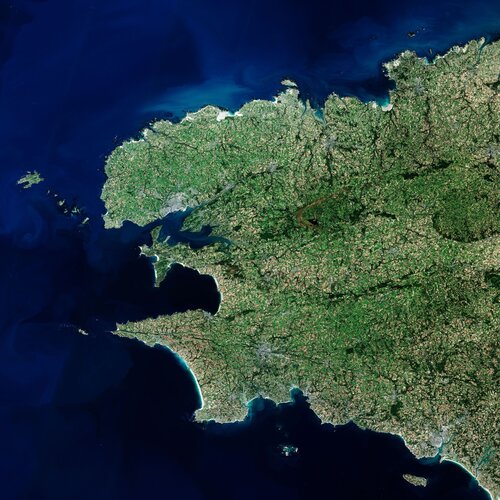 Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Finistère – a French department in the west of Brittany.
Image:
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Finistère – a French department in the west of Brittany.
Covid-19 - omezení provozu KP Kolín
3.4.2020 9:42 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kolin/Covid-19-omezeni-provozu-KP-KolinCovid-19 - omezení provozu KP Kolín
3.4.2020 9:42 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Covid-19 - omezení provozu KP KolínProvozní doba Podatelny KP Kolín: Po + St: 08:00-11:00
Poskytování údajů z KN, ani další jednání vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností, nebudou na pracovišti probíhat. Naplánovaná ústní jednání budou zrušena. Náhradní termín jednání bude stanoven po skončení krizového opatření.
Sběrný box - bezkontaktní podání
3.4.2020 9:35 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kolin/Sberny-box-bezkontaktni-podaniSběrný box - bezkontaktní podání
3.4.2020 9:33 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné vlevo od vstupních dveří do budovy. Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Uveďte v podání Váš mail a na vyžádání Vás budeme informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.Schránka je přístupná: pondělí a středa 11-17 hod, úterý a čtvrtek 8-14:30 hod, pátek 8-13hod. Schránka je pravidelně vybírána.
Sběrný box - bezkontaktní podání
3.4.2020 9:33 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Kolín zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Sběrný box - bezkontaktní podáníUpozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání bezkontaktně do schránky umístěné vlevo od vstupních dveří do budovy. Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Uveďte v podání Váš mail a na vyžádání Vás budeme informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.
Schránka je přístupná: pondělí a středa 11-17 hod, úterý a čtvrtek 8-14:30 hod, pátek 8-13hod. Schránka je pravidelně vybírána.
Sběrný box - bezkontaktní podání
3.4.2020 9:33 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Kolin/O-uradu/Aktuality/Sberny-box-bezkontaktni-podaniDruhé kolo přijímacího řízení
3.4.2020 8:00 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucZ nějakého důvodu jste zapomněli kliknout na odeslat e-přihlášku na geoinformatiku? 😜 Nevadí, otevíráme druhé kolo podávání přihlášek na bakalářské i magisterské studium ‼️ Budete mít přesně 87 dnů, od 15. dubna 2020 do 11. července 2020 🙃 Nenechte si to ujít: https://www.prf.upol.cz/zajemci-o-studium/#c13578
The post Druhé kolo přijímacího řízení appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Druhé kolo přijímacího řízení
3.4.2020 8:00 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucZ nějakého důvodu jste zapomněli kliknout na odeslat e-přihlášku na geoinformatiku? 😜 Nevadí, otevíráme druhé kolo podávání přihlášek na bakalářské i magisterské studium ‼️ Budete mít přesně 61 dnů, od 15. dubna 2020 do 11. července 2020 🙃 Nenechte si to ujít: https://www.prf.upol.cz/zajemci-o-studium/#c13578
The post Druhé kolo přijímacího řízení appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
Aktualizováno: Nový iPad Pro 2020 od Apple má v sobě lidarový skener
3.4.2020 7:00 GeoBusinessFirma Apple představila nové verze svých produktů. Jedním z nich je inovovaná verze tabletu iPad, který ve verzi Pro bude obsahovat lidarový skener. Je to poprvé, co se v konzumní elektronice objevuje lidar. Lidarový skener má dosah až pět metrů, funguje v interiéru i v exteriéru. Augmentovaná realita Apple intenzivně pracuje na rozvoji nástrojů pro […]
The post Aktualizováno: Nový iPad Pro 2020 od Apple má v sobě lidarový skener appeared first on GeoBusiness.
GeoKARTO 2020
3.4.2020 7:00 Česká asociace pro geoinformace Pozvánka na konferenci GEOKARTO 2020I když aktuální situace nepřeje konferencím, situace se rozhodně změní! 10. - 11. září se uskuteční na Univerzitě Pavla Jozefa Šafárika v Košiciach mezinárodní konference GeoKarto 2020. Podrobnější informace naleznete na
INSPIRE téma Rozšířené Parcely (CPX)
3.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Rozšíření má za cíl poskytovat katastrální mapu s obsahem podle vyhlášky ve vektorové podobě ve struktuře plně v souladu se strukturou danou směrnicí INSPIRE. Data rozšiřují směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP) o věcná břemena, geodetické body, další prvky mapy, původní obloukovou geometrii a o parcely určené definičním bodem (ty pouze v oblastech s analogovou mapou). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Publikovaná data obsahují katastrální území pro celou Českou Republiku, parcely a jejich hranice, věcná břemena, další prvky mapy a původní obloukovou geometrii z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 30. 03. 2020 je to 96,71% území České republiky, t.j. 76 275,92km2) a ve zbytku území katastrální parcely určené pouze definičním bodem (tedy bez hranic a polygonu). Katastrální parcely a hranice obsahují oproti datové sadě INSPIRE některé atributy navíc. Jedná se o typ hranice, způsob využití území, druh pozemku, vazbu na budovu a o mapové značky. Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro Rozšířené Parcely (CPX) ve verzi 4.0.INSPIRE téma Adresy (AD)
3.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma adresy (AD). Vychází především z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze adresní místa a jejich komponenty, kterými jsou stát, obec, část obce, městský obvod v Praze (MOP), městký obvod/městská část (MO/MČ), ulice a pošta a to na území celé České Republiky. Obsahují rozvněž geometrii, která určuje definiční bod adresního místa. V datové sadě nění uvedeno 1,19%, t.j. 34832 adresních míst (k 30. 03. 2020), protože neobsahují definiční bod, podle kterého by je bylo možné prostorově určit. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech a ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních a INSPIRE Data Specification on Addresses v 3.0.1 z 26.4.2010. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Adresy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.INSPIRE téma Budovy (BU)
3.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma budovy (BU). Data pochází částečně z projektu RÚIAN (Registr územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí), který je součástí základních registrů České Republiky a obsahuje informace o územní identifikaci, adresách a nemovitostech, a částečně z ISKN (Informační systém katastru nemovistostí). Zdrojem informací o budovách v ISKN je objekt Stavba, v RÚIAN je to Stavební objekt. Většina Staveb je zároveň Stavebními objekty, ale jsou případy, kdy tomu tak není. Kromě Budov datová sada obsahuje i části budov, které jsou pro potřeby INSPIRE vyjádřeny vchody z RÚIAN. Vchody obsahují informace o počtu podlaží, technickoekonomických atributech apod. Datová sada pokrývá celé území české republiky. V datové sadě není uvedeno 1,14%, t.j. 48421 budov (k 30. 03. 2020), protože neobsahují definiční bod ani polygon. Více v zákoně č. 111/2009 Sb., o základních registrech, ve vyhlášce č. 359/2011 Sb., o základním registru územní identifikace, adres a nemovitostí v platných zněních, v zákoně 256/2013 Sb., o katastru nemovitostí, v katastrální vyhlášce č. 357/2013 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Buildings v 3.0 z 13.12.2013. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Budovy ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě poskytovaná v e-shopu
3.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa v rastrové podobě je poskytována za úplatu a obsahuje analogovou mapu s kompletní kresbou. Analogová mapa pokrývá 3,04 % území České republiky, což je 2 393,95km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.Katastrální mapa ve formátech DGN a DXF poskytovaná v e-shopu
3.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Katastrální mapa je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě je poskytována zdarma ve formátu DGN a DXF a obsahuje prvky Digitální katastrální mapy (DKM) a Katastrální mapy digitalizované (KMD), tedy bodová pole, budovy, další prvky mapy, hranice parcel, katastrální hranice, parcely katastru nemovitostí, prvky orientační mapy a hranice věcného břemene. Z důvodu použití formátu DGN produkt neobsahuje značky na liniích a oblouky jsou nahrazeny lomenými čárami. Katastrální mapa ve vektorové podobě k 30. 03. 2020 pokrývá 96,71% území České republiky, t.j. 76 275,92km2. Více katastrální vyhláška č.357/2013 Sb. v platném znění.INSPIRE téma Parcely (CP)
3.4.2020 2:00 Cenia - Katalog metadat ČR - INSPIRE Data odpovídají směrnici INSPIRE pro téma katastrální parcely (CP). Vychází z katastrální mapy, která je závazným státním mapovým dílem velkého měřítka, obsahuje body polohového bodového pole, polohopis a popis a může mít formu digitální mapy, analogové mapy nebo digitalizované mapy. Data publikovaná v rámci INSPIRE obsahují pouze katastrální území (pro celou Českou Republiku) a parcely a jejich hranice z území, kde je digitální mapa (k 30. 03. 2020 je to 96,71% území České republiky, t.j. 76 275,92km2). Více katastrální zákon 344/1992 SB., katastrální vyhláška č.26/2007 Sb. v platném znění a INSPIRE Data Specification on Cadastral Parcels v 3.0.1. Data ve formátu GML 3.2.1 jsou validní proti schématu XML pro INSPIRE téma Parcely ve verzi 4.0 a proti schématu pro prostorová data ELF ve verzi 1.0.Cyient Provides Drone-Based Surveillance Technology to support Cyberabad Police in implementing COVID-19 Lockdown
3.4.2020 1:08 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HYDERABAD, India, April 2, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — Cyient, a global engineering and technology solutions company, today announced that it …St. Johns River Water Management District use satellite data analytics to drive a unique approach to vegetation management and burn control in Florida
2.4.2020 22:36 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Harwell, Oxfordshire, UK, 02 April 2020 – Rezatec, leading provider of satellite data analytics is deploying its unique satellite data …WISeKey Selected by Global Manufacturer to Secure Drone Flights
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars WISeKey Selected by Global Manufacturer to Secure Drone Flights The rapid expansion of commercial drone market raises serious security concerns …IDC Expects Worldwide IT Spending to Decline by 2.7% in 2020 as COVID-19 Drives Down Forecasts
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars FRAMINGHAM, Mass. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 2, 2020 —Worldwide IT spending is now expected to decline 2.7% in constant currency …
NV5’s Quantum Spatial Selected as a Prime Consultant on $40 Million NOAA Contract
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars HOLLYWOOD, Fla., April 02, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- NV5 Global, Inc. (the “Company” or “NV5”) (Nasdaq: NVEE), a provider of professional …Esri Commits to Grow Nation's Transit System with New Enterprise Licensing Program
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Small Transit Authorities in the US Can Now Benefit from Easier Access to GIS SoftwareREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 2, …
Genasys™ Inc. Issues Overview of Company’s Unified Public Safety Platform for Government and Emergency Management Agencies
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN DIEGO, April 02, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Genasys Inc. (NASDAQ: GNSS), a global provider of critical communications solutions, today issued an …Trade events for Lidar, Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing, 3D and Building Technology Professionals Rescheduled & Will Take Place Together July 27-29, 2020 in Chicago
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars International Lidar Mapping Forum, ASPRS Annual Conference, SPAR 3D Expo & Conference, AEC Next Technology Expo & Conference, USIBD Symposium and …Intermap Technologies Provides Filing Update
2.4.2020 22:35 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars DENVER, April 2, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — Intermap Technologies ("Intermap" or the "Company"), today provided updates on its business …DroneUp Acquires AeroVista Innovations
2.4.2020 22:03 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Acquisition Adds Training to Complete Drone Solutions Momentum
Virginia Beach, VA (April 2, 2020) -- DroneUp, LLC, an end-to-end …
Bentley Institute Announces “Digital Infrastructure Student Idea Challenge 2020”
2.4.2020 20:58 Bentley SystemsEXTON, Pa. April 2020 – Bentley Institute, a leading organization advancing infrastructure professions by empowering practitioners, students, and academic institutions through continuous learning, scholarships, internships, and applied research partnerships, recently announced its Digital Infrastructure Student Idea Challenge 2020. The challenge is continuing Bentley Institute’s undeterred mission of nurturing future professionals, helping them stay active, engaged, and enthusiastic amid the challenging times of school closures and self-isolation.
With migration, urbanization, and climate change placing increasing stress on the world's built environment, the industry must transform and innovate to deliver resilient infrastructure. Bentley Institute is looking for students from around the world to come up with visionary ideas and inventive concepts that could potentially transform infrastructure and make a positive impact in the world.
The challenge is open to individual students (or teams of two) from community colleges/ schools, polytechnics, technical institutes and universities. To participate, students need to select a challenge that is relevant to any infrastructure domain and propose a smart, ground-breaking solution concept. Students should submit a presentation and PDF document (with a minimum of 500 words) of their conceptual ideas, not a detailed technical solution with a design. However, students should describe how software technology could play a role in their proposed concept. It must also be supported by graphs, figures, videos, and pictures.
In addition to gaining recognition from Bentley Institute, the top winning team will receive a cash prize of USD 5,000. The winners of the Best Presentation, Best Challenge, and Best Solution categories will also win cash prizes of USD 2,000 each.
Bentley Institute encourages all students to use time at home constructively to suggest ideas for a better tomorrow.
To participate in the challenge, students must register before May 15th, 2020 and submit their projects by June 15th, 2020. Students need to register here. To learn more about the submissions, judging criteria, and other information, click here.
Image: https://communities.bentley.com/cfs-file/__key/communityserver-wikis-components-files/00-00-00-00-06/Facebook_5F00_BI_5F00_Digital_5F00_Infra_5F00_Ideas_5F00_Challenge_5F00_v2_5F00_1200x628.jpg
Caption: Bentley Institute announces “Digital Infrastructure student Idea Challenge”
About Bentley Institute
The Bentley Institute advances the infrastructure professions by empowering practitioners, students, and academic institutions through continuous learning, scholarships, internships, and applied research partnerships. Learning is provided online, in the classroom, or in-application, and includes publications, webinars, workflow videos, live and on-demand courses, conferences, events, and more. The Bentley Institute advances project delivery and asset performance best practices through Digital Advancement Academies, partnering with leading industry organizations, project delivery firms, and owner-operators
About Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems is a leading global provider of software solutions to engineers, architects, geospatial professionals, constructors, and owner-operators for the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure. Bentley’s MicroStation-based engineering and BIM applications, and its digital twin cloud services, advance the project delivery (ProjectWise) and the asset performance (AssetWise) of transportation and other public works, utilities, industrial and resources plants, and commercial and institutional facilities.
Bentley Systems employs more than 3,500 colleagues and generates annual revenues of more than $700 million in 172 countries. From inception in 1984, the company has remained majority-owned by its five founding Bentley brothers. www.bentley.com
Bentley Institute Announces “Digital Infrastructure Student Idea Challenge 2020”
2.4.2020 20:58 Bentley SystemsEXTON, Pa. April 2020 – Bentley Institute, a leading organization advancing infrastructure professions by empowering practitioners, students, and academic institutions through continuous learning, scholarships, internships, and applied research partnerships, recently announced its Digital Infrastructure Student Idea Challenge 2020. The challenge is continuing Bentley Institute’s undeterred mission of nurturing future professionals, helping them stay active, engaged, and enthusiastic amid the challenging times of school closures and self-isolation.
With migration, urbanization, and climate change placing increasing stress on the world's built environment, the industry must transform and innovate to deliver resilient infrastructure. Bentley Institute is looking for students from around the world to come up with visionary ideas and inventive concepts that could potentially transform infrastructure and make a positive impact in the world.
The challenge is open to individual students (or teams of two) either in university, or in graduate school. To participate, students need to select a challenge that is relevant to any infrastructure domain and propose a smart, ground-breaking solution concept. Students should submit a presentation and PDF document (with a minimum of 500 words) of their conceptual ideas, not a detailed technical solution with a design. However, students should describe how software technology could play a role in their proposed concept. It must also be supported by graphs, figures, videos, and pictures.
In addition to gaining recognition from Bentley Institute, the top winning team will receive a cash prize of USD 5,000. The winners of the Best Presentation, Best Challenge, and Best Solution categories will also win cash prizes of USD 2,000 each.
Bentley Institute encourages all students to use time at home constructively to suggest ideas for a better tomorrow.
To participate in the challenge, students must register before May 15th, 2020 and submit their projects by June 15th, 2020. Students need to register here. To learn more about the submissions, judging criteria, and other information, click here.
Image: https://communities.bentley.com/cfs-file/__key/communityserver-wikis-components-files/00-00-00-00-06/Facebook_5F00_BI_5F00_Digital_5F00_Infra_5F00_Ideas_5F00_Challenge_5F00_v2_5F00_1200x628.jpg
Caption: Bentley Institute announces “Digital Infrastructure student Idea Challenge”
About Bentley Institute
The Bentley Institute advances the infrastructure professions by empowering practitioners, students, and academic institutions through continuous learning, scholarships, internships, and applied research partnerships. Learning is provided online, in the classroom, or in-application, and includes publications, webinars, workflow videos, live and on-demand courses, conferences, events, and more. The Bentley Institute advances project delivery and asset performance best practices through Digital Advancement Academies, partnering with leading industry organizations, project delivery firms, and owner-operators
About Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems is a leading global provider of software solutions to engineers, architects, geospatial professionals, constructors, and owner-operators for the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure. Bentley’s MicroStation-based engineering and BIM applications, and its digital twin cloud services, advance the project delivery (ProjectWise) and the asset performance (AssetWise) of transportation and other public works, utilities, industrial and resources plants, and commercial and institutional facilities.
Bentley Systems employs more than 3,500 colleagues and generates annual revenues of more than $700 million in 172 countries. From inception in 1984, the company has remained majority-owned by its five founding Bentley brothers. www.bentley.com
Aktualizace údajů
2.4.2020 16:00 Ústecký kraj V Geoportálu ÚAP Ústeckého kraje byla provedena aktualizace údajů pro poskytovatele Česká telekomunikační infrastruktura a.s. – jev 82a, Ředitelství silnic a dálnic ČR – jev 93a, Ministerstvo obrany - jev 44, 47, 68, 70, 73, 75, 79, 80, 82a, 93a, 94a, 102a, 107, 108, České Radiokomunikace a.s. - jev 82a, Povodí Ohře, státní podnik - Jev 47, 53, 68, 93a, UPC Česká republika, s.r.o. - jev 82a, ČEPS, a.s. – jev 72, 73, Severočeské vodovody a kanalizace, a.s. – jev 44, 67, 68, 69, 70, 72, 73 a Národní památkový ústav – jev 5a, 8a, 10, 16Software collaboration tool from Bentley
2.4.2020 15:36 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
World Highways, USA
Read the articleTechnology, Trucks and Elbows: Top 10 Takes from CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2020
2.4.2020 15:33 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Spar3D, USA
Read the articleBentley Systems SYNCHRO Portfolio
2.4.2020 15:24 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Concrete Products, USA
Read the articleCOVID-19: how can satellites help?
2.4.2020 14:28 ESA Observing the Earth
The coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic has virtually paralysed daily life as we know it. Even when the spread of this highly infectious disease has been stemmed, the world will face huge challenges getting back to normal. To help support experts working in Europe’s research centres and technical organisations during these unprecedented times, ESA has issued two new initiatives related to understanding the effects that COVID-19 is imposing on society, the economy and the environment.
COVID-19: how can satellites help?
2.4.2020 14:28 ESA Observing the Earth
The coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic has virtually paralysed daily life as we know it. Even when the spread of this highly infectious disease has been stemmed, the world will face huge challenges getting back to normal. To help support experts working in Europe’s research centres and technical organisations during these unprecedented times, ESA has issued two new initiatives related to understanding the effects that COVID-19 is imposing on society, the economy and the environment.
Novinky na ArcGIS Online - duben 2020
2.4.2020 12:35 ARCDATAJe tu jaro, a to znamená pravidelnou aktualizaci prostředí ArcGIS Online. Vybrali jsme pro vás několik nejzajímavějších změn, které již nyní můžete na ArcGIS Online nalézt a pracovat s nimi.
Uživatelský profil: Stránka uživatelského profilu byla přepracována. Kromě základních nastavení můžete nyní v rámci profilu vidět i přehled obsahu daného uživatele, členství ve skupinách nebo přehled licencí a stav kreditů. A máte-li licenci ArcGIS Pro, můžete si ho odtud rovnou i stáhnout.
HTTPS readiness: Organizace aktivované před zářím 2018 stále ještě dovolují využívat nešifrovaného protokolu HTTP. Protože bude v prosinci 2020 podpora HTTP ukončena, přidává tento update varování, pokud by někdo z vaší organizace odkaz pomocí protokolu HTTP použil.
Aplikace ArcGIS Online Security Advisor dostupná na odkazu https://s3.amazonaws.com/ago-security-advisor/index.html ukazuje kompletní přehled zabezpečení vaší organizace ArcGIS Online a zároveň poskytuje doporučení, jak organizaci ještě lépe zabezpečit. Součástí jsou i logy, kde můžete sledovat aktivitu členů organizace a IP adresy, odkud k organizaci přistupují.
ArcGIS Notebooks, dobře známé z ArcGIS Enterprise či ArcGIS Pro, si konečně našly cestu i do prostředí ArcGIS Online, i když prozatím jen v beta verzi. ArcGIS Notebooks jsou výborné prostředí pro správu a analýzu v jazyce Python založeném na Jupyter notebooks. Administrátoři organizace uvidí přístup k ArcGIS Notebooks v rámci hlavního panelu. Ostatním členům je pro jejich zpřístupnění nutné přiřadit oprávnění.
Pár drobností na závěr. Pokud si nyní v ArcGIS Online zakládáte novou organizaci, můžete si zvolit, v jakém regionu budou data hostována – zda v USA, nebo v Evropě. U stávajících předplatných přímý přesun z USA není možný. Dalšími novinkami je například možnost aktualizace obsahu webové scény publikované ze Scene Layer package nebo navýšení maximální hodnoty pro velikost nahrávaného souboru z 200 GB na 500 GB.
Úplný přehled všech změn a novinek si můžete přečíst na stránkách Esri.
Galileo Masters 2020 now open!
2.4.2020 10:51 European GNSS Agency
The 2020 edition of the Galileo Masters opened for submissions on April 1. Seeking to award applications, services and new ideas that use Galileo and EGNOS also in synergy with other space programmes to respond to pressing needs facing business and society.
The 2020 competition has three GSA-sponsored challenges under the theme Space for Future Generations
Since it began in 2004, the Galileo Masters has scouted for the most forward‐thinking applications based on Galileo and EGNOS and this year is no different. Innovators and entrepreneurs are invited to submit their solutions to the competition by the deadline of 30 June 2020. The most innovative of these will be able to share in more than EUR 750,000 worth of cash prizes. Sounds interesting? To register, click here.
GSA Challenges
The GSA is partnering with Galileo Masters in three challenges in this year’s competition, all under the theme of: Space for Future Generations. The first of these, the Space for our Planet Challenge, aims to tackle climate change and environmental degradation, which represent an existential threat in Europe and worldwide. Services based on data from Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus Earth observation can be used to mitigate this threat by supporting more environmentally-conscious life choices, resulting in a healthier planet. Have an idea about how to save the planet? Let us know about it.
Currently very relevant, the Space for Being Safe and Healthy Challenge is looking for solutions that use downstream space data provided by Galileo, EGNOS and/or Copernicus as key enablers of innovative applications to help stem the spread of COVID-19. Solutions are expected to help public authorities to monitor and analyse emergency situations of this nature and increase public awareness about viruses like the coronavirus. To register for this challenge, click here.
Read this: Calling for GNSS apps supporting the COVID-19 emergency response and recovery
In its Space for Fun Challenge, the GSA is targeting solutions using data from Galileo and EGNOS in the gaming, sports, leisure and tourism markets, where GNSS enables the monitoring of user performance and helps make augmented reality games even more immersive. Covering a number of market segments, this challenge has a lot of scope for new ideas that need accurate and authenticated positioning information. Ready to accept the challenge? Sign up here!
In all three challenges, there is a cash prize of EUR 10,000 up for grabs, with another EUR 10,000 awarded to the concept that is selected at the Galileo Masters 2020 overall winner. What’s more, participants in this year’s competition are in with a chance of winning one of six tailored Galileo Incubation prizes worth up to EUR 62,000 each.
Inspiration from the past
Even if your concept is not yet fully formed, make sure to register early. That way you will receive information about all the great support activities and additional opportunities that arise throughout the submission phase. Registration is free and available to participants from around the world. To find out more, click here.
Meanwhile, as you are fine-tuning your concept, why not look to previous winners for inspiration:
• Performance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
• Smart Gate takes first place in GSA Special Prize at ESNC
• Winner of ‘EU at 60 – Space for Europe’ Special Prize helps keep kids safe
• Drones2GNSS takes this year’s GSA Special Prize
• He shoots, he scores! JOHAN wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2013
• Sound idea wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2012
• GSA satnav Prize winner creating system for Mini-UAVs in controlled airspace
• Next generation navigation system scoops 2010 GSA Prize
• GSA awards Special Topic Prize at Galileo Masters competition
Galileo Masters 2020 now open!
2.4.2020 10:51 European GNSS Agency
The 2020 edition of the Galileo Masters opened for submissions on April 1. Seeking to award applications, services and new ideas that use Galileo and EGNOS also in synergy with other space programmes to respond to pressing needs facing business and society.
The 2020 competition has three GSA-sponsored challenges under the theme Space for Future Generations
Since it began in 2004, the Galileo Masters has scouted for the most forward‐thinking applications based on Galileo and EGNOS and this year is no different. Innovators and entrepreneurs are invited to submit their solutions to the competition by the deadline of 30 June 2020. The most innovative of these will be able to share in more than EUR 750,000 worth of cash prizes. Sounds interesting? To register, click here.
GSA Challenges
The GSA is partnering with Galileo Masters in three challenges in this year’s competition, all under the theme of: Space for Future Generations. The first of these, the Space for our Planet Challenge, aims to tackle climate change and environmental degradation, which represent an existential threat in Europe and worldwide. Services based on data from Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus Earth observation can be used to mitigate this threat by supporting more environmentally-conscious life choices, resulting in a healthier planet. Have an idea about how to save the planet? Let us know about it.
Currently very relevant, the Space for Being Safe and Healthy Challenge is looking for solutions that use downstream space data provided by Galileo, EGNOS and/or Copernicus as key enablers of innovative applications to help stem the spread of COVID-19. Solutions are expected to help public authorities to monitor and analyse emergency situations of this nature and increase public awareness about viruses like the coronavirus. To register for this challenge, click here.
Read this: Calling for GNSS apps supporting the COVID-19 emergency response and recovery
In its Space for Fun Challenge, the GSA is targeting solutions using data from Galileo and EGNOS in the gaming, sports, leisure and tourism markets, where GNSS enables the monitoring of user performance and helps make augmented reality games even more immersive. Covering a number of market segments, this challenge has a lot of scope for new ideas that need accurate and authenticated positioning information. Ready to accept the challenge? Sign up here!
In all three challenges, there is a cash prize of EUR 10,000 up for grabs, with another EUR 10,000 awarded to the concept that is selected at the Galileo Masters 2020 overall winner. What’s more, participants in this year’s competition are in with a chance of winning one of six tailored Galileo Incubation prizes worth up to EUR 62,000 each.
Inspiration from the past
Even if your concept is not yet fully formed, make sure to register early. That way you will receive information about all the great support activities and additional opportunities that arise throughout the submission phase. Registration is free and available to participants from around the world. To find out more, click here.
Meanwhile, as you are fine-tuning your concept, why not look to previous winners for inspiration:
• Performance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
• Smart Gate takes first place in GSA Special Prize at ESNC
• Winner of ‘EU at 60 – Space for Europe’ Special Prize helps keep kids safe
• Drones2GNSS takes this year’s GSA Special Prize
• He shoots, he scores! JOHAN wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2013
• Sound idea wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2012
• GSA satnav Prize winner creating system for Mini-UAVs in controlled airspace
• Next generation navigation system scoops 2010 GSA Prize
• GSA awards Special Topic Prize at Galileo Masters competition
Galileo Masters 2020 now open!
2.4.2020 10:51 European GNSS Agency
The 2020 edition of the Galileo Masters opened for submissions on April 1st, seeking to award applications, services and new ideas that use Galileo and EGNOS also in synergy with other space programmes to respond to pressing needs facing business and society.
The 2020 competition has three GSA challenges under the theme Space for Future Generations
Since it began in 2004, the Galileo Masters has scouted for the most forward‐thinking applications based on Galileo and EGNOS and this year is no different. Innovators and entrepreneurs are invited to submit their solutions to the competition by the deadline of 30 June 2020. The most innovative of these will be able to share in more than EUR 750,000 worth of cash prizes. Sounds interesting? To register, click here.
GSA Challenges
The GSA is partnering with Galileo Masters in three challenges in this year’s competition, all under the theme of: Space for Future Generations. The first of these, the Space for our Planet Challenge, aims to tackle climate change and environmental degradation, which represent an existential threat in Europe and worldwide. Services based on data from Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus Earth observation can be used to mitigate this threat by supporting more environmentally-conscious life choices, resulting in a healthier planet. Have an idea about how to save the planet? Let us know about it.
Currently very relevant, the Space for Being Safe and Healthy Challenge is looking for solutions that use downstream space data provided by Galileo, EGNOS and/or Copernicus as key enablers of innovative applications to help stem the spread of COVID-19. Solutions are expected to help public authorities to monitor and analyse emergency situations of this nature and increase public awareness about viruses like the coronavirus. To register for this challenge, click here.
Read this: Calling for GNSS apps supporting the COVID-19 emergency response and recovery
In its Space for Fun Challenge, the GSA is targeting solutions using data from Galileo and EGNOS in the gaming, sports, leisure and tourism markets, where GNSS enables the monitoring of user performance and helps make augmented reality games even more immersive. Covering a number of market segments, this challenge has a lot of scope for new ideas that need accurate and authenticated positioning information. Ready to accept the challenge? Sign up here!
In all three challenges, there is a cash prize of EUR 10,000 up for grabs, with another EUR 10,000 awarded to the concept that is selected at the Galileo Masters 2020 overall winner. What’s more, participants in this year’s competition are in with a chance of winning one of six tailored Galileo Incubation prizes worth up to EUR 62,000 each.
Inspiration from the past
Even if your concept is not yet fully formed, make sure to register early. That way you will receive information about all the great support activities and additional opportunities that arise throughout the submission phase. Registration is free and available to participants from around the world. To find out more, click here.
Meanwhile, as you are fine-tuning your concept, why not look to previous winners for inspiration:
• Performance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
• Smart Gate takes first place in GSA Special Prize at ESNC
• Winner of ‘EU at 60 – Space for Europe’ Special Prize helps keep kids safe
• Drones2GNSS takes this year’s GSA Special Prize
• He shoots, he scores! JOHAN wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2013
• Sound idea wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2012
• GSA satnav Prize winner creating system for Mini-UAVs in controlled airspace
• Next generation navigation system scoops 2010 GSA Prize
• GSA awards Special Topic Prize at Galileo Masters competition
Galileo Masters 2020 now open!
2.4.2020 10:51 European GNSS Agency
The 2020 edition of the Galileo Masters opened for submissions on April 1st, seeking to award applications, services and new ideas that use Galileo and EGNOS also in synergy with other space programmes to respond to pressing needs facing business and society.
The 2020 competition has three GSA-sponsored challenges under the theme Space for Future Generations
Since it began in 2004, the Galileo Masters has scouted for the most forward‐thinking applications based on Galileo and EGNOS and this year is no different. Innovators and entrepreneurs are invited to submit their solutions to the competition by the deadline of 30 June 2020. The most innovative of these will be able to share in more than EUR 750,000 worth of cash prizes. Sounds interesting? To register, click here.
GSA Challenges
The GSA is partnering with Galileo Masters in three challenges in this year’s competition, all under the theme of: Space for Future Generations. The first of these, the Space for our Planet Challenge, aims to tackle climate change and environmental degradation, which represent an existential threat in Europe and worldwide. Services based on data from Galileo, EGNOS and Copernicus Earth observation can be used to mitigate this threat by supporting more environmentally-conscious life choices, resulting in a healthier planet. Have an idea about how to save the planet? Let us know about it.
Currently very relevant, the Space for Being Safe and Healthy Challenge is looking for solutions that use downstream space data provided by Galileo, EGNOS and/or Copernicus as key enablers of innovative applications to help stem the spread of COVID-19. Solutions are expected to help public authorities to monitor and analyse emergency situations of this nature and increase public awareness about viruses like the coronavirus. To register for this challenge, click here.
Read this: Calling for GNSS apps supporting the COVID-19 emergency response and recovery
In its Space for Fun Challenge, the GSA is targeting solutions using data from Galileo and EGNOS in the gaming, sports, leisure and tourism markets, where GNSS enables the monitoring of user performance and helps make augmented reality games even more immersive. Covering a number of market segments, this challenge has a lot of scope for new ideas that need accurate and authenticated positioning information. Ready to accept the challenge? Sign up here!
In all three challenges, there is a cash prize of EUR 10,000 up for grabs, with another EUR 10,000 awarded to the concept that is selected at the Galileo Masters 2020 overall winner. What’s more, participants in this year’s competition are in with a chance of winning one of six tailored Galileo Incubation prizes worth up to EUR 62,000 each.
Inspiration from the past
Even if your concept is not yet fully formed, make sure to register early. That way you will receive information about all the great support activities and additional opportunities that arise throughout the submission phase. Registration is free and available to participants from around the world. To find out more, click here.
Meanwhile, as you are fine-tuning your concept, why not look to previous winners for inspiration:
• Performance Cockpit takes overall prize at Galileo Masters 2019
• Smart Gate takes first place in GSA Special Prize at ESNC
• Winner of ‘EU at 60 – Space for Europe’ Special Prize helps keep kids safe
• Drones2GNSS takes this year’s GSA Special Prize
• He shoots, he scores! JOHAN wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2013
• Sound idea wins EGNOS prize at ESNC 2012
• GSA satnav Prize winner creating system for Mini-UAVs in controlled airspace
• Next generation navigation system scoops 2010 GSA Prize
• GSA awards Special Topic Prize at Galileo Masters competition
3. díl služby UtiltyReport je na světě
2.4.2020 10:34 Hrdlička V 3. díle Vám ukážeme, jaké náležitosti jsou potřeba při vyřízení žádosti o stavební povolení.HRDLIČKA spol. s r.o. - 3. díl služby UtiltyReport je na světě
2.4.2020 10:34 Hrdlička V 3. díle Vám ukážeme, jaké náležitosti jsou potřeba při vyřízení žádosti o stavební povolení.Schránka
2.4.2020 10:10 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Praha-východ zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání Katastrálnímu pracovišti Praha-východ bezkontaktně do sběrného boxu umístěného u vchodu do budovy! Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Pokud uvedete v podání Váš mail, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.Schránka je přístupná v pondělí a středu od 8:00 do 17:00, v úterý a čtvrtek od 8:00 do 15:00 a v pátek do 13hodin.
Schránka
2.4.2020 10:10 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Praha-vychod/O-uradu/Aktuality/SchrankaGeoKARTO 2020 (pozvánka)
2.4.2020 8:35 GISportal.cz
Chápeme, že nyní nevíte, co budete dělat o víkendu, natož plánovat konferenci v září, ale přesto sdílíme pozvánku od slovenských kolegů. Dovoľujeme si Vám zaslať pozvánku na medzinárodnú konferenciu GeoKARTO 2020, ktorá sa uskutoční 10. – 11. septembra 2020 v priestoroch Univerzity Pavla Jozefa Šafárika v Košiciach. Konferenciu organizuje Kartografická spoločnosť SR v spolupráci s […]
The post GeoKARTO 2020 (pozvánka) appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Informace k aktuálnímu stavu
2.4.2020 8:31 Katedra geoinformatiky UP OlomoucPřehled informací a důležitých termínů vzhledem k aktuálnímu dění a úpravě akademického roku na katedře od prof. RNDr. Víta Voženílka, CSc. ———————————————————————————- 👉 Výuka v letním semestru se prodlouží do 12. června 2020 👉 Termín pro splnění studijních povinností: ▶️ pro absolventské ročníky do 31. 5. 2020 ▶️ pro ostatní ročníky do 15. 9. 2020 […]
The post Informace k aktuálnímu stavu appeared first on Katedra geoinformatiky.
OmniSci Announces Expansion to Address Growing Demand in Asia, Adds Joseph Lee as Vice President, Global Sales
2.4.2020 0:46 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SAN FRANCISCO, April 1, 2020 /PRNewswire/ -- OmniSci, the pioneer in accelerated analytics, today announced its expansion to Asia, the next step …iPad Lidar Demos | DIY Laser Social Distancing
2.4.2020 0:28 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars 96Lidar | Software | Hardware | UAV/UAS | Related & New …
Esri to Provide Mapping Resources to WHO Member States
2.4.2020 0:27 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Advanced Geospatial Technology Offered to Global Communities During COVID-19 CrisisREDLANDS, Calif. — (BUSINESS WIRE) — April 1, 2020 …
Gladiator Technologies Introduces High Performance Integrated GNSS-Inertial Navigation Systems (INS/GPS) that Fit in the Palm of Your Hand.
1.4.2020 21:25 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Gladiator Technologies' low noise MEMS inertial sensor and systems technology coupled with VELOX™ high speed processing are now integrated with a …Quanergy Secures Capital to Accelerate Product Portfolio Expansion; Appoints Kevin Kennedy as Quanergy CEO
1.4.2020 20:56 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars New funding, led by Rising Tide, will support strategic investments in product development and the expansion of R&D and global distribution …Results of OGC’s biggest Innovation Initiative in 2019, Testbed-15, are now available
1.4.2020 19:54 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars The latest advances in Geospatial Data Processing, Analysis, and Visualization have been documented in Testbed-15’s Sixteen Engineering …NEARMAP TO PROVIDE FREE HIGH-RESOLUTION AERIAL IMAGERY TO HEALTH OFFICIALS AND GOVERNMENT AGENCIES FOR COVID-19 RELIEF EFFORTS
1.4.2020 17:31 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SALT LAKE CITY, April 01, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Leading aerial imagery company Nearmap announced today that it is making its high-resolution …Nearmap to provide free high-resolution aerial imagery to health officials and government agencies for covid-19 relief efforts
1.4.2020 17:31 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars SALT LAKE CITY, April 01, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Leading aerial imagery company Nearmap announced today that it is making its high-resolution …Draganfly to Webcast Live at VirtualInvestorConferences.com April 2nd
1.4.2020 17:31 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Draganfly invites individual and institutional investors, as well as advisors and analysts, to attend real-time, interactive presentations on …Submissions open for Copernicus Masters 2020
1.4.2020 17:00 ESA Observing the Earth
Awarding innovative solutions, developments and ideas that use Earth observation data to tackle challenges faced by business and society, the Copernicus Masters 2020 competition is now open for submissions.
City of Burbank Improves Address Accuracy with Melissa Data Quality Tools
1.4.2020 16:41 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars RANCHO SANTA MARGARITA, Calif., April 01, 2020 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Melissa, a leading provider of global address, name, email, phone, and identity …Bentley digitises the Pan Borneo Highway
1.4.2020 16:14 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
Roads & Infrastructure, Australia/New Zealand
Read the articleDigital Twin Rises in Construction
1.4.2020 16:06 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
ConstrucTech TV, USA
Read the article4D/5D Construction – Now for Heavy Civil Projects Too!
1.4.2020 16:02 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
BuiltWorld, USA
Read the articleMicrosoft rolls out digital twin for Singapore office
1.4.2020 15:59 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
BIM+, UK
Read the articleBentley acquires SaaS provider GroupBC
1.4.2020 15:53 Bentley SystemsPress Coverage
BIM+, UK
Read the articleLet's Hrdlička - Podcast s Lukášem Opatem
1.4.2020 13:40 Hrdlička Přinášíme Vám Podcast s Lukášem Opatem, ředitelem marketingu a komunikaceHRDLIČKA spol. s r.o. - Let's Hrdlička - Podcast s Lukášem Opatem
1.4.2020 13:40 Hrdlička Přinášíme Vám Podcast s Lukášem Opatem, ředitelem marketingu a komunikaceJak na práci s mapou v T-MAPY aplikacích?
1.4.2020 13:22 T-MAPYThe post Jak na práci s mapou v T-MAPY aplikacích? appeared first on T-MAPY spol. s r.o..
Pozvánka na webinář "HERE Technologies a (městská) mobilita"
1.4.2020 12:29 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČUPozvánka na webinář "HERE Technologies a (městská) mobilita" ve čtvrtek 2. 4. 2020 od 15:45
1.4.2020 12:29 Blogující geomatici - FAV ZČUDatum konání: čtvrtek 2. 4. 2020 od 15:45
Czech GIS
1.4.2020 11:59 ARCDATAVytvořili jsme český prostor Czech GIS na fóru GeoNet. Přijďte se přidat i vy!
Co je GeoNet?
GeoNet je rozsáhlé internetové fórum, které založila a spravuje společnost Esri. Naleznete na něm informace a blogy k jednotlivým produktům a aplikacím, uživatelé zde sdílejí svoje zkušenosti a řeší otázky, se kterými jim pomáhají ostatní uživatelé i odborníci z Esri.
A co je Czech GIS?
Na fóru GeoNet jsme vytvořili stránku, kde se mohou potkávat čeští uživatelé. Můžete na ní komunikovat v češtině, probírat zde specificky českou GIS problematiku nebo se prostě jen na něco zeptat a podělit se o novinku či zajímavost.
Na fórum GeoNet se přihlásíte prostřednictvím svého uživatelského účtu ArcGIS.
Těšíme se s vámi na viděnou.
GeoCzech
1.4.2020 11:59 ARCDATAVytvořili jsme český prostor GeoCzech na fóru GeoNet. Přijďte se přidat i vy!
Co je GeoNet?
GeoNet je rozsáhlé internetové fórum, které založila a spravuje společnost Esri. Naleznete na něm informace a blogy k jednotlivým produktům a aplikacím, uživatelé zde sdílejí svoje zkušenosti a řeší otázky, se kterými jim pomáhají ostatní uživatelé i odborníci z Esri.
A co je GeoCzech?
Na fóru GeoNet jsme vytvořili stránku, kde se mohou potkávat čeští uživatelé. Můžete na ní komunikovat v češtině, probírat zde specificky českou GIS problematiku nebo se prostě jen na něco zeptat a podělit se o novinku či zajímavost.
Na fórum GeoNet se přihlásíte prostřednictvím svého uživatelského účtu ArcGIS.
Těšíme se s vámi na viděnou.
Apríl bez mapových vtípků?
1.4.2020 8:56 GISportal.cz
Google Maps pravidelně publikují nějaký mapový vtípek právě na Apríla, například hraní hada (2019) nebo pac-man (2017) patřily mezi legendární vtípky, ale letos se s ohledem na COVID-19 rozhodli žádný vtípek nepublikovat. Podobně tomu je asi i u české jedničky Mapy.cz, která v minulých letech publikovala například textovou mapu. Pokud narazíte na nějaký aprílový vtípek […]
The post Apríl bez mapových vtípků? appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Omezení
1.4.2020 8:09 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Melnik/O-uradu/Aktuality/OmezeniOmezení
1.4.2020 8:09 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Mělník zveřejnil novou aktualitu:Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj v návaznosti na
USNESENÍ VLÁDY ČESKÉ REPUBLIKY
ze dne 15. března 2020 č. 215
o přijetí krizového opatření
oznamuje
S účinností ode dne 16. března 2020 mají všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj výrazně omezeny služby vyžadující přímý kontakt s veřejností. V neodkladných případech bude možné učinit návrh na vklad práv či jiné podání osobně pouze v pondělí a ve středu v době od 8 do 11 hodin.
Po dobu omezení bude možné návrh na vklad práv i ostatní podání katastrálním úřadům činit prostřednictvím provozovatele poštovních služeb nebo elektronicky (e-mailem nebo prostřednictvím datových schránek). Účastníci řízení o vkladu budou v těchto případech vyzváni k úhradě správního poplatku, který lze uhradit převodem na účet. Podrobnosti o elektronických podáních a parametrech přijímaných datových zpráv zde: https://www.cuzk.cz/Katastr-nemovitosti/Zapisy-do-KN/Informace-o-elektronickem-podani.aspx .
Základní informace z katastru nemovitostí je možné získat rovněž elektronicky prostřednictvím aplikace Nahlížení do katastru nemovitostí https://nahlizenidokn.cuzk.cz/ .
V této aplikaci je možné prostřednictvím e-shopu získat i úplný výpis z katastru nemovitostí v elektronické podobě bez nutnosti návštěvy katastrálního pracoviště.
Naplánovaná ústní jednání budou přesunuta na období po ukončení krizového opatření. Prosíme o pochopení, že nebudeme až do odvolání provádět ústní jednání v terénu (např. v souvislosti s revizemi nebo zjišťování průběhu hranic) ani v budově katastrálního pracoviště.
V případě dotazů k probíhajícím řízením nebo neodkladným záležitostem se obracejte na telefon:315636311
ředitel úřadu
Mgr. Ing. Štěpán Hudec
V Praze dne 16. 3. 2020
Omezení provozu KPÚ pro Královéhradecký kraj
1.4.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad Z důvodu přerušení dodávky elektrického proudu bude dne 3. 4. 2020 omezen provoz pracoviště KPÚ pro Královéhradecký kraj. Zachován bude pouze provoz podatelny.V době nouzového stavu platí i čerstvě propadlé osobní doklady
1.4.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad V době nouzového stavu se občané mohou nadále prokazovat občanským průkazem nebo cestovním pasem, jehož platnost skončila po 1. březnu 2020.Po tuto dobu neplatí dočasně ani povinnost požádat do 15 pracovních dnů o vydání nového občanského průkazu z důvodu skončení jeho platnosti, a to ani z dalších zákonem stanovených důvodů jako je ztráta, odcizení, změna či zrušení trvalého pobytu, po obdržení oddacího listu nebo dokladu o partnerství, po nabytí právní moci rozhodnutí o rozvodu manželství atd.
V době nouzového stavu platí i čerstvě propadlé osobní doklady
1.4.2020 0:00 Státní pozemkový úřad V době nouzového stavu se občané mohou nadále prokazovat občanským průkazem nebo cestovním pasem, jehož platnost skončila po 1. březnu 2020.Po tuto dobu neplatí dočasně ani povinnost požádat do 15 pracovních dnů o vydání nového občanského průkazu z důvodu skončení jeho platnosti, a to ani z dalších zákonem stanovených důvodů jako je ztráta, odcizení, změna či zrušení trvalého pobytu, po obdržení oddacího listu nebo dokladu o partnerství, po nabytí právní moci rozhodnutí o rozvodu manželství atd.
MGISS Appoints Dave George as Head of Professional Services Division
31.3.2020 20:43 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Liverpool, UK, 31 March 2020 –MGISS has appointed Dave George as Technical Lead within its Professional Services division. Working …OGC and Natural Resources Canada issue a Request For Information concerning the modernization of spatial data infrastructures
31.3.2020 20:18 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars RFI will feed into a study to help modernize spatial data infrastructures by integrating new tools, standards, and techniques (such as machine …New survey: Expectations for infrastructure investment plummet globally, as COVID-19 outbreak shakes confidence
31.3.2020 20:15 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Expectations for infrastructure investment plummet globally, as COVID-19 outbreak shakes confidenceAccording to a new survey taken before and after …
Leica Geosystems announces new 3D laser scanning bundle
31.3.2020 20:13 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Leica Cyclone is a purpose-built solution for reality capture(HEERBRUGG, Switzerland, 31 March 2020) – Leica Geosystems, a Hexagon company, …
Hexagon's Nomination Committee Proposes Board of Directors
31.3.2020 19:30 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NACKA STRAND, Sweden, March 31, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — Hexagon AB's Nomination Committee proposes the election of Patrick Söderlund as a …S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller Index Shows Continued Growth in Annual Home Price Gains to Start 2020
31.3.2020 17:59 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars NEW YORK, March 31, 2020 — (PRNewswire) — S&P Dow Jones Indices today released the latest results for the S&P CoreLogic …Bentley Institute Press Announces Availability of “Inside MicroStation” CONNECT Edition Book Series
31.3.2020 16:05 Bentley Systems EXTON, Pa. March 31, 2020 – Bentley Institute Press, publisher of cutting-edge textbooks and professional reference works for the advancement of the engineering, architectural, construction, operations, geospatial, and educational communities, has announced the availability of a new publication series titled Inside MicroStation CONNECT Edition, now available in print at www.bentley.com/books and as an e-book at www.ebook.bentley.com.The three-volume set focusses on developing a strong understanding of the basics of MicroStation and follows a step-by-step approach that includes exercises and real-world example complete with illustrations. The publications instruct readers on how to use the 2D design fundamentals of MicroStation and lay a foundation for advanced learning. The series can be found on Amazon Kindle (volumes I, II, III) and Apple books (volumes I,II, III). The book series serves as a powerful learning tool and a quick reference guide for students, beginners, and practicing professionals.
The book series reflects the benefits of using the CONNECT Edition and discusses the features of MicroStation CONNECT Edition, including new CAD capabilities and its power and versatility to precisely view, model, document, and visualize information-rich designs of all types and scales. MicroStation CONNECT Edition is for professionals working in every discipline on infrastructure projects of every type.
Vinayak Trivedi, vice president, and global head of Bentley Institute, said, “We are pleased to offer this much-awaited title from Bentley Institute Press, which will help engineers take a massive leap forward in their productivity, while working with MicroStation. Bentley experts Samir Haque, Smrutirekha Mahapatra, and Shaylesh Lunawat have brought together their years of experience and lessons learned to write these three volumes. I anticipate that all readers of this series will be able to increase their mastery of MicroStation CONNECT Edition and enhance their careers with this book set.”
Volume I is geared to users who need to know the basics of the software, and it explains how to set up the drawing environment. Volume II guides readers through the process of creating elements and modifying elements using various capabilities. Volume III introduces advanced workflows such as creating and placing cells, annotating drawings, attaching references, composing sheets, and printing.
To find out more information about Inside MicroStation CONNECT Edition, please contact Monica Jedhe at monica.jedhe@bentley.com.
Image:
https://www.bentley.com/-/media/Images/Press Release Images/2020/covers_Inside MicroStation CE
Caption: The three-volume set of Inside MicroStation CONNECT Edition is available now at bentley.com or ebook.bentley.com.
VIDEO:
Brightcove Link:
https://players.brightcove.net/5209582030001/default_default/index.html?videoId=6144674611001
Caption: Two minutes with Keith Bentley on “Inside MicroStation” CONNECT Edition.
About the authors
Samir Haque
Samir Haque is an engineer and scientist with degrees in biology, biochemistry, electrical engineering and physics. He started in CAD as a researcher at UCLA where he used MicroStation to design 3D parts for experiments in space flight for the study of muscle physics and muscle re-enervation. Haque also used the software to map the brain in 3D at the Brain Research Institute. During the past 23 years with Bentley, Haque has trained thousands of users on MicroStation and has written several manuals on the software. Currently, Haque leads oversees the development of PowerPlatform, leading the product management and quality assurance teams.
Shaylesh Lunawat
Shaylesh Lunawat earned a degree in engineering from the University of Pune. Began a career manufacturing defense equipment, before working at Bentley from 2008 to 2019 as a technical writing manager. In this position, Lunawat was responsible for producing several manuals on MicroStation and other Bentley applications.
Smrutirekha Mahapatra
Smrutirekha joined Bentley in 2016 as a technical writer and leads the PowerPlatform Documentation team. Before joining Bentley, Mahapatra was an architect with various firms in designing industrial complexes, commercial buildings, and hospitals. Throughout her architectural career, she used various CAD tools for project delivery. Mahapatra earned an AA degree in energy management from the Kirsch Center for Environmental Studies.
About Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems is a leading global provider of software solutions to engineers, architects, geospatial professionals, constructors, and owner-operators for the design, construction, and operations of infrastructure. Bentley’s MicroStation-based engineering and BIM applications, and its digital twin cloud services, advance the project delivery (ProjectWise) and the asset performance (AssetWise) of transportation and other public works, utilities, industrial and resources plants, and commercial and institutional facilities.
Bentley Systems employs more than 3,500 colleagues and generates annual revenues of more than $700 million in 172 countries. From inception in 1984, the company has remained majority-owned by its five founding Bentley brothers. www.bentley.com
Informace o možnosti bezkontaktního podání
31.3.2020 13:55 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Informace o možnosti bezkontaktního podání Informace o možnosti bezkontaktního podáníNa všech katastrálních pracovištích Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj je možné i mimo upravené úřední hodiny vhodit podání v zalepené obálce do uzavřené sběrné schránky, která je umístěna v blízkosti vstupu do budovy příslušného katastrálního pracoviště. Dobu, po kterou je zpřístupněna, naleznete na stránkách jednotlivých katastrálních pracovišť. Pokud bude v podání uvedena e-mailová adresa, bude na ní zasláno potvrzení o přijetí podání. Za okamžik podání návrhu na vklad se považuje okamžik výběru sběrné schránky. V případě, že je s podáním spojena poplatková povinnost, bude účastníkům zaslána i výzva k úhradě správního poplatku převodem na účet. Děkujeme, že budete v co největší míře využívat této zcela bezkontaktní možnosti podání vůči katastrálnímu úřadu.
Informace o možnosti bezkontaktního podání
31.3.2020 13:55 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Informace-o-moznosti-bezkontaktniho-podaniOznámení o omezeném provozu katastrálních pracovišť
31.3.2020 13:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Omezení provozu Oznámení o omezeném provozu katastrálních pracovišť:S účinností ode dne 16. března 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj omezení všech úředních hodin:
pondělí 8.00 – 11.00 hodin
středa 8.00 – 11.00 hodin
V rámci těchto úředních hodin budou pouze přijímána podání včetně návrhů na vklad do katastru. Platbu za podání návrhu na vklad bude možno učinit pouze platební kartou nebo bezhotovostně převodem z účtu.
Obecné informace : tel. 284 041 111
KP Benešov - tel. 317 716 488
KP Beroun - tel. 311 625 147
KP Kladno - tel. 312 610 307
KP Kolín - tel. 321 737 011
KP Kutná Hora - tel. 327 551 254, 327 551 253
KP Mělník - tel. 315 636 311
KP Mladá Boleslav - tel. 326 722 771
KP Nymburk - tel. 325 501 001
KP Praha-východ - tel. 284 043 377, 284 043 378, 284 043 379, 284 043 381
KP Praha-západ - tel. 284 044 161, 284 044 140, 284 044 139
KP Příbram - tel. 318 401 611
KP Rakovník - tel. 313 521 611
KP Slaný - tel. 312 574 211, 312 522 312
Oznámení o omezeném provozu katastrálních pracovišť
31.3.2020 13:51 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Omezení provozu Oznámení o omezeném provozu katastrálních pracovišť:S účinností ode dne 16. března 2020 platí pro všechna katastrální pracoviště v územní působnosti Katastrálního úřadu pro Středočeský kraj omezení všech úředních hodin:
pondělí 8.00 – 11.00 hodin
středa 8.00 – 11.00 hodin
V rámci těchto úředních hodin budou pouze přijímána podání včetně návrhů na vklad do katastru. Platbu za podání návrhu na vklad bude možno učinit pouze platební kartou nebo bezhotovostně převodem z účtu.
Obecné informace : tel. 284 041 111
KP Benešov - tel. 317 716 488
KP Beroun - tel. 311 625 147
KP Kladno - tel. 312 610 307
KP Kolín - tel. 321 737 011
KP Kutná Hora - tel. 327 551 254, 327 551 253
KP Mělník - tel. 315 636 311
KP Mladá Boleslav - tel. 326 722 771
KP Nymburk - tel. 325 501 001
KP Praha-východ - tel. 284 041 111
KP Praha-západ - tel. 284 044 161, 284 044 140, 284 044 139
KP Příbram - tel. 318 401 611
KP Rakovník - tel. 313 521 611
KP Slaný - tel. 312 574 211, 312 522 312
Oznámení o omezeném provozu katastrálních pracovišť
31.3.2020 13:51 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Oznameni-o-omezenem-provozu-katastralnich-pracovisKoronavirus 2
31.3.2020 13:47 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Moravskoslezsky-kraj/O-uradu/Aktuality/Koronavirus-2Koronavirus 2
31.3.2020 13:47 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Moravskoslezský kraj zveřejnil novou aktualitu: V souvislosti s vydáním usnesení vlády ČR č. 348 ze dne 30. března 2020 o vydání některých mimořádných opatřeních Ministerstva zdravotnictví na další období s účinností od 1. 4. 2020 od 6:00 hod. do 11. 4. 2020 do 6:00 hod. platí na všech pracovištích katastrálních úřadů nadále omezený provoz pro veřejnost. Katastrální úřady přijímají bez omezení elektronická podání ve stanovené formě a poštovní zásilky. K získání informací z katastru nemovitostí využijte aplikaci Nahlížení do katastru, která umožňuje vyřízení úplného výpisu z katastru přes e-shop. Neodkladné záležitosti bude možné vyřídit v omezených úředních hodinách v pondělí a ve středu od 8 do 11 hodin. Prosíme, abyste se před případnou návštěvou řídili pokyny uvedenými na webových stránkách příslušných katastrálních pracovišť.Děkujeme za pochopení.
eCall: 2 years of saving lives
31.3.2020 10:38 European GNSS Agency
In the two years since the launch of the EU’s eCall emergency response system, which automatically calls emergency services in the event of a road accident, manufacturers have been quick to implement the life-saving technology, with around 3 million eCall-enabled vehicles already sold in Europe.
The EU launched its eCall emergency response system with the publication, on 31 March 2018, of the European eCall regulation, requiring all new car and light van types sold in the EU to be fitted with the system. Manufacturers were quick to respond, with Volvo Cars being the first to certify the system for use in its vehicles and the first to launch an eCall-equipped model to the market – presenting the V60 at the ITS World Congress 2018 in Copenhagen in September 2018.
GSA helps pave the way
European Commission services – specifically the Joint Research Centre – and the GSA helped pave the way for a quick and smooth uptake by the automobile industry, publishing a set of guidelines to help the eCall industry value chain to pre-test the accuracy of their new devices and understand how to reap the benefits of Galileo.
Other manufacturers were quick to follow Volvo’s lead and currently there are 27 car brands offering over 65 models that are equipped with the system, with around 3 million vehicles sold on the EU market to date. To see which car models are currently available, check the UseGalileo site.
Watch this: eCall - Emergency Positioning
“eCall is a true success story for Europe,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani. “The system leverages EU technology – specifically Galileo precise positioning – to save our citizens lives.” she said.
According to European Commission figures, 25,300 people were killed and 135,000 people were seriously injured in road accidents in the EU in 2017. While new automotive technologies have resulted in a sharp drop in the number of fatalities – which have fallen by 57.5% since 2001, the numbers are still high. By speeding up emergency response times by 40% in urban areas and 50% in the countryside, it is estimated that eCall could help prevent 2,500 road deaths and save EUR 26 billion every year.
How does it work?
eCall is activated automatically as soon as in-vehicle sensors detect a serious crash. Once activated, the system dials the European emergency number 112 and establishes a telephone link to the appropriate emergency call centre.
Leveraging EGNSS (Galileo and EGNOS), the system sends the accurate position of the crashed vehicle and the direction of travel to the emergency services, enabling the emergency responders to get to the accident site faster. An eCall can also be triggered manually by pushing a button in the car, for example by a witness to a serious accident.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
eCall: 2 years of saving lives
31.3.2020 10:38 European GNSS Agency
In the two years since the launch of the EU’s eCall emergency response system, which automatically calls emergency services in the event of a road accident, manufacturers have been quick to implement the life-saving technology, with around 3 million eCall-enabled vehicles already sold in Europe.
The EU launched its eCall emergency response system with the publication, on 31 March 2018, of the European eCall regulation, requiring all new car and light van types sold in the EU to be fitted with the system. Manufacturers were quick to respond, with Volvo Cars being the first to certify the system for use in its vehicles and the first to launch an eCall-equipped model to the market – presenting the V60 at the ITS World Congress 2018 in Copenhagen in September 2018.
GSA helps pave the way
European Commission services – specifically the Joint Research Centre – and the GSA helped pave the way for a quick and smooth uptake by the automobile industry, publishing a set of guidelines to help the eCall industry value chain to pre-test the accuracy of their new devices and understand how to reap the benefits of Galileo.
Other manufacturers were quick to follow Volvo’s lead and currently there are 27 car brands offering over 65 models that are equipped with the system, with around 3 million vehicles sold on the EU market to date. To see which car models are currently available, check the UseGalileo site.
Watch this: eCall - Emergency Positioning
“eCall is a true success story for Europe,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani. “The system leverages EU technology – specifically Galileo precise positioning – to save our citizens lives.” she said.
According to European Commission figures, 25,300 people were killed and 135,000 people were seriously injured in road accidents in the EU in 2017. While new automotive technologies have resulted in a sharp drop in the number of fatalities – which have fallen by 57.5% since 2001, the numbers are still high. By speeding up emergency response times by 40% in urban areas and 50% in the countryside, it is estimated that eCall could help prevent 2,500 road deaths and save EUR 26 billion every year.
How does it work?
eCall is activated automatically as soon as in-vehicle sensors detect a serious crash. Once activated, the system dials the European emergency number 112 and establishes a telephone link to the appropriate emergency call centre.
Leveraging EGNSS (Galileo and EGNOS), the system sends the accurate position of the crashed vehicle and the direction of travel to the emergency services, enabling the emergency responders to get to the accident site faster. An eCall can also be triggered manually by pushing a button in the car, for example by a witness to a serious accident.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
eCall: 2 years of saving lives
31.3.2020 10:38 European GNSS Agency
In the two years since the launch of the EU’s eCall emergency response system, which automatically calls emergency services in the event of a road accident, manufacturers have been quick to implement the life-saving technology, with around 3 million eCall-enabled vehicles already sold in Europe.
The EU launched its eCall emergency response system with the publication, on 31 March 2018, of the European eCall regulation, requiring all new car and light van types sold in the EU to be fitted with the system. Manufacturers were quick to respond, with Volvo Cars being the first to certify the system for use in its vehicles and the first to launch an eCall-equipped model to the market – presenting the V60 at the ITS World Congress 2018 in Copenhagen in September 2018.
GSA helps pave the way
European Commission services – specifically the Joint Research Centre – and the GSA helped pave the way for a quick and smooth uptake by the automobile industry, publishing a set of guidelines to help the eCall industry value chain to pre-test the accuracy of their new devices and understand how to reap the benefits of Galileo.
Other manufacturers were quick to follow Volvo’s lead and currently there are 27 car brands offering over 65 models that are equipped with the system, with around 3 million vehicles sold on the EU market to date. To see which car models are currently available, check the UseGalileo site.
Watch this: eCall - Emergency Positioning
“eCall is a true success story for Europe,” said GSA Head of Market Development Fiammetta Diani. “The system leverages EU technology – specifically Galileo precise positioning – to save our citizens lives.” she said.
According to European Commission figures, 25,300 people were killed and 135,000 people were seriously injured in road accidents in the EU in 2017. While new automotive technologies have resulted in a sharp drop in the number of fatalities – which have fallen by 57.5% since 2001, the numbers are still high. By speeding up emergency response times by 40% in urban areas and 50% in the countryside, it is estimated that eCall could help prevent 2,500 road deaths and save EUR 26 billion every year.
How does it work?
eCall is activated automatically as soon as in-vehicle sensors detect a serious crash. Once activated, the system dials the European emergency number 112 and establishes a telephone link to the appropriate emergency call centre.
Leveraging EGNSS (Galileo and EGNOS), the system sends the accurate position of the crashed vehicle and the direction of travel to the emergency services, enabling the emergency responders to get to the accident site faster. An eCall can also be triggered manually by pushing a button in the car, for example by a witness to a serious accident.
Media note: This feature can be republished without charge provided the European GNSS Agency (GSA) is acknowledged as the source at the top or the bottom of the story. You must request permission before you use any of the photographs on the site. If you republish, we would be grateful if you could link back to the GSA website (http://www.gsa.europa.eu).
Mobilní crowdsourcingová aplikace Stop Corona! i v české mutaci
31.3.2020 9:26 GISportal.cz
“Nahlašte Vaše zdravotní příznaky a zastavte coronavirus!”, takto láká mobilní aplikace Stop Corona! uživatele do sběru informací o symptomech a poloze pozitivně testovaných pacientů. Cílem je sestavit největší světovou databázi symptomů a na základě ní vytvořit předpovědní mapu s nejvyšším výskytem nemoci a poskytneme přehled potencionálního šíření coronaviru (tedy další z mnoha aplikací využívajících heatmapy či […]
The post Mobilní crowdsourcingová aplikace Stop Corona! i v české mutaci appeared first on GISportal.cz.
Důležité upozornění
31.3.2020 9:23 ČÚZK - předpisy a opatření Katastrální úřad pro Středočeský kraj - Katastrální pracoviště Příbram zveřejnil novou aktualitu: Upozorňujeme na možnost učinit podání Katastrálnímu pracovišti Příbram bezkontaktně do sběrného boxu umístěného u vchodu do budovy (vstupní mezidveří)! Lze tak podat i návrh na vklad v zalepené obálce. Pokud uvedete v podání Váš mail, budeme Vás informovat o přijetí, případně vyzveme k zaplacení poplatku převodem na účet.Schránka je přístupná v pondělí a středu od 11:00 do 17:00 a v úterý a čtvrtek od 7:30 do 11:00 a od 11:30 do 15:00 a v pátek od 7:30 do 11:00 a od 11:30 do 13:00.
Důležité upozornění
31.3.2020 9:23 ČÚZK /Urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urady/Katastralni-urad-pro-Stredocesky-kraj/Katastralni-pracoviste/KP-Pribram/O-uradu/Aktuality/Dulezite-upozorneni-(1)SOLV3D Embraces Market and Client Requirements in Their Latest Product Release
31.3.2020 9:00 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars CALGARY, AB – March 31, 2020 – SOLV3D, a leading provider of 3D processing, geospatial data visualization and collaboration solutions, is …Atlas rozvoje venkova
31.3.2020 8:20 GISportal.cz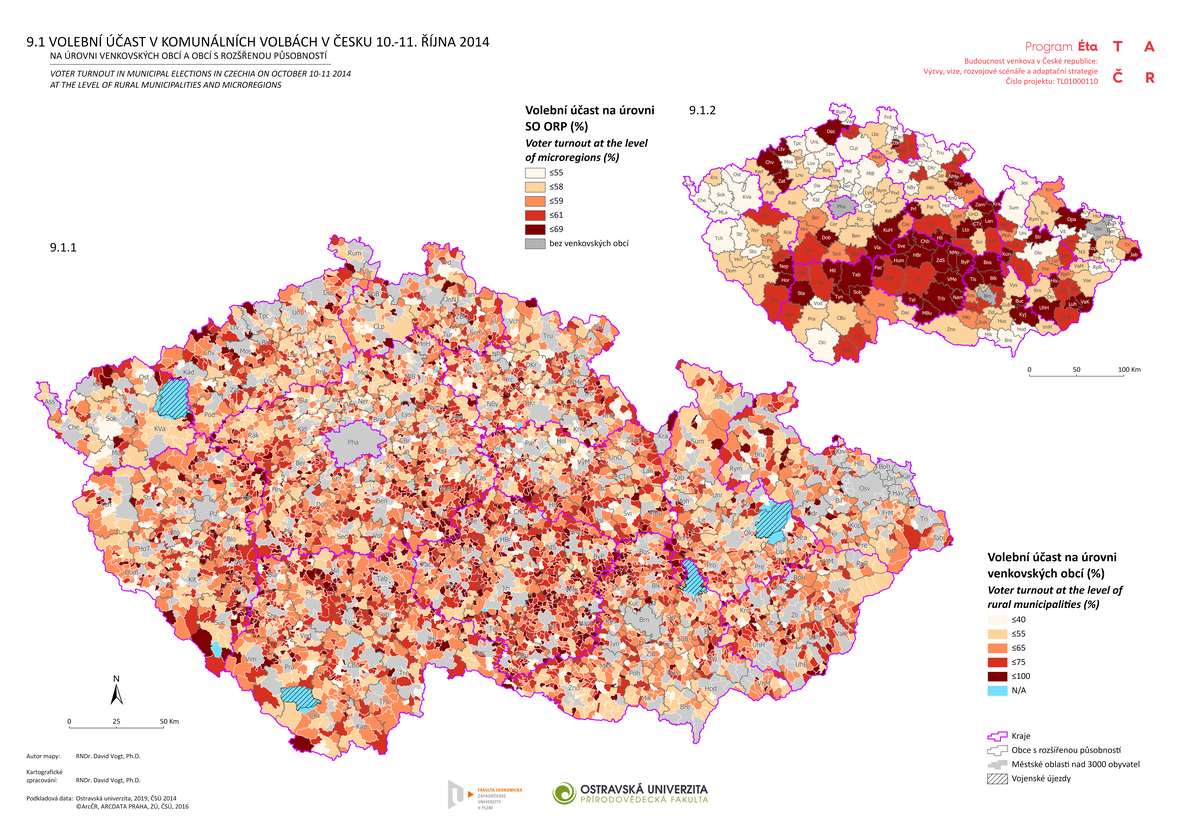
Atlas rozvoje venkova je společný projekt (TAČR) pracovníků Západočeské univerzity v Plzni a Ostravské univerzity, který se zabývá přípravou českého venkova na budoucnost. Klíčovou pozornost věnuje otázkám ekonomického rozvoje a možnostem jeho veřejné podpory (pracovní a podnikatelské příležitosti, základní občanská vybavenost). Cílem projektu je během tří let (2018-2020): analyzovat problémy, rozvojové příležitosti a investiční potřeby venkova, […]
The post Atlas rozvoje venkova appeared first on GISportal.cz.
OneWeb Files for Chapter 11 Restructuring to Execute Sale Process
31.3.2020 0:04 GISCafe.com Webcasts-Webinars Negotiating Debtor-in-Possession Financing to Support its Ongoing Business and a Sale Process
LONDON, UK, March 27, 2020 – …




















